After 15+ years in precision manufacturing, I’ve seen countless hydraulic cylinder failures due to poorly designed cylinder heads. It’s a costly mistake that can shut down entire production lines.
A hydraulic cylinder head is a crucial component that seals the cylinder, guides the piston rod, and maintains system pressure. It needs precise machining tolerances and proper material selection to ensure reliable performance and prevent hydraulic fluid leakage.

I want to share my experience with you because choosing the right cylinder head is crucial for your system’s success. In my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve helped hundreds of clients optimize their hydraulic systems with precisely machined cylinder heads. Let me walk you through what really matters when it comes to cylinder head design and manufacturing.
What Are Hydraulic Cylinder Heads?
Every day in my manufacturing facility, I witness the crucial role that hydraulic cylinder heads play in modern machinery. These components are the unsung heroes that keep hydraulic systems running smoothly, from construction equipment to precision manufacturing tools.
A hydraulic cylinder head is a vital component that seals and guides the piston rod while directing fluid flow in hydraulic systems. It serves as both an end cap and a control point, converting hydraulic pressure into mechanical force through precisely engineered channels and sealing mechanisms.
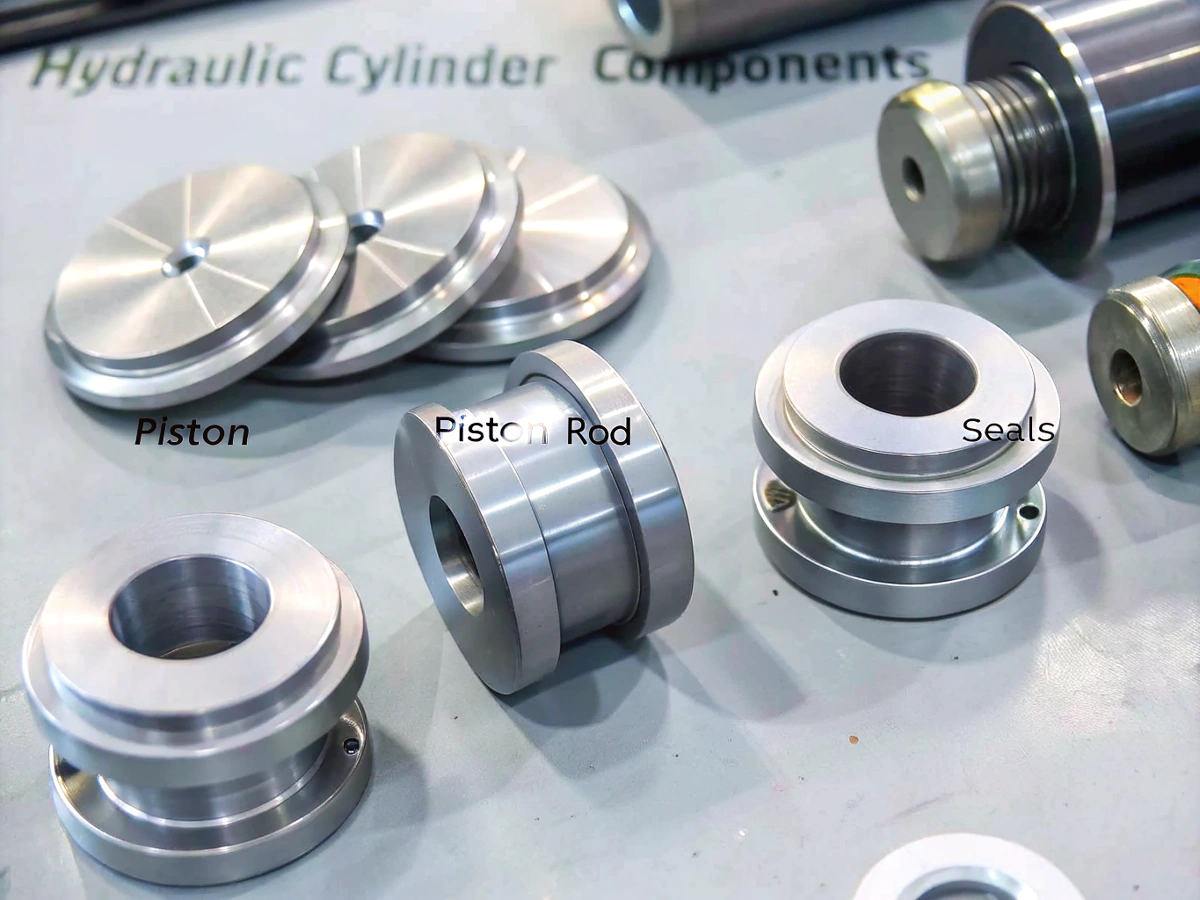

Core Functions and Design Features
The design of hydraulic cylinder heads is far more complex than meets the eye. From my experience working with various manufacturers, I’ve identified several critical functions these components must perform:
- Sealing System Integration
- Rod Guidance
- Fluid Flow Management
- Pressure Containment
- Heat Dissipation
Material Selection and Performance
When it comes to manufacturing hydraulic cylinder heads, material choice is crucial. Here’s a breakdown of common materials and their applications:
| Material Type | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Heavy-duty cylinders | High wear resistance, good thermal stability |
| Steel Alloys | High-pressure systems | Superior strength, excellent durability |
| Aluminum | Mobile applications | Lightweight, good heat dissipation |
| Bronze | Guide bushings | Low friction, self-lubricating properties |
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process for hydraulic cylinder heads requires precise machining techniques. The most common methods include:
- CNC Machining: Ensures precise dimensional accuracy
- Boring: Creates smooth internal surfaces
- Threading: Allows secure attachment
- Surface finishing: Improves sealing capabilities
Design Considerations for Different Applications
The design of hydraulic cylinder heads varies significantly based on:
Operating Pressure
- Low pressure (up to 2000 psi)
- Medium pressure (2000-5000 psi)
- High pressure (above 5000 psi)
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature extremes
- Exposure to corrosive elements
- Dust and debris presence
Maintenance Requirements
- Accessibility for seal replacement
- Serviceability of guide bushings
- Inspection points
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure reliability, hydraulic cylinder heads undergo rigorous testing:
- Dimensional Inspection
- Material Hardness Testing
- Pressure Testing
- Surface Finish Verification
- Seal Integration Testing
Integration with Hydraulic Systems
The effectiveness of a hydraulic cylinder head depends heavily on its integration with other system components:
Piston Rod Compatibility
- Surface finish requirements
- Hardness specifications
- Dimensional tolerances
Seal Selection
- Static seals
- Dynamic seals
- Wiper seals
- Guide rings
Mounting Considerations
- Flange mounting
- Threaded mounting
- Tie-rod mounting
Performance Optimization
To maximize the performance of hydraulic cylinder heads:
Fluid Flow Analysis
- Port sizing optimization
- Flow path design
- Pressure drop minimization
Thermal Management
- Heat dissipation features
- Material thermal properties
- Cooling considerations
Wear Resistance
- Surface treatment options
- Coating selections
- Material hardening processes
Common Issues and Solutions
Through my manufacturing experience, I’ve encountered several common challenges:
Seal Failure
- Solution: Proper material selection and installation procedures
- Regular maintenance schedules
- Environmental protection
Alignment Issues
- Solution: Precise machining tolerances
- Proper installation procedures
- Regular inspection protocols
Pressure Limitations
- Solution: Appropriate design safety factors
- Material strength considerations
- Proper pressure relief systems
The success of any hydraulic system largely depends on the quality and proper functioning of its cylinder heads. Understanding these components’ complexities helps ensure optimal performance and longevity in various applications, from mobile equipment to industrial machinery.
From materials selection to manufacturing processes, each aspect of hydraulic cylinder head design and production requires careful consideration and expertise. This comprehensive approach ensures reliable operation and long service life in demanding applications.
What Are the Key Components of Hydraulic Cylinder Heads?
Ever wondered why some hydraulic cylinders last for years while others fail prematurely? The secret lies in the quality and design of their cylinder heads. As a precision manufacturer, I’ve seen how these seemingly simple components can make or break entire hydraulic systems.
A hydraulic cylinder head consists of five critical components: seals, retaining rings, ports, fittings, and guide bushings. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining pressure, preventing leakage, and ensuring smooth operation of the hydraulic system.
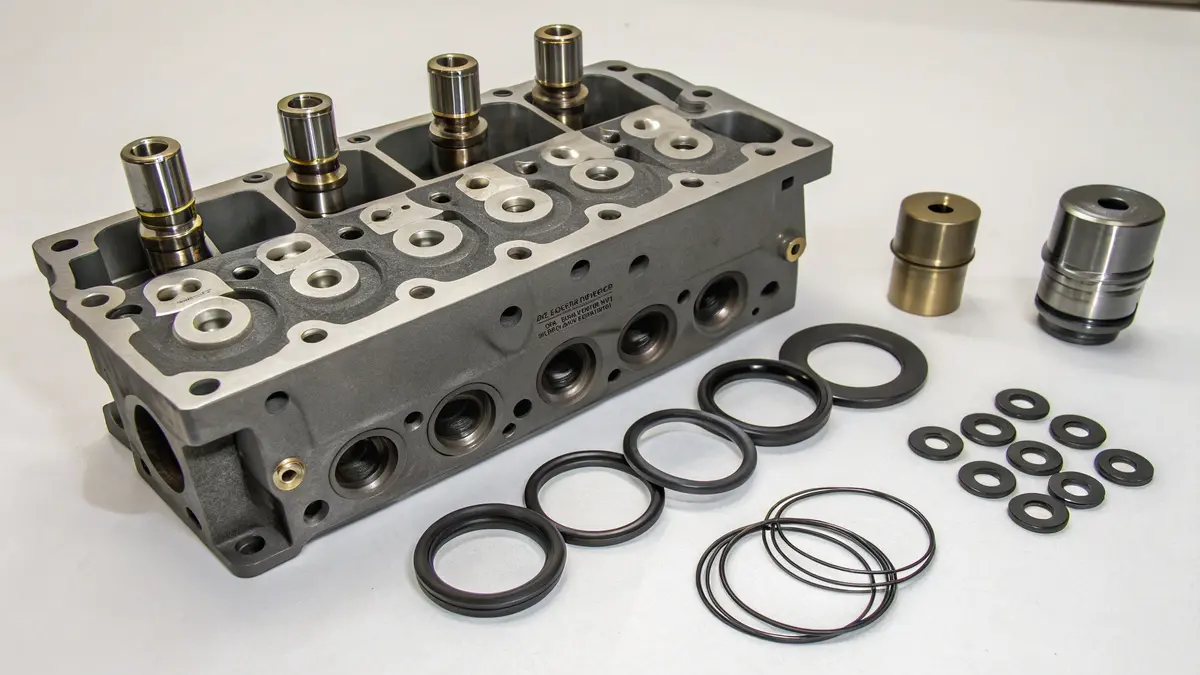

Sealing Systems
The sealing system is perhaps the most crucial aspect of any hydraulic cylinder head. We use three main types of seals:
Primary Rod Seals
- Prevents external leakage
- Usually made from polyurethane or PTFE compounds
- Must withstand high pressure and temperature variations
Wiper Seals
- Keeps contaminants out
- Protects internal components
- Typically manufactured from NBR or polyurethane
Buffer Seals
- Manages pressure spikes
- Extends primary seal life
- Made from specialized elastomers
Retaining Ring Configuration
Retaining rings serve as mechanical fasteners that secure components within the cylinder head. Here’s what makes them essential:
| Ring Type | Primary Function | Material Choice |
|---|---|---|
| External | Component retention | Spring steel |
| Internal | Groove securing | Carbon steel |
| Wave | Vibration dampening | Stainless steel |
Port Design and Configuration
Ports are critical pathways for hydraulic fluid movement. The design must consider:
Flow Characteristics
- Port size optimization
- Flow direction control
- Pressure drop minimization
Threading Options
- SAE standard ports
- BSPP configurations
- NPT alternatives
Guide Bushings
Guide bushings provide essential support and alignment:
Material Selection
- Bronze for general applications
- Composite materials for high-load scenarios
- Steel-backed variants for extreme conditions
Surface Finish
- Precision-ground surfaces
- Specific roughness requirements
- Wear-resistant coatings
Mounting and Connection Fittings
The connection system requires careful consideration:
Standard Fittings
- JIC fittings
- SAE flange connections
- ORFS (O-Ring Face Seal)
Custom Solutions
- Application-specific designs
- Load-bearing capacity
- Installation requirements
Material Considerations
Material selection greatly impacts performance:
Head Body
- Ductile iron for standard applications
- Steel alloys for high-pressure systems
- Aluminum for weight-sensitive applications
Surface Treatments
- Hard chrome plating
- Nickel coating
- Heat treatment options
Quality Control Measures
For optimal performance, we implement strict quality control:
Dimensional Accuracy
- Precision measurements
- Tolerance verification
- Surface finish inspection
Performance Testing
- Pressure testing
- Leak detection
- Cyclic testing
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial:
Installation Guidelines
- Torque specifications
- Alignment requirements
- Assembly sequence
Maintenance Schedule
- Regular inspection intervals
- Seal replacement criteria
- Lubrication requirements
The complexity of hydraulic cylinder heads requires careful attention to detail during design and manufacturing. Every component must work in perfect harmony to ensure reliable operation. Through careful material selection, precise manufacturing processes, and rigorous quality control, we can create cylinder heads that deliver exceptional performance and longevity.
From my manufacturing experience, the most successful hydraulic systems are those where each component is carefully selected and precisely manufactured to work together. This attention to detail in component selection and integration is what separates high-performing hydraulic systems from those that frequently require maintenance or replacement.
How Are Hydraulic Cylinder Heads Manufactured?
Ever wondered what makes hydraulic cylinder heads so crucial yet complex to manufacture? As someone who oversees precision manufacturing daily, I’ve witnessed the fascinating evolution of their production processes from traditional methods to cutting-edge technologies.
Manufacturing hydraulic cylinder heads requires precision CNC machining, careful material selection, and rigorous quality control. The process combines advanced manufacturing techniques with strict tolerances to ensure optimal performance and reliability in hydraulic systems.
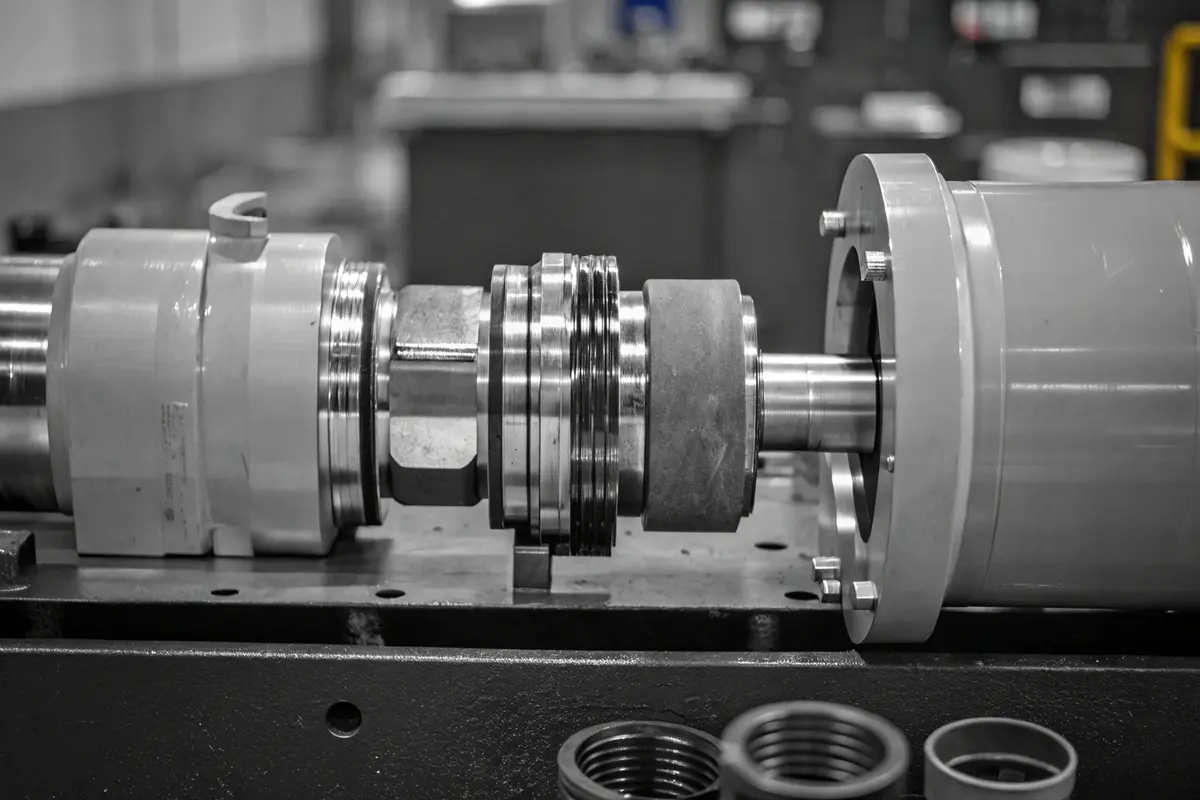
Material Selection Fundamentals
The choice of material significantly impacts the performance and durability of hydraulic cylinder heads. From my experience working with various manufacturers, I’ve observed that material selection depends on several key factors:
| Material Type | Advantages | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, cost-effective | Standard pressure systems |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, durable | Marine and chemical processing |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, good heat dissipation | Mobile hydraulic systems |
| Ductile Iron | Excellent wear resistance, shock absorption | Heavy machinery |
Precision CNC Machining Process
The manufacturing process begins with CNC machining, which ensures exceptional accuracy and repeatability. The key steps include:
Surface Preparation
- Initial facing and squaring of raw material
- Establishing reference surfaces
- Verification of material specifications
Core Operations
- Boring of main cylinder cavity
- Threading for port connections
- Creation of mounting surfaces
- Machining of seal grooves
Secondary Features
- Port drilling and tapping
- Relief groove machining
- Surface finishing operations
Quality Control Measures
We implement comprehensive quality control throughout the manufacturing process:
Dimensional Inspection
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) verification
- Surface roughness testing
- Geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T) checks
Material Testing
- Hardness testing
- Chemical composition analysis
- Structural integrity verification
Innovation in Manufacturing Technologies
Recent technological advances have revolutionized hydraulic cylinder head manufacturing:
Advanced CNC Programming
- 5-axis simultaneous machining
- Adaptive toolpath optimization
- Real-time tool monitoring
Automation Integration
- Robotic material handling
- Automated inspection systems
- Smart manufacturing protocols
Cost Optimization Strategies
To maintain competitive pricing while ensuring quality:
Process Optimization
- Minimizing setup times
- Optimizing tool life
- Reducing material waste
Production Planning
- Batch size optimization
- Just-in-time manufacturing
- Efficient resource allocation
Tolerance Management
Maintaining tight tolerances is critical for hydraulic cylinder heads:
| Feature | Typical Tolerance | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Bore Diameter | ±0.025mm | Seal effectiveness |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.4-0.8 | Wear resistance |
| Perpendicularity | 0.01mm | Assembly alignment |
| Thread Quality | 6g/6H | Pressure integrity |
Manufacturing Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges we encounter include:
Material-Related Issues
- Heat treatment distortion
- Material inconsistency
- Stress relief requirements
Technical Solutions
- Advanced fixturing methods
- In-process inspection
- Thermal compensation systems
Environmental Considerations
Modern manufacturing must address environmental concerns:
Sustainable Practices
- Coolant recycling
- Energy-efficient machinery
- Waste reduction programs
Material Recovery
- Metal chip recycling
- Cutting fluid filtration
- Packaging reuse
These comprehensive manufacturing processes ensure that hydraulic cylinder heads meet the demanding requirements of modern hydraulic systems. Through continuous improvement and adoption of new technologies, we maintain high quality while optimizing costs and efficiency.
Our focus on precision, quality control, and innovative manufacturing techniques has enabled us to consistently produce hydraulic cylinder heads that meet or exceed industry standards. The combination of proper material selection, advanced machining processes, and rigorous quality control ensures reliable performance in demanding applications.
Understanding these manufacturing processes is crucial for anyone involved in hydraulic system design or maintenance. It helps in making informed decisions about specifications, maintenance requirements, and expected performance parameters.
What Are the Common Applications of Hydraulic Cylinder Heads?
Have you ever wondered why hydraulic cylinder heads are everywhere in modern industry? From towering construction cranes to precision aerospace equipment, these components are the unsung heroes powering our industrial world.
Hydraulic cylinder heads are critical components used across multiple industries including construction, automotive, aerospace, agriculture, and heavy machinery. They provide the essential force transmission and control needed for various hydraulic systems, enabling precise movement and power application.

Construction Industry Applications
The construction sector heavily relies on hydraulic cylinder heads for various equipment. In excavators, these components enable precise control of the boom, arm, and bucket movements. Having worked with many construction equipment manufacturers, I’ve observed how crucial proper cylinder head design is for:
- Excavator arm control systems
- Mobile crane lifting mechanisms
- Concrete pump trucks
- Foundation drilling equipment
- Demolition equipment
The demanding nature of construction work requires cylinder heads that can withstand high pressure cycles and harsh environmental conditions.
Automotive Manufacturing and Service
In the automotive industry, hydraulic cylinder heads play vital roles in both manufacturing and maintenance:
| Application Area | Specific Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Assembly Lines | Robot arm movements, press operations |
| Vehicle Lifts | Two-post and four-post service lifts |
| Testing Equipment | Brake testing systems, suspension testing |
| Manufacturing Presses | Sheet metal forming, component assembly |
| Paint Shop Systems | Automated painting equipment movement |
Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry demands the highest precision and reliability from hydraulic cylinder heads. These components are used in:
- Aircraft landing gear systems
- Flight control surface actuators
- Cargo door mechanisms
- Ground support equipment
- Testing and maintenance equipment
The specifications for aerospace applications are particularly stringent, requiring special materials and manufacturing processes that we regularly handle at PTSMAKE.
Agricultural Equipment
Modern farming relies heavily on hydraulic systems. Key applications include:
- Tractor implement control systems
- Harvester mechanisms
- Irrigation system controls
- Grain handling equipment
- livestock handling equipment
These applications often require cylinder heads that can operate reliably in dusty, corrosive environments while maintaining precise control.
Heavy Machinery Applications
The heavy machinery sector represents one of the largest markets for hydraulic cylinder heads:
| Machine Type | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Mining Equipment | Rock breakers, conveyor systems |
| Material Handling | Forklifts, container handlers |
| Steel Mills | Rolling mill equipment, furnace doors |
| Paper Mills | Roll handling systems, press sections |
| Marine Equipment | Deck machinery, steering systems |
Specialized Industrial Applications
Beyond the major industries, hydraulic cylinder heads find use in specialized applications:
Plastic Injection Molding
- Mold clamping systems
- Material injection units
- Core pull mechanisms
Metal Processing
- Press brakes
- Shearing machines
- Rolling mills
Energy Sector
- Wind turbine pitch control
- Hydroelectric dam gates
- Oil and gas drilling equipment
Design Considerations Across Industries
While working with various industries, I’ve noticed that each application requires specific design considerations:
Pressure Requirements
- Construction: High pressure capability
- Aerospace: Precise pressure control
- Agriculture: Moderate but consistent pressure
Environmental Factors
- Marine: Corrosion resistance
- Mining: Dust and debris protection
- Food Processing: Hygiene standards
Operational Parameters
- Temperature ranges
- Cycle frequencies
- Service life expectations
Performance Optimization
To ensure optimal performance across different applications, we focus on:
Material Selection
- High-strength alloys for heavy-duty applications
- Corrosion-resistant materials for exposed environments
- Lightweight materials for mobile equipment
Surface Treatments
- Hard chrome plating
- Nitriding
- Specialized coatings
Quality Control
- Dimensional accuracy
- Surface finish requirements
- Performance testing
This comprehensive understanding of diverse applications helps us deliver cylinder heads that meet specific industry requirements while maintaining the highest standards of quality and reliability.
What Challenges Do Hydraulic Cylinder Heads Face?
Every day in my manufacturing facility, I witness hydraulic cylinder heads battling against intense pressures and demanding operating conditions. These critical components face challenges that can make or break entire hydraulic systems.
Hydraulic cylinder heads encounter five main challenges: wear and tear from continuous operation, fluid leakage through seals, material deformation under extreme pressures, fatigue from cyclic loading, and corrosion from harsh environments. These issues directly impact system efficiency and reliability.
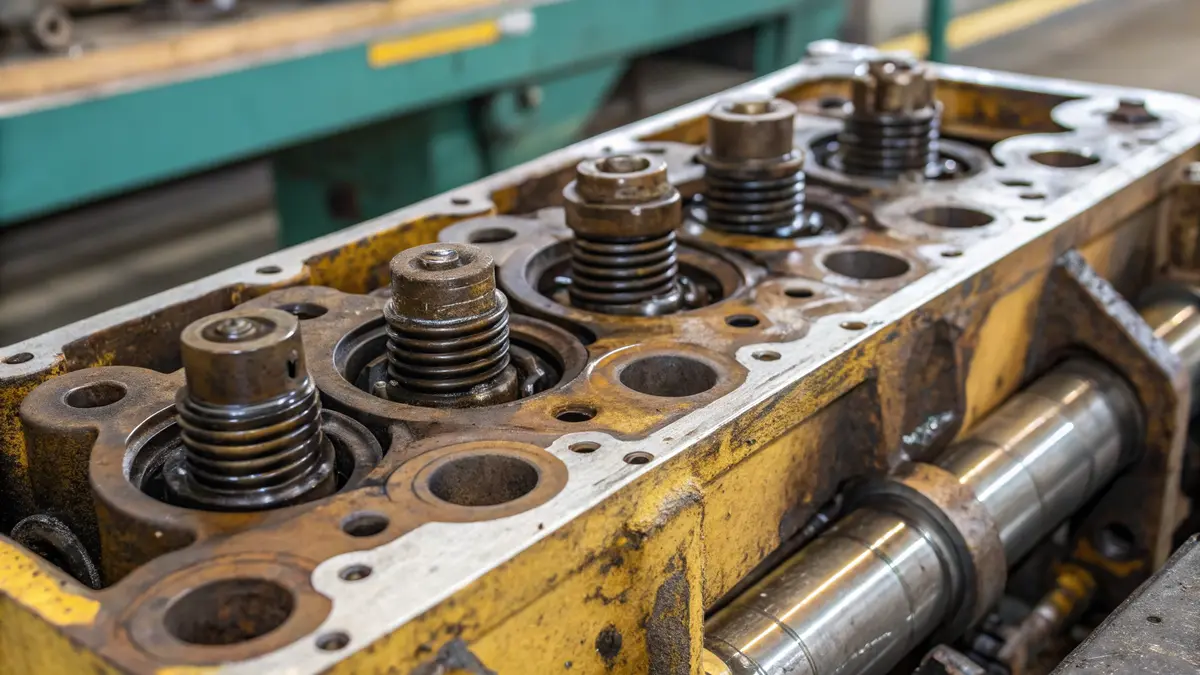

Wear and Tear: The Silent Performance Killer
In my experience working with precision hydraulic components, wear and tear stands out as the most common challenge. The constant metal-to-metal contact between the cylinder head and moving parts creates friction points that gradually deteriorate. This issue particularly affects:
- Internal bore surfaces
- Seal grooves
- Guide bushings
- Mounting points
The wear patterns often accelerate when contaminated hydraulic fluid enters the system, acting like liquid sandpaper against precision surfaces.
Leakage Issues and Their Impact
One of the most frustrating challenges I regularly encounter is fluid leakage. This problem typically stems from:
| Leak Source | Common Causes | Impact on System |
|---|---|---|
| Static Seals | Installation damage, aging | Gradual pressure loss |
| Dynamic Seals | Wear, improper sizing | Immediate performance drop |
| Port Connections | Loose fittings, vibration | External fluid loss |
| Material Joints | Temperature cycling | Internal bypass |
Deformation Under High Pressure
The constant battle against high-pressure loads creates several deformation risks:
Elastic Deformation
- Temporary shape changes during operation
- Recovery when pressure releases
- Potential alignment issues
Plastic Deformation
- Permanent structural changes
- Compromised sealing surfaces
- Required replacement of components
Material Fatigue Considerations
Material fatigue represents a particularly complex challenge that develops over time. Key factors include:
Cyclic Loading Effects
- Microscopic crack formation
- Progressive weakness development
- Sudden failure risks
Environmental Factors
- Temperature fluctuations
- Chemical exposure
- Moisture presence
Corrosion and Environmental Degradation
The presence of moisture and aggressive fluids can lead to:
- Surface pitting
- Material weakening
- Seal deterioration
- Reduced component lifespan
Performance Impact on Hydraulic Systems
These challenges create a cascade effect throughout the hydraulic system:
Efficiency Losses
- Reduced operating pressure
- Increased energy consumption
- Lower output force
Reliability Issues
- Unpredictable operation
- Increased downtime
- Higher maintenance costs
Innovative Solutions and Preventive Measures
To address these challenges, we implement several strategies:
Material Selection
- High-strength alloys for pressure resistance
- Corrosion-resistant coatings
- Optimized surface treatments
Design Improvements
- Enhanced sealing systems
- Reinforced stress points
- Improved fluid flow patterns
Maintenance Practices
- Regular inspection schedules
- Preventive seal replacement
- Fluid analysis programs
Monitoring and Early Detection
I’ve found that implementing robust monitoring systems helps identify issues before they become critical:
Pressure Monitoring
- Continuous pressure tracking
- Leak detection systems
- Performance trend analysis
Visual Inspections
- Regular seal checks
- Surface condition assessment
- Alignment verification
Predictive Maintenance
- Oil analysis programs
- Vibration monitoring
- Temperature tracking
Understanding these challenges has helped us develop better manufacturing processes and maintenance protocols. By addressing each issue systematically, we can extend component life and maintain optimal system performance. The key lies in combining proper design, material selection, and maintenance practices to create resilient hydraulic cylinder heads that can withstand demanding operating conditions.
How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Cylinder Head?
Selecting the right hydraulic cylinder head can feel overwhelming with countless options in the market. As someone who has helped numerous clients optimize their hydraulic systems, I know the significance of making the right choice.
The key to choosing the right hydraulic cylinder head lies in evaluating five critical factors: system compatibility, material selection, pressure requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term reliability. A well-matched cylinder head ensures optimal performance and extends system life.

System Compatibility Analysis
The first step in selecting a hydraulic cylinder head is ensuring complete compatibility with your existing system. Your cylinder head must match the specific dimensions and mounting configurations of your hydraulic cylinder. Here’s a comprehensive compatibility checklist:
| Component | Compatibility Factors |
|---|---|
| Bore Size | Must match cylinder bore exactly |
| Port Configuration | Thread type and size alignment |
| Mounting Pattern | Bolt pattern and spacing requirements |
| Seal Design | Compatible with system fluid and pressure |
Material Selection Considerations
Material selection plays a crucial role in cylinder head performance. Different applications require specific material properties:
Cast Iron Heads
- Excellent wear resistance
- Good thermal stability
- Cost-effective for standard applications
- Suitable for most industrial environments
Steel Alloy Heads
- Superior strength-to-weight ratio
- Enhanced pressure capacity
- Better corrosion resistance
- Ideal for high-performance applications
Aluminum Heads
- Lightweight construction
- Excellent heat dissipation
- Corrosion resistant
- Perfect for mobile applications
Pressure Rating Requirements
Understanding your system’s pressure requirements is fundamental. I recommend following these guidelines:
| Operating Pressure (PSI) | Recommended Head Type |
|---|---|
| 0-1500 | Standard duty heads |
| 1500-3000 | Medium duty heads |
| 3000-5000 | Heavy duty heads |
| 5000+ | Ultra-heavy duty heads |
Environmental Considerations
The operating environment significantly impacts cylinder head selection:
Temperature Range
- Standard heads: -20°F to 180°F
- High-temperature heads: Up to 400°F
- Low-temperature heads: Down to -40°F
Exposure Conditions
- Indoor vs. outdoor use
- Chemical exposure
- Dust and debris presence
- Moisture levels
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
When evaluating cost-effectiveness, consider these factors:
Initial Investment
- Material costs
- Manufacturing complexity
- Quality certifications
Long-term Value
- Maintenance requirements
- Expected service life
- Replacement part availability
- Warranty coverage
Working with Reliable Suppliers
Choosing the right supplier is as important as selecting the correct cylinder head. Look for suppliers who:
Offer Technical Support
- Design assistance
- Application engineering
- Performance optimization guidance
Maintain Quality Standards
- ISO certifications
- Quality control processes
- Material traceability
- Testing capabilities
Provide Documentation
- Technical specifications
- Test reports
- Installation guides
- Maintenance manuals
Performance Optimization
To maximize cylinder head performance:
Regular Inspection Points
- Seal condition
- Surface wear
- Alignment accuracy
- Port integrity
Maintenance Schedule
- Periodic seal replacement
- Surface cleaning
- Torque verification
- Fluid analysis
Future-Proofing Your Selection
Consider these aspects for long-term success:
Scalability
- Future system upgrades
- Pressure increases
- Flow rate changes
Adaptability
- Alternative fluid compatibility
- Temperature range flexibility
- Pressure range adjustability
The selection process requires careful consideration of multiple factors. By focusing on system requirements, material properties, environmental conditions, and supplier reliability, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic system.
Remember that investing time in proper selection often prevents costly issues down the line. Work closely with reputable suppliers who can provide detailed technical support and documentation. This approach will help you achieve the best possible outcome for your specific application needs.
What Are the Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips?
Have you ever faced unexpected hydraulic cylinder head failures that brought your entire production line to a halt? These situations not only cause significant downtime but also lead to substantial financial losses that could have been prevented with proper maintenance.
Effective maintenance of hydraulic cylinder heads requires a systematic approach combining regular inspections, proper cleaning procedures, and timely troubleshooting. Implementing these practices can significantly extend component life and prevent costly breakdowns.
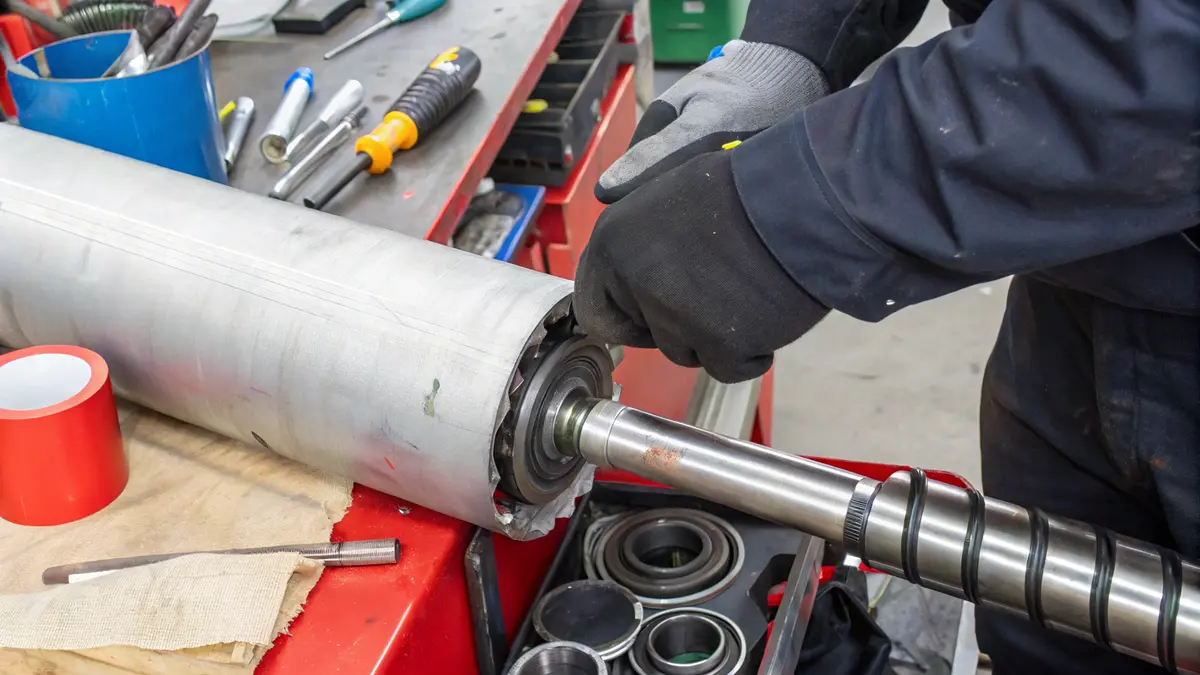

Regular Inspection Protocols
Regular inspections form the cornerstone of effective hydraulic cylinder head maintenance. I’ve developed a comprehensive inspection checklist that our clients at PTSMAKE use to maintain optimal performance:
| Inspection Point | Frequency | What to Look For |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Wear | Weekly | Scratches, scoring marks, uneven wear patterns |
| Seal Condition | Bi-weekly | Signs of deterioration, hardening, or leakage |
| Mounting Bolts | Monthly | Proper torque, signs of loosening |
| Alignment | Monthly | Proper positioning, no misalignment |
| Port Threads | Quarterly | Thread wear, damage, or contamination |
Cleaning and Maintenance Procedures
Proper cleaning is crucial for maintaining hydraulic cylinder heads. The cleaning process should be systematic and thorough:
- Remove surface contaminants using approved cleaning solutions
- Inspect all passages and ports for debris
- Clean sealing surfaces with lint-free materials
- Use compressed air to dry components thoroughly
- Apply appropriate lubricants before reassembly
Identifying Common Issues
Early detection of problems can prevent catastrophic failures. Here are key issues to watch for:
Seal Failures
- Excessive leakage around seals
- Unusual noises during operation
- Inconsistent cylinder movement
- Temperature variations in the system
Surface Warping
- Uneven wear patterns
- Difficulty maintaining pressure
- Irregular cylinder operation
- Excessive heat generation
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
I recommend implementing this preventive maintenance schedule:
| Maintenance Task | Interval | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Daily | High |
| Seal Check | Weekly | High |
| Torque Verification | Monthly | Medium |
| Full Disassembly Check | Quarterly | Medium |
| Component Replacement | Yearly/As Needed | Variable |
Troubleshooting Guide
When issues arise, follow this systematic troubleshooting approach:
Document Symptoms
- Record specific operational issues
- Note any unusual sounds or vibrations
- Document pressure readings and variations
- Track temperature changes
Analyze Operating Conditions
- Review system pressure requirements
- Check operating temperature ranges
- Verify fluid cleanliness levels
- Examine duty cycle parameters
Implement Solutions
- Replace worn components
- Adjust system settings
- Update maintenance procedures
- Document corrective actions
Best Practices for Extended Service Life
To maximize the lifespan of hydraulic cylinder heads:
Maintain Proper Fluid Conditions
- Use recommended hydraulic fluid
- Monitor fluid cleanliness
- Change fluids according to schedule
- Check fluid temperature regularly
Ensure Proper Installation
- Follow torque specifications
- Verify alignment during assembly
- Use appropriate tools
- Document installation procedures
Monitor Operating Parameters
- Track system pressures
- Record operating temperatures
- Monitor cycle times
- Document performance metrics
Emergency Response Protocol
When failures occur, having an emergency response plan is crucial:
Immediate Actions
- Safely shut down equipment
- Assess damage extent
- Document failure conditions
- Contact maintenance team
Recovery Steps
- Gather necessary tools and parts
- Follow proper repair procedures
- Test system thoroughly
- Update maintenance records
The key to successful hydraulic cylinder head maintenance lies in consistency and attention to detail. By following these guidelines and maintaining detailed records, you can significantly reduce downtime and extend component life. Remember that proactive maintenance is always more cost-effective than reactive repairs.
This comprehensive approach to maintenance and troubleshooting has helped our clients at PTSMAKE achieve excellent reliability and performance from their hydraulic systems. The investment in proper maintenance practices pays dividends through reduced downtime and longer component life.
What Are Technological Advancements in Hydraulic Cylinder Heads?
As a manufacturing expert, I’ve witnessed a revolutionary transformation in hydraulic cylinder head technology. The integration of smart sensors, advanced materials, and innovative design approaches has completely changed how we think about hydraulic systems.
Modern hydraulic cylinder heads combine cutting-edge materials with intelligent monitoring systems, resulting in enhanced performance and reliability. These advancements include sensor integration, wear-resistant coatings, and optimized design geometries that significantly improve operational efficiency.
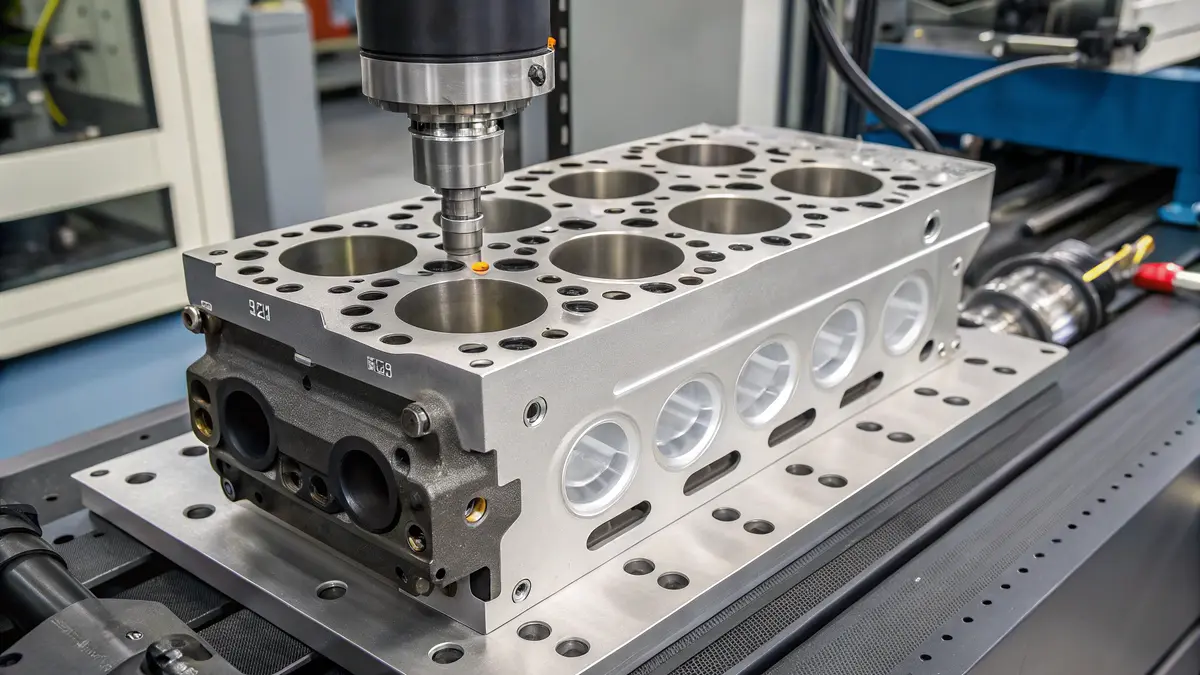

Advanced Materials Revolution
The evolution of materials used in hydraulic cylinder heads has been remarkable. Traditional steel and cast iron are being replaced by advanced composites and exotic alloys. These new materials offer:
- Enhanced wear resistance
- Improved thermal stability
- Reduced weight without compromising strength
- Better corrosion resistance
One of the most significant developments is the use of ceramic-coated components. These coatings provide exceptional wear resistance and can extend the service life of cylinder heads by up to 300%.
Smart Technology Integration
The integration of smart technology has transformed hydraulic cylinder heads from simple mechanical components into intelligent systems. Modern cylinder heads now feature:
| Technology Feature | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Sensors | Real-time monitoring of system pressure | Industrial machinery |
| Temperature Monitors | Prevention of overheating | Heavy equipment |
| Position Sensors | Precise movement control | Robotics systems |
| Wear Indicators | Predictive maintenance | Manufacturing equipment |
Design Optimization Through CFD
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has revolutionized the design process of hydraulic cylinder heads. Using advanced simulation software, we can:
- Analyze flow patterns
- Optimize channel geometry
- Reduce pressure drops
- Minimize energy losses
These simulations have led to designs that are 25% more efficient than traditional models.
Surface Treatment Innovations
Modern surface treatment techniques have significantly improved cylinder head durability:
- Plasma nitriding
- Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings
- Laser surface hardening
- Nano-structured coatings
These treatments can increase surface hardness by up to 70% while reducing friction coefficients by 40%.
Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
Environmental considerations have driven innovations in manufacturing processes:
- Near-net-shape manufacturing
- Additive manufacturing capabilities
- Eco-friendly surface treatments
- Energy-efficient production methods
These processes reduce material waste by up to 50% compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Performance Monitoring Systems
Modern cylinder heads incorporate sophisticated monitoring systems that provide:
| Monitoring Feature | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Twins | Virtual system modeling | Predictive maintenance |
| IoT Integration | Remote monitoring | Real-time optimization |
| Data Analytics | Performance tracking | Efficiency improvements |
| Condition Monitoring | Early warning system | Reduced downtime |
Maintenance-Friendly Designs
New designs focus on ease of maintenance and serviceability:
- Modular construction
- Quick-release connections
- Self-diagnosing systems
- Easy-access service points
These features can reduce maintenance time by up to 60% compared to traditional designs.
Material Selection Optimization
The selection of materials has become more sophisticated:
| Material Type | Application | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| High-strength Alloys | High-pressure systems | Superior durability |
| Composite Materials | Weight-critical applications | Reduced mass |
| Hybrid Materials | Special applications | Custom properties |
| Smart Materials | Adaptive systems | Self-adjusting capabilities |
Future Trends
Looking ahead, several emerging technologies show promise:
- Self-healing materials
- Nano-engineered surfaces
- Bio-inspired design principles
- AI-driven optimization
These innovations could potentially double the service life of hydraulic cylinder heads while reducing maintenance requirements by 75%.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Modern designs focus on energy efficiency through:
- Optimized flow paths
- Reduced internal friction
- Better thermal management
- Advanced sealing systems
These improvements have resulted in energy savings of up to 30% in typical applications.
The technological advancements in hydraulic cylinder heads represent a significant leap forward in hydraulic system design and performance. Through the combination of smart technology, advanced materials, and innovative design approaches, modern hydraulic cylinder heads offer unprecedented levels of efficiency, durability, and functionality. These improvements continue to drive the evolution of hydraulic systems across various industries, from manufacturing to heavy machinery.
Why Is Quality Assurance Crucial for Hydraulic Cylinder Heads?
Every day, thousands of hydraulic systems fail due to poor quality cylinder heads. These failures not only cost businesses millions in repairs but can also lead to catastrophic accidents. The stakes are simply too high to ignore quality assurance.
Quality assurance in hydraulic cylinder heads is essential because it ensures operational safety, extends equipment lifespan, and maintains system efficiency. Proper QA processes prevent costly failures, reduce maintenance needs, and guarantee consistent performance in demanding industrial applications.
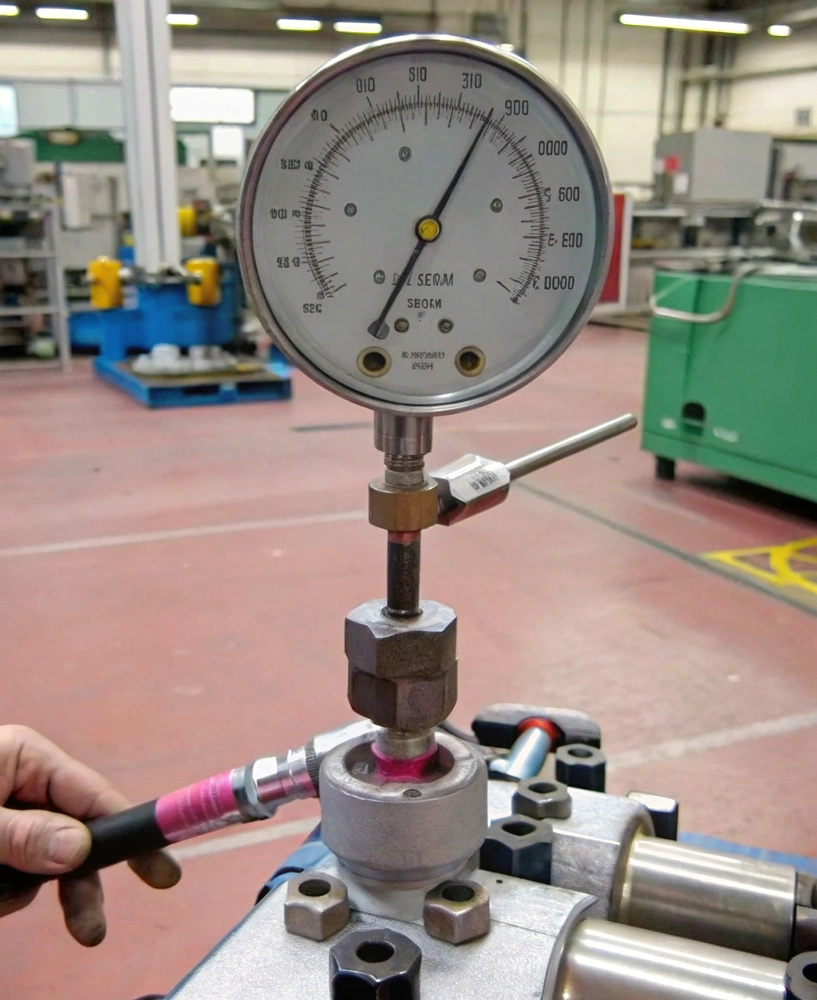
The Foundation of System Reliability
In my experience at PTSMAKE, the reliability of hydraulic systems starts with the cylinder head. It’s the component that houses critical seals, guides the piston rod, and maintains proper pressure distribution. A well-manufactured cylinder head ensures smooth operation and prevents catastrophic failures that could harm both equipment and operators.
Key Quality Metrics We Monitor
At our facility, we focus on several critical measurements:
| Metric | Acceptable Range | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Roughness | 0.4-0.8 Ra | Affects seal life and friction |
| Dimensional Tolerance | ±0.02mm | Ensures proper fitting and alignment |
| Material Hardness | 28-32 HRC | Determines wear resistance |
| Concentricity | 0.01mm max | Prevents premature seal wear |
Advanced Testing Procedures
Our quality assurance process involves multiple stages of testing:
Material Verification
- Chemical composition analysis
- Hardness testing
- Microstructure examination
Dimensional Inspection
- 3D coordinate measuring
- Laser scanning
- Thread gauge verification
Performance Testing
- Pressure cycling tests
- Leak detection
- Load capacity verification
Industry Standards Compliance
We strictly adhere to international standards including:
- ISO 9001:2015 for quality management
- SAE J1074 for hydraulic cylinder specifications
- DIN 24333 for mounting dimensions
- API standards for oil and gas applications
Critical Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount in hydraulic systems. Quality cylinder heads prevent:
- Sudden pressure loss
- Fluid leakage
- Component misalignment
- Premature seal failure
- System instability
Economic Impact of Quality Assurance
Investing in quality assurance yields significant returns:
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Extended system lifespan
- Minimized downtime
- Lower warranty claims
- Enhanced operational efficiency
Innovation in Testing Methods
Modern quality assurance has evolved with technology. We now employ:
- Ultrasonic testing for internal defects
- Digital pressure mapping
- Real-time performance monitoring
- Automated inspection systems
- Data analytics for trend analysis
Environmental and Sustainability Aspects
Quality assurance also contributes to environmental protection:
- Reduced waste from rejected parts
- Lower energy consumption through efficient operation
- Minimized fluid leakage and contamination
- Extended product lifecycle
- Recyclability considerations in material selection
Documentation and Traceability
Every cylinder head we produce comes with:
- Material certificates
- Dimensional inspection reports
- Testing documentation
- Batch traceability
- Quality compliance certificates
Future Trends in Quality Assurance
The industry is moving towards:
- AI-powered inspection systems
- Real-time monitoring capabilities
- Predictive quality analytics
- Digital twin technology
- Blockchain-based traceability
Quality assurance in hydraulic cylinder heads is not just about meeting specifications; it’s about ensuring safety, reliability, and efficiency throughout the entire system lifecycle. Our comprehensive approach combines traditional testing methods with modern technology to deliver components that exceed industry standards and customer expectations.
The investment in quality assurance may seem significant initially, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the costs. When you consider the potential consequences of failure – from costly downtime to safety hazards – it becomes clear why rigorous quality control is not just important, but essential in hydraulic cylinder head manufacturing.
How to Work with Reliable Manufacturing Partners?
Finding reliable manufacturing partners can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Many businesses struggle with inconsistent quality, missed deadlines, and poor communication, leading to costly delays and compromised product integrity.
The key to successful manufacturing partnerships lies in selecting suppliers who demonstrate consistent quality, meet deadlines reliably, maintain clear communication channels, and offer customization flexibility. These core traits form the foundation of a lasting and profitable business relationship.

Core Traits of Reliable Manufacturing Partners
When evaluating potential manufacturing partners, I focus on these essential characteristics:
| Trait | Description | Impact on Business |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Consistency | Maintains stable production standards | Reduces defects and returns |
| On-time Delivery | Meets agreed deadlines consistently | Improves supply chain efficiency |
| Communication Skills | Responds promptly and clearly | Prevents misunderstandings |
| Technical Capability | Has advanced equipment and expertise | Ensures product specifications |
| Customization Ability | Adapts to specific requirements | Enables product innovation |
Streamlining the Procurement Process
A well-structured procurement process saves time and resources. Here’s my recommended approach:
Initial Screening
- Review supplier credentials and certifications
- Check manufacturing capabilities
- Evaluate financial stability
- Assess geographical location and logistics
Quality Assessment
- Request sample products
- Review quality control procedures
- Verify testing capabilities
- Check compliance with industry standards
Communication Protocol
- Establish primary contact points
- Define response time expectations
- Set up regular review meetings
- Implement progress tracking systems
Building Long-term Relationships
Strong partnerships don’t happen overnight. These strategies help foster lasting relationships:
Clear Expectations
- Document all requirements thoroughly
- Set realistic timelines
- Define quality standards explicitly
- Agree on pricing structures
Regular Performance Reviews
- Monitor quality metrics
- Track delivery performance
- Evaluate communication effectiveness
- Discuss improvement opportunities
Mutual Growth Planning
- Share future business projections
- Discuss capacity expansion needs
- Plan for technology upgrades
- Explore new market opportunities
Risk Management Strategies
Protecting your supply chain requires proactive risk management:
Diversification
- Maintain backup suppliers
- Split orders strategically
- Consider geographical distribution
- Balance cost versus risk
Quality Assurance
- Implement regular audits
- Conduct surprise inspections
- Monitor defect rates
- Track customer feedback
Contract Protection
- Include quality guarantees
- Define penalty clauses
- Specify intellectual property rights
- Outline dispute resolution procedures
Technology Integration
Modern manufacturing partnerships benefit from digital integration:
Communication Platforms
- Use project management software
- Implement real-time tracking systems
- Share design files securely
- Enable virtual meetings
Quality Control Systems
- Deploy automated inspection tools
- Use statistical process control
- Implement traceability systems
- Share quality data digitally
Financial Considerations
Smart financial planning strengthens partnerships:
Payment Terms
- Structure fair payment schedules
- Consider volume discounts
- Plan for material cost fluctuations
- Include early payment incentives
Cost Management
- Track total ownership costs
- Monitor pricing trends
- Evaluate value-added services
- Consider long-term contracts
Moving Forward Together
The most successful manufacturing partnerships evolve through:
Continuous Improvement
- Regular process reviews
- Joint innovation projects
- Shared efficiency goals
- Ongoing training programs
Market Adaptation
- Monitor industry trends
- Plan for market changes
- Share market intelligence
- Adapt strategies together
These comprehensive guidelines reflect my experience in building successful manufacturing partnerships. Each element contributes to creating relationships that deliver value, maintain quality, and support growth for both parties. Remember that successful partnerships require commitment, clear communication, and mutual trust. By following these principles, businesses can develop strong, lasting relationships with their manufacturing partners.







