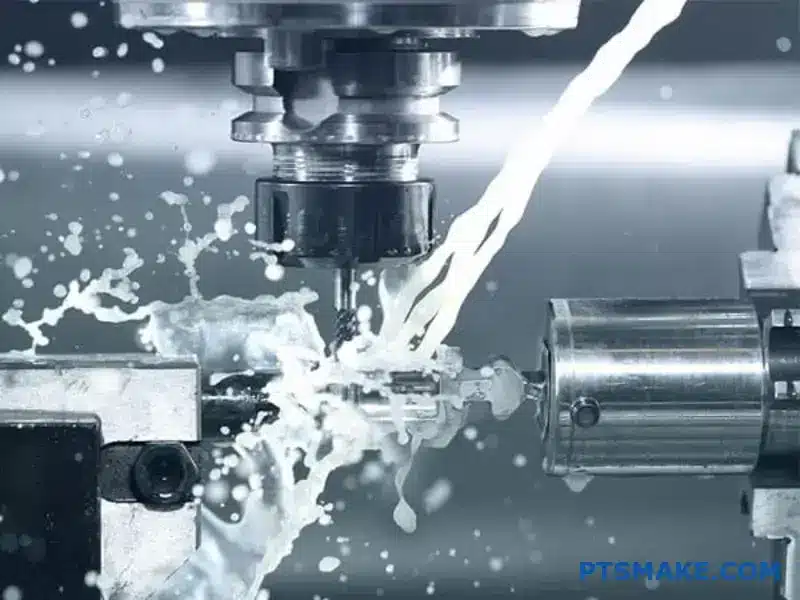
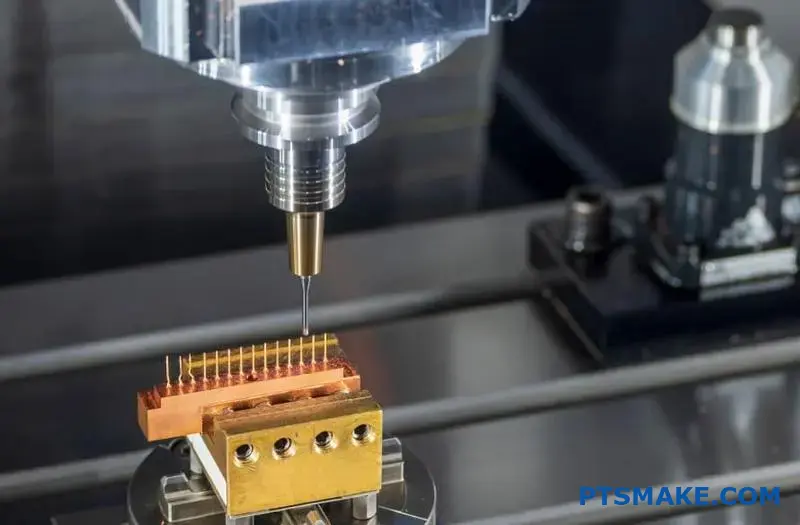
Achieving precision in 316L stainless steel machining can be frustrating. I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with tool wear, poor surface finish, and dimensional inaccuracies. These issues not only waste valuable materials but also lead to costly production delays and rejected parts.
To achieve precision in 316L stainless steel machining, use sharp carbide tools, maintain proper cutting speeds (100-150 SFM), and ensure rigid workpiece fixturing. Apply abundant coolant, take light cuts, and monitor tool wear regularly to maintain tight tolerances.

I want to share more detailed insights about 316L stainless steel machining. The strategies I’ve outlined above are just the basics. Below, I’ll explain specific cutting parameters, tool selection criteria, and advanced techniques that will help you achieve exceptional results with this challenging material.
What is 316L Stainless Steel?
Have you ever faced challenges with metal components corroding or failing in critical applications? The consequences of using the wrong grade of stainless steel can be severe – from costly equipment failures to potential safety hazards. Many engineers and manufacturers struggle to find a material that offers both exceptional corrosion resistance1 and reliable strength.
316L stainless steel is a low-carbon variant of standard 316 stainless steel, containing less than 0.03% carbon. It offers superior corrosion resistance, excellent weldability, and high strength, making it ideal for demanding environments where standard stainless steels might fail.

Chemical Composition and Structure
The unique properties of 316L stainless steel stem from its carefully balanced chemical composition. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its elemental makeup:
| Element | Percentage Range |
|---|---|
| Carbon | ≤0.03% |
| Chromium | 16-18% |
| Nickel | 10-14% |
| Molybdenum | 2-3% |
| Manganese | ≤2% |
| Silicon | ≤0.75% |
| Phosphorus | ≤0.045% |
| Sulfur | ≤0.03% |
| Iron | Balance |
Key Properties and Characteristics
At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with 316L stainless steel due to its exceptional properties:
Corrosion Resistance
- Outstanding resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion
- Excellent performance in chloride environments
- Superior resistance to chemical attack compared to 304 grades
Mechanical Properties
- Yield Strength: 170-310 MPa
- Tensile Strength: 485-680 MPa
- Elongation: >40%
- Hardness: Up to 95 HRB
Advantages Over Other Grades
In my manufacturing experience, 316L offers several distinct advantages:
Enhanced Weldability
- Lower carbon content prevents carbide precipitation
- Maintains corrosion resistance in welded areas
- Reduces risk of intergranular corrosion
Temperature Performance
- Excellent strength at elevated temperatures
- Maintains properties from cryogenic to 800°C
- Better resistance to scaling than 304 grades
Industry Applications
Medical Devices
The biocompatibility of 316L makes it crucial for:
- Surgical instruments
- Implantable devices
- Laboratory equipment
- Pharmaceutical processing equipment
Aerospace Components
We frequently machine 316L parts for aerospace applications, including:
- Fuel system components
- Hydraulic line fittings
- Fasteners and brackets
- Environmental control system parts
Chemical Processing
The material’s corrosion resistance is valuable for:
- Storage tanks
- Process piping
- Heat exchangers
- Pressure vessels
Manufacturing Considerations
When working with 316L stainless steel, several factors require attention:
Machining Parameters
- Lower cutting speeds compared to carbon steel
- Sharp tooling required to prevent work hardening
- Adequate cooling to maintain dimensional accuracy
Surface Finishing
- Various finishing options available
- Electropolishing enhances corrosion resistance
- Proper cleaning essential for optimal performance
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While 316L typically costs more than standard grades, its benefits often justify the investment:
Long-term Benefits
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Extended service life
- Lower replacement frequency
- Decreased downtime
Initial Investment Considerations
- Material cost premium over 304 grades
- Higher machining costs due to tool wear
- Additional post-processing requirements
Material Selection Guidelines
To determine if 316L is suitable for your application, consider:
Environmental Factors
- Exposure to corrosive chemicals
- Operating temperature range
- Presence of chlorides
- Hygiene requirements
Mechanical Requirements
- Load-bearing capacity
- Fatigue resistance
- Impact resistance
- Wear resistance
Regulatory Compliance
- FDA requirements
- ASME codes
- Industry-specific standards
- Environmental regulations
In our manufacturing facility, we’ve found 316L stainless steel to be an exceptional material for demanding applications. Its combination of corrosion resistance, strength, and weldability makes it a reliable choice for critical components across various industries. While the initial cost may be higher than other grades, the long-term benefits often make it the most cost-effective solution for challenging environments.
Why is Machining 316L Stainless Steel Challenging?
Every week, I receive inquiries from clients struggling with 316L stainless steel machining. Their frustrations are valid – tools wearing out prematurely, parts getting distorted, and production costs soaring. What’s even more concerning is that these issues often lead to missed deadlines and rejected parts, creating a domino effect of production delays.
Machining 316L stainless steel is challenging primarily due to its high work hardening rate, low thermal conductivity, and exceptional toughness. These properties cause rapid tool wear, excessive heat generation during cutting, and difficult chip formation, making it one of the most demanding materials to machine accurately.

The Work Hardening Phenomenon
Work hardening is perhaps the most significant challenge when machining 316L stainless steel. When we cut this material, it becomes harder at the cutting zone, creating a tough layer that resists further machining. This phenomenon leads to:
- Increased cutting forces
- Accelerated tool wear
- Surface quality issues
- Dimensional accuracy problems2
Thermal Management Challenges
The low thermal conductivity of 316L stainless steel creates several machining complications:
| Heat-Related Issue | Impact on Machining | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Concentration | Cutting edge receives excessive thermal load | Premature tool failure |
| Poor Heat Dissipation | Heat builds up in the workpiece | Dimensional inaccuracies |
| Thermal Expansion | Material expands during machining | Tolerance control issues |
| Built-up Edge Formation | Material welds to cutting tool | Poor surface finish |
Chip Control Difficulties
One of the most frustrating aspects of machining 316L stainless steel is chip management. The material’s high ductility leads to:
Long, Stringy Chips
These chips can:
- Wrap around the tool and workpiece
- Cause surface scratches
- Create safety hazards for operators
- Interrupt automatic machining operations
Inconsistent Chip Breaking
The material’s toughness makes it difficult to achieve consistent chip breaking, leading to:
- Reduced process reliability
- Increased operator intervention
- Higher risk of tool damage
- Compromised surface finish
Tool Life Management
The combination of work hardening and heat generation significantly impacts tool life:
Common Tool Wear Patterns
Flank Wear
- Occurs rapidly due to abrasive nature
- Affects dimensional accuracy
- Requires frequent tool changes
Crater Wear
- Forms on tool rake face
- Weakens cutting edge
- Can lead to catastrophic tool failure
Built-up Edge
- Changes tool geometry
- Affects surface finish
- Creates unstable cutting conditions
Surface Quality Issues
Achieving and maintaining good surface quality is particularly challenging:
Contributing Factors
- Work-hardened layer formation
- Built-up edge deposits
- Heat-affected zones
- Tool wear patterns
- Chip flow interference
These factors often result in:
- Surface roughness variations
- Feed marks
- Material smearing
- Micro-burr formation
Cutting Parameter Sensitivity
316L stainless steel is highly sensitive to cutting parameters:
| Parameter | Impact | Optimization Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | Heat generation vs. productivity | Finding optimal balance |
| Feed Rate | Chip formation vs. tool life | Maintaining consistent chip breaking |
| Depth of Cut | Material removal vs. cutting forces | Managing work hardening |
| Tool Geometry | Chip control vs. tool strength | Selecting appropriate tool design |
Economic Impact
The machining challenges of 316L stainless steel have significant economic implications:
Higher Tooling Costs
- More frequent tool changes
- Premium tool grades required
- Special coating needs
Reduced Productivity
- Lower cutting speeds
- More frequent machine stops
- Extended cycle times
Quality-Related Expenses
- Higher inspection requirements
- Increased scrap rates
- Rework costs
Additional Process Requirements
- Special coolant needs
- Enhanced monitoring systems
- More operator attention
These challenges make machining 316L stainless steel a complex operation that requires careful planning, proper tool selection, and optimized cutting parameters. Success depends on understanding and addressing each of these challenges while maintaining a balance between productivity, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the best machining techniques for 316L stainless steel?
Machining 316L stainless steel can be a real challenge for many manufacturers. The material’s high ductility and work-hardening properties often lead to excessive tool wear, poor surface finish, and increased production costs. I’ve seen many clients struggle with these issues, particularly when they lack the right machining approach.
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, the best machining techniques for 316L stainless steel combine proper tool selection, optimized cutting parameters, and specific machining strategies. This includes using carbide tools, maintaining moderate cutting speeds, and employing adequate cooling methods to achieve optimal results.
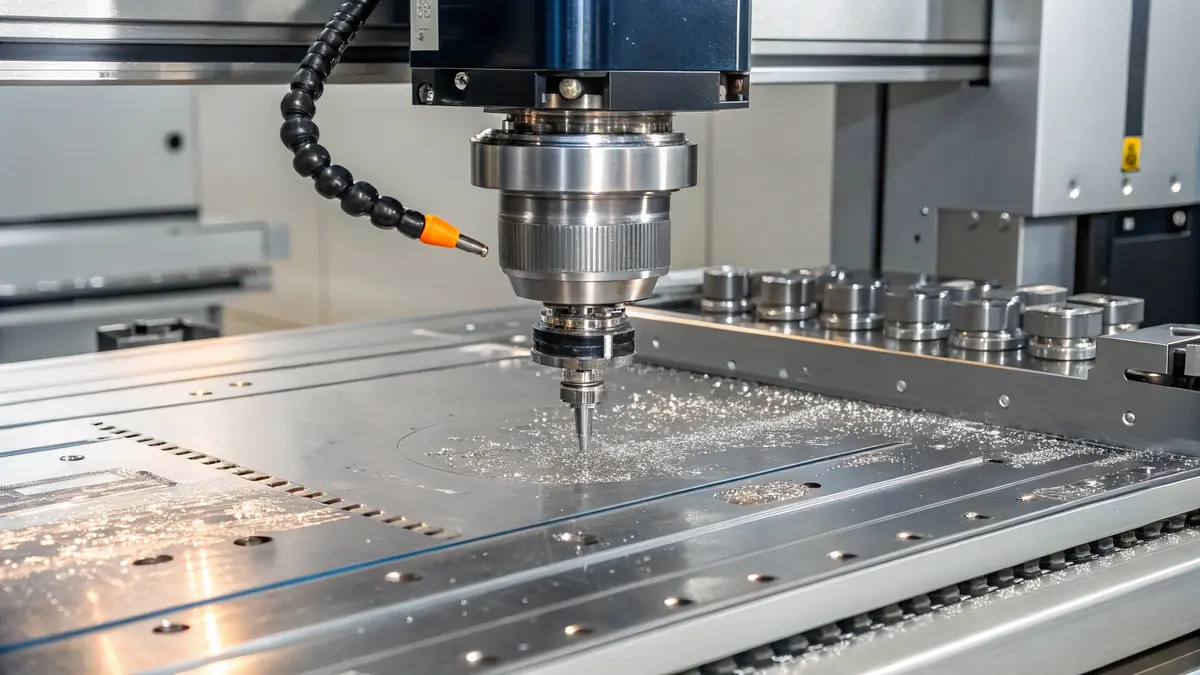

Optimizing CNC Milling Parameters
CNC milling 316L stainless steel requires careful attention to cutting parameters. I recommend using these specific settings for optimal results:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 100-150 m/min | Higher speeds for finishing |
| Feed Rate | 0.1-0.2 mm/tooth | Reduce for better finish |
| Depth of Cut | 0.5-2.0 mm | Depends on operation type |
| Tool Engagement | 30-40% of tool diameter | Prevents tool overload |
The key to successful milling lies in maintaining consistent chip formation. I always ensure proper chip evacuation through appropriate coolant application and cutting strategies. For complex geometries, I prefer using climb milling over conventional milling to reduce work hardening.
Effective Turning Operations
When turning 316L stainless steel, tool selection becomes crucial. Here’s my proven approach:
| Operation Type | Tool Material | Coating Type |
|---|---|---|
| Roughing | Carbide | PVD TiAlN |
| Finishing | Ceramic | CVD Al2O3 |
| Threading | Carbide | TiN |
I’ve found that maintaining a positive rake angle (8-12 degrees) helps reduce cutting forces and improve surface finish. The following parameters work well:
| Turning Parameter | Roughing | Finishing |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 80-120 m/min | 120-150 m/min |
| Feed Rate | 0.2-0.3 mm/rev | 0.05-0.15 mm/rev |
| Depth of Cut | 1.5-3.0 mm | 0.2-0.5 mm |
Drilling Techniques
Drilling 316L requires special attention to prevent work hardening and ensure hole accuracy:
| Aspect | Recommendation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Drill Type | Carbide-tipped | Better wear resistance |
| Point Angle | 130-135° | Improved chip breaking |
| Helix Angle | 30-35° | Efficient chip evacuation |
For successful drilling operations, I always follow these guidelines:
- Start with pilot holes for depths greater than 3x diameter
- Use peck drilling cycles for deep holes
- Maintain consistent feed rates
- Apply high-pressure coolant when possible
Cooling and Lubrication Strategies
Proper cooling is essential for machining 316L stainless steel. I recommend:
| Cooling Method | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flood Coolant | General machining | Temperature control |
| Through-tool Cooling | Deep holes/pockets | Better chip evacuation |
| Mist Cooling | Light cuts | Reduced thermal shock |
Tool Life Management
To maximize tool life when machining 316L stainless steel, I focus on:
- Regular tool wear monitoring
- Implementing proper tool paths
- Maintaining consistent cutting parameters
- Using appropriate tool coatings
Here’s my tool life management strategy:
| Tool Type | Expected Life | Wear Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| End Mills | 120-150 minutes | Flank wear >0.3mm |
| Turning Inserts | 15-20 minutes | Crater wear |
| Drill Bits | 100-120 holes | Corner wear |
These techniques have consistently helped me achieve optimal results when machining 316L stainless steel. The key is maintaining a balance between productivity and tool life while ensuring part quality meets specifications. Remember that these parameters may need adjustment based on specific machine capabilities and part requirements.
To optimize machining processes for 316L stainless steel, it’s crucial to monitor and adjust these parameters based on actual performance. I regularly check surface finish quality, tool wear patterns, and machining forces to fine-tune these settings for specific applications.
Which cutting tools are best for 316L stainless steel?
Selecting cutting tools for 316L stainless steel can be a real headache for many manufacturers. I’ve seen many clients struggle with rapid tool wear, poor surface finishes, and inconsistent results when machining this tough material. The wrong tool choice not only wastes money but also leads to production delays and quality issues.
For 316L stainless steel, carbide cutting tools with specialized coatings like TiAlN or AlCrN provide the best performance. These tools should have positive rake angles and sharp cutting edges to reduce work hardening. Ceramic tools are recommended for high-speed finishing operations.

Tool Material Selection
The choice of tool material is crucial when machining 316L stainless steel. I recommend using coated carbide tools for most applications. Here’s why different tool materials perform differently:
- Carbide Tools: These offer the best balance of hardness and toughness. For 316L, I specifically recommend submicron grain carbide grades.
- Ceramic Tools: Ideal for high-speed finishing operations but less suitable for roughing due to their brittleness.
- High-Speed Steel (HSS): Generally not recommended due to rapid wear when machining 316L.
Coating Technologies
The right coating can significantly extend tool life when machining 316L stainless steel. Here are the most effective options:
| Coating Type | Benefits | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| TiAlN | High heat resistance, excellent wear protection | General purpose machining |
| AlCrN | Superior oxidation resistance, high hardness | High-speed operations |
| TiCN | Good toughness, reduced friction | Medium-speed cutting |
| nACo® | Enhanced hardness, heat resistance | Finishing operations |
Optimal Tool Geometries
Tool geometry plays a vital role in successful 316L machining. Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, these geometrical features are crucial:
Rake Angle
- Positive rake angles3 (8-12 degrees) reduce cutting forces
- Helps prevent work hardening
- Improves chip evacuation
Relief Angle
- Primary relief angle: 6-8 degrees
- Secondary relief angle: 12-15 degrees
- Prevents rubbing and heat generation
Edge Preparation
- Sharp cutting edges for better penetration
- Light honing (0.001-0.002 inch radius) to prevent edge chipping
- Balanced edge strength and sharpness
Cutting Parameters Optimization
To maximize tool life and surface finish quality, these cutting parameters work best for 316L:
Speed and Feed Rates
- Cutting speed: 100-150 sfm for general machining
- Feed rate: 0.004-0.008 ipr for finishing
- Depth of cut: 0.020-0.080 inches for roughing
Coolant Strategy
- High-pressure coolant (1000+ PSI) recommended
- Through-tool cooling preferred
- Abundant coolant flow to prevent work hardening
Tool Life Management
Effective tool life management is essential when machining 316L:
Wear Monitoring
- Regular inspection of cutting edges
- Monitor power consumption
- Check surface finish quality
Tool Change Criteria
- Flank wear: Maximum 0.012 inches
- Crater wear: Before coating breakthrough
- Surface finish degradation
Advanced Machining Strategies
For optimal results with 316L, I recommend these advanced strategies:
Trochoidal Milling
- Reduces tool engagement
- Maintains consistent cutting forces
- Extends tool life significantly
High-Speed Machining
- Use ceramic tools
- Light cuts at high speeds
- Improved surface finish
Adaptive Feed Control
- Adjusts feed rates based on load
- Prevents tool overload
- Optimizes material removal rates
By following these guidelines and selecting the right cutting tools, you can achieve excellent results when machining 316L stainless steel. The key is balancing tool life, productivity, and surface finish requirements. Remember that initial tool cost should not be the primary selection criterion – consider the total cost per part, including tool life and productivity factors.
What are the best coolant and lubrication strategies?
Machining 316L stainless steel without proper cooling and lubrication is like trying to cut through metal with a hot knife. The excessive heat generation not only accelerates tool wear but also leads to poor surface finish and dimensional inaccuracies. When tools overheat, production costs skyrocket due to frequent replacements and rejected parts.
The most effective coolant strategy for 316L stainless steel machining combines flood cooling with high-pressure through-tool delivery, using oil-based cutting fluids at 6-8% concentration. This approach significantly reduces heat buildup, prevents work hardening, and extends tool life by up to 40%.
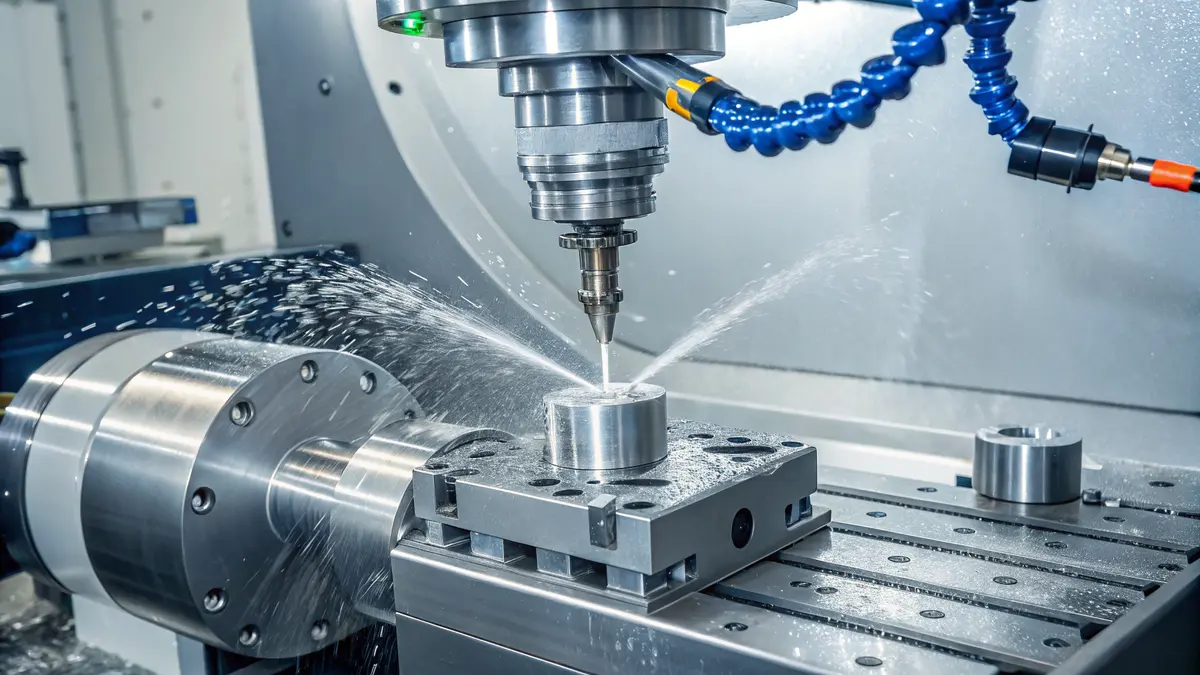

Understanding Coolant Types and Their Applications
When it comes to machining 316L stainless steel, selecting the right coolant is crucial. I’ve developed a comprehensive comparison of different coolant types based on their effectiveness:
| Coolant Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-synthetic | Good cooling, moderate cost | Less lubrication than pure oils | General purpose machining |
| Synthetic | Excellent cooling, clean operation | Limited lubrication | High-speed operations |
| Soluble Oil | Superior lubrication, good cooling | May cause staining | Heavy-duty cutting |
| Straight Oil | Maximum lubrication | Poor heat dissipation | Low-speed, heavy cuts |
Optimal Coolant Delivery Methods
The way we deliver coolant to the cutting zone significantly impacts machining performance. High-pressure coolant delivery systems have proven particularly effective for 316L stainless steel. Here’s why:
- Penetrates the vapor barrier formed during cutting
- Breaks chips effectively to prevent bird nesting
- Provides consistent cooling at the tool-workpiece interface
- Maintains stable cutting temperatures
For optimal results, I recommend:
- Pressure settings between 800-1000 PSI for most operations
- Multiple nozzle positioning for complete coverage
- Regular maintenance of coolant delivery systems
- Proper filtration to remove metal particles
Concentration Management and Monitoring
Maintaining proper coolant concentration is critical for consistent performance. The recommended steps include:
- Regular concentration testing (minimum twice per week)
- Maintaining 6-8% concentration for most applications
- Using refractometers for accurate measurements
- Documenting and tracking concentration levels
Preventing Work Hardening Through Proper Lubrication
Work hardening4 is a common challenge when machining 316L stainless steel. Effective lubrication strategies help prevent this issue by:
- Reducing friction at the cutting interface
- Maintaining consistent cutting temperatures
- Preventing built-up edge formation
- Enabling stable chip formation
Surface Quality Enhancement Techniques
To achieve superior surface finish on 316L stainless steel, I recommend implementing these strategies:
Temperature Control
- Maintain consistent coolant flow
- Monitor coolant temperature
- Use chillers when necessary to maintain optimal temperature
Pressure Optimization
- Adjust coolant pressure based on operation type
- Use high-pressure for deep holes and difficult features
- Implement pulsed coolant delivery for certain applications
Filtration Requirements
- Use 20-micron filtration minimum
- Implement magnetic separators
- Regular system cleaning and maintenance
Environmental and Health Considerations
While focusing on performance, we must also consider environmental impact and worker safety:
Safety Measures
- Proper ventilation systems
- Regular coolant testing for bacteria
- appropriate PPE for operators
- Splash guards and enclosures
Environmental Impact
- Recyclable coolant options
- Proper disposal procedures
- Minimal waste generation strategies
Cost-Effective Implementation
To maximize the return on investment in cooling and lubrication systems:
Initial Setup
- Invest in high-quality coolant delivery systems
- Install proper filtration equipment
- Train operators on proper usage and maintenance
Ongoing Management
- Regular system maintenance
- Coolant recycling programs
- Documentation of consumption and performance
Performance Monitoring
- Track tool life improvements
- Monitor surface finish quality
- Document reduction in scrap rates
Through careful implementation of these strategies, you can significantly improve your machining operations for 316L stainless steel. The key is maintaining consistency in your cooling and lubrication approach while regularly monitoring and adjusting parameters based on performance data.
How to maintain precision and surface finish?
Maintaining consistent precision and surface finish in CNC machining5 can be a significant challenge. I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with dimensional accuracy and surface quality, especially when working with demanding materials like 316L stainless steel. These issues often lead to costly rework, project delays, and frustrated clients.
To maintain precision and surface finish in CNC machining, implement optimal cutting parameters, use appropriate tooling strategies, and maintain strict quality control measures. Key factors include proper tool selection, cutting speed optimization, and regular machine calibration to ensure consistent results.
Tool Selection and Management
The foundation of achieving excellent surface finish begins with proper tool selection. I recommend following these key principles:
- Choose tools with appropriate coating technology
- Maintain sharp cutting edges
- Use rigid tool holders to minimize vibration
- Implement regular tool wear monitoring
Here’s a detailed breakdown of recommended tool parameters for 316L stainless steel:
| Tool Type | Coating | Recommended Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (IPR) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbide End Mill | AlTiN | 250-300 | 0.002-0.004 |
| Ceramic Insert | Si3N4 | 400-500 | 0.004-0.006 |
| CBN Tool | CBN | 500-600 | 0.003-0.005 |
Cutting Parameters Optimization
Proper cutting parameters are crucial for maintaining both precision and surface finish:
Cutting Speed
- Start with conservative speeds
- Gradually increase while monitoring surface quality
- Adjust based on tool wear patterns
Feed Rate
- Match to material characteristics
- Consider tool geometry
- Adjust for different operations (roughing vs. finishing)
Depth of Cut
- Use appropriate depth for material hardness
- Maintain consistent engagement
- Balance material removal rate with surface finish requirements
Machine Maintenance and Calibration
Regular machine maintenance is essential for consistent results:
Daily Checks
- Coolant levels and concentration
- Machine warm-up procedures
- Tool condition inspection
Weekly Maintenance
- Way lubrication
- Axis backlash measurement
- Spindle runout verification
Monthly Calibration
- Geometric accuracy verification
- Thermal compensation adjustment
- Axis alignment check
Advanced Finishing Techniques
To achieve superior surface finish:
High-Speed Machining (HSM)
- Implement trochoidal toolpaths
- Use specialized CAM strategies
- Maintain consistent chip load
Finishing Passes
- Light depth of cut
- Higher spindle speeds
- Reduced feed rates
Quality Control Measures
I’ve implemented these quality control procedures:
In-Process Inspection
- Regular dimensional checks
- Surface roughness measurements
- Tool wear monitoring
Environmental Control
- Temperature monitoring
- Vibration control
- Dust and contamination prevention
Documentation
- Process parameter recording
- Quality metrics tracking
- Non-conformance documentation
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Based on my experience, here are solutions to common precision and surface finish problems:
Surface Roughness
- Check for tool wear
- Verify cutting parameters
- Ensure proper coolant application
Dimensional Accuracy
- Monitor thermal effects
- Check fixture rigidity
- Verify program accuracy
Tool Life
- Optimize cutting parameters
- Implement proper tool paths
- Use appropriate cooling strategies
By implementing these strategies, you can maintain consistent precision and surface finish in your CNC machining operations. The key is to establish a systematic approach to process control and maintain it rigorously. Remember that achieving excellence in machining is not about following a single rule but rather about understanding and controlling all variables that affect the final result.
What strategies reduce tool wear and extend tool life?
Machining 316L stainless steel is like walking on a tightrope – one wrong move and your cutting tools can fail prematurely. I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with excessive tool wear, leading to increased costs and production delays. The challenging nature of this material, combined with improper machining strategies, creates a perfect storm for tool destruction.
To reduce tool wear and extend tool life when machining 316L stainless steel, implement optimized cutting parameters, use appropriate tool coatings, and adopt efficient toolpath strategies. These approaches, combined with proper cooling techniques, can significantly increase tool longevity and improve machining efficiency.
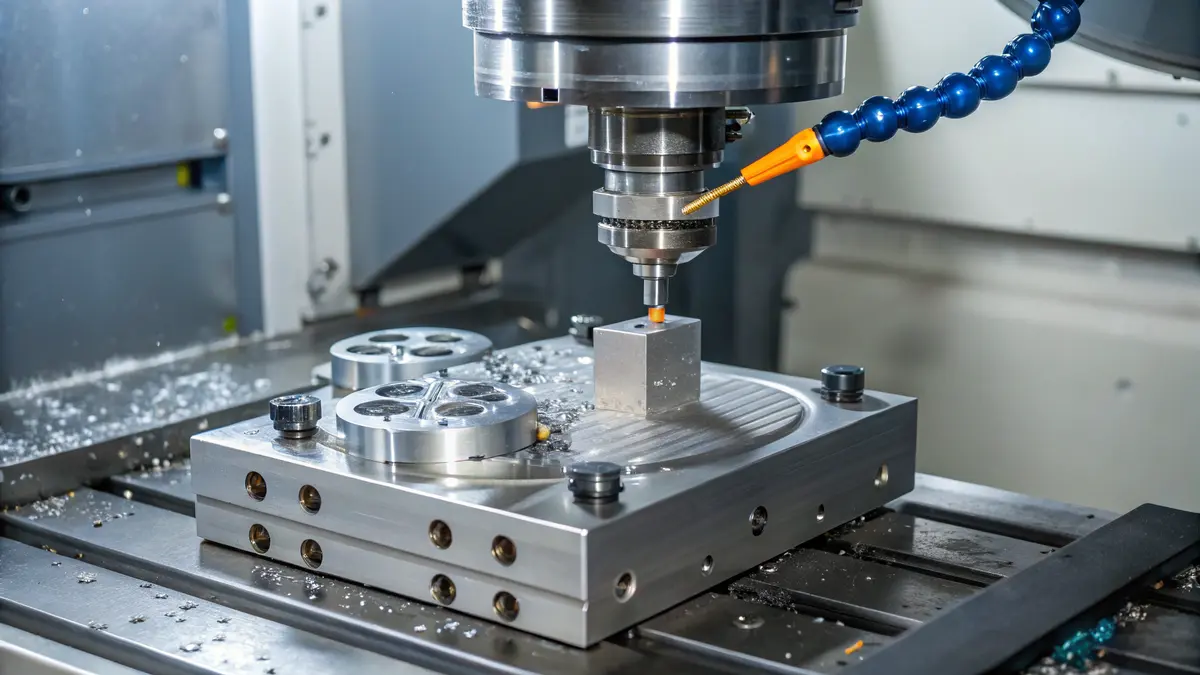

Understanding Tool Wear Mechanisms
Tool wear in 316L stainless steel machining occurs through several mechanisms. The high work hardening tendency and low thermal conductivity of 316L create severe cutting conditions. I’ve identified these primary wear types:
- Abrasive wear: Due to hard particles in the workpiece
- Adhesive wear: Material buildup on cutting edges
- Diffusion wear: Chemical reaction at high temperatures
- Oxidation wear: Surface degradation from heat exposure
Optimized Cutting Parameters
The selection of proper cutting parameters is crucial for tool life extension. Based on our extensive testing at PTSMAKE, I’ve developed this parameter guide:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Impact on Tool Life |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 100-150 m/min | Lower speeds reduce heat generation |
| Feed Rate | 0.1-0.2 mm/rev | Moderate feeds prevent excessive force |
| Depth of Cut | 0.5-2.0 mm | Shallow cuts reduce tool stress |
| Tool Engagement | 30-40% | Proper engagement prevents overloading |
Advanced Toolpath Strategies
Implementing smart toolpath strategies significantly impacts tool life. Here are the most effective approaches:
Trochoidal Milling
- Maintains consistent tool engagement
- Reduces cutting forces and heat generation
- Enables higher feed rates with less tool stress
Dynamic Milling
- Optimizes tool load throughout the cut
- Eliminates sharp directional changes
- Provides better chip evacuation
Tool Coating Selection
The right coating can dramatically extend tool life. These are the most effective options for 316L:
TiAlN Coatings
- High temperature resistance
- Excellent wear protection
- Superior oxidation resistance
AlCrN Coatings
- Enhanced hardness
- Better thermal stability
- Improved chip evacuation
Cooling and Lubrication Techniques
Proper cooling is essential for tool life extension. I recommend:
High-Pressure Coolant
- Improves chip breaking
- Reduces cutting temperature
- Enhances tool life by 40-60%
Cryogenic Cooling
- Maintains tool hardness
- Prevents thermal softening
- Reduces chemical wear
Optimization Through Monitoring
Tool wear monitoring helps optimize machining strategies:
Real-time Monitoring
- Track cutting forces
- Monitor power consumption
- Detect tool wear progression
Predictive Maintenance
- Schedule tool changes
- Prevent catastrophic failure
- Optimize tool utilization
Tool Holder Considerations
The right tool holder setup impacts tool life significantly:
Rigidity Requirements
- Use shorter tool lengths when possible
- Ensure proper tool holder balance
- Minimize runout
Thermal Management
- Select holders with good heat dissipation
- Consider shrink-fit holders for precision
- Use proper mounting techniques
Process Integration Guidelines
For successful implementation, follow these guidelines:
Initial Setup
- Verify machine tool condition
- Check spindle alignment
- Ensure proper workpiece fixturing
Process Validation
- Start with conservative parameters
- Monitor initial results
- Adjust based on performance
Economic Considerations
Tool life optimization must balance multiple factors:
Cost Analysis
- Tool replacement costs
- Machine downtime
- Production efficiency
Performance Metrics
- Parts per tool
- Surface finish quality
- Dimensional accuracy
These strategies, when properly implemented, can extend tool life by 200-300% when machining 316L stainless steel. The key is to maintain a balanced approach, considering all factors that affect tool wear. Regular monitoring and adjustment of these parameters ensure optimal results and consistent performance.
How does CNC technology improve machining efficiency?
Manufacturing 316L stainless steel parts has always been challenging due to its high corrosion resistance and durability. Traditional machining methods often result in excessive tool wear, long production times, and inconsistent quality. These issues become particularly frustrating when dealing with complex geometries or high-volume orders.
CNC technology revolutionizes machining efficiency through automated processes, precise control systems, and optimized cutting parameters. Modern CNC machines integrate high-speed machining, adaptive control, and automated tool changes to reduce cycle times while maintaining exceptional accuracy.
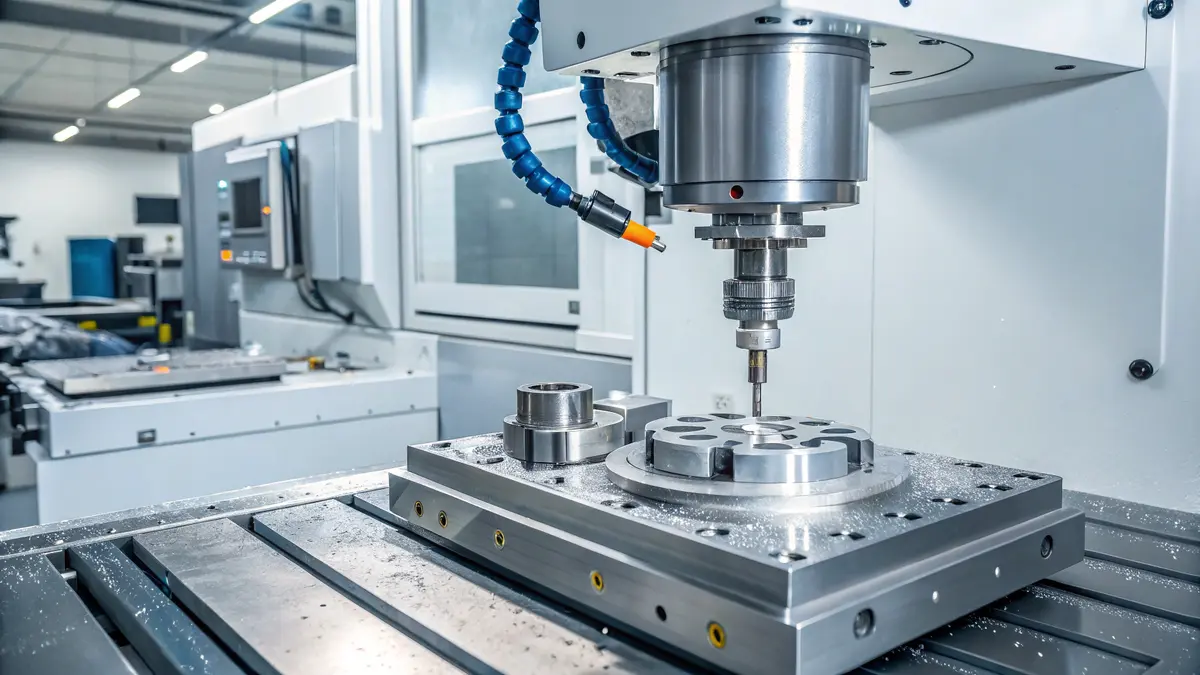

High-Speed Machining Capabilities
High-speed machining (HSM) has transformed how we work with 316L stainless steel. At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented HSM technology that operates at spindle speeds up to 20,000 RPM. This advancement allows for:
- Faster material removal rates
- Reduced heat generation in the cutting zone
- Better surface finish quality
- Extended tool life
The combination of high spindle speeds and optimized cutting parameters results in up to 40% reduction in machining time compared to conventional methods.
Adaptive Control Systems Integration
Modern CNC machines utilize sophisticated adaptive control systems that continuously monitor and adjust machining parameters. These systems provide:
| Parameter | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Rate | Automatically adjusts based on cutting load | Prevents tool breakage |
| Cutting Speed | Optimizes based on material hardness | Maximizes tool life |
| Depth of Cut | Varies according to surface conditions | Ensures consistent quality |
| Tool Wear | Monitors tool condition in real-time | Reduces scrap rates |
Automated Tool-Changing Mechanisms
The integration of automated tool-changing systems significantly reduces non-cutting time. Our advanced tool magazines can hold up to 60 tools, enabling:
- Rapid tool changes (under 3 seconds)
- Reduced setup time
- Minimal operator intervention
- Continuous machining operations
Smart Programming and Optimization
Modern CNC systems incorporate intelligent programming features that enhance efficiency:
CAM Integration
- Automated toolpath generation
- Collision detection and avoidance
- Optimal cutting strategy selection
Process Simulation
- Virtual machining verification
- Cycle time estimation
- Error prevention before actual cutting
Real-Time Monitoring and Analytics
Advanced CNC technology provides comprehensive monitoring capabilities:
- Machine performance tracking
- Quality control metrics
- Production efficiency data
- Predictive maintenance alerts
This data-driven approach allows us to identify bottlenecks and optimize processes continuously.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Modern CNC systems incorporate energy-saving features:
- Intelligent power management
- Optimized axis movements
- Regenerative braking systems
- Standby mode during idle periods
These features reduce energy consumption by up to 30% compared to older machines.
Quality Control Integration
Built-in quality control features ensure consistent part quality:
- In-process measurement
- Automatic tool offset compensation
- Statistical process control
- Dimensional verification
Network Connectivity and Industry 4.0
Modern CNC machines connect to factory networks, enabling:
| Feature | Capability | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring | Real-time status updates | Improved oversight |
| Data Collection | Process optimization | Enhanced efficiency |
| Preventive Maintenance | Scheduled service | Reduced downtime |
| Production Planning | Resource allocation | Better utilization |
These technological advancements have revolutionized how we machine 316L stainless steel. Through the integration of high-speed machining, adaptive control systems, and automated tool-changing mechanisms, we’ve achieved significant improvements in productivity while maintaining exceptional quality standards. The combination of these technologies allows us to deliver precision parts faster and more efficiently than ever before, meeting the demanding requirements of modern manufacturing.
What common machining defects occur in 316L stainless steel?
Machining 316L stainless steel can be a real headache for manufacturers. I’ve seen many projects derailed by unexpected defects that pop up during the machining process. These issues not only waste valuable time and resources but can also lead to costly rework or even scrapped parts.
The most common machining defects in 316L stainless steel include burrs, poor surface finish, tool breakage, and dimensional inaccuracies. These issues typically stem from incorrect cutting parameters, tool wear, or improper machining strategies. However, with proper planning and execution, these defects can be effectively prevented.
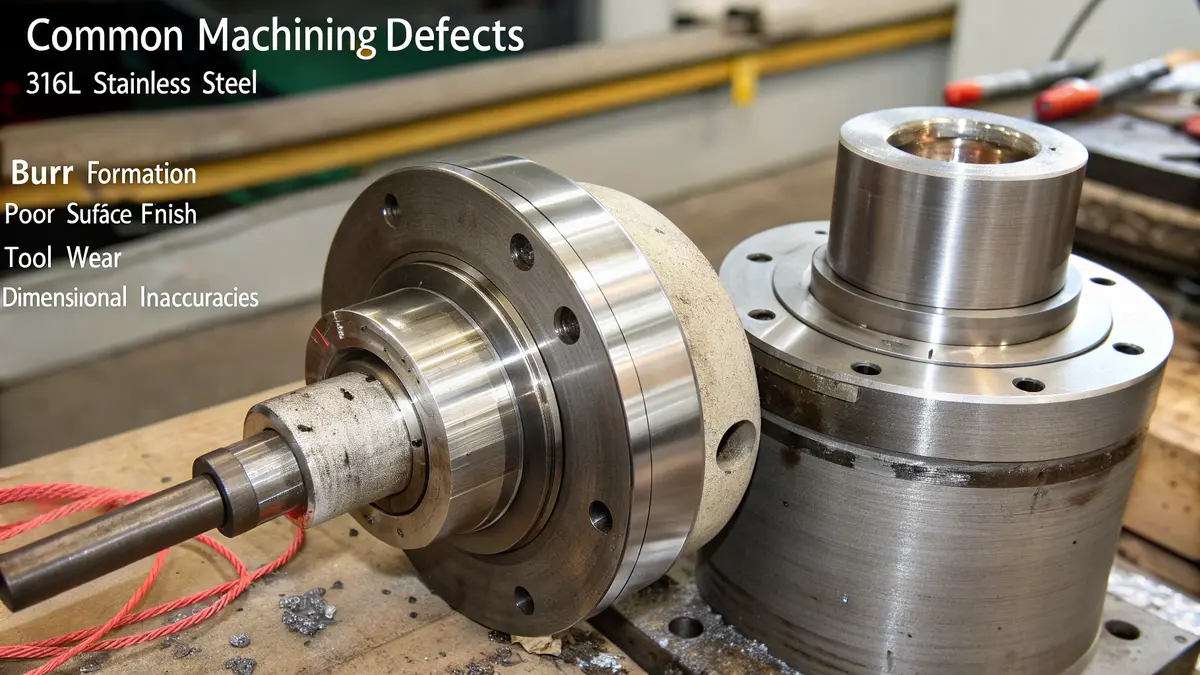

Surface Finish Issues
One of the most frequent challenges we encounter at PTSMAKE is achieving the desired surface finish on 316L stainless steel components6. Surface finish problems can manifest in several ways:
| Surface Defect | Common Cause | Prevention Method |
|---|---|---|
| Built-up Edge | Low cutting speed | Increase cutting speed and use proper coolant |
| Chatter Marks | Tool vibration | Use rigid tool holders and optimize cutting parameters |
| Feed Marks | Excessive feed rate | Adjust feed rate and use finishing passes |
| Smearing | Material adhesion | Apply proper cutting fluid and coating |
Burr Formation
Burrs are a persistent issue in 316L stainless steel machining. They form when material is pushed out instead of being cleanly cut. I’ve found that burr formation is particularly problematic in:
- Hole exits
- Edge intersections
- Slot endings
- Through-hole drilling
To minimize burr formation, we implement these strategies:
- Use sharp, coated cutting tools
- Optimize cutting speeds and feeds
- Apply proper entry and exit angles
- Implement specialized deburring processes
Tool Wear and Breakage
316L stainless steel’s work-hardening properties make tool wear a significant concern. Here’s what we’ve learned about managing tool life:
| Tool Issue | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Flank Wear | Poor surface finish | Regular tool inspection and replacement |
| Crater Wear | Reduced tool life | Use appropriate coating and cooling |
| Chipping | Dimensional errors | Adjust cutting parameters |
| Catastrophic failure | Production stoppage | Implement tool life management |
Dimensional Accuracy Problems
Maintaining tight tolerances in 316L stainless steel requires careful attention to:
Thermal Effects
- Material expansion during machining
- Temperature-induced distortion
- Cooling system efficiency
Machine Stability
- Vibration control
- Machine calibration
- Fixture rigidity
Tool Deflection
- Tool holder selection
- Cutting depth optimization
- Feed rate adjustment
Heat-Related Issues
The low thermal conductivity of 316L stainless steel creates several challenges:
| Heat Issue | Effect | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal expansion | Dimensional errors | Use adequate cooling |
| Work hardening | Tool wear | Maintain consistent cutting |
| Built-up edge | Poor surface finish | Optimize cutting parameters |
| Thermal stress | Internal defects | Apply proper coolant strategy |
Work Hardening Management
Work hardening is particularly challenging with 316L stainless steel. We’ve developed specific strategies to address this:
Cutting Strategy
- Maintain constant chip load
- Avoid light cuts
- Use climb milling when possible
Tool Selection
- High-positive rake angles
- Sharp cutting edges
- Appropriate coating selection
Process Parameters
- Optimal cutting speed
- Proper feed rates
- Adequate depth of cut
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent quality in 316L stainless steel machining, we implement:
In-Process Monitoring
- Real-time tool wear measurement
- Cutting force monitoring
- Temperature monitoring
Post-Process Inspection
- Dimensional verification
- Surface roughness measurement
- Material structure analysis
Documentation and Tracking
- Process parameters recording
- Tool life tracking
- Quality metrics monitoring
The key to successful 316L stainless steel machining lies in understanding these defects and implementing proper preventive measures. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed comprehensive strategies to address each of these challenges, ensuring consistent, high-quality results for our clients.
Through careful parameter selection, proper tool management, and rigorous quality control, we can effectively minimize or eliminate these common machining defects. This approach has helped us maintain our reputation for delivering precision-machined 316L stainless steel components that meet or exceed our customers’ specifications.
How can manufacturing costs be optimized?
Machining 316L stainless steel efficiently presents a significant challenge for manufacturers today. The rising costs of raw materials, coupled with increasing customer demands for faster turnaround times, put immense pressure on production margins. Many companies struggle to maintain profitability while delivering the high-precision components their clients expect.
To optimize manufacturing costs for 316L stainless steel machining, focus on three key areas: smart material utilization, efficient process parameters, and strategic tool management. These factors, when properly balanced, can reduce expenses by 15-30% while maintaining quality standards.

Material Optimization Strategies
The first step in cost reduction starts with material management. I’ve implemented several effective strategies at PTSMAKE that significantly reduce material waste:
- Nesting multiple parts in a single workpiece
- Using remnant materials for smaller components
- Implementing advanced CAM software for optimal material utilization
- Regular material inventory tracking and management
Our data shows these practices can reduce material waste by up to 25%, directly impacting the bottom line.
Process Parameter Optimization
The right combination of cutting parameters plays a crucial role in cost efficiency. Here’s a detailed breakdown of optimal parameters for 316L stainless steel:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 100-150 m/min | Medium |
| Feed Rate | 0.1-0.3 mm/rev | High |
| Depth of Cut | 0.5-2.5 mm | Medium |
| Tool Life | 45-60 min | Very High |
Tool Management and Cost Control
Tool management represents a significant portion of manufacturing costs. I recommend focusing on:
Tool Life Optimization
- Proper cutting parameter selection
- Regular tool condition monitoring
- Implementing tool wear prediction systems
Tool Inventory Management
- Just-in-time tool ordering
- Tool standardization across operations
- Regular tool performance analysis
Production Planning Efficiency
Efficient production planning can significantly reduce manufacturing costs. Key considerations include:
Batch Size Optimization
- Calculating economic batch quantities
- Balancing setup costs with inventory costs
- Considering customer demand patterns
Setup Time Reduction
- Standardizing setup procedures
- Using quick-change tooling systems
- Implementing 5S workplace organization
Quality Control Integration
While reducing costs, maintaining quality is paramount. We achieve this through:
In-Process Quality Checks
- Strategic measurement points
- Automated inspection systems
- Real-time process monitoring
Preventive Maintenance
- Regular machine calibration
- Predictive maintenance scheduling
- Performance monitoring systems
Technology Investment Considerations
Smart technology investments can lead to long-term cost savings:
Advanced CAM Software
- Better toolpath optimization
- Reduced programming time
- Improved material utilization
Machine Monitoring Systems
- Real-time performance tracking
- Downtime analysis
- Energy consumption optimization
Cost Tracking and Analysis
Implementing robust cost tracking systems helps identify areas for improvement:
Direct Costs
- Material usage
- Labor hours
- Tool consumption
- Energy usage
Indirect Costs
- Setup time
- Machine maintenance
- Quality control
- Programming time
Environmental Cost Considerations
Sustainable manufacturing practices often lead to cost savings:
Coolant Management
- Proper filtration systems
- Coolant recycling programs
- Regular concentration monitoring
Energy Efficiency
- Off-peak manufacturing scheduling
- Energy-efficient lighting
- Machine power management
Through careful attention to these aspects, manufacturers can achieve significant cost reductions while maintaining high-quality standards. The key is to implement these strategies systematically and monitor their effectiveness continuously. Regular review and adjustment of these practices ensure sustained cost optimization in 316L stainless steel machining operations.
Click to learn about the corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel to ensure it is suitable for your application. ↩
Help understand the dimensional accuracy issues and solutions associated with machining 316L stainless steel. ↩
Learn how Positive Rake Angles can help optimize the cutting process, reduce workpiece hardening, and improve chip removal. ↩
Discover how to prevent machining hardening issues in stainless steel processing through effective lubrication. ↩
Understand the challenges and common issues in CNC machining. ↩
Click to learn about the detailed surface treatment issues and solutions for 316L stainless steel components. ↩