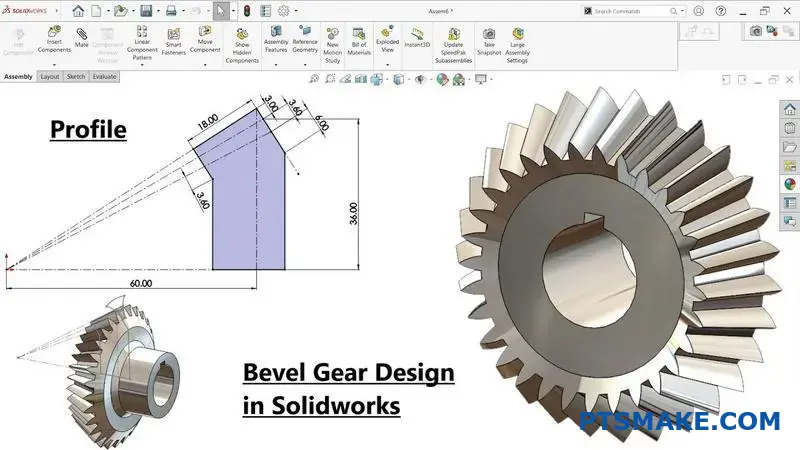
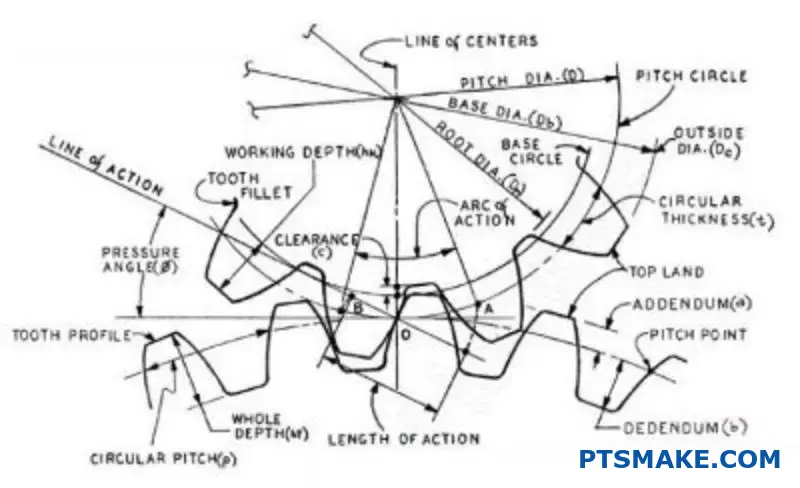
When choosing between aluminum materials, I often see engineers struggle with the cast vs. regular aluminum decision. Many have wasted time and money on the wrong choice, leading to failed projects and costly rework.
Cast aluminum and regular (wrought) aluminum each have their distinct advantages. Cast aluminum offers better complex shapes and is more cost-effective for high-volume production, while regular aluminum provides superior strength and machinability for precision parts.
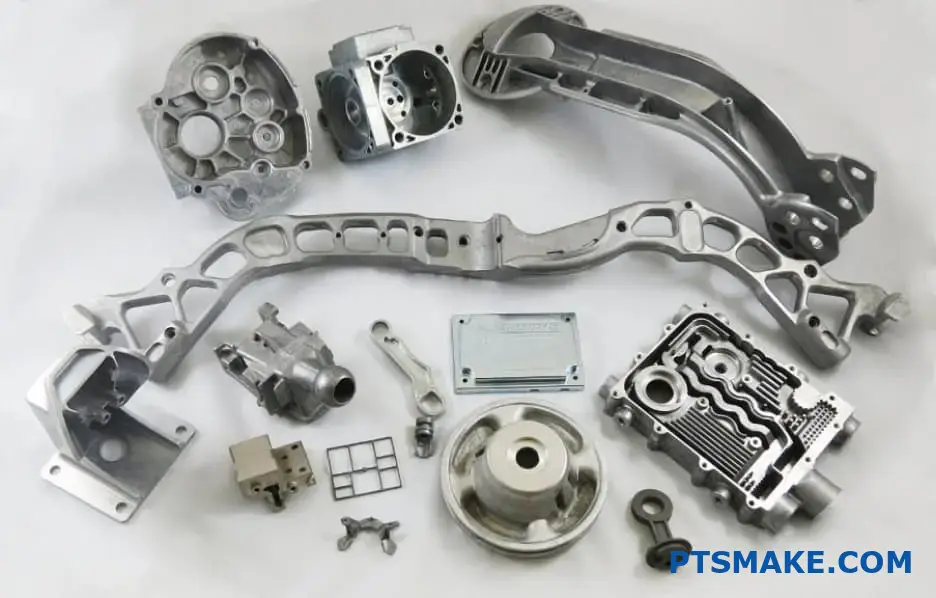

I know you’re probably wondering about the specific applications and detailed comparisons of these materials. Let me share my direct experience from manufacturing thousands of aluminum parts at PTSMAKE. We’ll explore the key differences that will help you make the right choice for your project.
What Are the Disadvantages and Advantages of Cast Aluminum?
Have you ever wondered why some manufacturers choose cast aluminum while others avoid it? When selecting materials for your next project, this decision can mean the difference between success and costly setbacks, especially when dealing with complex part designs or high-volume production runs.
Cast aluminum offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio, good corrosion resistance, and cost-effective production for complex shapes. However, it also has limitations such as lower tensile strength compared to wrought aluminum, potential porosity issues, and size restrictions in the casting process.
Understanding Cast Aluminum Properties
Cast aluminum has become increasingly popular in various industries due to its versatile properties. The material’s characteristics make it suitable for numerous applications, from automotive components to aerospace parts. At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented cast aluminum solutions in various projects, particularly when clients need lightweight yet durable components.
Physical Properties
When examining cast aluminum, several key physical properties stand out:
| Property | Typical Range | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2.6-2.9 g/cm³ | Lightweight construction |
| Melting Point | 660-720°C | Good thermal properties |
| Thermal Conductivity | 150-180 W/m·K | Excellent heat dissipation |
| Electrical Conductivity | 16-20 MS/m | Suitable for electrical applications |
Advantages of Cast Aluminum
1. Design Flexibility
Cast aluminum allows for complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. The metal solidification pattern1 during casting enables the creation of intricate internal passages and varying wall thicknesses.
2. Cost-Effective Production
For medium to high-volume production runs, cast aluminum offers significant cost advantages:
- Lower tooling costs compared to other manufacturing methods
- Reduced material waste
- Faster production cycles
- Minimal secondary operations required
3. Weight Reduction
In my experience working with automotive and aerospace clients, cast aluminum’s lightweight properties often provide crucial advantages:
- 66% lighter than steel
- Maintains structural integrity
- Improves fuel efficiency in vehicles
- Reduces overall system loads
Disadvantages of Cast Aluminum
1. Mechanical Limitations
The casting process can introduce certain mechanical limitations:
| Limitation | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Porosity | Reduced strength | Advanced casting techniques |
| Surface finish | May require post-processing | Proper mold design |
| Internal defects | Quality inconsistency | Strict process control |
2. Size Restrictions
Casting size limitations can affect large-scale projects:
- Maximum practical size depends on casting method
- Large castings may require special equipment
- Risk of defects increases with size
3. Material Property Variations
Cast aluminum can exhibit variations in properties:
- Different cooling rates affect strength
- Potential for inconsistent mechanical properties
- May require additional heat treatment
Applications and Industry Uses
Cast aluminum finds extensive use across various sectors:
Automotive Industry
- Engine blocks
- Transmission housings
- Wheel components
- Structural frames
Aerospace Applications
- Engine components
- Structural elements
- Housing units
- Control systems
Consumer Products
- Electronic housings
- Furniture components
- Decorative elements
- Sporting equipment
Best Practices for Cast Aluminum Selection
To maximize the benefits of cast aluminum, consider these factors:
Design Optimization
- Incorporate proper draft angles
- Maintain uniform wall thickness
- Account for shrinkage allowances
- Include appropriate radii and fillets
Process Selection
- Choose appropriate casting method
- Consider production volume
- Evaluate surface finish requirements
- Account for dimensional tolerance needs
Quality Control
- Implement proper testing procedures
- Monitor process parameters
- Maintain consistent material properties
- Verify critical dimensions
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed comprehensive quality control processes to ensure our cast aluminum components meet the strictest industry standards. Our engineering team works closely with clients to select the optimal casting methods and design parameters for their specific applications.
What Kind of Aluminum Is Used in Casting?
Have you ever struggled to choose the right aluminum alloy for your casting project? The overwhelming number of options and their varying properties can make this decision feel like navigating through a maze, potentially leading to costly mistakes and project delays.
The most commonly used aluminum alloys for casting are A356/A357 (high strength), 319 (good machinability), and 713 (excellent fluidity). Each type offers specific advantages based on the casting method, part complexity, and end-use requirements.
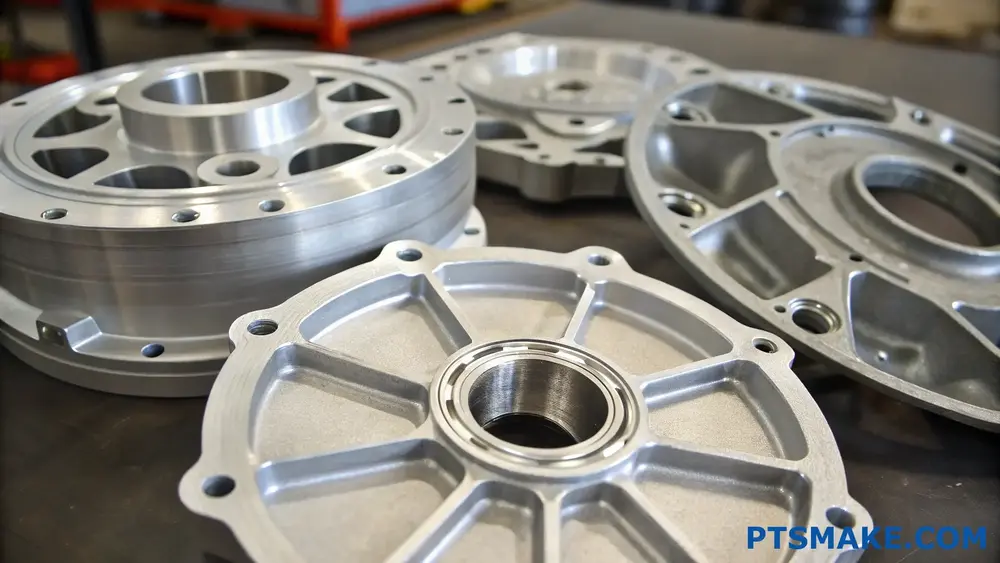

Understanding Aluminum Casting Alloys
A356/A357 Series: The Industry Standard
A356 and A357 are premium casting alloys that dominate the aerospace and automotive industries. Their excellent dendrite coherency2 during solidification makes them ideal for complex geometries. At PTSMAKE, we frequently use these alloys for structural components that require high strength-to-weight ratios.
The composition typically includes:
| Element | A356 (%) | A357 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon | 6.5-7.5 | 6.5-7.5 |
| Magnesium | 0.25-0.45 | 0.45-0.7 |
| Iron | 0.2 max | 0.2 max |
| Titanium | 0.2 max | 0.2 max |
319 Alloy: The Versatile Choice
319 aluminum alloy offers excellent machinability and good pressure tightness. Its balanced properties make it suitable for various applications, from engine blocks to transmission cases. Based on my experience working with automotive clients, 319 provides consistent results in both thin and thick sections.
Key characteristics include:
- Excellent fluidity
- Good resistance to hot cracking
- Superior machinability
- Moderate strength properties
713 Alloy: The Pressure Die Casting Champion
713 alloy excels in pressure die casting applications due to its exceptional fluidity and die-filling capabilities. When casting thin-walled components, this alloy consistently delivers superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Factors Influencing Alloy Selection
Application Requirements
The end-use application heavily influences alloy selection:
| Application Type | Recommended Alloy | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Parts | A356/A357 | High strength |
| Engine Components | 319 | Heat resistance |
| Thin-wall Parts | 713 | Fluidity |
Casting Process Compatibility
Different casting methods require specific alloy characteristics:
Sand Casting
- Requires good fluidity
- Lower cooling rates
- A356 works exceptionally well
Die Casting
- Needs excellent flow characteristics
- Rapid solidification
- 713 is often the preferred choice
Permanent Mold Casting
- Moderate cooling rates
- Good surface finish requirements
- 319 provides balanced properties
Heat Treatment Possibilities
The ability to heat treat the casting can significantly impact alloy selection:
| Heat Treatment | Suitable Alloys | Strength Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| T6 | A356, A357 | 30-40% |
| T5 | 713 | 15-20% |
| T7 | 319 | 25-35% |
Cost Considerations and Availability
When selecting an aluminum casting alloy, consider these economic factors:
Raw Material Cost
- A356/A357: Premium pricing
- 319: Mid-range cost
- 713: Economical option
Processing Costs
- Heat treatment requirements
- Machining complexity
- Rejection rates
Production Volume Impact
Different alloys may be more cost-effective at various production volumes:
| Production Volume | Recommended Alloy | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Low Volume | A356 | Medium |
| Medium Volume | 319 | High |
| High Volume | 713 | Very High |
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure consistent casting quality, implement these testing procedures:
Chemical Analysis
- Regular composition verification
- Trace element monitoring
- Impurity level control
Mechanical Testing
- Tensile strength
- Yield strength
- Elongation measurements
Non-Destructive Testing
- X-ray inspection
- Dye penetrant testing
- Ultrasonic examination
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Modern casting operations must consider environmental factors:
Recyclability
- All these alloys are 100% recyclable
- Minimal material loss during reprocessing
- Lower carbon footprint compared to new material production
Energy Efficiency
- Different alloys require varying processing temperatures
- Heat treatment energy consumption varies
- Melting point differences affect energy usage
At PTSMAKE, we prioritize sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining high-quality standards in our aluminum casting processes. Our expertise in aluminum casting has helped numerous clients optimize their material selection for both performance and sustainability.
How Does Metal Casting Aluminum Compare to CNC Machining for Complex Parts?
Have you ever faced the dilemma of choosing between aluminum casting and CNC machining for your complex parts? The decision becomes even more challenging when considering factors like cost, lead time, and quality requirements – especially when your project’s success hangs in the balance.
Both aluminum casting and CNC machining offer distinct advantages for manufacturing complex parts. Casting excels in producing high-volume, geometrically complex parts at lower costs, while CNC machining provides superior precision, better surface finish, and greater design flexibility for lower quantities.
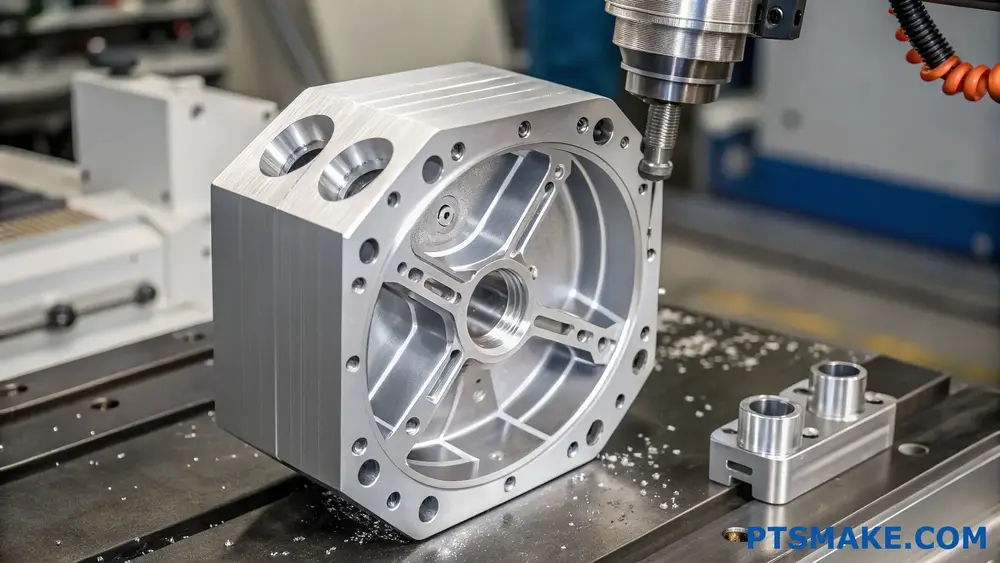

Design Complexity Considerations
Geometric Freedom vs. Precision
When it comes to complex parts, aluminum casting offers excellent geometric freedom3 for intricate internal features and complex shapes. However, at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that CNC machining provides tighter tolerances and better control over critical dimensions. For example, while casting can achieve tolerances of ±0.005 inches, CNC machining regularly achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.0005 inches.
Surface Finish and Quality
The surface finish comparison between these processes shows significant differences:
| Process | Typical Surface Finish (Ra) | Post-Processing Needs |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | 125-300 microinches | Often requires secondary operations |
| CNC Machining | 16-125 microinches | Minimal to none |
| Sand Casting | 250-900 microinches | Extensive finishing required |
Production Volume and Cost Analysis
Initial Investment
Die casting requires significant upfront costs for tooling and molds, while CNC machining needs minimal initial investment. Here’s a typical cost breakdown:
| Manufacturing Method | Tooling Cost Range | Break-Even Point (Parts) |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | $10,000 – $100,000 | 3,000 – 5,000 |
| CNC Machining | $0 – $1,000 | 1 – 500 |
Material Utilization
Casting typically has better material utilization rates compared to CNC machining. In my experience at PTSMAKE, casting can achieve material efficiency rates of up to 90%, while CNC machining might only utilize 30-40% of the raw material for complex parts.
Lead Time and Production Speed
Production Rate Comparison
For high-volume production, casting generally offers faster cycle times:
| Process | Setup Time | Cycle Time per Part |
|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | 2-4 weeks | 30-60 seconds |
| CNC Machining | 1-3 days | 10-60 minutes |
Material Properties and Performance
Mechanical Properties
The manufacturing process significantly affects the final part properties:
Cast aluminum parts often have:
- Lower tensile strength
- More consistent internal structure
- Better resistance to thermal cycling
- Higher porosity levels
CNC machined parts typically feature:
- Higher strength and hardness
- Better fatigue resistance
- More predictable material properties
- Lower internal stress
Quality Control Considerations
When manufacturing complex parts, quality control becomes crucial. CNC machining offers:
- Real-time dimensional verification
- Consistent part-to-part repeatability
- Lower defect rates
- Better documentation and traceability
Casting processes require:
- More extensive quality control measures
- X-ray or CT scanning for internal defects
- Higher sampling rates
- More sophisticated inspection protocols
Design Optimization Tips
To maximize the benefits of each process, consider these design guidelines:
For Casting:
- Design with uniform wall thickness
- Include proper draft angles (typically 1-3 degrees)
- Avoid sharp corners and sudden transitions
- Plan for parting lines and gate locations
For CNC Machining:
- Minimize deep pockets and complex internal features
- Consider tool access and fixturing requirements
- Design for standard cutting tool sizes
- Allow for adequate clamping surfaces
Cost-Effective Decision Making
The choice between casting and CNC machining often depends on:
Production Volume Requirements
- Low volume (1-1000 units): CNC machining
- High volume (1000+ units): Casting
Tolerance Requirements
- Ultra-precise (±0.001" or better): CNC machining
- Standard precision (±0.005" or greater): Casting
Surface Finish Needs
- Aesthetic finish required: CNC machining
- Functional finish acceptable: Casting
Budget Constraints
- Limited upfront investment: CNC machining
- Long-term cost optimization: Casting
At PTSMAKE, we help clients navigate these decisions by providing detailed analysis and recommendations based on their specific requirements. Our expertise in both processes ensures optimal manufacturing solutions for complex aluminum parts.
What Surface Finishing Options Are Available for Metal Casting Aluminum Components?
Have you ever received aluminum cast parts that looked perfect in dimensions but lacked the desired surface appearance? It’s frustrating when components meet all technical specifications but fall short on aesthetic requirements, potentially delaying your entire project timeline.
Surface finishing for metal cast aluminum components encompasses various methods including mechanical, chemical, and electrochemical processes. Each technique offers unique advantages, from improving aesthetic appeal to enhancing functional properties like corrosion resistance and wear protection.

Mechanical Finishing Methods
Shot Blasting and Sand Blasting
Shot blasting and sand blasting are versatile finishing methods that use high-pressure propulsion of abrasive materials. These techniques effectively remove surface imperfections and create uniform textures. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found that shot blasting works particularly well for larger aluminum castings, while sand blasting offers better control for intricate components.
Polishing and Buffing
Polishing creates a smooth, reflective surface through progressive abrasion. The process typically involves multiple stages:
| Stage | Grit Size | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Rough | 80-120 | Remove major imperfections |
| Medium | 240-400 | Smooth surface preparation |
| Fine | 800-1200 | Create initial shine |
| Final | 1500+ | Achieve mirror finish |
Chemical Finishing Processes
Chemical Etching
Chemical etching uses specialized solutions to remove a thin layer of material, creating unique surface textures. This process is particularly effective for achieving uniform finishes on complex geometries where mechanical methods might struggle to reach.
Anodizing
Anodization4 stands out as one of the most popular finishing methods for aluminum castings. The process creates a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer that can be dyed in various colors.
The three main types of anodizing are:
Type I (Chromic Acid)
- Thin coating (0.00002-0.0001 inches)
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Commonly used in aerospace applications
Type II (Sulfuric Acid)
- Medium coating (0.0001-0.001 inches)
- Good wear resistance
- Standard for general industrial use
Type III (Hard Anodizing)
- Thick coating (0.001-0.004 inches)
- Superior wear resistance
- Ideal for high-stress applications
Electrochemical Processes
Electropolishing
Electropolishing provides a highly reflective finish by removing material through an electrochemical process. This technique is particularly valuable for:
- Reducing surface roughness
- Improving corrosion resistance
- Enhancing cleanability
- Creating a bright, decorative finish
Specialized Coatings
Powder Coating
Powder coating offers excellent durability and a wide range of color options. The process involves:
| Step | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Surface cleaning and pretreatment | Ensure coating adhesion |
| Application | Electrostatic spray of powder | Even coverage |
| Curing | Heat treatment | Create final finish |
Conversion Coatings
Chemical conversion coatings create protective layers that enhance:
- Paint adhesion
- Corrosion resistance
- Electrical insulation
- Surface hardness
Selecting the Right Finish
When choosing a surface finish for aluminum castings, consider:
Environmental Exposure
- Indoor vs. outdoor use
- Chemical exposure
- UV exposure
Functional Requirements
- Wear resistance needs
- Corrosion protection
- Thermal considerations
- Electrical conductivity
Aesthetic Requirements
- Color preferences
- Texture requirements
- Gloss level
- Visual consistency
Cost Considerations
- Production volume
- Processing time
- Material costs
- Equipment requirements
Our team at PTSMAKE helps clients navigate these options by considering their specific application requirements. We evaluate factors like part geometry, production volume, and performance specifications to recommend the most suitable finishing method.
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent surface finish quality, we implement:
- Regular process monitoring
- Surface roughness measurements
- Coating thickness testing
- Adhesion testing
- Visual inspection protocols
- Documentation of all finishing parameters
How to Ensure Dimensional Accuracy in Aluminum Casting for Industrial Applications?
Have you ever received aluminum castings that simply didn’t fit your specifications? The frustration of dealing with dimensional inaccuracies can be overwhelming, especially when these parts are critical components of your industrial applications. Tight deadlines and quality requirements hang in the balance.
The key to ensuring dimensional accuracy in aluminum casting lies in implementing a comprehensive quality control system that combines proper mold design, precise temperature control, and advanced measurement techniques. This systematic approach helps maintain consistent part dimensions throughout the production process.
Understanding Dimensional Control Factors
Mold Design Considerations
The foundation of dimensional accuracy begins with proper mold design. At PTSMAKE, we focus on several critical aspects:
- Proper gating and runner systems
- Adequate venting placement
- Strategic parting line location
- Optimized cooling channel design
The success of aluminum casting heavily depends on how well the shrinkage rate5 is accounted for during the design phase. We carefully calculate shrinkage allowances based on the specific aluminum alloy being used.
Temperature Management
Temperature control plays a crucial role in maintaining dimensional accuracy:
| Temperature Phase | Optimal Range (°C) | Impact on Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Pouring | 660-750 | Affects flow and filling |
| Mold | 200-300 | Controls solidification rate |
| Cooling | 25-100 | Influences final dimensions |
Quality Control Measures
Pre-casting Verification
Before starting production, we implement several verification steps:
- Pattern equipment inspection
- Mold cavity measurements
- Core box verification
- Sand system testing
In-process Controls
During the casting process, we monitor:
- Metal composition through spectrographic analysis
- Pour temperature using digital thermocouples
- Cooling rate with thermal imaging
- Mold alignment and closing pressure
Advanced Measurement Techniques
Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) Integration
We utilize state-of-the-art CMM technology to:
- Perform automated dimensional inspection
- Generate detailed measurement reports
- Track dimensional trends
- Identify potential process drift
3D Scanning Applications
Modern 3D scanning technology allows us to:
- Create complete part geometry maps
- Compare actual parts to CAD models
- Document surface conditions
- Archive digital part data
Process Optimization
Statistical Process Control
We implement SPC methods to:
- Monitor key dimensional characteristics
- Establish control limits
- Identify process variations
- Take corrective actions proactively
Continuous Improvement Protocols
Our improvement system includes:
- Regular process audits
- Team feedback sessions
- Customer input integration
- Technology updates
Material Considerations
Alloy Selection Impact
Different aluminum alloys exhibit varying characteristics:
| Alloy Series | Typical Shrinkage (%) | Dimensional Stability |
|---|---|---|
| 356 | 1.3 | Excellent |
| 319 | 1.4 | Very Good |
| A380 | 1.2 | Good |
Heat Treatment Effects
Post-casting heat treatment can affect dimensions through:
- Solution heat treatment
- Quenching procedures
- Aging processes
- Stress relief methods
Documentation and Traceability
Record Keeping
We maintain detailed records of:
- Material certifications
- Process parameters
- Inspection results
- Non-conformance reports
Traceability Systems
Our traceability protocol includes:
- Unique part identification
- Batch tracking
- Process documentation
- Quality certificates
By implementing these comprehensive controls and utilizing advanced technology, we at PTSMAKE consistently achieve tight dimensional tolerances in aluminum casting. This systematic approach ensures that our industrial clients receive parts that meet their exact specifications, reducing assembly issues and improving overall product quality.
What Quality Control Measures Are Critical for Metal Casting Aluminum Production?
Have you ever received aluminum castings that failed to meet specifications, leading to costly project delays and rework? The challenges of maintaining consistent quality in aluminum casting can be overwhelming, especially when dealing with complex geometries and tight tolerances.
Quality control in metal casting aluminum production requires a comprehensive approach focusing on material testing, process monitoring, and final inspection. Key measures include chemical composition analysis, temperature control, mold inspection, and dimensional verification to ensure consistent product quality.
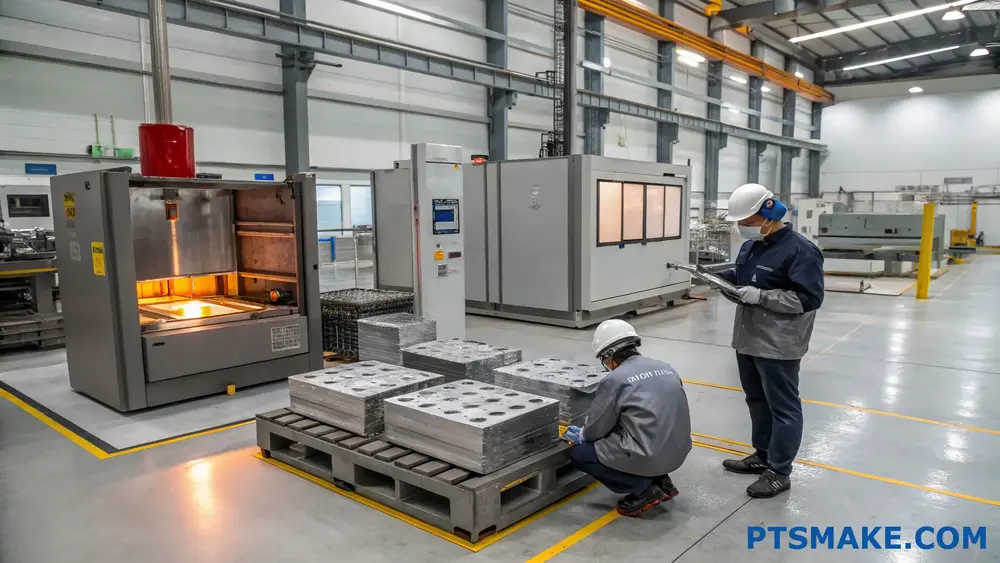

Material Testing and Verification
Raw Material Analysis
Raw material quality directly impacts the final casting quality. At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous testing protocols for incoming materials:
| Test Type | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Analysis | Verify aluminum composition | Every batch |
| Density Testing | Ensure material consistency | Daily |
| Contamination Check | Detect impurities | Per shipment |
Material Storage Controls
Proper storage prevents contamination and maintains material integrity. Our facility maintains strict environmental controls for storing aluminum alloys and implements hygroscopic6 storage conditions to prevent moisture absorption.
Process Control Measures
Temperature Monitoring
Temperature control is crucial for successful aluminum casting. We employ:
- Digital thermocouples for real-time monitoring
- Automated temperature logging systems
- Regular calibration of temperature measurement devices
- Documentation of temperature profiles for each production run
Mold Quality Verification
Mold integrity significantly affects casting quality:
- Regular inspection of mold surfaces
- Dimensional verification before each production run
- Documentation of mold maintenance history
- Coating thickness measurement and control
Production Monitoring
In-Process Inspection
Continuous monitoring during production helps identify issues early:
- Visual inspection of molten metal flow
- Real-time monitoring of casting parameters
- Regular sampling for quality checks
- Documentation of process deviations
Environmental Controls
Environmental factors affecting casting quality must be monitored:
- Humidity levels in production areas
- Ambient temperature control
- Air quality monitoring
- Dust particle measurement
Final Product Inspection
Dimensional Verification
Precise measurement ensures compliance with specifications:
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection
- 3D scanning for complex geometries
- Gauge calibration and maintenance
- Statistical process control implementation
Surface Quality Assessment
Surface finish quality affects both appearance and functionality:
- Visual inspection under controlled lighting
- Surface roughness measurement
- Porosity testing
- Documentation of surface defects
Documentation and Traceability
Quality Records
Maintaining comprehensive records ensures traceability:
- Material certificates
- Process parameters
- Inspection results
- Non-conformance reports
- Corrective action documentation
Statistical Analysis
Data analysis helps identify trends and improvement opportunities:
- Process capability studies
- Defect rate tracking
- Root cause analysis
- Continuous improvement initiatives
Advanced Testing Methods
Non-Destructive Testing
Various methods ensure internal quality:
- X-ray inspection for internal defects
- Ultrasonic testing for material integrity
- Magnetic particle inspection where applicable
- Dye penetrant testing for surface defects
Mechanical Testing
Physical properties verification ensures performance:
- Tensile strength testing
- Hardness testing
- Impact resistance verification
- Fatigue testing when required
Quality System Integration
The success of quality control measures depends on system integration:
- Employee training programs
- Standard operating procedures
- Quality management system certification
- Regular audits and reviews
- Supplier quality management
- Customer feedback integration
Through our comprehensive quality control system at PTSMAKE, we maintain consistent quality in aluminum casting production. Our approach combines traditional inspection methods with advanced testing technologies, ensuring that every casting meets or exceeds customer specifications.
I’ve found that implementing these measures systematically has helped us achieve a remarkably low defect rate in our aluminum casting operations. By focusing on prevention rather than detection, we’ve created a robust quality control system that delivers reliable results consistently.
How to Optimize Cost-Efficiency in High-Volume Aluminum Casting Projects?
Have you ever faced skyrocketing costs in your aluminum casting projects that seem to spiral out of control? Many manufacturers struggle with balancing quality and cost-efficiency, especially when dealing with high-volume production demands that leave little room for error or waste.
To optimize cost-efficiency in high-volume aluminum casting projects, focus on strategic material selection, implement lean manufacturing principles, utilize advanced process monitoring, and invest in preventive maintenance. These approaches can significantly reduce waste while maintaining quality standards.

Understanding Cost Drivers in Aluminum Casting
Before diving into optimization strategies, it’s crucial to identify the main cost drivers in aluminum casting operations. The primary factors affecting production costs include:
Material Costs
- Raw aluminum and alloying elements
- Melting and holding costs
- metallurgical treatment7 expenses
- Recycling and scrap handling
Production Efficiency Factors
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Optimization Potential |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | Direct correlation with output | High |
| Energy Consumption | 20-30% of operating costs | Medium |
| Labor Requirements | 15-25% of total costs | Medium |
| Equipment Utilization | Affects overhead distribution | High |
Implementing Smart Material Management
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed several effective strategies for material cost optimization:
Strategic Sourcing
- Establish long-term supplier relationships
- Implement bulk purchasing programs
- Monitor market trends for optimal timing
- Maintain quality while negotiating better prices
Efficient Material Handling
| Practice | Benefit | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Automated feeding systems | Reduced waste | Medium |
| Real-time inventory tracking | Better stock control | Low |
| Organized storage systems | Decreased damage risk | Low |
| Proper material rotation | Reduced obsolescence | Low |
Process Optimization Techniques
Advanced Monitoring Systems
- Install real-time monitoring equipment
- Track key performance indicators
- Implement predictive maintenance
- Document process parameters
Quality Control Integration
| Control Method | Quality Impact | Cost Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| In-line testing | Immediate feedback | High |
| Statistical process control | Reduced variations | Medium |
| Automated inspection | Faster detection | High |
| Digital documentation | Better traceability | Medium |
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Melting Operations
- Optimize furnace loading patterns
- Implement heat recovery systems
- Schedule production for off-peak hours
- Maintain proper insulation
Temperature Management
| Area | Energy Saving Potential | Investment Required |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace efficiency | 15-25% | High |
| Heat recovery | 10-20% | Medium |
| Insulation upgrade | 5-15% | Low |
| Process optimization | 10-20% | Medium |
Labor Optimization Strategies
Training and Development
- Regular skill enhancement programs
- Cross-training for flexibility
- Documentation of best practices
- Performance monitoring systems
Workflow Enhancement
| Initiative | Productivity Impact | Implementation Time |
|---|---|---|
| Standard operating procedures | High | Medium |
| Visual management systems | Medium | Low |
| Team-based problem solving | High | Medium |
| Continuous improvement culture | High | Long-term |
Equipment Maintenance and Upgrade
Preventive Maintenance
- Scheduled inspections
- Regular calibration
- Component replacement planning
- Performance tracking
Technology Integration
| Technology | ROI Timeline | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|
| Automation systems | 2-3 years | 20-30% |
| Digital controls | 1-2 years | 15-25% |
| Monitoring devices | 1 year | 10-20% |
| Data analytics | 6 months | 5-15% |
Supply Chain Optimization
Inventory Management
- Just-in-time delivery systems
- Safety stock optimization
- Supplier performance metrics
- Digital tracking solutions
Logistics Enhancement
| Strategy | Cost Reduction | Implementation Effort |
|---|---|---|
| Route optimization | 10-15% | Medium |
| Packaging improvement | 5-10% | Low |
| Load consolidation | 8-12% | Medium |
| Carrier selection | 5-8% | Low |
What Are the Key Considerations for Aluminum Casting in Automotive Applications?
Have you ever wondered why some automotive parts fail prematurely while others last for years? In the automotive industry, choosing the wrong aluminum casting process or overlooking critical parameters can lead to catastrophic part failures, compromising vehicle safety and performance.
Aluminum casting in automotive applications requires careful consideration of several key factors including alloy selection, design optimization, process control, and quality testing. The right approach ensures parts meet strict automotive standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness and production efficiency.

Material Selection and Properties
Alloy Composition
The selection of the right aluminum alloy is crucial for automotive casting applications. At PTSMAKE, we primarily work with A356 and A380 alloys due to their excellent dendrite arm spacing8 and mechanical properties. These alloys offer:
- Superior strength-to-weight ratio
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good thermal conductivity
- Enhanced castability
Heat Treatment Considerations
Heat treatment significantly influences the final properties of cast aluminum components:
| Heat Treatment Type | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| T6 | Maximum strength and hardness | Engine blocks, cylinder heads |
| T4 | Good ductility, moderate strength | Body panels, structural components |
| T7 | Better dimensional stability | Transmission cases |
Design Optimization
Wall Thickness Control
Proper wall thickness design is essential for:
- Preventing porosity formation
- Ensuring uniform solidification
- Reducing material waste
- Optimizing weight reduction
I recommend maintaining wall thickness between 3-8mm for most automotive components, with variations depending on specific application requirements.
Draft Angles and Parting Lines
Critical design elements include:
- Minimum draft angle of 2° for external surfaces
- 3° or greater for internal surfaces
- Strategic placement of parting lines to minimize flash
- Consideration of ejection requirements
Process Control Parameters
Die Temperature Management
Maintaining optimal die temperature is crucial for quality castings:
| Temperature Range (°C) | Effects | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 200-250 | Better surface finish | Decorative parts |
| 250-300 | Reduced porosity | Structural components |
| 300-350 | Enhanced mechanical properties | High-stress components |
Pressure Control
Proper pressure control during casting affects:
- Fill patterns
- Solidification rates
- Surface quality
- Internal defect formation
Quality Assurance Methods
Non-Destructive Testing
Implementation of various testing methods ensures part quality:
- X-ray inspection for internal defects
- Dye penetrant testing for surface cracks
- Ultrasonic testing for material integrity
- Dimensional verification using CMM
Process Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of key parameters:
- Metal temperature
- Die temperature
- Injection pressure
- Cycle time
- Cooling rate
Cost Optimization Strategies
Tooling Considerations
Effective tooling design impacts overall costs:
- Multi-cavity dies for high-volume production
- Modular tool designs for flexibility
- Proper venting and cooling channels
- Material selection for tool longevity
Production Efficiency
Optimizing production parameters:
- Minimizing cycle time
- Reducing scrap rates
- Implementing automated handling
- Maintaining preventive maintenance schedules
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability Practices
Modern automotive casting must address environmental concerns:
- Using recycled aluminum
- Implementing closed-loop cooling systems
- Reducing energy consumption
- Minimizing waste generation
Emissions Control
Managing environmental impact through:
- Proper ventilation systems
- Dust collection equipment
- Waste heat recovery
- Water treatment systems
Future Trends
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
Emerging technologies shaping the future:
- Computer simulation for process optimization
- Real-time monitoring systems
- Artificial intelligence for quality control
- Automated process adjustment
Material Innovations
Developments in aluminum casting:
- New alloy compositions
- Nano-particle reinforcement
- Hybrid materials
- Bio-inspired designs
How Does Heat Treatment Affect the Performance of Cast Aluminum Parts?
Have you ever received cast aluminum parts that didn’t meet your strength requirements? Or maybe you’ve dealt with components that failed prematurely despite meeting dimensional specifications? These issues can cause significant project delays and unexpected costs.
Heat treatment is a crucial process that enhances cast aluminum parts’ mechanical properties by modifying their microstructure. Through controlled heating and cooling cycles, it can significantly improve strength, hardness, and durability while reducing internal stresses in the components.

Understanding the Fundamentals of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment for cast aluminum involves several key processes that transform the material’s properties. The process begins with careful temperature control and timing to achieve optimal results. During this process, the precipitation hardening9 occurs at the microscopic level, fundamentally changing the metal’s characteristics.
Types of Heat Treatment for Cast Aluminum
There are several common heat treatment methods used for cast aluminum parts:
Solution Heat Treatment
- Heats the alloy to near melting point
- Dissolves soluble elements into solution
- Creates a homogeneous structure
Quenching
- Rapid cooling process
- Prevents unwanted precipitation
- Maintains supersaturated solution
Aging
- Natural aging at room temperature
- Artificial aging at elevated temperatures
- Controls precipitation for desired properties
Impact on Mechanical Properties
The effects of heat treatment on cast aluminum parts are substantial and measurable:
| Property | Before Treatment | After Treatment | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 180-220 MPa | 250-320 MPa | Up to 45% |
| Yield Strength | 90-120 MPa | 165-220 MPa | Up to 83% |
| Elongation | 2-3% | 5-8% | Up to 167% |
| Hardness | 70-80 HB | 95-115 HB | Up to 44% |
Optimization of Treatment Parameters
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed precise control methods for heat treatment parameters:
Temperature Control
- Accurate monitoring systems
- Uniform heat distribution
- Prevention of overheating
Time Management
- Optimized heating duration
- Controlled cooling rates
- Precise aging periods
Environmental Factors
- Humidity control
- Atmospheric conditions
- Contamination prevention
Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring consistent results requires rigorous testing and monitoring:
Common Testing Methods
Mechanical Testing
- Tensile testing
- Hardness testing
- Impact testing
Structural Analysis
- Microscopic examination
- X-ray analysis
- Density measurements
Industry Applications and Considerations
Different industries require specific heat treatment approaches:
Automotive Applications
- Engine components
- Suspension parts
- Transmission housings
Aerospace Requirements
- Structural components
- Control surfaces
- Landing gear parts
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common challenges and their solutions:
Distortion
- Proper fixturing during treatment
- Controlled cooling rates
- Stress relief procedures
Inconsistent Properties
- Regular calibration of equipment
- Standardized procedures
- Detailed documentation
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Understanding the economic impact of heat treatment:
| Factor | Without Treatment | With Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifecycle Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Performance | Standard | Enhanced |
| Warranty Claims | More Frequent | Reduced |
Best Practices for Optimal Results
To achieve the best results in heat treating cast aluminum parts:
Design Considerations
- Uniform wall thickness
- Proper draft angles
- Stress concentration reduction
Process Controls
- Temperature monitoring
- Time management
- Quality verification
Documentation
- Process parameters
- Test results
- Traceability records
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Modern heat treatment processes focus on:
Energy Efficiency
- Optimized heating cycles
- Heat recovery systems
- Modern equipment selection
Waste Reduction
- Process optimization
- Material recycling
- Emission control
What Certifications Should Suppliers Have for Aerospace-Grade Aluminum Casting?
Have you ever faced the challenge of selecting the right supplier for aerospace aluminum casting projects? The stakes are incredibly high – one small oversight in certification requirements could lead to catastrophic failures in aircraft components, potentially risking lives and millions in damages.
For aerospace-grade aluminum casting suppliers, essential certifications include AS9100D, NADCAP for special processes, ISO 9001:2015, and specific OEM approvals. These certifications ensure quality management systems, process controls, and compliance with stringent aerospace industry standards.

Understanding AS9100D Certification
AS9100D represents the gold standard in aerospace quality management systems. At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented this certification to ensure our metallurgical processes10 meet the highest industry standards. This certification encompasses:
Key Requirements of AS9100D
- Risk Management protocols
- Configuration Management
- Product Safety considerations
- Counterfeit Part prevention
- Supply Chain control
Benefits for Aerospace Manufacturers
- Enhanced quality consistency
- Improved documentation systems
- Better traceability
- Reduced operational risks
- Increased customer confidence
NADCAP Accreditation Requirements
NADCAP (National Aerospace and Defense Contractors Accreditation Program) certification is crucial for special processes in aerospace manufacturing. This includes:
| Process Category | Specific Requirements | Validation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Temperature uniformity | Pyrometric testing |
| Chemical Processing | Process control | Chemical analysis |
| Non-destructive Testing | Equipment calibration | Performance validation |
| Material Testing | Mechanical properties | Lab certification |
ISO 9001:2015 Foundation
While AS9100D builds upon ISO 9001:2015, having this baseline certification demonstrates:
Quality Management Principles
- Customer focus
- Leadership commitment
- Process approach
- Evidence-based decision making
Documentation Requirements
- Quality manual
- Process procedures
- Work instructions
- Quality records
OEM-Specific Approvals
Different aerospace manufacturers have unique requirements:
Boeing Requirements
- D1-4426 Approval
- Special Process Certification
- Material handling specifications
- Quality system requirements
Airbus Standards
- AIMS specifications
- Process qualification
- Material certification
- Testing requirements
Environmental and Safety Certifications
ISO 14001:2015
Environmental management certification ensures:
- Waste reduction
- Resource optimization
- Environmental compliance
- Sustainable practices
OHSAS 18001/ISO 45001
Safety management certification covers:
- Worker safety protocols
- Risk assessment
- Emergency preparedness
- Health monitoring
Material-Specific Certifications
For aluminum casting, specific certifications include:
Chemical Composition Verification
- Spectrographic analysis
- Heat lot testing
- Material traceability
- Composition documentation
Mechanical Property Testing
- Tensile strength
- Yield strength
- Elongation
- Hardness testing
Quality Control Certifications
Suppliers must maintain:
| Certification Type | Focus Area | Renewal Period |
|---|---|---|
| PMI Testing | Material verification | Annual |
| NDT Level III | Inspection qualification | 3 years |
| CQI-9 | Heat treat assessment | Annual |
| CQI-11 | Plating system assessment | Annual |
Digital Security Certifications
Modern aerospace manufacturing requires:
Cybersecurity Standards
- ISO 27001 compliance
- NIST framework adoption
- Data protection protocols
- Access control systems
Digital Process Control
- Industry 4.0 integration
- Digital twin capabilities
- Real-time monitoring
- Data analytics certification
Continuous Improvement Requirements
Certification maintenance involves:
- Regular audits
- Process monitoring
- Performance metrics
- Corrective actions
- Preventive measures
Click to learn about metal solidification patterns and how they affect your part quality. ↩
Click to learn more about crystal formation during metal solidification and its impact on casting quality. ↩
Click here to learn more about how geometric freedom impacts your part design and manufacturing costs. ↩
Click to learn more about anodizing processes and how they can enhance your aluminum components. ↩
Click to learn more about calculating shrinkage rates for optimal dimensional accuracy in aluminum casting. ↩
Click to learn more about moisture control in aluminum casting storage. ↩
Click to learn advanced metal treatment techniques that can significantly reduce production costs. ↩
Click to learn more about dendrite spacing’s critical role in casting strength and durability. ↩
Click here to learn more about the science behind precipitation hardening and its benefits. ↩
Click to learn advanced metallurgical techniques for aerospace-grade aluminum casting. ↩