When sourcing plastic materials, I often hear engineers using "Delrin" and "POM" interchangeably. This confusion can lead to costly mistakes in material selection and potentially impact the final product’s performance.
While Delrin and POM are related, they’re not exactly the same. Delrin is DuPont’s trademark name for their POM homopolymer, while POM (Polyoxymethylene) is the generic name for a family of engineering thermoplastic materials.

I want to clarify something important here. Many engineers I work with initially think these materials are completely interchangeable, but there are subtle differences that can significantly impact your project’s success. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed material choices for your applications, and I’ll explain why.
What Kind Of Plastic Is Delrin?
Have you ever struggled to choose the right plastic material for your precision parts? In the world of engineering plastics, making the wrong choice can lead to premature part failure, costly replacements, and production delays that could seriously impact your project timeline.
Delrin, also known as Polyoxymethylene (POM), is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength, stiffness, and dimensional stability. It belongs to the acetal family of plastics and offers excellent wear resistance, low friction, and good machinability.

Chemical Composition and Structure
The unique properties of Delrin stem from its molecular structure. When we look at its composition, Delrin consists of alternating methylene groups (-CH2-) connected by oxygen atoms, forming a homopolymer1 chain. This structure gives Delrin its characteristic strength and stability.
Basic Chemical Properties
- Molecular Formula: (-CH2O-)n
- Density: 1.41-1.43 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 175°C (347°F)
- Glass Transition Temperature: -60°C (-76°F)
Key Material Properties
At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with Delrin for various precision parts. Here are the main properties that make it stand out:
Mechanical Properties
- High tensile strength
- Superior fatigue resistance
- Excellent creep resistance
- Good impact resistance
- Low friction coefficient
Physical Properties
- Outstanding dimensional stability
- Low moisture absorption
- Good electrical insulation
- Chemical resistance to many solvents
- Natural lubricity
Common Grades and Classifications
Delrin comes in various grades, each optimized for specific applications:
| Grade Type | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Grades | Basic mechanical properties | General purpose parts |
| High Performance | Enhanced strength and stiffness | Precision gears, bearings |
| UV Stabilized | Better weather resistance | Outdoor applications |
| Food Grade | FDA compliant | Food processing equipment |
Manufacturing Methods
In my experience at PTSMAKE, we primarily process Delrin through:
CNC Machining
- Excellent machinability
- Tight tolerances achievable
- Complex geometries possible
- Smooth surface finish
Injection Molding
- Good flow characteristics
- Minimal shrinkage
- Consistent part quality
- High volume production capability
Applications Across Industries
Delrin finds extensive use in various industries:
Automotive
- Fuel system components
- Interior mechanisms
- Belt tensioners
- Door lock systems
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphone components
- Laptop hinges
- Camera mechanisms
- Audio equipment parts
Industrial Equipment
- Conveyor components
- Pump parts
- Valve bodies
- Precision gears
Medical Devices
- Surgical instruments
- Drug delivery devices
- Dental applications
- Laboratory equipment
Performance Comparison
Let’s compare Delrin with other common engineering plastics:
| Property | Delrin | Nylon | PEEK | PET |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | High | Medium | Very High | Medium |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High | Low |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Fair | Excellent | Good |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Fair |
Design Considerations
When designing parts with Delrin, consider these factors:
Material Selection
- Operating temperature requirements
- Chemical exposure conditions
- Load-bearing requirements
- Cost constraints
Manufacturing Guidelines
- Wall thickness uniformity
- Draft angles for molded parts
- Gate locations
- Cooling considerations
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully manufactured countless precision components using Delrin. The material’s versatility and reliability make it an excellent choice for many engineering applications. Our experience with both CNC machining and injection molding of Delrin allows us to optimize part design and manufacturing processes for optimal performance.
Why Is Delrin So Expensive?
The rising cost of Delrin has become a significant concern for manufacturers and engineers. I’ve noticed many clients struggling with budget constraints when sourcing this material, especially when prices keep climbing year after year. The situation becomes even more challenging when projects require large quantities of Delrin parts.
Delrin’s high price is primarily due to its complex manufacturing process, superior mechanical properties, and the increasing demand from various industries. The material requires specialized production facilities, strict quality control, and premium raw materials, all contributing to its elevated cost structure.

Raw Material Production Complexity
Advanced Polymerization Process
The production of Delrin, or polyoxymethylene (POM), involves a sophisticated polymerization2 process. This process requires precise control of temperature, pressure, and chemical conditions. At PTSMAKE, we’ve observed that the complexity of this process significantly impacts the final material cost.
Quality Control Requirements
The manufacturing of Delrin demands rigorous quality control measures:
| Quality Parameter | Control Requirement | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | Strict monitoring | High |
| Crystallinity | Precise control | Medium |
| Thermal Stability | Continuous testing | High |
| Chemical Purity | Advanced filtration | Very High |
Market Dynamics
Supply Chain Factors
The global supply chain for Delrin raw materials faces several challenges:
- Limited number of qualified manufacturers
- Transportation costs for specialized handling
- Storage requirements for maintaining material properties
- Inventory management complexities
Industry Demand Patterns
Different sectors contribute to the high demand for Delrin:
| Industry | Usage Volume | Price Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Very High | Medium |
| Electronics | High | High |
| Medical | Medium | Low |
| Aerospace | Low | Very Low |
Technical Advantages That Justify the Cost
Superior Mechanical Properties
Delrin’s exceptional characteristics make it worth the investment:
- High tensile strength and stiffness
- Excellent fatigue resistance
- Low friction coefficient
- Outstanding dimensional stability
Long-term Cost Benefits
While initial material costs are high, Delrin often provides better value over time:
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Extended component lifespan
- Lower replacement frequency
- Minimal lubrication needs
Processing Requirements
Specialized Equipment Needs
Manufacturing Delrin parts requires specific machinery and tooling:
- Temperature-controlled processing equipment
- Wear-resistant tooling
- Precise cooling systems
- Advanced quality control instruments
Technical Expertise
The processing of Delrin demands skilled operators and engineers who understand:
- Material behavior during processing
- Optimal processing parameters
- Quality control procedures
- Troubleshooting techniques
Cost Optimization Strategies
Design Optimization
At PTSMAKE, we help clients optimize their designs to reduce material usage while maintaining performance:
- Wall thickness optimization
- Strategic placement of ribs and supports
- Part consolidation opportunities
- Material selection alternatives where appropriate
Production Efficiency
We implement various strategies to manage costs:
- Batch size optimization
- Process automation
- Scrap reduction
- Efficient tooling design
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability Impact
Environmental factors affecting Delrin’s cost include:
- Energy-intensive production processes
- Environmental compliance requirements
- Recycling challenges
- Waste management costs
Regulatory Compliance
Meeting environmental regulations adds to the cost:
- Emissions control equipment
- Waste treatment systems
- Documentation requirements
- Certification processes
Future Price Trends
Market Outlook
Several factors suggest continued price pressure:
- Growing demand from emerging industries
- Raw material availability
- Energy cost fluctuations
- Technology advancement requirements
Innovation Impact
Ongoing research and development may affect future pricing:
- New production methods
- Alternative materials development
- Process efficiency improvements
- Quality enhancement techniques
This comprehensive analysis shows why Delrin commands premium pricing in the market. While the cost may seem high initially, the material’s superior properties and long-term benefits often justify the investment for critical applications. At PTSMAKE, we work closely with our clients to optimize designs and processes, ensuring they get the best value from their Delrin components while maintaining the highest quality standards.
Is Delrin The Same As Teflon?
When working with engineering plastics, I often encounter confusion from clients about Delrin and Teflon. Many believe these materials are interchangeable, leading to costly design mistakes and project delays. The misunderstanding becomes even more problematic when critical components fail due to incorrect material selection.
Delrin and Teflon are distinctly different engineering plastics. While Delrin (POM) is a thermoplastic known for its high strength and stiffness, Teflon (PTFE) is renowned for its low friction and non-stick properties. Each material serves unique purposes in engineering applications.
Physical Properties and Chemical Composition
The fundamental differences between these materials start at the molecular level. Delrin, also known as Polyoxymethylene (POM), features a highly crystalline structure that gives it exceptional mechanical properties. In contrast, Teflon’s polytetrafluoroethylene3 structure creates its unique non-stick characteristics.
Material Structure Comparison
| Property | Delrin (POM) | Teflon (PTFE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | (-CH2O-)n | (-CF2-CF2-)n |
| Crystallinity | 75-85% | 92-98% |
| Density (g/cm³) | 1.41-1.43 | 2.13-2.20 |
| Melting Point (°C) | 175 | 327 |
Performance Characteristics
At PTSMAKE, I’ve worked with both materials extensively in various manufacturing projects. Here’s what makes each unique:
Mechanical Properties
Delrin Strengths
- High tensile strength (63-70 MPa)
- Excellent fatigue resistance
- Superior dimensional stability
- Good wear resistance
- High stiffness
Teflon Advantages
- Extremely low friction coefficient (0.1)
- Outstanding chemical resistance
- Excellent thermal stability
- Non-stick properties
- Self-lubricating
Application Differences
Based on my manufacturing experience, these materials serve different purposes:
Delrin Best Uses
- Precision mechanical parts
- Gears and bearings
- Automotive components
- Consumer electronics
- Medical devices
Teflon Optimal Applications
- Non-stick coatings
- Chemical processing equipment
- Electrical insulation
- Bearings and seals
- Medical implants
Cost and Processing Considerations
The manufacturing process significantly impacts material selection:
Processing Methods
| Manufacturing Process | Delrin | Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Excellent | Limited |
| Machining | Good | Excellent |
| Compression Molding | Not Common | Common |
| Extrusion | Good | Excellent |
Temperature and Environmental Factors
Understanding environmental limitations is crucial:
Temperature Performance
| Temperature Range | Delrin | Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Continuous Use (°C) | 82-105 | 260 |
| Minimum Service Temperature (°C) | -40 | -200 |
| Heat Deflection Temperature (°C) | 115 | 55 |
Industry-Specific Considerations
In my experience at PTSMAKE, material selection often depends on industry requirements:
Automotive Industry
- Delrin: Fuel system components, window systems
- Teflon: Engine seals, brake system components
Medical Industry
- Delrin: Surgical instruments, dental applications
- Teflon: Implants, pharmaceutical processing equipment
Electronics Industry
- Delrin: Connectors, spring elements
- Teflon: Cable insulation, printed circuit boards
Maintenance and Longevity
The materials differ significantly in maintenance requirements:
Long-term Performance
| Aspect | Delrin | Teflon |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| UV Resistance | Fair | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | None |
Through my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that proper material selection significantly impacts project success. While both Delrin and Teflon are excellent engineering plastics, they serve different purposes and shouldn’t be considered interchangeable. Understanding these differences helps ensure optimal performance and longevity in your applications.
I always recommend conducting thorough material testing and consulting with experts before making final material selections. At PTSMAKE, we provide comprehensive material selection guidance and manufacturing solutions to help you make the best choice for your specific application needs.
Does DuPont Still Own Delrin?
When manufacturing engineers and procurement managers search for Delrin suppliers, they often face uncertainty about its current ownership. The market confusion stems from DuPont’s various corporate restructurings and spin-offs over the years, leaving many wondering about the authentic source of this critical engineering material.
No, DuPont no longer owns Delrin. Since 2019, DuPont’s former Performance Materials division, including Delrin, has been operated by Celanese Corporation following a $11 billion acquisition deal. Celanese now manufactures and distributes Delrin acetal homopolymer resins globally.

The Journey of Delrin Ownership
The history of Delrin ownership reflects the dynamic nature of the chemical industry. As someone deeply involved in precision manufacturing, I’ve witnessed the evolution of this material’s ownership firsthand. The timeline of ownership changes helps us understand the current situation better:
Historical Timeline
| Year | Major Event | Impact on Delrin |
|---|---|---|
| 1956 | Initial Development | DuPont introduces Delrin |
| 2015 | DowDuPont Merger | Combined chemical operations |
| 2019 | DuPont Spin-off | Performance Materials division separated |
| 2022 | Celanese Acquisition | Complete transfer of ownership |
Impact on Manufacturing Industry
The transfer of Delrin ownership to Celanese has brought several changes to the manufacturing landscape. The material’s polymerization4 process remains consistent, but there have been subtle shifts in:
Supply Chain Dynamics
- Distribution networks have been reorganized
- New quality control protocols implemented
- Updated certification processes established
- Modified pricing structures introduced
Product Development and Innovation
At PTSMAKE, we’ve adapted to these changes while maintaining our high-quality injection molding services. The transition has actually opened up new opportunities for innovation in Delrin applications:
- Enhanced material grades for specific industries
- Improved processing guidelines
- New technical support systems
- Expanded application possibilities
Market Response and Quality Assurance
The market’s response to the ownership change has been largely positive. As a manufacturer working extensively with Delrin, I can confirm that Celanese has maintained the material’s renowned qualities:
Quality Parameters
- Mechanical properties remain consistent
- Chemical resistance standards upheld
- Thermal stability specifications maintained
- Processing characteristics preserved
Future Outlook and Industry Implications
The future of Delrin under Celanese ownership looks promising. Based on current market trends and our experience at PTSMAKE, we anticipate:
Short-term Developments
- Increased material availability
- More specialized grades for specific applications
- Enhanced technical support
- Competitive pricing structures
Long-term Industry Impact
- Greater innovation in material properties
- Expanded global distribution networks
- More sustainable manufacturing processes
- Improved end-user support systems
Practical Considerations for Manufacturers
For manufacturers and engineers working with Delrin, the ownership change requires attention to several key aspects:
Material Specification Updates
- Review material certifications
- Update supplier documentation
- Verify quality control processes
- Confirm compliance requirements
Supply Chain Adjustments
- Evaluate new distribution channels
- Assess lead time changes
- Review pricing structures
- Update supplier agreements
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully navigated these changes while maintaining our high standards in precision manufacturing. Our experience with both DuPont and Celanese Delrin has enabled us to provide consistent quality in our injection molding services.
Technical Support and Resources
The transition has brought changes to technical support structures. Manufacturers should be aware of:
Available Resources
- Updated material datasheets
- New processing guidelines
- Technical consultation services
- Quality assurance documentation
Industry Compliance
While ownership has changed, Delrin’s core specifications and industry certifications remain intact. This includes:
- FDA compliance for food-grade applications
- ISO certifications
- Industry-specific standards
- Environmental regulations
The ownership transition from DuPont to Celanese represents a significant shift in the industry, but one that has been managed effectively to maintain product quality and reliability. As a manufacturing professional, I’ve observed that the material’s fundamental characteristics and performance capabilities remain unchanged, ensuring continuity for manufacturers and end-users alike.
What Plastic Is Similar To Delrin?
Finding the right plastic material for your project can be overwhelming. With countless options available, identifying alternatives to Delrin that offer similar properties while potentially being more cost-effective or better suited for specific applications can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack.
Several plastics share properties similar to Delrin, with POM-C (Polyoxymethylene Copolymer) being the closest alternative. It offers comparable strength, wear resistance, and machinability, making it an excellent substitute in many engineering applications.
Understanding POM-C as a Delrin Alternative
POM-C stands out as the primary alternative to Delrin due to its nearly identical molecular structure. At PTSMAKE, I’ve worked extensively with both materials, and their similarities in terms of mechanical properties are remarkable. The main difference lies in their crystallization5 process, which affects their dimensional stability slightly.
Key Properties Comparison
| Property | Delrin (POM-H) | POM-C |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 70 MPa | 65 MPa |
| Hardness (Rockwell M) | 94 | 90 |
| Melting Point | 175°C | 165°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Other Notable Alternatives
Nylon (PA6 and PA66)
Nylon serves as another viable alternative to Delrin, particularly in applications where impact resistance is crucial. While working with various clients at PTSMAKE, I’ve noticed that Nylon often outperforms Delrin in terms of:
- Impact resistance
- Flexibility
- Cost-effectiveness
- Wear resistance in wet conditions
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
PEEK represents a high-performance alternative, albeit at a higher price point. It excels in:
- Higher temperature resistance
- Superior chemical resistance
- Better wear properties
- Enhanced strength characteristics
Application-Specific Alternatives
Automotive Applications
For automotive components, I’ve found that these materials often serve as excellent Delrin alternatives:
- Glass-filled POM-C
- Impact-modified PBT
- Reinforced PA66
Medical Applications
In medical device manufacturing, these alternatives have proven successful:
- Medical-grade PEEK
- USP Class VI POM-C
- Medical-grade PPSU
Cost Considerations
| Material | Relative Cost (1-10) | Performance Rating (1-10) |
|---|---|---|
| Delrin | 7 | 8 |
| POM-C | 6 | 8 |
| Nylon | 5 | 7 |
| PEEK | 10 | 9 |
Manufacturing Considerations
When selecting a Delrin alternative, manufacturing processes play a crucial role. At PTSMAKE, we consider several factors:
Machining Properties
- Tool wear
- Surface finish requirements
- Dimensional stability
- Heat generation during processing
Injection Molding Characteristics
- Mold shrinkage
- Gate location options
- Cooling requirements
- Cycle time optimization
Environmental Impact
Recyclability Comparison
| Material | Recyclability | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Delrin | Moderate | Medium |
| POM-C | Good | Medium |
| Nylon | Excellent | Low |
| PEEK | Limited | High |
Performance in Specific Environments
Understanding environmental factors is crucial when selecting alternatives:
High Temperature Applications
- PEEK excels in high-temperature environments
- PPS offers good temperature resistance
- Modified POM-C maintains stability
Chemical Exposure
- POM-C shows excellent chemical resistance
- PEEK provides superior chemical resistance
- Modified Nylon offers good chemical resistance
Quality Control Considerations
When working with Delrin alternatives, proper quality control measures are essential:
- Dimensional stability monitoring
- Moisture content testing
- Mechanical property verification
- Visual inspection protocols
Decision-Making Framework
To help select the right Delrin alternative, consider:
- Application requirements
- Environmental conditions
- Cost constraints
- Manufacturing processes
- Quality requirements
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that successful material selection often depends on carefully balancing these factors rather than focusing solely on material properties. We maintain comprehensive material databases and testing capabilities to help clients make informed decisions about Delrin alternatives.
By understanding these alternatives and their specific characteristics, you can make an informed decision that best suits your application requirements while potentially reducing costs or improving performance. Each alternative offers unique advantages, and the key lies in matching these benefits to your specific needs.
Does Delrin Break Easily?
Are you concerned about the durability of Delrin for your critical engineering applications? Many designers and engineers face sleepless nights worrying about material failure, especially when their projects demand both strength and precision.
Delrin doesn’t break easily under normal conditions. It offers exceptional mechanical strength, fatigue resistance, and dimensional stability. With a tensile strength ranging from 8,000 to 10,000 PSI, Delrin is one of the most durable engineering plastics available for precision parts.

Understanding Delrin’s Break Resistance
At PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that Delrin’s break resistance is directly related to its unique molecular structure. The material exhibits homopolymer crystallization6, which provides superior mechanical properties. This crystalline structure creates a robust framework that resists breaking under various conditions.
Factors Affecting Delrin’s Break Resistance
Several key factors influence how well Delrin resists breaking:
- Temperature Exposure
- Chemical Environment
- Load Type and Duration
- Manufacturing Quality
- Design Considerations
Comparative Strength Analysis
Let’s examine how Delrin compares to other common engineering plastics:
| Material | Tensile Strength (PSI) | Impact Resistance (ft-lb/in) | Temperature Resistance (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delrin | 8,000-10,000 | 1.0-2.0 | -40 to 180 |
| Nylon 6 | 7,000-8,000 | 0.8-1.5 | -40 to 170 |
| PEEK | 14,000-16,000 | 1.6-3.0 | -40 to 480 |
| POM-C | 7,500-9,000 | 0.9-1.8 | -40 to 160 |
Breaking Mechanisms and Prevention
Impact Resistance
Delrin demonstrates excellent impact resistance due to its high crystallinity. At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented Delrin in various high-impact applications, from automotive components to industrial machinery parts.
Fatigue Resistance
One of Delrin’s standout features is its exceptional fatigue resistance. The material can withstand repeated stress cycles without significant degradation, making it ideal for:
- Gear mechanisms
- Bearing components
- Moving parts
- High-cycle applications
Chemical Resistance
The material’s resistance to chemicals plays a crucial role in preventing degradation and subsequent breaking. Delrin maintains its structural integrity when exposed to:
- Most solvents
- Neutral chemicals
- Weak acids
- Automotive fluids
Design Considerations for Break Prevention
Proper Wall Thickness
To optimize break resistance, consider these wall thickness guidelines:
- Minimum wall thickness: 0.040 inches
- Recommended thickness: 0.060-0.120 inches
- Maximum thickness: 0.250 inches
Stress Distribution
Even stress distribution is crucial for preventing breaks. Implementation of proper design features includes:
- Rounded corners
- Gradual transitions
- Reinforcement ribs
- Uniform wall thickness
Manufacturing Impact on Break Resistance
The manufacturing process significantly influences Delrin’s break resistance. At PTSMAKE, we employ:
- Precise temperature control during molding
- Optimal cooling rates
- Proper gate locations
- Quality material handling procedures
Quality Control Measures
To ensure maximum break resistance, we implement:
- Material certification checks
- In-process monitoring
- Post-production testing
- Dimensional verification
Real-World Applications
Delrin’s break resistance makes it ideal for:
Industrial Applications
- Conveyor components
- Precision bushings
- Industrial fasteners
- Machine parts
Consumer Products
- High-end appliance parts
- Sports equipment components
- Electronic device housings
- Automotive interior components
Environmental Factors
Understanding environmental influences helps predict and prevent breaking:
Temperature Effects
- Optimal performance range: 32°F to 180°F
- Reduced strength at elevated temperatures
- Increased brittleness at low temperatures
Moisture Impact
- Limited moisture absorption
- Stable dimensional properties
- Consistent mechanical performance
Long-Term Performance
For sustained break resistance:
- Regular maintenance inspection
- Proper loading conditions
- Environmental control
- Periodic part replacement when needed
Professional Recommendations
As a manufacturing professional, I recommend:
- Thorough material selection analysis
- Comprehensive design review
- Proper manufacturing process control
- Regular quality assurance testing
Through these various aspects, it’s clear that Delrin’s break resistance is exceptional when properly designed, manufactured, and applied. At PTSMAKE, we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with this versatile material, ensuring our clients receive components that meet or exceed their durability requirements.
What Material Is Equivalent To Delrin?
Finding alternative materials to Delrin can be challenging when you need specific mechanical properties for your projects. I’ve seen many engineers struggle to identify suitable replacements, often leading to project delays and increased costs due to limited material options.
The closest equivalents to Delrin (POM) are Nylon (PA), PEEK, PTFE, and UHMW-PE. Each material offers similar mechanical properties but with varying strengths in different applications. The best choice depends on specific requirements like chemical resistance, temperature range, and cost considerations.
Understanding Delrin and Its Properties
Before exploring alternatives, it’s essential to understand what makes Delrin unique. Delrin, also known as acetal homopolymer, is a high-performance engineering plastic known for its excellent mechanical properties. The material’s crystalline structure7 provides outstanding dimensional stability and wear resistance.
Key Properties of Delrin:
- High tensile strength and stiffness
- Excellent fatigue resistance
- Low friction coefficient
- Good dimensional stability
- Chemical resistance
- Easy to machine
Comparable Materials and Their Characteristics
Nylon (PA)
Nylon serves as one of the most common alternatives to Delrin. At PTSMAKE, we frequently recommend Nylon for various applications due to its versatility.
Key advantages of Nylon include:
- Better impact resistance than Delrin
- Higher heat resistance
- More cost-effective
- Superior wear properties
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
PEEK represents a high-end alternative with exceptional properties:
| Property | PEEK vs Delrin |
|---|---|
| Temperature Resistance | Superior (up to 260°C vs 180°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Better |
| Cost | Significantly higher |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent |
| Machining Difficulty | More challenging |
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
PTFE offers unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications:
- Lowest coefficient of friction
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Wide temperature range
- FDA compliant
UHMW-PE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene)
This material provides an economical alternative with specific advantages:
| Property | UHMW-PE Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Impact Strength | Excellent |
| Wear Resistance | Very Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Good |
| Cost | Lower than Delrin |
| Weight | Lighter |
Application-Specific Comparisons
Automotive Applications
In automotive components, where precision and durability are crucial, different materials show varying performance:
- Delrin: Ideal for fuel system components
- Nylon: Better for under-hood applications
- PEEK: Perfect for high-temperature environments
- PTFE: Excellent for bearing applications
- UHMW-PE: Suitable for wear plates and guides
Medical Applications
For medical devices, material selection becomes even more critical:
- Delrin: Commonly used in surgical instruments
- PEEK: Preferred for implantable devices
- PTFE: Ideal for non-stick applications
- Nylon: Used in disposable medical tools
Industrial Equipment
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, industrial applications require careful material selection:
| Application | Recommended Material | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Gears | Delrin/Nylon | Excellent wear resistance |
| Bearings | PTFE/PEEK | Low friction |
| Conveyor Components | UHMW-PE | Cost-effective wear resistance |
| Precision Parts | Delrin/PEEK | Dimensional stability |
Cost Considerations and Value Analysis
Understanding the cost implications helps in making informed decisions:
- PEEK: 5-7x more expensive than Delrin
- PTFE: 2-3x more expensive than Delrin
- Nylon: Similar or slightly less expensive
- UHMW-PE: Generally less expensive
Environmental Factors and Sustainability
Different materials have varying environmental impacts:
- Recyclability potential
- Energy consumption during production
- End-of-life disposal considerations
- Carbon footprint
Making the Right Choice
To select the right Delrin alternative, consider:
- Operating temperature requirements
- Chemical exposure conditions
- Mechanical load requirements
- Cost constraints
- Regulatory compliance needs
At PTSMAKE, we guide our clients through this selection process by analyzing these factors comprehensively. This ensures optimal material selection for each specific application while maintaining cost-effectiveness and performance requirements.
Machining and Processing Considerations
Different materials require different machining approaches:
- Tool selection
- Cutting speeds and feeds
- Cooling requirements
- Post-processing needs
Through our experience in precision manufacturing, we’ve developed specific protocols for each material to ensure optimal results.
What Is The Cost Of Delrin Material?
When sourcing Delrin material for manufacturing projects, determining the exact cost can be challenging. Price fluctuations, market conditions, and varying supplier quotes often leave engineers and procurement managers confused and frustrated.
Delrin material typically costs between $3 to $8 per pound for standard grades, with specialty grades ranging from $10 to $15 per pound. The final price depends on grade quality, order quantity, market conditions, and supplier relationships.
Understanding Delrin Material Cost Components
The cost of Delrin material is influenced by several key factors that create its molecular composition8. Let me break down these components to help you make informed purchasing decisions.
Raw Material Base Price
The foundation of Delrin pricing starts with the base material cost. At PTSMAKE, we source high-quality Delrin from certified suppliers to ensure consistent quality. The base price typically includes:
- Resin production costs
- Manufacturing overhead
- Quality control processes
- Initial processing fees
Grade Quality Impact on Price
Different grades of Delrin command different prices based on their properties:
| Grade Type | Price Range ($/lb) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Grade | 3-8 | General purpose parts |
| Medical Grade | 12-15 | Medical devices |
| High-Performance | 10-13 | Precision components |
| UV-Stabilized | 8-11 | Outdoor applications |
Volume-Based Pricing Structure
Order quantity significantly affects the per-unit cost of Delrin material:
Bulk Purchase Benefits
- Large orders (1000+ lbs): 15-20% discount
- Medium orders (500-999 lbs): 10-15% discount
- Small orders (100-499 lbs): 5-10% discount
Market Factors Affecting Delrin Costs
Supply Chain Influences
The global supply chain impacts Delrin pricing through:
- Transportation costs
- Import/export regulations
- Regional availability
- Market demand fluctuations
Economic Factors
Several economic conditions affect pricing:
- Oil prices (raw material source)
- Currency exchange rates
- Manufacturing capacity
- Global economic conditions
Additional Cost Considerations
Processing Requirements
The final cost often includes:
- Material preparation
- Special handling
- Custom packaging
- Quality certification costs
Quality Certification Expenses
| Certification Type | Additional Cost (%) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ISO compliance | 5-8 | Quality assurance |
| Medical grade | 10-15 | Healthcare applications |
| FDA approval | 12-18 | Food contact |
| Custom testing | 8-12 | Specific requirements |
Cost Optimization Strategies
At PTSMAKE, we help our clients optimize their Delrin material costs through:
Strategic Purchasing
- Long-term supply agreements
- Volume consolidation
- Market timing optimization
- Supplier relationship management
Material Selection Optimization
- Application-specific grade selection
- Alternative material evaluation
- Design optimization support
- Waste reduction strategies
Regional Price Variations
Different regions have varying price structures:
| Region | Price Range ($/lb) | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 4-9 | Local production |
| Europe | 5-10 | Import costs |
| Asia | 3-8 | Manufacturing proximity |
| Other regions | 6-12 | Transportation costs |
Future Price Trends
Based on market analysis and industry expertise, we anticipate:
- Steady price increases of 2-3% annually
- Continued impact of raw material costs
- Growing demand in emerging markets
- Technology advancements affecting production costs
Value-Added Services Impact
Additional services can affect the final cost:
- Custom cutting and sizing
- Special packaging requirements
- Technical support services
- Quality documentation
Cost-Saving Recommendations
To optimize your Delrin material costs:
- Plan purchases strategically
- Consider bulk ordering
- Evaluate grade requirements carefully
- Maintain strong supplier relationships
- Monitor market conditions
Through PTSMAKE’s expertise in material sourcing and manufacturing, we help clients navigate these cost factors effectively. Our global supply network and industry relationships enable us to secure competitive pricing while maintaining high-quality standards.
What Is Another Name For Delrin?
Finding the right plastic material for your project can be confusing when the same material goes by different names. Many engineers and designers struggle with this terminology challenge, which can lead to costly mistakes in material selection and procurement.
Delrin is the DuPont trade name for Polyoxymethylene (POM), also commonly known as acetal. This engineering thermoplastic offers exceptional mechanical properties, dimensional stability, and wear resistance, making it ideal for precision parts.

Understanding the Different Names of Delrin
In my experience working with various manufacturing projects, I’ve noticed that material naming conventions often cause confusion. Let me clarify the different names associated with Delrin:
Common Trade Names
The material we know as Delrin is marketed under various trade names by different manufacturers:
| Manufacturer | Trade Name |
|---|---|
| DuPont | Delrin |
| Ticona | Celcon |
| BASF | Ultraform |
| KEP | Kepital |
| Polyplastics | Duracon |
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyacetal homopolymer9 forms the basis of Delrin, giving it unique properties that set it apart from other engineering plastics. At PTSMAKE, we often recommend this material for its exceptional performance in demanding applications.
Key Properties of Delrin/POM
Mechanical Properties
- High tensile strength
- Excellent fatigue resistance
- Low friction coefficient
- Superior wear resistance
- Good dimensional stability
Chemical Properties
The material demonstrates remarkable resistance to:
- Most solvents
- Chemical compounds
- Fuel and hydrocarbons
- Hot water exposure
Applications Across Industries
Automotive Components
- Fuel system components
- Interior trim parts
- Gears and bearings
- Door lock systems
Consumer Electronics
- Mobile phone components
- Laptop hinges
- Camera parts
- Electronic housings
Industrial Equipment
- Conveyor components
- Pump parts
- Valve bodies
- Industrial gears
Manufacturing Considerations
Machining Guidelines
When machining Delrin at our PTSMAKE facilities, we follow specific guidelines:
- Use sharp cutting tools
- Maintain moderate cutting speeds
- Provide adequate cooling
- Ensure proper chip evacuation
Injection Molding Parameters
Based on our extensive molding experience:
| Parameter | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 180-215°C |
| Mold Temperature | 80-120°C |
| Injection Pressure | 70-120 MPa |
| Drying Time | 2-4 hours |
Material Selection Criteria
Performance Requirements
- Load-bearing capacity needed
- Operating temperature range
- Chemical exposure conditions
- Wear resistance requirements
Cost Considerations
- Material cost per unit
- Processing costs
- Tool wear factors
- Production volume impact
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous quality control procedures:
Testing Methods
- Dimensional inspection
- Hardness testing
- Impact resistance evaluation
- Chemical resistance verification
Documentation Requirements
- Material certificates
- Process parameters
- Quality control reports
- Traceability records
Environmental Impact
Sustainability Aspects
- Recyclability potential
- Energy consumption in processing
- Waste reduction strategies
- Environmental compliance
Industry Standards and Compliance
Relevant Standards
- ISO 9001 certification
- ASTM testing methods
- RoHS compliance
- FDA approvals (where applicable)
Comparison with Alternative Materials
| Property | Delrin/POM | Nylon | PEEK |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Strength | High | Medium | Very High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Good | Good | Excellent |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Processing Problems
- Warpage control
- Dimensional stability
- Surface finish quality
- Gate location optimization
Material Storage
- Temperature control
- Humidity management
- Inventory rotation
- Contamination prevention
Through our experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve developed effective solutions for these common challenges, ensuring consistent quality in our manufacturing processes.
Which Plastic Is Also Called Teflon?
The confusion around plastic names can be overwhelming for engineers and manufacturers. With numerous trade names, chemical formulas, and industry terminology, it’s challenging to keep track of which plastic is which, especially when it comes to high-performance materials like Teflon.
Teflon is the trademarked brand name for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene. This versatile plastic is known for its non-stick properties, high heat resistance, and chemical inertness, making it invaluable in both industrial applications and consumer products.

The Chemical Composition of PTFE
PTFE’s unique properties stem from its molecular structure. The material consists of carbon and fluorine atoms forming a strong bond that creates a fluoropolymer10 structure. This composition gives PTFE its exceptional characteristics:
Molecular Structure Benefits
- Strong carbon-fluorine bonds
- Regular crystalline structure
- Low surface energy
- High molecular weight
Key Properties That Make PTFE Special
Temperature Resistance
PTFE can withstand temperatures from -200°C to +260°C without degrading. This remarkable temperature range makes it ideal for various applications:
| Temperature Range | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| -200°C to 0°C | Cryogenic equipment seals |
| 0°C to 150°C | Non-stick cookware |
| 150°C to 260°C | Industrial bearings |
Chemical Resistance
One of PTFE’s most valuable properties is its resistance to almost all chemicals. In my experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve seen PTFE perform exceptionally well in aggressive chemical environments where other plastics fail.
Industrial Applications of PTFE
Manufacturing Industry
- Bearings and bushings
- Seals and gaskets
- Conveyor belts
- Machine components
Chemical Processing
- Pipeline linings
- Valve components
- Pump parts
- Chemical storage containers
Medical and Food Industry Applications
The FDA has approved PTFE for food contact and medical applications due to its:
- Non-toxic nature
- Bio-compatibility
- Easy sterilization
- Chemical inertness
Comparing PTFE with Other High-Performance Plastics
Here’s how PTFE stacks up against other common engineering plastics:
| Property | PTFE | PEEK | POM (Delrin) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | 260°C | 250°C | 180°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good | Good |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Cost | High | Very High | Moderate |
Processing Methods for PTFE
Ram Extrusion
This process involves:
- Compressing PTFE powder
- Heating to sintering temperature
- Cooling under controlled conditions
- Final machining to specifications
Compression Molding
At PTSMAKE, we’ve optimized our compression molding process for PTFE components, ensuring:
- Uniform density
- Minimal voids
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Superior mechanical properties
Maintenance and Care of PTFE Components
To maximize the lifespan of PTFE parts:
- Avoid mechanical scratching
- Clean with appropriate solvents
- Store at moderate temperatures
- Prevent exposure to direct UV light
Environmental Considerations
While PTFE offers exceptional performance, it’s important to consider:
- Recycling challenges
- End-of-life disposal
- Environmental impact
- Sustainable alternatives
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement strict quality control procedures for PTFE products:
- Material certification
- Dimensional inspection
- Surface finish testing
- Performance validation
Cost Considerations and ROI
When evaluating PTFE for your application, consider:
- Initial material costs
- Processing expenses
- Maintenance requirements
- Lifetime value
- Replacement frequency
Future Developments in PTFE Technology
Current research focuses on:
- Modified PTFE grades
- Improved processing methods
- Enhanced mechanical properties
- Sustainable manufacturing
Common Misconceptions About PTFE
It’s important to address some common misunderstandings:
- PTFE is not just for cookware
- It’s more than a coating material
- High cost is offset by longevity
- Processing limitations can be overcome
Through our work at PTSMAKE, we’ve helped numerous clients select and implement PTFE solutions that perfectly match their requirements. The key is understanding both the material’s capabilities and limitations to make informed decisions about its application in specific scenarios.
How Does Delrin Perform In High-Temperature Environments?
Working with engineering plastics can be challenging, especially when dealing with high-temperature applications. Many manufacturers struggle to find materials that maintain their structural integrity and performance under elevated temperatures, leading to costly failures and production delays.
Delrin exhibits stable performance in high-temperature environments up to 180°F (82°C) for continuous use, maintaining its mechanical properties and dimensional stability. However, its performance gradually declines as temperatures approach its melting point of 347°F (175°C).
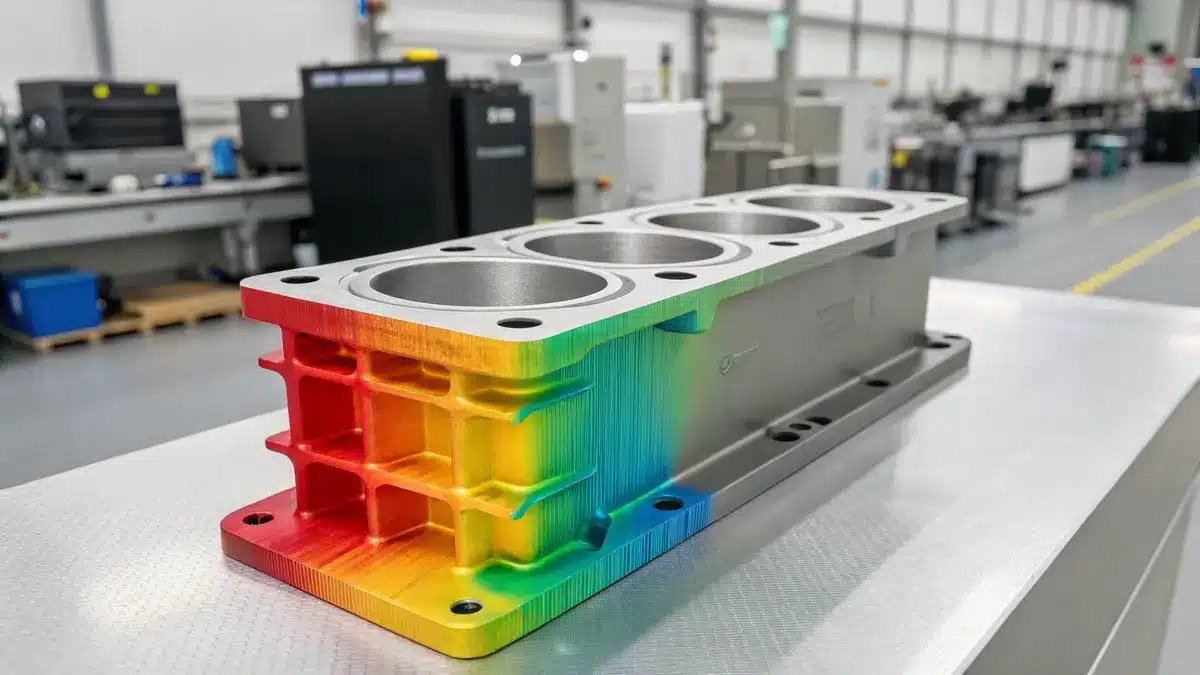

Temperature Resistance Characteristics
Delrin, also known as polyoxymethylene (POM), displays remarkable thermal properties that make it suitable for various high-temperature applications. I’ve observed that its crystalline structure provides excellent dimensional stability even as temperatures rise. The material’s behavior can be categorized into different temperature ranges:
Short-Term Temperature Exposure
During my work with clients in automotive and industrial sectors, I’ve found that Delrin can withstand short-term exposure to temperatures up to:
| Temperature Range | Duration | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 180-220°F (82-104°C) | 24-48 hours | Minimal property changes |
| 220-280°F (104-138°C) | 2-4 hours | Moderate softening |
| 280-347°F (138-175°C) | < 1 hour | Significant property degradation |
Mechanical Properties at Elevated Temperatures
The material’s crystallinity11 plays a crucial role in maintaining its mechanical properties under heat stress. Based on my testing experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve documented these key performance aspects:
Tensile Strength Retention
- At room temperature: 100% baseline strength
- At 150°F (65°C): 85-90% strength retention
- At 180°F (82°C): 70-75% strength retention
Dimensional Stability
Heat can affect Delrin’s dimensional accuracy, but proper design considerations can minimize this impact:
| Temperature Range | Linear Expansion Rate | Design Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 70-120°F (21-49°C) | 0.00022 inch/inch/°F | Standard tolerances acceptable |
| 120-180°F (49-82°C) | 0.00025 inch/inch/°F | Enhanced tolerances needed |
Applications in High-Temperature Environments
Through our manufacturing experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented Delrin in various high-temperature applications:
Automotive Components
- Engine compartment components
- Transmission parts
- Cooling system components
Industrial Equipment
- Hot water system components
- Heat exchanger parts
- Processing equipment components
Design Considerations for High-Temperature Use
To ensure optimal performance, consider these design factors:
Material Grade Selection
- Standard grades for moderate temperatures
- High-temperature grades for demanding applications
- Reinforced grades for enhanced stability
Thermal Management Strategies
Heat Dissipation
- Incorporate cooling fins when possible
- Allow for adequate airflow
- Consider thermal barriers
Stress Distribution
- Design for uniform heat distribution
- Avoid sharp corners that concentrate stress
- Include expansion joints where necessary
Performance Optimization Techniques
To maximize Delrin’s performance in high-temperature environments, I recommend:
Surface Treatment Options
- Annealing for improved stability
- Surface finishing for reduced friction
- Coating applications for additional protection
Assembly Considerations
- Use appropriate clearances for thermal expansion
- Select compatible fastening methods
- Consider thermal cycling effects
Material Limitations and Alternatives
While Delrin performs well in many high-temperature applications, it’s important to recognize its limitations:
Temperature Thresholds
| Condition | Maximum Temperature | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Use | 180°F (82°C) | Indefinite |
| Intermittent Use | 250°F (121°C) | < 24 hours |
| Peak Exposure | 347°F (175°C) | Minutes |
At PTSMAKE, we often recommend alternative materials when applications exceed these limits:
- PEEK for higher temperature requirements
- PPS for chemical resistance at elevated temperatures
- Modified POM grades for specific performance needs
Testing and Validation Procedures
To ensure reliable performance, we implement comprehensive testing:
Thermal Analysis Methods
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
- Heat Deflection Temperature Testing
Quality Assurance
- Dimensional stability monitoring
- Mechanical property verification
- Long-term performance testing
Through careful material selection and proper design implementation, Delrin can effectively serve in high-temperature environments within its specified limits. Understanding these performance characteristics enables successful application in demanding thermal conditions while maintaining the material’s beneficial properties.
What Are The Best Practices For Machining Delrin Parts?
Machining Delrin parts can be challenging due to their unique material properties. Many engineers struggle with issues like dimensional instability, tool wear, and surface finish problems. I’ve seen projects delayed and costs increase due to improper machining techniques, causing frustration for both manufacturers and clients.
The best practices for machining Delrin parts include using sharp cutting tools, maintaining appropriate speeds and feeds, ensuring proper cooling, and implementing specific design considerations. These practices help achieve optimal results while preventing common issues like material deformation and poor surface finish.
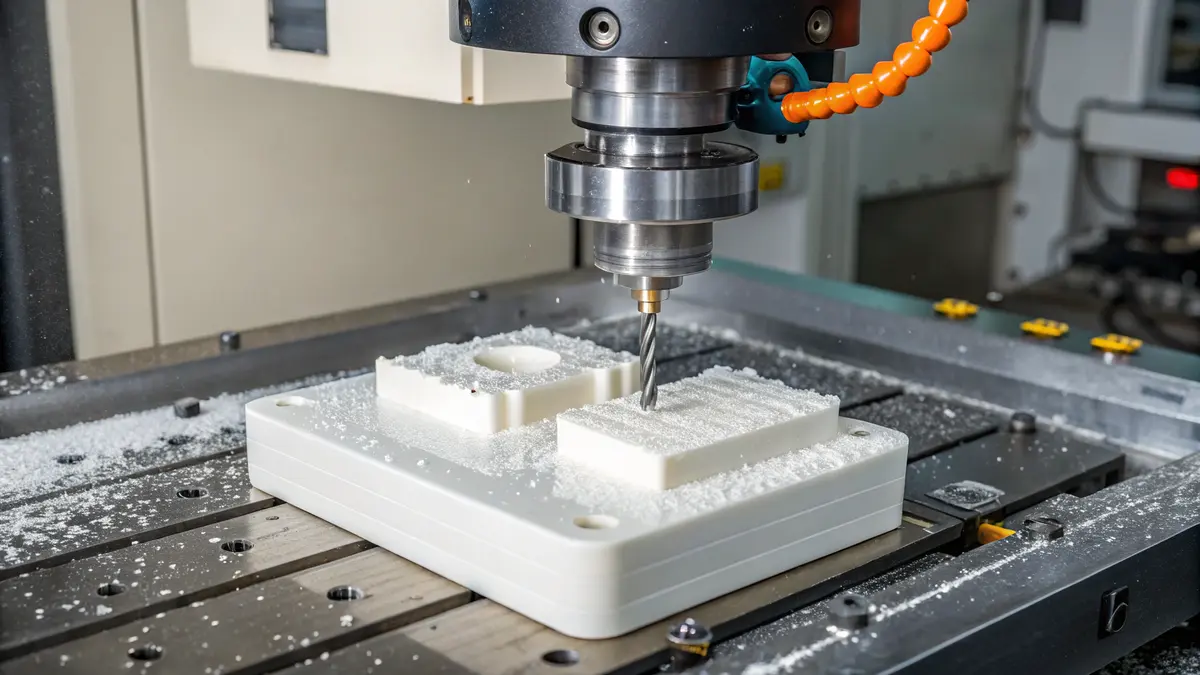

Understanding Delrin’s Material Properties
Delrin, also known as acetal homopolymer, exhibits unique characteristics that directly influence machining strategies. The material’s crystallinity12 affects its behavior during machining operations. I’ve found that understanding these properties is crucial for successful machining:
Key Material Characteristics
- Low friction coefficient
- High mechanical strength
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Good wear resistance
- Natural lubricity
Cutting Tool Selection and Preparation
The success of Delrin machining heavily depends on proper tool selection. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific guidelines for tool selection:
Recommended Tool Types
| Tool Type | Application | Recommended Geometry |
|---|---|---|
| End Mills | General milling | 2-4 flutes, 30° helix angle |
| Drills | Hole making | 118° point angle, polished flutes |
| Face Mills | Surface finishing | High positive rake angle |
| Reamers | Precision holes | Straight flute, 45° chamfer |
Optimal Cutting Parameters
Speed and Feed Rates
Proper cutting parameters are essential for achieving high-quality results:
| Operation | Surface Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (IPR) |
|---|---|---|
| Turning | 300-1000 | 0.004-0.012 |
| Milling | 400-1200 | 0.003-0.010 |
| Drilling | 200-400 | 0.005-0.015 |
Cooling and Temperature Control
Temperature management is crucial when machining Delrin. Here’s why:
- Prevents material softening
- Maintains dimensional accuracy
- Improves surface finish
- Extends tool life
Cooling Methods
- Flood coolant
- Compressed air
- Mist cooling systems
- Cryogenic cooling for specialized applications
Design Considerations for Machinability
Wall Thickness Requirements
I recommend following these guidelines for wall thickness:
- Minimum wall thickness: 0.040 inches
- Optimal wall thickness: 0.125 inches or greater
- Maximum thickness variation: 25% within same feature
Feature Design Guidelines
- Avoid sharp corners (use minimum 0.015" radius)
- Design self-supporting structures
- Consider shrinkage allowance
- Plan for proper fixturing points
Surface Finish Optimization
To achieve excellent surface finish:
Recommended Practices
- Use high-speed finishing passes
- Maintain sharp cutting edges
- Apply consistent cutting pressure
- Consider post-machining treatments
Quality Control Measures
Implementing proper quality control is essential:
Inspection Methods
- Dimensional verification
- Surface roughness testing
- Visual inspection for defects
- Material property validation
Common Machining Issues and Solutions
Problem-Solution Matrix
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Poor surface finish | Dull tools | Replace or sharpen tools |
| Dimensional inaccuracy | Thermal expansion | Proper cooling implementation |
| Tool wear | Incorrect speeds | Adjust cutting parameters |
| Chipping | Improper support | Improve workpiece fixturing |
Advanced Machining Techniques
At PTSMAKE, we employ several advanced techniques:
High-Speed Machining
- Reduced heat generation
- Better surface finish
- Increased productivity
- Enhanced dimensional accuracy
Specialized Fixturing
- Custom workholding solutions
- Multiple setup reduction
- Improved repeatability
- Enhanced part stability
Cost Optimization Strategies
To maintain cost-effectiveness:
- Optimize tool life
- Minimize material waste
- Reduce setup times
- Implement efficient processes
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable Practices
- Proper chip recycling
- Coolant management
- Energy-efficient machining
- Waste reduction strategies
Can Delrin Be Recycled Or Repurposed After Use?
The growing concern about plastic waste has left many engineers and manufacturers wondering about the recyclability of engineering plastics like Delrin. As landfills continue to fill up and environmental regulations tighten, finding sustainable solutions for used Delrin components has become a pressing challenge.
Yes, Delrin can be recycled and repurposed. Through mechanical recycling processes, used Delrin parts can be ground into pellets and reprocessed. However, the material’s properties may degrade after recycling, making it more suitable for less demanding applications.
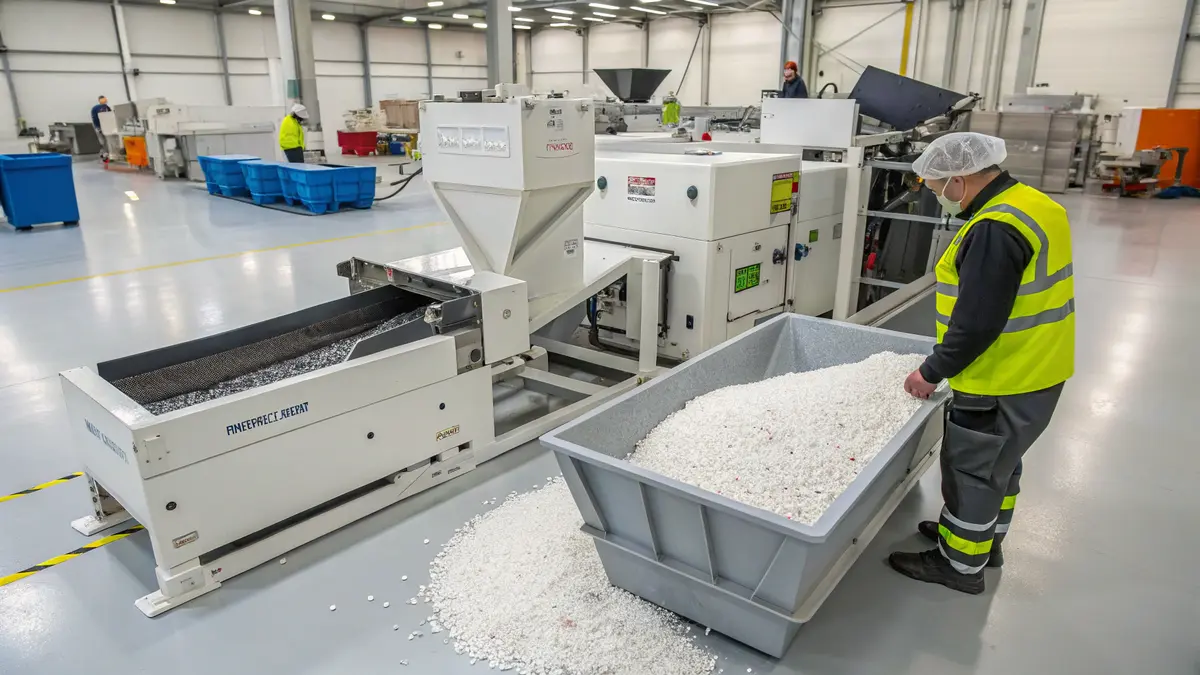

Understanding Delrin’s Recycling Potential
Chemical Composition and Recyclability
Delrin, also known as polyoxymethylene (POM), possesses unique chemical properties that affect its recyclability. The material undergoes a process called depolymerization13 during recycling, which can impact its mechanical properties. At PTSMAKE, we’ve observed that proper sorting and processing methods are crucial for successful recycling.
Types of Recycling Methods
There are several methods to recycle Delrin:
Mechanical Recycling
- Grinding into smaller particles
- Melting and reforming
- Blending with virgin material
Chemical Recycling
- Depolymerization
- Chemical breakdown
- Recovery of base materials
Best Practices for Delrin Recycling
Collection and Sorting
For effective recycling, proper collection and sorting are essential. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Collection | Gathering used Delrin parts | Ensure parts are clean and separated |
| Sorting | Separating Delrin from other plastics | Use proper identification methods |
| Cleaning | Removing contaminants | Avoid chemical contamination |
| Storage | Proper storage before processing | Maintain dry conditions |
Processing Guidelines
The recycling process must follow specific guidelines to maintain quality:
Temperature Control
- Optimal processing temperature
- Careful monitoring during melting
- Cooling rate management
Contamination Prevention
- Remove metal inserts
- Separate different grades
- Clean thoroughly
Applications for Recycled Delrin
Primary Uses
Recycled Delrin finds applications in various industries:
Automotive Components
- Non-critical parts
- Interior components
- Secondary assemblies
Industrial Applications
- Material handling equipment
- Low-stress components
- Protective covers
Quality Considerations
When using recycled Delrin, consider these factors:
| Property | Virgin Material | Recycled Material |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High | Slightly reduced |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Dimensional Stability | Very good | Acceptable |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good |
Environmental Impact and Benefits
Sustainability Advantages
Recycling Delrin offers several environmental benefits:
Reduced Landfill Waste
- Less plastic in landfills
- Lower environmental impact
- Conservation of resources
Energy Savings
- Reduced production energy
- Lower carbon footprint
- Resource efficiency
Economic Benefits
The economic advantages of recycling Delrin include:
Cost Reduction
- Lower material costs
- Reduced waste disposal fees
- Energy savings
Market Opportunities
- Growing demand for recycled materials
- New business opportunities
- Compliance with regulations
Future Trends and Innovations
Emerging Technologies
New technologies are improving Delrin recycling:
Advanced Sorting Systems
- Automated identification
- Improved separation
- Higher purity yields
Enhanced Processing Methods
- Better quality control
- Improved property retention
- More efficient systems
Industry Developments
The industry continues to evolve:
Circular Economy Integration
- Closed-loop systems
- Improved collection networks
- Better recycling infrastructure
Market Growth
- Increasing demand
- New applications
- Expanding opportunities
What Industries Commonly Use Delrin Components?
Finding the right material for manufacturing precision components can be challenging. Many engineers and product designers struggle to identify materials that offer the perfect balance of strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness for their specific applications.
Delrin components are widely used across multiple industries due to their exceptional mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability. From automotive and electronics to medical devices and consumer products, these versatile components serve crucial roles in various applications.
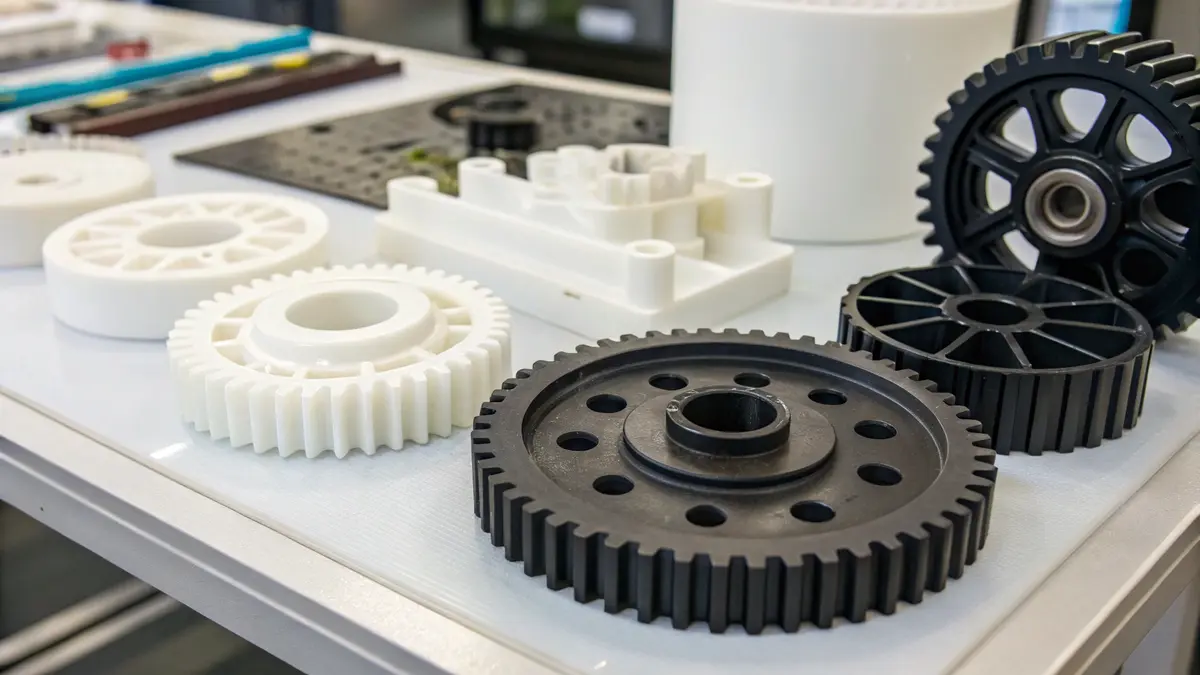

Automotive Industry Applications
The automotive sector heavily relies on Delrin components for both interior and exterior applications. I’ve observed that modern vehicles contain numerous Delrin parts, particularly in areas requiring high wear resistance and low friction properties.
Key Automotive Applications
- Gear systems and bearings
- Door locking mechanisms
- Fuel system components
- Window regulators
- Steering column components
The tribological properties of Delrin make it especially suitable for these applications, as it provides excellent wear resistance and low friction without requiring additional lubrication.
Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical industry, Delrin’s biocompatibility and sterilization capabilities make it an ideal choice for various medical devices and equipment.
Common Medical Applications
- Surgical instruments
- Drug delivery devices
- Diagnostic equipment components
- Medical device housings
- Laboratory equipment parts
Electronics and Consumer Electronics
The electronics industry benefits from Delrin’s electrical insulation properties and dimensional stability. At PTSMAKE, we frequently manufacture Delrin components for:
| Application Type | Key Benefits | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Connectors | High strength, electrical insulation | Cable management systems |
| Housing Components | Dimensional stability | Device enclosures |
| Switch Components | Wear resistance | Toggle mechanisms |
| Terminal Blocks | Chemical resistance | Power distribution |
Industrial Equipment and Machinery
The industrial sector represents one of the largest markets for Delrin components. Based on our manufacturing experience at PTSMAKE, these parts are crucial in:
Manufacturing Equipment
- Conveyor system components
- Assembly line mechanisms
- Packaging machinery parts
- Industrial automation components
Heavy Machinery
- Bearing housings
- Wear plates
- Guide rails
- Bushings
Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace industry demands materials that offer reliability under extreme conditions. Delrin components serve various purposes in:
- Control system components
- Interior cabin fittings
- Ground support equipment
- Satellite components
- Navigation system housings
Food Processing Equipment
Delrin’s FDA compliance makes it suitable for food processing equipment. Common applications include:
| Component Type | Application Area | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Conveyor Parts | Food Transport | Chemical Resistance |
| Mixing Equipment | Food Preparation | Wear Resistance |
| Packaging Systems | Product Handling | Low Friction |
| Storage Solutions | Food Storage | Durability |
Consumer Products and Appliances
The consumer goods sector extensively uses Delrin components in:
Home Appliances
- Washing machine components
- Dishwasher parts
- Coffee maker mechanisms
- Small appliance gears
Sports Equipment
- Bicycle components
- Fitness equipment parts
- Sporting good accessories
- Recreation equipment
Renewable Energy Sector
The growing renewable energy sector increasingly utilizes Delrin components in:
- Solar panel mounting systems
- Wind turbine components
- Energy storage systems
- Power distribution equipment
Having worked with numerous industries at PTSMAKE, I’ve noticed that the versatility of Delrin makes it indispensable across these diverse applications. Our manufacturing capabilities allow us to produce precise Delrin components that meet the specific requirements of each industry, whether it’s high-volume production for automotive applications or specialized components for medical devices.
The trend toward lightweight, durable materials continues to drive the adoption of Delrin components across industries. At PTSMAKE, we maintain strict quality control measures and leverage advanced manufacturing technologies to ensure our Delrin components meet or exceed industry standards.
For companies considering Delrin components for their applications, it’s crucial to partner with experienced manufacturers who understand the material’s properties and processing requirements. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of the final products while maintaining cost-effectiveness in production.
How Does Delrin Compare To Nylon In Wear Resistance?
Engineers often face challenges when selecting the right material for parts that require high wear resistance. I’ve seen many projects fail due to incorrect material choices, leading to premature wear, increased maintenance costs, and production downtime.
Delrin generally shows superior wear resistance compared to Nylon due to its higher mechanical strength, lower friction coefficient, and better dimensional stability. However, the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and cost considerations should guide the final material selection.

Understanding Wear Resistance Fundamentals
At PTSMAKE, we frequently work with both materials in our precision manufacturing processes. The tribological properties14 of these materials play a crucial role in their wear performance. Let me break down the key factors that influence wear resistance:
Surface Hardness
Delrin typically exhibits higher surface hardness than Nylon, which contributes to its better wear resistance. The harder surface helps prevent material loss during sliding contact and abrasive conditions.
Friction Coefficient
One of Delrin’s notable advantages is its naturally low coefficient of friction. This characteristic results in:
- Less heat generation during operation
- Smoother movement in sliding applications
- Reduced wear on mating surfaces
Moisture Absorption
Nylon’s higher moisture absorption rate can affect its dimensional stability and wear characteristics. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Property | Delrin | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Absorption (24h) | 0.25% | 1.5-3.0% |
| Dimensional Change | Minimal | Moderate |
| Performance Stability | High | Variable |
Performance Under Different Operating Conditions
Temperature Effects
Based on my experience with numerous manufacturing projects, temperature significantly impacts wear resistance:
Low Temperature (-40°C to 0°C)
- Delrin maintains better dimensional stability
- Nylon becomes more brittle
Room Temperature (20°C to 25°C)
- Both materials perform well
- Delrin shows slightly better wear characteristics
Elevated Temperature (60°C to 82°C)
- Delrin retains strength better
- Nylon’s wear resistance decreases more rapidly
Load Bearing Capacity
The wear resistance under different loads varies significantly:
| Load Condition | Delrin Performance | Nylon Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Light Load (<1 MPa) | Excellent | Very Good |
| Medium Load (1-5 MPa) | Very Good | Good |
| Heavy Load (>5 MPa) | Good | Fair |
Application-Specific Considerations
Speed and Motion Type
Different motion types affect wear patterns:
Rotary Motion
- Delrin excels in gears and bearings
- Better for high-speed applications
Linear Motion
- Both materials perform well
- Delrin preferred for precision movements
Intermittent Motion
- Both materials suitable
- Delrin shows better long-term wear resistance
Environmental Factors
The operating environment plays a crucial role:
Chemical Exposure
- Delrin: Better resistance to hydrocarbons
- Nylon: Superior resistance to certain chemicals
Moisture Presence
- Delrin: Maintains properties better
- Nylon: Properties can vary significantly
Cost-Performance Analysis
When considering wear resistance versus cost:
| Aspect | Delrin | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance Cost | Lower | Variable |
| Lifetime Value | Better | Good |
| Replacement Frequency | Less Frequent | More Frequent |
Real-World Applications
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented both materials in various applications:
Automotive Components
- Delrin: Ideal for precision bushings and gears
- Nylon: Suitable for less critical wear applications
Industrial Equipment
- Delrin: Preferred for high-precision automation components
- Nylon: Good for general-purpose applications
Consumer Products
- Delrin: Used in high-end products requiring durability
- Nylon: Suitable for cost-sensitive applications
Optimization Strategies
To maximize wear resistance:
Surface Treatment
- Consider surface finishing options
- Evaluate coating possibilities
Design Optimization
- Incorporate proper clearances
- Account for thermal expansion
Lubrication Considerations
- Determine if lubrication is needed
- Select compatible lubricants
Making the Final Decision
The choice between Delrin and Nylon should consider:
Operating Requirements
- Speed and load conditions
- Temperature range
- Environmental factors
Economic Factors
- Initial material cost
- Expected service life
- Maintenance requirements
Design Parameters
- Dimensional stability needs
- Precision requirements
- Assembly considerations
Through these considerations and my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that while both materials have their place, Delrin generally offers superior wear resistance in demanding applications. However, Nylon remains a cost-effective choice for less critical wear situations.
What Surface Finishes Work Best With Delrin?
Working with Delrin can be tricky when it comes to surface finishes. Many engineers struggle to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional properties. I’ve seen projects delayed and costs increase because of improper surface finish selections, leading to parts that don’t meet specifications or fail prematurely.
The best surface finishes for Delrin include bead blasting, polishing, and light texturing. These finishes enhance both aesthetics and functionality while maintaining the material’s inherent properties. Each finish serves specific purposes, from reducing friction to improving appearance.

Understanding Delrin’s Surface Properties
Delrin, also known as acetal homopolymer, has unique characteristics that influence its surface finish options. Its crystalline structure15 makes it naturally slippery and self-lubricating. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found that this property affects how different surface treatments interact with the material.
Natural Surface Characteristics
- Low friction coefficient
- Good wear resistance
- Moisture resistance
- Dimensional stability
Common Surface Finish Options
Bead Blasting
Bead blasting creates a uniform matte finish on Delrin surfaces. This process involves propelling fine glass beads at high pressure against the material surface. I recommend this finish when you need:
- Enhanced grip properties
- Uniform appearance
- Light texture without aggressive patterns
- Masked minor surface imperfections
Polishing Techniques
Manual and mechanical polishing can achieve different gloss levels on Delrin parts. Here’s a breakdown of common polishing methods:
| Polishing Method | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Best Applications | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Buffing | 0.2-0.4 μm | Aesthetic parts | Medium |
| Diamond Polish | 0.1-0.2 μm | High-precision components | High |
| Mechanical Polish | 0.3-0.6 μm | Production parts | Low |
Texturing Options
Light Texturing
Light texturing works particularly well with Delrin due to its molecular structure. Common patterns include:
- Leather grain
- Stipple
- Random matte
- Fine geometric patterns
Medium Texturing
Medium texturing requires careful consideration with Delrin:
- Ensures proper material flow
- Maintains dimensional accuracy
- Provides better grip properties
- Enhances aesthetic appeal
Surface Finish Selection Criteria
When selecting a surface finish for Delrin parts, consider these factors:
Functional Requirements
- Friction requirements
- Wear resistance needs
- Chemical exposure
- Operating environment
Aesthetic Considerations
- Visual appearance
- Touch and feel
- Brand consistency
- End-user expectations
Special Considerations
Temperature Effects
Surface finishes must account for Delrin’s thermal properties:
- Thermal expansion
- Heat dissipation
- Operating temperature range
- Processing temperature limits
Chemical Compatibility
Different surface treatments may affect chemical resistance:
- Solvent exposure
- Cleaning agent compatibility
- Environmental factors
- Chemical processing requirements
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent surface finish quality, we at PTSMAKE implement:
Inspection Methods
| Method | Parameters Measured | Frequency | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Appearance, defects | Every part | Quality assurance |
| Profilometer | Surface roughness | Sampling basis | Technical compliance |
| Gloss Meter | Reflectivity | Batch testing | Aesthetic consistency |
Documentation Requirements
- Surface finish specifications
- Process parameters
- Quality control results
- Traceability records
Cost Considerations
Different surface finishes impact overall part costs:
Direct Costs
- Processing time
- Equipment requirements
- Material preparation
- Labor expenses
Indirect Costs
- Quality control
- Setup and changeover
- Tool maintenance
- Process validation
Maintenance Recommendations
To maintain surface finish quality:
- Regular cleaning procedures
- Proper handling methods
- Storage recommendations
- Periodic inspection schedules
Environmental Impact
Surface finish selection affects environmental factors:
- Process waste generation
- Energy consumption
- Chemical use
- Recyclability considerations
Through careful selection and implementation of surface finishes, Delrin parts can achieve optimal performance and appearance. At PTSMAKE, we work closely with our clients to determine the most suitable surface finish based on their specific requirements and applications. Our expertise in precision manufacturing ensures that each surface finish not only meets technical specifications but also provides long-term value and performance.
How To Prevent Delrin Parts From Warping During Production?
Manufacturing Delrin parts comes with its unique challenges, and warping is one of the most frustrating issues I encounter. When these precision components deform, it not only leads to rejected parts but also causes production delays and increased costs. The frustration intensifies when dealing with tight-tolerance requirements for critical applications.
To prevent Delrin parts from warping during production, maintain consistent cooling rates, optimize mold design with proper gate locations, and control processing parameters like melt temperature and injection pressure. Additional measures include using appropriate mold temperatures and implementing proper part design with uniform wall thickness.

Understanding the Root Causes of Warping
The first step in preventing warping is understanding why it occurs. Delrin, or polyoxymethylene16, exhibits specific characteristics that make it susceptible to warping. I’ve identified several key factors that contribute to this issue:
Molecular Structure Impact
The semi-crystalline nature of Delrin means it undergoes significant volumetric changes during cooling. The material contracts more in the flow direction than in the cross-flow direction, leading to potential warping issues if not properly managed.
Temperature-Related Factors
Temperature control plays a crucial role in preventing warping. Here’s what I’ve found to be most important:
| Temperature Zone | Recommended Range (°F) | Critical Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 380-420 | Must be consistent throughout the material |
| Mold Temperature | 160-200 | Should be uniform across the mold surface |
| Cooling Rate | Controlled | Gradual and even cooling required |
Optimizing Processing Parameters
Injection Pressure Control
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific guidelines for injection pressure control:
- Maintain consistent pressure throughout the injection phase
- Use appropriate holding pressure to compensate for material shrinkage
- Implement gradual pressure transitions
Speed and Time Management
The injection speed and cooling time must be carefully balanced:
- Use moderate injection speeds to prevent material stress
- Allow sufficient cooling time before ejection
- Implement a staged injection approach for complex geometries
Design Considerations for Warping Prevention
Wall Thickness Optimization
From my experience working with various clients, proper wall thickness design is crucial:
- Maintain uniform wall thickness throughout the part
- Avoid sudden thickness transitions
- Design appropriate reinforcement ribs when needed
Gate Location and Design
The placement and design of gates significantly impact warping:
- Position gates to promote uniform filling
- Use multiple gates for large or complex parts
- Consider gate size relative to wall thickness
Material Handling and Preparation
Proper material handling is essential for preventing warping:
- Store Delrin in a dry environment
- Pre-dry material when necessary
- Maintain proper material temperature before processing
Advanced Techniques for Complex Parts
For particularly challenging components, I recommend these advanced approaches:
Simulation and Analysis
- Utilize mold flow analysis software
- Predict potential warping issues before production
- Optimize processing parameters virtually
Specialized Tooling Solutions
At PTSMAKE, we implement various tooling solutions:
- Conformal cooling channels
- Strategic venting placement
- Advanced mold surface treatments
Quality Control and Monitoring
Implementing proper quality control measures is essential:
Measurement and Verification
- Use precise measuring equipment
- Implement regular quality checks
- Document all process parameters
Process Monitoring
Continuous monitoring helps maintain consistency:
| Parameter | Monitoring Frequency | Action Points |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Every cycle | Adjust if deviation > 5°F |
| Pressure | Continuous | Modify if inconsistent |
| Cooling Time | Each batch | Optimize based on results |
Post-Processing Considerations
After production, certain steps can help maintain part stability:
- Controlled cooling after molding
- Proper packaging and storage
- Environmental condition management
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When warping occurs, I follow this systematic approach:
- Identify the pattern of warping
- Analyze process parameters
- Check material conditions
- Review design features
- Implement corrective actions
Industry-Specific Solutions
Different industries require specific approaches:
Automotive Applications
- Focus on dimensional stability
- Consider thermal cycling requirements
- Implement rigorous testing protocols
Medical Device Components
- Maintain strict tolerance control
- Ensure material traceability
- Follow validated processes
Through implementing these comprehensive strategies at PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully minimized warping issues in Delrin parts across various applications. This approach has helped us maintain our position as a trusted partner for precision manufacturing, particularly in challenging projects requiring tight tolerances and complex geometries.
What Tolerances Can Be Achieved With CNC-Machined Delrin?
Getting the right tolerances for CNC-machined Delrin parts can be a challenging task. Many engineers struggle with specifying appropriate tolerances, leading to either overly tight specifications that drive up costs or loose tolerances that compromise part functionality.
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, CNC-machined Delrin can typically achieve tolerances of ±0.002 to ±0.005 inches (0.05 to 0.13mm) for most features. With proper setup and tooling, even tighter tolerances down to ±0.001 inches (0.025mm) are possible for critical dimensions.

Understanding Delrin’s Machining Characteristics
Delrin, also known as acetal homopolymer, is highly regarded in precision manufacturing for its excellent dimensional stability and machinability. The material’s crystalline structure17 contributes to its consistent machining behavior, allowing for predictable and repeatable results.
Material Properties Affecting Tolerances
When working with Delrin, several material properties influence achievable tolerances:
Low Moisture Absorption
- Maintains dimensional stability in varying environments
- Reduces post-machining warpage
- Enables tighter tolerance maintenance over time
Thermal Stability
- Minimal thermal expansion during machining
- Consistent performance across temperature ranges
- Better tolerance control during complex operations
Achievable Tolerances by Feature Type
Different features require different approaches to achieve optimal tolerances. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Feature Type | Standard Tolerance | Premium Tolerance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| External Diameters | ±0.003" | ±0.001" | Achievable with proper cutting speeds |
| Internal Bores | ±0.004" | ±0.002" | Requires specialized tooling |
| Linear Dimensions | ±0.005" | ±0.002" | Dependent on part size |
| Hole Position | ±0.004" | ±0.002" | Based on datum references |
| Surface Flatness | 0.003" | 0.001" | Per inch of surface |
Factors Influencing Tolerance Achievement
Machine Capability
- Modern CNC equipment with high precision
- Regular calibration and maintenance
- Advanced tool monitoring systems
Tooling Selection
- Carbide tooling for better surface finish
- Specialized cutting geometries
- Proper tool wear management
Process Parameters
- Optimized cutting speeds
- Appropriate feed rates
- Controlled chip formation
Best Practices for Tight Tolerance Machining
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific strategies to consistently achieve tight tolerances:
Setup and Fixturing
Temperature Control
- Climate-controlled manufacturing environment
- Material temperature stabilization
- Monitoring of thermal expansion
Workholding
- Custom fixtures for complex geometries
- Multiple setups for critical features
- Minimal clamping distortion
Machining Strategy
Tool Path Optimization
- Progressive cutting depths
- Appropriate step-over rates
- Finish passes for critical dimensions
Quality Control
- In-process measurement
- Statistical process control
- Regular CMM verification
Design Considerations for Optimal Tolerances
To achieve the best results, consider these design guidelines:
Feature Relationships
- Establish clear datum structures
- Consider geometric dimensioning and tolerancing (GD&T)
- Plan for inspection access
Wall Thickness
- Maintain minimum 0.060" thickness where possible
- Account for deflection in thin sections
- Consider support structures for delicate features
Corner Radii
- Specify appropriate internal radii
- Allow for standard tool sizes
- Balance aesthetics with manufacturability
Cost Implications of Tolerance Specifications
Tighter tolerances generally increase manufacturing costs:
| Tolerance Range | Cost Factor | Application |
|---|---|---|
| ±0.005" | 1.0x | General purpose |
| ±0.003" | 1.5x | Precision fit |
| ±0.002" | 2.0x | High precision |
| ±0.001" | 3.0x | Critical features |
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully manufactured various Delrin components with tight tolerances:
Medical Device Components
- Surgical instrument parts with ±0.001" tolerance
- FDA-compliant material handling
- 100% inspection protocol
Aerospace Components
- Critical positioning components
- High-reliability applications
- Full material traceability
Robotics Applications
- Precision gear components
- Bearing housings
- Motion control elements
Tips for Specifying Tolerances
Essential Guidelines
- Specify tolerances only where necessary
- Consider functional requirements
- Account for assembly needs
Documentation
- Clear drawing specifications
- Defined inspection points
- Material requirements
Remember, achieving optimal tolerances with CNC-machined Delrin requires a balance of proper design, capable equipment, and experienced machinists. At PTSMAKE, we combine these elements to deliver consistently high-quality parts that meet or exceed specifications.
Does Delrin Require Special Storage Conditions?
Storing Delrin incorrectly can lead to material degradation and costly manufacturing issues. I’ve seen companies waste thousands of dollars on damaged materials due to improper storage, leading to project delays and quality problems that could have been easily prevented.
Delrin does require specific storage conditions. It should be kept in a clean, dry environment with temperatures between 50-77°F (10-25°C) and relative humidity below 50%. Proper storage helps maintain material properties and prevents moisture absorption that could affect part quality.

Temperature and Humidity Control
Temperature and humidity control are crucial factors in Delrin storage. The material’s performance can be significantly affected by environmental conditions, particularly during long-term storage. At PTSMAKE, we maintain strict environmental controls in our storage facilities to ensure optimal material conditions.
Temperature Management
- Keep temperature between 50-77°F (10-25°C)
- Avoid sudden temperature changes
- Monitor storage area temperature regularly
- Install temperature control systems if needed
Humidity Considerations
- Maintain relative humidity below 50%
- Use dehumidifiers in storage areas
- Monitor humidity levels consistently
- Implement moisture barriers when necessary
Packaging and Protection Methods
The hygroscopic nature18 of Delrin requires proper packaging to maintain its quality. Based on my experience handling various engineering plastics, I recommend the following storage practices:
| Protection Method | Purpose | Recommended Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Sealed Bags | Moisture barrier | Primary packaging |
| Desiccant Packs | Moisture absorption | Include with material |
| Original Packaging | Material integrity | Keep until use |
| Protective Films | Surface protection | For sheets and rods |
Storage Area Requirements
Physical Space Considerations
- Clean, dust-free environment
- Away from direct sunlight
- Adequate ventilation
- Easy access for material handling
Storage Duration Guidelines
I’ve established these guidelines at our facility for optimal storage periods:
| Storage Duration | Special Requirements | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term (<3 months) | Standard packaging | Monthly |
| Medium-term (3-6 months) | Enhanced moisture barrier | Bi-monthly |
| Long-term (>6 months) | Climate-controlled area | Quarterly |
Material Handling Practices
Pre-Processing Preparations
- Allow material to acclimate to processing environment
- Check for any visible damage or contamination
- Verify material certification and properties
- Document storage conditions and duration
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement comprehensive quality control procedures for stored Delrin:
- Regular material property testing
- Moisture content verification
- Visual inspection protocols
- Tracking system for storage duration
- Documentation of environmental conditions
Impact of Improper Storage
Poor storage conditions can lead to various issues:
Material Degradation
- Reduced mechanical properties
- Dimensional instability
- Surface quality problems
- Increased processing difficulties
Manufacturing Consequences
- Higher rejection rates
- Increased production costs
- Extended processing times
- Quality inconsistencies
Best Practices for Material Management
Inventory Control
- Implement FIFO (First-In-First-Out) system
- Regular stock rotation
- Clear labeling and identification
- Detailed record-keeping
Storage Area Organization
We organize our storage facilities using these principles:
| Zone Type | Purpose | Access Level |
|---|---|---|
| Reception | Material verification | Limited |
| Main Storage | Long-term storage | Controlled |
| Processing Area | Ready-to-use material | Authorized |
| Quality Control | Testing and inspection | Restricted |
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability Practices
- Minimize material waste through proper storage
- Reduce energy consumption in climate control
- Implement recyclable packaging solutions
- Optimize storage space utilization
Safety Measures
- Proper ventilation systems
- Fire safety protocols
- Emergency response procedures
- Personal protective equipment requirements
Cost Implications
Proper storage of Delrin is an investment that pays off through:
- Reduced material waste
- Consistent part quality
- Lower processing costs
- Fewer production delays
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed these comprehensive storage protocols through years of experience working with engineering plastics. Our attention to proper material storage has helped us maintain our position as a trusted partner in precision manufacturing, consistently delivering high-quality parts to our clients worldwide.
Learn about homopolymers to understand Delrin’s molecular structure and its crucial strength properties. ↩
Learn about the intricate processes that make Delrin unique and understand its higher costs. ↩
Learn about Teflon’s unique characteristics and applications to avoid costly mistakes. ↩
Learn about the polymerization process for better material understanding and improved product performance. ↩
Learn about crystallization to understand material properties and improve your project outcomes. ↩
Learn how this process enhances material strength and durability for engineering applications. ↩
Learn how crystalline structure affects material properties for better performance in your projects. ↩
Understand how molecular structure affects Delrin pricing and enhance your purchasing decisions. ↩
Learn about its key properties and applications for improved material selection and project success. ↩
Learn about fluoropolymer benefits and applications for enhanced chemical resistance and durability. ↩
Learn about crystallinity to understand its impact on material performance under various temperatures. ↩
Learn how crystallinity influences machining behavior and optimize your processes effectively. ↩
Learn about depolymerization to understand how recycled materials retain or lose their properties. ↩
Understand how material interactions affect wear performance for better selection. ↩
Learn about Delrin’s unique properties and how they influence surface finish choices. ↩
Learn about Delrin’s unique properties and how they influence warping issues during production. ↩
Learn how crystalline structure enhances machining precision and part performance in manufacturing. ↩
Learn how proper storage conditions improve Delrin quality and reduce manufacturing costs. ↩







