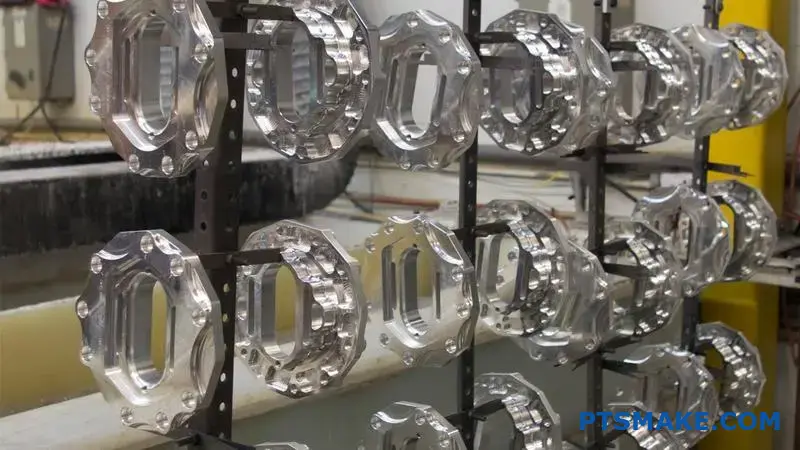
When investing in metal parts, many manufacturers struggle with material selection. I’ve witnessed countless projects derailed by choosing the wrong material, leading to costly repairs, product failures, and disappointed customers.
Cast aluminum offers good quality for many applications, combining lightweight properties with decent strength and corrosion resistance. While it may not match the strength of steel, its excellent castability, cost-effectiveness, and versatility make it a reliable choice for various manufacturing needs.

I understand you might be wondering about specific applications and limitations of cast aluminum. Let me share my experience working with different aluminum casting grades and how they perform in real-world applications. I’ve helped many clients make informed decisions about using cast aluminum in their projects, and I can guide you through its key benefits and potential drawbacks.
What’s The Difference Between Aluminum And Cast Aluminum?
Have you ever stood in a hardware store, puzzling over aluminum materials for your project? The confusion between aluminum and cast aluminum is more common than you might think, especially when durability and cost considerations come into play. This decision can make or break your project’s success.
The main difference between aluminum and cast aluminum lies in their manufacturing processes. While aluminum is wrought or formed from solid metal, cast aluminum is created by pouring molten aluminum into molds to achieve specific shapes. This fundamental difference affects their strength, applications, and cost.
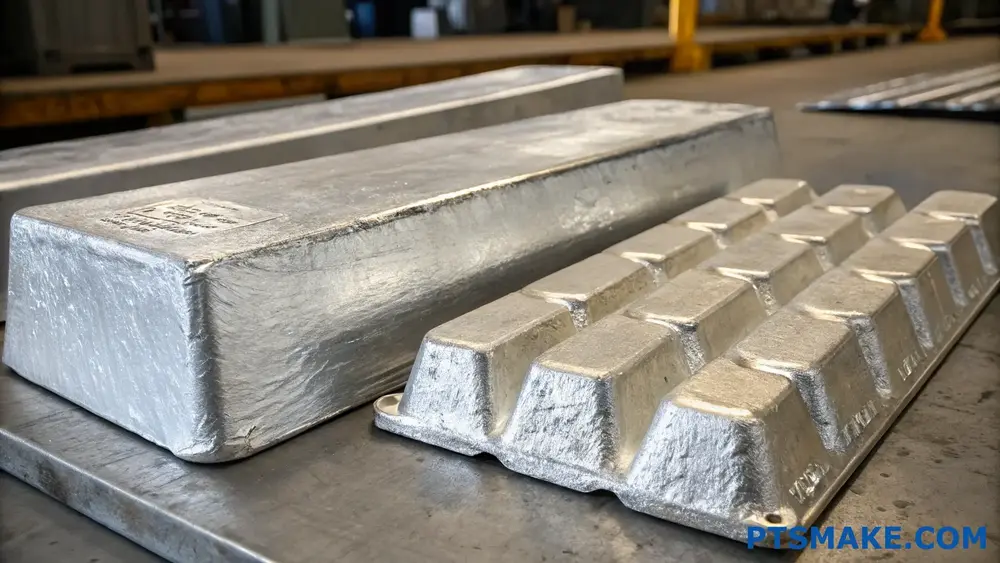

Understanding the Manufacturing Process
Pure Aluminum Production
Pure aluminum starts its journey from bauxite ore through the Hall-Héroult process1. At PTSMAKE, we typically work with various grades of aluminum that have already been refined and processed. The raw aluminum undergoes several stages of processing before reaching its final form:
- Mining and Extraction
- Refining
- Electrolysis
- Formation into ingots or billets
Cast Aluminum Formation
Cast aluminum manufacturing involves melting aluminum alloys and pouring them into molds. Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed three primary casting methods:
- Die Casting
- Sand Casting
- Permanent Mold Casting
Material Properties Comparison
The following table illustrates the key differences between aluminum and cast aluminum:
| Property | Pure Aluminum | Cast Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Higher tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Weight | Slightly heavier | Slightly lighter |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good to Excellent |
| Cost | Generally higher | Usually more economical |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, consistent | May show casting marks |
Applications and Uses
Pure Aluminum Applications
- Aerospace components
- Electronics housings
- Food packaging
- Construction materials
- Transportation equipment
Cast Aluminum Applications
- Engine blocks
- Transmission housings
- Architectural components
- Furniture
- Decorative items
Cost Considerations
The cost difference between aluminum and cast aluminum can be significant. Several factors influence the final price:
Production Volume
- Small quantities: Pure aluminum typically more cost-effective
- Large quantities: Cast aluminum usually more economical
Processing Requirements
Pure aluminum often requires:
- Multiple machining operations
- More material waste
- Higher labor costs
Cast aluminum benefits include:
- Near-net-shape production
- Reduced machining
- Lower material waste
Durability and Maintenance
When it comes to durability, both materials have their strengths:
Pure Aluminum
- Better fatigue resistance
- Higher impact resistance
- More consistent material properties
- Superior mechanical strength
Cast Aluminum
- Good wear resistance
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Better vibration dampening
- Complex shape capability
Environmental Impact
Both materials offer sustainability benefits:
Recyclability
- Both are 100% recyclable
- Minimal quality loss during recycling
- Lower energy consumption compared to initial production
Energy Efficiency
- Cast aluminum requires less energy for complex shapes
- Pure aluminum processing may need more energy for fabrication
Selection Criteria
To help choose between aluminum and cast aluminum, consider these factors:
Application Requirements
- Load-bearing needs
- Environmental exposure
- Temperature conditions
- Aesthetic requirements
Production Volumes
- Prototype quantities
- Production run size
- Future scaling needs
Budget Constraints
- Initial tooling costs
- Per-unit costs
- Long-term maintenance costs
At PTSMAKE, we guide our clients through this selection process by analyzing their specific requirements and recommending the most suitable material and manufacturing method. Our expertise in both CNC machining and casting processes allows us to provide comprehensive solutions that optimize cost, performance, and production efficiency.
What Are The Benefits And Drawbacks Of Cast Aluminum?
Have you ever found yourself torn between different manufacturing materials for your project? The decision between cast aluminum and other metals can be particularly challenging, especially when considering factors like cost, durability, and performance.
Cast aluminum offers excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance while being cost-effective. However, it may have limitations in high-temperature applications and can be susceptible to porosity issues. The choice depends on specific project requirements and operating conditions.
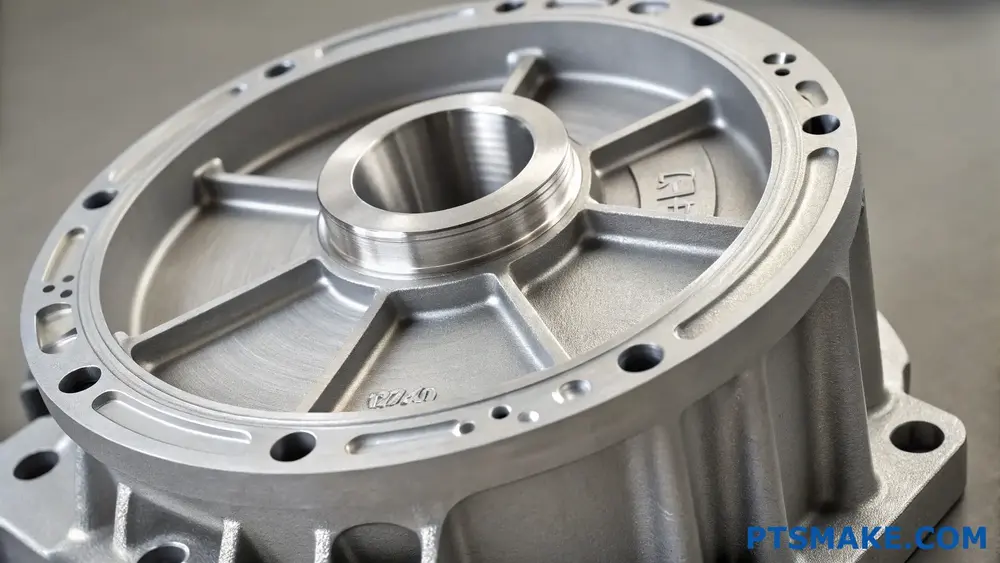

Understanding Cast Aluminum Properties
Cast aluminum has become increasingly popular in various industries due to its unique combination of properties. The material undergoes a solidification process2 during casting, which significantly influences its final characteristics. At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully utilized cast aluminum in numerous projects, particularly in automotive and aerospace components.
Physical Properties
- Density: 2.7 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 660°C (1220°F)
- Thermal Conductivity: High
- Electrical Conductivity: Excellent
Key Advantages of Cast Aluminum
1. Weight Reduction
Cast aluminum components typically weigh about one-third as much as comparable steel parts. This weight advantage makes it particularly valuable in:
- Automotive applications
- Aerospace components
- Portable equipment
- Energy-efficient machinery
2. Cost-Effectiveness
The economic benefits of cast aluminum include:
| Cost Factor | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Material Cost | Lower than many metals |
| Processing Cost | Reduced energy requirements |
| Maintenance Cost | Minimal due to corrosion resistance |
| Recycling Value | High scrap value |
3. Versatility in Design
Cast aluminum offers exceptional design flexibility, allowing for:
- Complex geometries
- Thin walls
- Integrated features
- Smooth surface finishes
Notable Disadvantages
1. Mechanical Limitations
While strong for its weight, cast aluminum has some mechanical constraints:
- Lower absolute strength compared to steel
- Reduced performance at high temperatures
- Potential for porosity issues
- Limited fatigue resistance
2. Production Challenges
Manufacturing considerations include:
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Shrinkage | Requires careful mold design |
| Gas Porosity | Can affect part integrity |
| Surface Finish | May need secondary operations |
| Tool Wear | Higher than some materials |
3. Environmental Factors
Environmental considerations when working with cast aluminum:
- Energy-intensive initial production
- Potential for oxidation
- Surface treatment requirements
- Recycling process complexity
Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive Industry
Cast aluminum excels in:
- Engine blocks
- Transmission housings
- Wheel components
- Structural elements
Aerospace Applications
Common uses include:
- Aircraft fittings
- Interior components
- Non-structural elements
- Equipment housings
Best Practices for Cast Aluminum Selection
To maximize the benefits of cast aluminum:
- Conduct thorough material analysis
- Consider operating conditions
- Evaluate design requirements
- Assess cost implications
- Review maintenance needs
Quality Control Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we emphasize these quality control measures:
- Comprehensive material testing
- Advanced inspection techniques
- Strict process controls
- Regular quality audits
Future Trends
The cast aluminum industry is evolving with:
- Advanced alloy development
- Improved casting techniques
- Enhanced surface treatments
- Innovative design approaches
The future of cast aluminum looks promising, with ongoing research into:
- New alloy compositions
- Advanced processing methods
- Improved surface treatments
- Enhanced design capabilities
How Durable Is Cast Aluminum In Industrial Applications?
Have you ever questioned whether your cast aluminum components could withstand the demanding conditions of your industrial application? The constant exposure to harsh environments, heavy loads, and temperature fluctuations can make any engineer second-guess their material choice.
Cast aluminum offers remarkable durability in industrial applications, typically lasting 15-20 years with proper maintenance. Its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, and ability to withstand temperatures up to 400°F make it ideal for long-term industrial use.

Understanding Cast Aluminum’s Core Properties
Cast aluminum’s durability stems from several key characteristics that make it particularly suitable for industrial applications. The material undergoes precipitation hardening3 during the casting process, which significantly enhances its strength and wear resistance.
Mechanical Properties
Cast aluminum exhibits impressive mechanical properties that contribute to its longevity:
| Property | Typical Range | Industrial Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 27,000-45,000 PSI | Excellent load-bearing capacity |
| Yield Strength | 11,000-35,000 PSI | Resists permanent deformation |
| Elongation | 2-8% | Good ductility for stress distribution |
| Hardness | 75-150 Brinell | Wear resistance in demanding environments |
Environmental Resistance Factors
The durability of cast aluminum in industrial settings is largely attributed to its natural resistance to various environmental factors. At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented cast aluminum solutions in numerous challenging environments.
Corrosion Resistance
Cast aluminum forms a protective oxide layer that prevents further oxidation, making it highly resistant to:
- Atmospheric corrosion
- Chemical exposure
- Marine environments
- Industrial pollutants
Temperature Performance
The material maintains its structural integrity across a wide temperature range:
- Low-temperature applications down to -320°F
- High-temperature stability up to 400°F
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Low thermal expansion
Industry-Specific Applications and Durability
Different industrial sectors leverage cast aluminum’s durability in various ways:
Automotive Industry
- Engine components
- Transmission housings
- Structural components
- Wheel components
Aerospace Applications
- Aircraft fittings
- Interior components
- Non-structural elements
- Ground support equipment
Manufacturing Equipment
- Machine guards
- Tool housings
- Control panels
- Structural frames
Factors Affecting Longevity
Several key factors influence the durability of cast aluminum components:
Design Considerations
- Proper wall thickness
- Appropriate draft angles
- Strategic placement of ribs and gussets
- Smooth transitions between sections
Environmental Factors
- Exposure to chemicals
- Temperature cycling
- UV radiation
- Mechanical stress
Maintenance Requirements
To maximize the durability of cast aluminum components:
Regular Inspection
- Visual examination for surface defects
- Checking for stress points
- Monitoring for corrosion
- Assessment of wear patterns
Preventive Measures
- Regular cleaning
- Proper lubrication where required
- Protection from harsh chemicals
- Addressing minor issues promptly
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When considering cast aluminum’s durability:
| Factor | Benefit | Long-term Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher than some alternatives | Lower total ownership cost |
| Maintenance | Minimal requirements | Reduced operating expenses |
| Replacement | Less frequent | Lower long-term investment |
| Performance | Consistent over time | Improved reliability |
Performance Optimization Tips
Based on our experience at PTSMAKE, these practices enhance cast aluminum durability:
- Specify appropriate alloy selection for the application
- Implement proper surface treatments
- Ensure correct installation procedures
- Maintain regular inspection schedules
- Use appropriate cleaning methods and materials
Future Trends and Developments
The durability of cast aluminum continues to improve through:
- Advanced alloy development
- Enhanced casting techniques
- Improved surface treatments
- Better design optimization tools
- More effective quality control methods
These ongoing developments make cast aluminum an increasingly attractive option for demanding industrial applications, offering improved performance and longevity while maintaining its core benefits of lightweight construction and excellent corrosion resistance.
Does Cast Aluminum Crack Easily?
Have you ever discovered hairline cracks in your aluminum castings just when you thought everything was perfect? It’s frustrating when these defects appear unexpectedly, potentially compromising the integrity of your entire project and forcing you back to square one.
Cast aluminum doesn’t crack easily when properly manufactured and handled. While it can develop cracks under specific conditions like thermal stress, improper cooling, or excessive load, these issues are preventable through correct casting processes and proper material handling.

Understanding Crack Formation in Cast Aluminum
The susceptibility of cast aluminum to cracking depends on several critical factors. The formation of cracks often relates to the metallurgical structure4 during the casting process. As an aluminum casting expert, I’ve identified the following key aspects that influence crack formation:
Thermal Stress Factors
- Rapid temperature changes
- Uneven cooling rates
- Internal stress buildup
- Heat treatment processes
Material Composition Impact
Different aluminum alloys exhibit varying crack resistance properties. Here’s a breakdown of common casting alloys and their crack resistance:
| Alloy Series | Crack Resistance | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| A356 | Excellent | Automotive parts |
| A380 | Very Good | Electronics housings |
| 319 | Good | Engine components |
| 713 | Moderate | Aircraft parts |
Prevention Strategies and Best Practices
At PTSMAKE, we implement several proven methods to minimize cracking risks in cast aluminum components:
Design Considerations
- Uniform wall thickness
- Proper draft angles
- Strategic placement of ribs
- Smooth transitions between sections
Process Control Measures
The casting process itself requires careful attention to prevent crack formation:
Temperature Management
- Controlled cooling rates
- Proper preheating
- Monitored post-casting cooling
Mold Design
- Adequate venting
- Proper gating system
- Optimized runner layout
Quality Control Procedures
Implementing robust quality control measures helps ensure crack-free castings:
- Visual Inspection
- Dye Penetrant Testing
- X-ray Analysis
- Ultrasonic Testing
Factors Affecting Crack Resistance
Several elements influence the crack resistance of cast aluminum:
Environmental Conditions
- Operating temperature
- Exposure to corrosive substances
- Humidity levels
- Mechanical stress
Service Requirements
- Load conditions
- Cycling frequency
- Impact resistance needs
- Fatigue considerations
Industry-Specific Solutions
Different industries require varying approaches to prevent aluminum casting cracks:
Automotive Industry
- Enhanced cooling control
- Specialized alloy selection
- Stress-relieving heat treatment
- Regular quality inspections
Aerospace Applications
- Premium grade materials
- Advanced testing protocols
- Stringent quality standards
- Specialized heat treatment
Consumer Electronics
- Thin-wall casting techniques
- Precise temperature control
- Optimized cooling strategies
- Regular process monitoring
Maintenance and Long-term Prevention
To maintain the integrity of cast aluminum components:
Regular Inspection Schedule
- Visual checks
- Non-destructive testing
- Performance monitoring
- Stress point evaluation
Environmental Control
- Temperature regulation
- Humidity management
- Corrosion prevention
- Proper storage conditions
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When cracks do occur, systematic analysis helps prevent future issues:
Root Cause Analysis
- Process evaluation
- Material testing
- Design review
- Environmental assessment
Corrective Actions
- Process adjustments
- Design modifications
- Material changes
- Quality control updates
Future Developments
The field of aluminum casting continues to evolve with new technologies:
Advanced Simulation Tools
- Flow analysis
- Solidification modeling
- Stress prediction
- Optimization software
Innovative Materials
- New alloy development
- Enhanced properties
- Improved processability
- Better crack resistance
What Factors Affect The Lifespan Of Cast Aluminum Components?
Have you ever invested in cast aluminum components only to find them failing prematurely? It’s frustrating when these supposedly durable parts deteriorate faster than expected, especially when they’re crucial to your production line’s efficiency and your bottom line.
The lifespan of cast aluminum components is influenced by multiple factors including environmental conditions, stress loads, material quality, casting process, surface treatment, and maintenance practices. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing component longevity and performance.

Environmental Impact on Component Durability
Temperature Fluctuations
Temperature changes can significantly affect cast aluminum parts through thermal fatigue5. At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented specialized testing procedures to ensure our components can withstand various temperature ranges. The key is understanding how different aluminum alloys respond to thermal stress:
| Temperature Range | Impact on Components | Recommended Alloy Series |
|---|---|---|
| -40°C to 0°C | Increased brittleness | 356, A356 |
| 0°C to 150°C | Optimal performance | 319, 380 |
| 150°C to 200°C | Strength reduction | 242, 535 |
Chemical Exposure
Different environments expose cast aluminum to various chemicals that can accelerate corrosion:
- Industrial atmospheres with high sulfur content
- Coastal areas with salt spray exposure
- Areas with high humidity levels
- Locations with acid rain presence
Mechanical Stress Factors
Load Distribution
The way stress is distributed across a component significantly impacts its lifespan. Proper design considerations include:
- Even load distribution
- Stress concentration minimization
- Appropriate wall thickness
- Strategic reinforcement placement
Vibration Effects
Continuous vibration can lead to:
- Structural fatigue
- Component loosening
- Surface wear
- Internal stress buildup
Manufacturing Quality Considerations
Material Selection
The choice of aluminum alloy directly affects component durability:
| Alloy Type | Primary Benefits | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| A356 | High strength | Structural parts |
| 319 | Good machinability | Engine components |
| 380 | Pressure tight | Complex housings |
Casting Process Control
Quality control during casting is essential for long-term durability:
- Proper mold temperature management
- Controlled cooling rates
- Minimized porosity
- Optimal grain structure formation
Surface Treatment and Protection
Protective Coatings
Various surface treatments can enhance component longevity:
- Anodizing for increased wear resistance
- Powder coating for chemical protection
- Chromate conversion for corrosion resistance
- Clear coating for aesthetic preservation
Surface Finishing
The quality of surface finish affects:
- Wear resistance
- Corrosion susceptibility
- Fatigue strength
- Overall appearance
Maintenance and Usage Practices
Regular Inspection
Implementing routine inspection protocols helps identify:
- Early signs of wear
- Corrosion development
- Structural changes
- Performance degradation
Proper Cleaning
Maintaining clean surfaces is crucial for longevity:
- Remove corrosive substances promptly
- Use appropriate cleaning agents
- Avoid abrasive cleaning methods
- Ensure thorough drying after cleaning
Operating Conditions
Adhering to specified operating parameters:
- Stay within designed load limits
- Maintain appropriate operating temperatures
- Follow lubrication schedules
- Avoid excessive impact loads
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed comprehensive testing procedures to evaluate these factors during production. Our quality control processes ensure that each cast aluminum component meets or exceeds industry standards for durability and performance. We work closely with clients to understand their specific application requirements and recommend the most suitable alloy and treatment combinations.
The key to maximizing the lifespan of cast aluminum components lies in addressing these factors during the design, manufacturing, and maintenance phases. Through careful consideration of environmental conditions, proper material selection, and appropriate maintenance practices, organizations can significantly extend the service life of their cast aluminum components while maintaining optimal performance levels.
Is Cast Aluminum Better Than Regular Aluminum?
Have you ever stood in front of two aluminum parts, scratching your head over which manufacturing method to choose? The decision between cast and regular (wrought) aluminum isn’t just about cost – it’s about ensuring your product performs exactly as intended, yet many engineers get stuck at this crossroads.
Cast aluminum and regular aluminum each have their distinct advantages. Cast aluminum excels in complex geometries and is often more cost-effective for large production runs, while regular (wrought) aluminum typically offers superior strength and better surface finish for simpler shapes.
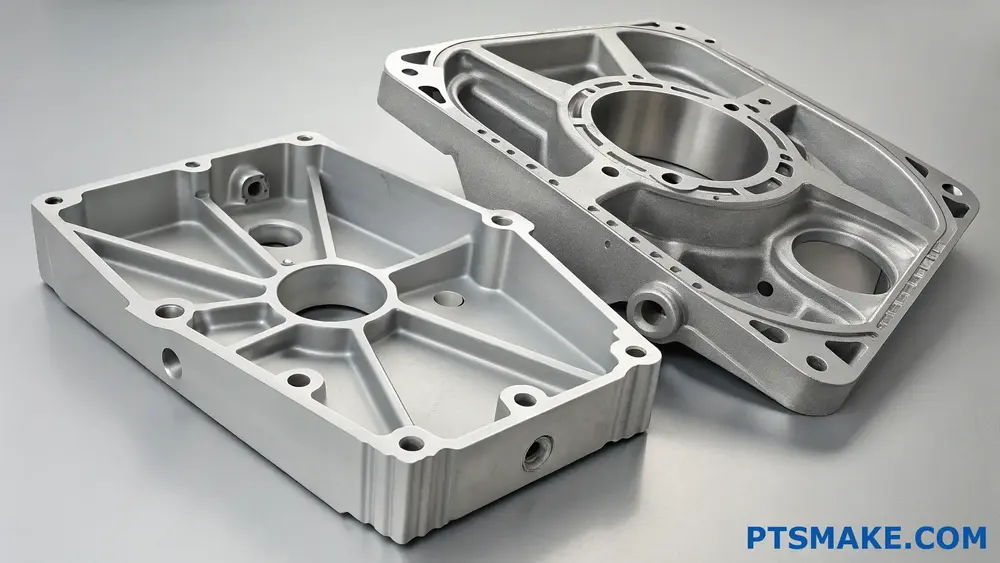
Understanding the Fundamental Differences
Cast and wrought aluminum differ primarily in their manufacturing processes and resulting microstructures. Cast aluminum is melted and poured into molds, while wrought aluminum is worked mechanically through processes like rolling, forging, or extrusion. The dendrite structure6 formed during casting creates unique properties that set it apart from wrought aluminum.
Material Properties Comparison
Material properties vary significantly between cast and wrought aluminum:
| Property | Cast Aluminum | Regular (Wrought) Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Lower (15-30 ksi) | Higher (30-70 ksi) |
| Ductility | Lower | Higher |
| Porosity | Higher | Lower |
| Shape Complexity | Excellent | Limited |
| Cost Efficiency | Better for complex parts | Better for simple shapes |
Advantages of Cast Aluminum
Complex Geometry Capability
Cast aluminum shines when it comes to creating intricate shapes. At PTSMAKE, we regularly produce complex components that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to machine from wrought aluminum. The casting process allows for internal passages, varying wall thicknesses, and organic shapes that serve specific functional requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness in High Volume
For large production runs, casting typically offers significant cost advantages:
- Lower material waste
- Reduced machining requirements
- Faster production cycles
- Lower labor costs per unit
Benefits of Regular (Wrought) Aluminum
Superior Mechanical Properties
Wrought aluminum typically exhibits:
- Higher strength-to-weight ratio
- Better fatigue resistance
- More predictable performance under stress
- Greater resistance to impact
Excellent Surface Finish
The mechanical working process of wrought aluminum results in:
- Smoother surface finish
- Better dimensional accuracy
- Reduced need for secondary operations
- Higher aesthetic quality
Making the Right Choice
Application-Specific Considerations
The choice between cast and regular aluminum should be based on:
Production Volume
- Low volume: Consider wrought aluminum
- High volume: Cast aluminum often more economical
Design Complexity
- Simple shapes: Wrought aluminum
- Complex geometries: Cast aluminum
Performance Requirements
- High strength needs: Wrought aluminum
- Moderate strength acceptable: Cast aluminum
Cost Constraints
- Initial tooling budget
- Per-unit cost targets
- Secondary processing requirements
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries favor different forms:
Automotive Industry
- Cast aluminum: Engine blocks, transmission housings
- Wrought aluminum: Body panels, structural components
Aerospace Sector
- Cast aluminum: Complex bracket designs, pump housings
- Wrought aluminum: Structural members, wing components
Consumer Electronics
- Cast aluminum: Device housings, heat sinks
- Wrought aluminum: Simple enclosures, frames
Quality Control Considerations
When working with cast aluminum, special attention must be paid to:
- Porosity levels
- Wall thickness variations
- Internal defects
- Surface finish requirements
Regular aluminum requires focus on:
- Grain direction
- Work hardening effects
- Surface treatment consistency
Cost Analysis Factors
Several elements influence the total cost:
| Cost Factor | Cast Aluminum | Regular Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Tooling | Higher | Lower |
| Per-Unit Cost | Lower for high volume | Lower for low volume |
| Secondary Operations | Often required | Minimal |
| Material Waste | Minimal | Can be significant |
Environmental Impact
Both materials offer recycling benefits, but their environmental impact differs:
Cast Aluminum
- Often uses recycled content
- Lower energy in production
- Minimal material waste
Regular Aluminum
- Higher virgin material use
- More energy-intensive processing
- More material waste in manufacturing
How Does Cast Aluminum Perform Under High Temperatures?
Have you ever watched your cast aluminum parts gradually lose their strength as temperatures rise? The uncertainty about how these components will perform in high-temperature environments can keep any engineer awake at night, especially when safety and reliability are at stake.
Cast aluminum’s performance under high temperatures depends on its specific alloy composition and heat treatment. Generally, it maintains structural integrity up to 350°F (177°C), though strength decreases as temperature rises. Beyond this point, mechanical properties begin to deteriorate significantly.

Understanding Temperature Effects on Cast Aluminum
At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with various cast aluminum alloys, and their behavior under high temperatures is crucial for many applications. The performance of cast aluminum at elevated temperatures is influenced by several key factors:
Mechanical Property Changes
Cast aluminum undergoes several changes when exposed to high temperatures:
- Tensile Strength Reduction
- Yield Strength Decrease
- Hardness Changes
- Dimensional Stability Variations
The impact varies depending on the specific alloy and exposure duration. Here’s a typical performance breakdown:
| Temperature Range (°F) | Strength Retention | Notable Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 0-200 | 95-100% | Minimal impact |
| 200-350 | 85-95% | Slight softening |
| 350-500 | 70-85% | Moderate strength loss |
| Above 500 | Below 70% | Significant deterioration |
Critical Temperature Thresholds
When working with cast aluminum, understanding the recrystallization temperature7 is essential. This phenomenon occurs at approximately 50% of the material’s melting point and can significantly affect its properties.
Permanent Changes vs. Temporary Effects
The temperature exposure duration plays a crucial role:
Short-term Exposure:
- Temporary strength reduction
- Reversible dimensional changes
- Minimal microstructural alterations
Long-term Exposure:
- Permanent strength loss
- Irreversible structural changes
- Potential component failure
Alloy-Specific Considerations
Different cast aluminum alloys exhibit varying heat resistance:
A356 Alloy Performance
- Excellent casting characteristics
- Good strength retention up to 300°F
- Popular in automotive applications
319 Alloy Characteristics
- Superior mechanical properties
- Better high-temperature stability
- Commonly used in engine components
Design Strategies for High-Temperature Applications
To optimize cast aluminum performance in high-temperature environments:
Material Selection:
- Choose appropriate alloy grades
- Consider thermal cycling requirements
- Evaluate cost-effectiveness
Design Modifications:
- Incorporate thermal expansion allowances
- Add cooling features where possible
- Optimize wall thickness
Surface Treatment Options:
- Thermal barrier coatings
- Oxidation protection
- Wear-resistant treatments
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous testing protocols:
Pre-production Testing:
- Material composition verification
- Heat treatment validation
- Prototype performance evaluation
Production Monitoring:
- Temperature control during casting
- Cooling rate optimization
- Dimensional stability checks
Post-production Analysis:
- Mechanical property testing
- Microstructure examination
- Performance validation
Industry Applications and Success Stories
Cast aluminum’s high-temperature performance makes it suitable for various applications:
Automotive Industry:
- Engine blocks
- Cylinder heads
- Transmission housings
Aerospace Sector:
- Engine components
- Structural elements
- Interior fittings
Industrial Equipment:
- Heat exchangers
- Pump housings
- Compressor parts
Preventive Measures and Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance:
Regular Inspections:
- Visual examination
- Dimensional checks
- Performance testing
Environmental Controls:
- Temperature monitoring
- Exposure time tracking
- Cooling system maintenance
Documentation:
- Operating temperature records
- Maintenance history
- Performance data
Which Is Better: Cast Iron Or Cast Aluminum?
Have you ever stood in your workshop, holding two different casting samples, wondering which material would be the perfect choice for your project? The decision between cast iron and cast aluminum isn’t just about weight or cost – it’s about finding the right balance of properties that could make or break your design.
Cast iron and cast aluminum each have their distinct advantages. Cast iron excels in strength, wear resistance, and heat handling, while cast aluminum offers superior weight reduction, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The better choice depends entirely on your specific application requirements.

Understanding Material Properties
Mechanical Properties
Cast iron and cast aluminum present different mechanical characteristics that significantly influence their applications. Cast iron typically offers higher tensile strength and better wear resistance, while aluminum provides excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
| Property | Cast Iron | Cast Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 150-400 MPa | 130-280 MPa |
| Density | 7.2 g/cm³ | 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 150-300 HB | 55-150 HB |
Thermal Characteristics
The thermal properties of these materials play a crucial role in their performance. Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that thermal conductivity particularly affects the heat dissipation rate8 in different applications.
| Property | Cast Iron | Cast Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 50 W/mK | 150-180 W/mK |
| Melting Point | 1150-1200°C | 660°C |
| Thermal Expansion | 10.8 µm/m-K | 23.6 µm/m-K |
Cost Considerations
Material Costs
Cast aluminum typically costs more per pound than cast iron, but its lighter weight often means less material is needed overall. Here’s what I’ve learned from working with various clients:
- Raw material pricing fluctuates with market conditions
- Volume requirements affect final pricing
- Processing costs vary between materials
- Secondary operations impact total cost
Manufacturing Expenses
The manufacturing process for each material carries different costs:
Tooling Requirements
- Cast iron requires more robust tooling
- Aluminum tools typically have longer life
- Temperature considerations affect tool design
Processing Time
- Aluminum casts faster due to lower melting point
- Iron requires more careful cooling procedures
- Post-processing needs differ significantly
Application-Specific Considerations
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, both materials serve specific purposes:
Cast Iron:
- Engine blocks (high-performance)
- Brake components
- Cylinder heads
- Transmission cases
Cast Aluminum:
- Modern engine blocks
- Wheel components
- Body structural components
- Heat exchangers
Industrial Equipment
For industrial applications, the choice often depends on operating conditions:
Cast Iron Benefits:
- Better vibration dampening
- Higher wear resistance
- Superior thermal stability
- Lower cost for large components
Cast Aluminum Advantages:
- Reduced equipment weight
- Better corrosion resistance
- Easier maintenance
- More design flexibility
Design Considerations
Surface Finish
Cast iron typically provides:
- Better as-cast surface finish
- Easier machining characteristics
- More consistent surface quality
While aluminum offers:
- Smoother final finish potential
- Better aesthetic possibilities
- More coating options
Wall Thickness
Design limitations vary:
- Cast iron allows for thinner walls in some cases
- Aluminum requires careful consideration of cooling rates
- Both materials need proper gating and risering
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully manufactured both cast iron and aluminum components for various industries. Our experience shows that neither material is universally superior – it’s all about matching the material properties to your specific requirements.
Environmental Impact
Recyclability
Both materials offer excellent recyclability:
- Aluminum has a higher scrap value
- Iron recycling is well-established
- Both reduce environmental impact
- Energy savings through recycling
Energy Consumption
Manufacturing energy requirements differ:
- Aluminum requires more initial energy
- Iron processing is more energy-efficient
- Lifecycle energy use varies by application
- Transportation energy costs favor aluminum
Maintenance Requirements
Cast iron typically requires:
- Regular rust prevention
- Less frequent replacement
- Simple maintenance procedures
- Basic surface treatment
Aluminum needs:
- Minimal corrosion protection
- More careful handling
- Special cleaning procedures
- Specific coating systems
Both materials can provide excellent service life when properly maintained and used in appropriate applications. The key is understanding your specific needs and choosing accordingly.
What Are The Cost-Effective Alternatives To Cast Aluminum?
Have you ever faced budget constraints while working with cast aluminum components? The rising costs of aluminum casting processes and raw materials can strain project budgets, leaving engineers and manufacturers searching for viable alternatives that won’t compromise quality or performance.
Several cost-effective alternatives to cast aluminum exist, including injection-molded plastics, zinc die casting, and steel fabrication. These options can reduce production costs by 30-50% while maintaining similar mechanical properties and performance characteristics for many applications.

Understanding Material Selection Criteria
When considering alternatives to cast aluminum, it’s essential to evaluate several key factors. The selection process involves analyzing mechanical properties, production costs, and application requirements. During my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve helped numerous clients transition from cast aluminum to more cost-effective solutions while maintaining or even improving product performance.
Performance Requirements Analysis
Before selecting an alternative material, consider these critical factors:
- Strength-to-weight ratio
- Temperature resistance
- Chemical resistance
- Dimensional stability
- Surface finish requirements
- Environmental conditions
Cost-Effective Material Alternatives
1. Engineering Plastics
Engineering plastics offer excellent cost savings compared to cast aluminum. Materials like Glass-Filled Polyamide9 provide comparable strength at a fraction of the cost. These materials are particularly suitable for:
- Electronic enclosures
- Automotive components
- Consumer products
- Industrial equipment housing
The cost advantage becomes even more significant in high-volume production scenarios. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Material Type | Cost per Unit (USD) | Tooling Cost | Production Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Aluminum | 8-12 | Medium | Moderate |
| Engineering Plastics | 3-5 | Low | Fast |
| Glass-Filled PA | 4-6 | Low | Fast |
2. Zinc Die Casting
Zinc die casting presents another viable alternative, offering:
- Lower material costs
- Faster production cycles
- Excellent surface finish
- Good dimensional accuracy
3. Steel Fabrication
For applications requiring high strength, steel fabrication can be more cost-effective than cast aluminum:
- Sheet metal forming
- Welded assemblies
- Stamped components
- Structural elements
Manufacturing Process Considerations
Injection Molding vs. Casting
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented injection molding as an alternative to aluminum casting, achieving:
- Reduced cycle times
- Lower per-part costs
- Improved consistency
- Minimal post-processing requirements
Design Optimization Strategies
To maximize cost savings:
- Incorporate design for manufacturing principles
- Optimize wall thickness
- Eliminate unnecessary features
- Consider assembly requirements
Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive Components
Many automotive parts traditionally made from cast aluminum can be replaced with:
- Composite materials
- Engineering plastics
- Hybrid solutions
Consumer Electronics
The electronics industry has successfully transitioned many components from aluminum to alternatives:
- Housing components
- Internal structural elements
- Heat management components
- Mounting brackets
Cost Analysis and ROI
Initial Investment Comparison
| Manufacturing Method | Tooling Cost | Setup Time | Annual Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Casting | $50,000+ | 4-6 weeks | $5,000 |
| Injection Molding | $15,000-30,000 | 2-3 weeks | $2,000 |
| Zinc Die Casting | $30,000-40,000 | 3-4 weeks | $3,500 |
Long-term Cost Benefits
The cost advantages of alternative materials become more apparent when considering:
- Lower material costs
- Reduced energy consumption
- Faster production cycles
- Decreased labor requirements
- Minimal finishing costs
Quality Assurance Considerations
To ensure successful implementation of alternative materials:
- Conduct thorough material testing
- Implement robust quality control procedures
- Monitor production processes
- Maintain detailed documentation
- Perform regular audits
Environmental Impact
Alternative materials often offer environmental benefits:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Lower carbon footprint
- Improved recyclability
- Decreased waste generation
Making the Transition
When switching from cast aluminum to alternative materials:
- Start with pilot projects
- Validate designs thoroughly
- Train production staff
- Establish clear quality metrics
- Monitor performance closely
Future Trends
The industry continues to evolve with:
- New material developments
- Improved processing technologies
- Advanced design tools
- Enhanced recycling capabilities
Click to learn more about this crucial aluminum production process and its industrial applications. ↩
Click to learn more about metal solidification techniques and how they affect final product quality. ↩
Click to learn about advanced metallurgical processes that enhance material strength. ↩
Click to learn more about metallurgical structures and their impact on casting quality. ↩
Click to learn more about thermal fatigue analysis and prevention strategies in aluminum casting. ↩
Click to learn more about dendrite structures and their impact on aluminum properties. ↩
Click here to learn about how material properties change during heat exposure. ↩
Click to learn more about thermal management in casting applications. ↩
Click to learn more about glass-filled materials and their applications in modern manufacturing. ↩







