If you’re familiar with injection molding, you might have come across the term 2K injection molding1. But what does it actually mean, and how does it work in the manufacturing process? Let’s dive in.
2K injection molding, also known as two-shot molding, involves the injection of two different materials into a single mold to create a multi-material product. This technique is often used to combine materials with different properties, enhancing functionality and design flexibility.
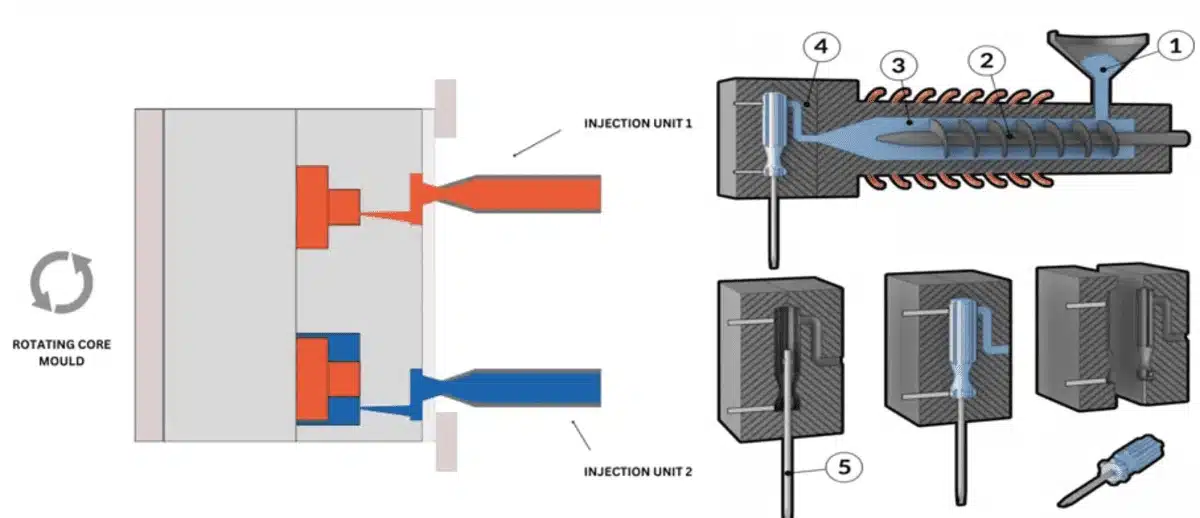
The 2K process offers several benefits, including improved part functionality, reduced assembly costs, and the ability to integrate multiple features into a single product. But like any advanced manufacturing technique, it requires precision and careful planning. In this article, I will break down the 2K injection molding process, including how it compares to other molding methods and the stages involved.
What is 2K technology in molding?
In 2K injection molding, "2K" refers to the use of two different materials or colors that are injected into the mold during two separate stages. Each material is injected into the mold one after the other, allowing for the creation of parts with multiple characteristics—like hard-soft combinations, two different colors, or materials with varied performance properties.
This process is used in industries such as automotive, medical devices, consumer electronics, and packaging, where parts need to offer a combination of strength, flexibility, or aesthetic features2.
Key features of 2K molding include:
- Multi-material molding: The ability to mold two different materials at once.
- Cost savings: Reduces the need for assembly processes since the product is made in a single mold.
- Design flexibility: Ideal for complex parts that need different properties in various sections.
In the 2K molding process, each material can be injected in different sequences, and the two materials may be bonded or layered, depending on the design requirements. This technique significantly reduces the number of production steps, which can increase overall efficiency and lower costs.
What is 2K and 3K molding?
When we talk about 2K molding, you might hear the term 3K molding3 as well. So, what exactly is the difference?
2K Molding:
As we discussed earlier, 2K molding involves injecting two different materials into the same mold. These materials can be different in color, texture, or functionality. It’s a highly efficient process that is often used in industries requiring multi-material parts.
3K Molding:
The 3K molding process is similar to 2K, but instead of using two materials, three different materials or colors are injected into the mold. This technique is used when parts require more complex properties, such as combining three different levels of hardness or creating multi-color products.
| Feature | 2K Molding | 3K Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Used | Two materials or colors | Three materials or colors |
| Complexity | Medium | High |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, medical devices | Automotive, consumer products, complex electronics |
| Cost | Moderate | High |

While 3K molding allows for even more complex combinations, 2K molding is typically sufficient for most applications that require two materials with distinct properties4.
What is the difference between 1K and 2K molding?
The key difference between 1K and 2K molding lies in the number of materials involved in the process.
1K Molding:
- In 1K injection molding, only one material is used to create the part.
- This is the simplest form of injection molding and is used for single-material products.
- It is cost-effective and ideal for parts that don’t need multiple material properties.
2K Molding:
- As explained earlier, 2K molding uses two materials injected into the same mold.
- This process allows for the creation of parts with different material properties or multiple colors, offering increased functionality and design flexibility.
| Feature | 1K Molding | 2K Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Used | One material | Two materials |
| Applications | Simple parts, low-cost products | Parts requiring multi-material features or colors |
| Complexity | Simple | Medium to high |
| Cost | Low | Higher due to multi-materials |
The main advantage of 2K molding over 1K molding is the ability to combine materials with different properties, which can improve the functionality of the final product. However, 2K molding requires more precise machinery and expertise, which makes it a more expensive process compared to 1K molding5.
What are the 4 stages of 2k injection molding?
The 2K injection molding process follows the same general stages as traditional injection molding6, but with an additional step to accommodate the use of two materials. Below are the four main stages:
1. Injection of First Material (Primary Shot)
The first material is injected into the mold cavity. This is usually the base material, which forms the bulk of the product. The material is injected at high pressure and fills the mold cavity completely.
2. Cooling of First Material
After the first material is injected, it needs time to cool and solidify. This step ensures that the base material holds its shape before the second material is injected.
3. Injection of Second Material (Secondary Shot)
Once the first material has solidified, the second material is injected. This material can either be injected into the remaining cavity or overmolded onto the first material, depending on the design. This is where the two materials are combined to form the final product.
4. Cooling and Ejection
After the second material is injected and solidified, the entire part cools. Once it has fully cooled, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
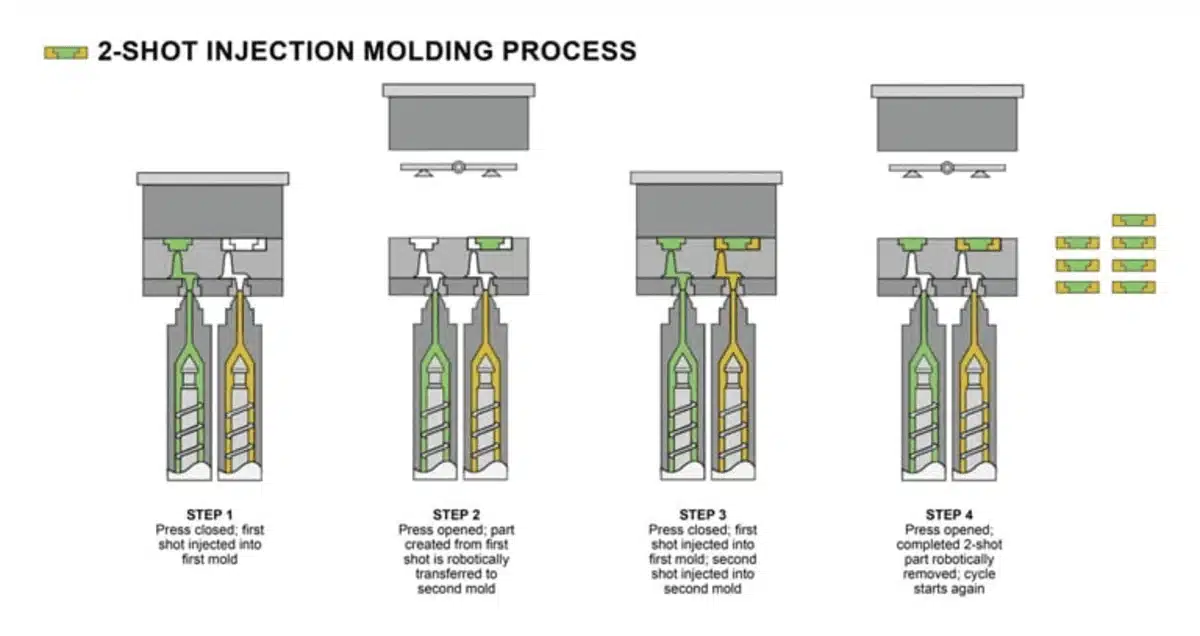
In summary, the four stages of injection molding are:
- Injection of First Material
- Cooling of First Material
- Injection of Second Material
- Cooling and Ejection
These stages are followed in sequence to ensure that the two materials are properly molded and bonded together to create a durable, multi-material part.
Conclusion
2K injection molding offers an efficient way to produce multi-material parts with enhanced functionality and design flexibility. By using two different materials, manufacturers can create complex parts with multiple properties, reducing the need for additional processes like assembly. While more advanced and costly than 1K molding, it provides significant benefits in terms of part performance and overall cost savings7 in the long run.
Explore this link to gain a comprehensive understanding of 2K injection molding, its process, and its advantages in manufacturing. ↩
Understanding aesthetic features can significantly enhance your design projects by focusing on elements that appeal visually and emotionally. ↩
This resource will explain how 3K molding allows for more complex product designs and functionalities, ideal for advanced manufacturing needs. ↩
Learn how to select the right materials with distinct properties for your molding projects to achieve optimal results. ↩
Exploring the differences between 1K and 2K molding can provide insights into cost, efficiency, and application suitability, aiding in selecting the right process for your needs. ↩
This resource provides detailed insights into traditional injection molding, helping you compare it with 2K injection molding for better decision-making. ↩
Learning about cost-saving strategies in manufacturing can significantly impact your production efficiency and profitability. ↩