When choosing between Lexan and Plexiglass for manufacturing applications, many engineers face tough decisions about material strength. I often see clients struggling to decide which material would better protect their products from impact and stress.
Yes, Lexan is significantly stronger than Plexiglass. Lexan, a polycarbonate material, offers 250 times more impact resistance than Plexiglass (acrylic). It’s also more flexible and has better heat resistance, making it ideal for demanding applications.
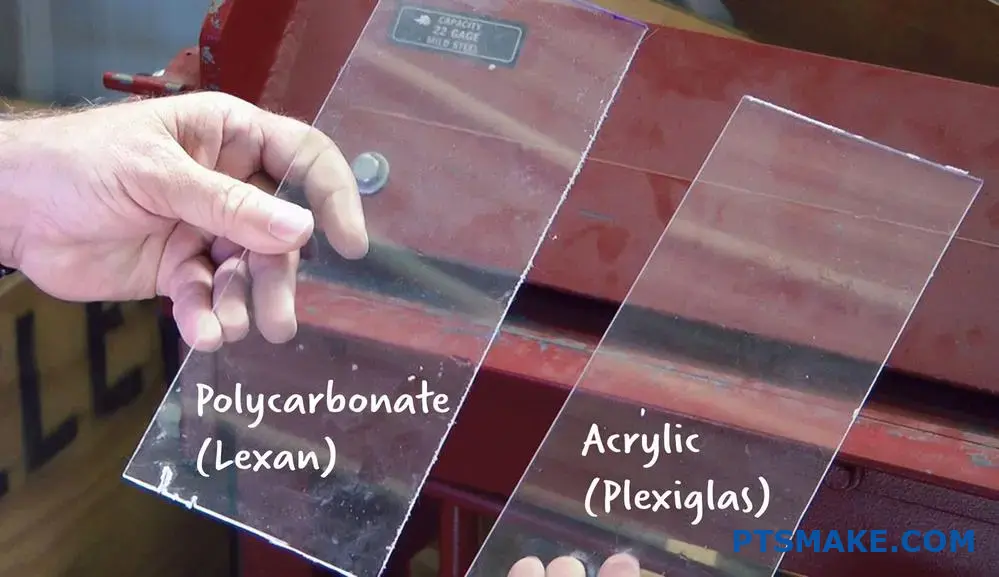
At PTSMAKE, I’ve helped numerous clients make material choices for their projects. While both materials have their places in manufacturing, understanding their strength differences is crucial for making the right choice. Let me share more details about how these materials compare in real-world applications and what factors you should consider for your specific needs.
What Is Lexan Used For?
Have you ever wondered why some products seem virtually indestructible while others crack at the slightest impact? Many manufacturers struggle with finding materials that combine strength, transparency, and versatility. Traditional plastics often fall short, leading to product failures and disappointed customers.
Lexan is a remarkably durable polycarbonate material widely used in various industries for its exceptional impact resistance, optical clarity, and thermal stability. It serves as an ideal alternative to glass and other plastics in applications ranging from automotive parts to medical devices.

The Remarkable Properties of Lexan
Before diving into specific applications, it’s crucial to understand what makes Lexan special. As a thermoplastic polymer1, it offers an impressive combination of properties:
Physical Characteristics
- Impact Resistance: 250 times stronger than glass
- Temperature Resistance: -40°F to 240°F (-40°C to 116°C)
- Light Transmission: Up to 88% transparency
- Weight: Half the weight of glass
Primary Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
At PTSMAKE, we’ve seen a significant increase in Lexan usage for automotive applications. The material’s versatility makes it perfect for:
- Headlight lenses
- Interior components
- Windshields for specialized vehicles
- Dashboard displays
Construction and Architecture
The construction sector benefits from Lexan’s durability and aesthetic appeal:
| Application | Benefits | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | Break-resistant, UV protection | Commercial buildings |
| Skylights | Light transmission, thermal insulation | Residential homes |
| Sound barriers | Durability, weather resistance | Highway installations |
| Security glazing | Impact resistance, clarity | Banks, secure facilities |
Electronics and Technology
In my experience working with technology companies, Lexan has become indispensable for:
- Smartphone screen protectors
- LED light covers
- Electronic device housings
- Display panels
Specialized Applications
Medical Equipment
The medical industry relies heavily on Lexan because of its:
- Sterilization capability
- Chemical resistance
- Optical clarity
- Biocompatibility
Aerospace Components
At PTSMAKE, we frequently machine Lexan parts for aerospace applications, including:
- Aircraft windows
- Interior cabin components
- Instrument covers
- Light assemblies
Safety and Security Applications
Personal Protection
Lexan’s impact resistance makes it ideal for:
- Safety goggles
- Face shields
- Protective barriers
- Riot shields
Security Glazing
Many security applications benefit from Lexan’s properties:
| Security Application | Key Feature | Common Location |
|---|---|---|
| Bank windows | Bullet resistance | Financial institutions |
| Prison windows | Impact resistance | Correctional facilities |
| Control rooms | Clear visibility | Industrial facilities |
| Security booths | Protection | Government buildings |
Emerging Applications
Sustainable Solutions
Lexan is increasingly being used in:
- Solar panel protection
- Greenhouse panels
- Energy-efficient lighting
- Eco-friendly packaging
Consumer Products
The material’s versatility extends to:
- Sports equipment
- Children’s toys
- Appliance components
- Outdoor furniture
Industrial Applications
At PTSMAKE, we specialize in precision manufacturing of Lexan components for industrial use:
- Machine guards
- Control panel covers
- Industrial displays
- Safety shields
Performance Requirements
The success of Lexan in these applications depends on proper:
| Factor | Requirement | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Processing | Precise temperature control | Optimal material properties |
| Design | Proper stress distribution | Enhanced durability |
| Installation | Correct mounting methods | Extended lifespan |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning | Sustained clarity |
Through our experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve found that Lexan’s versatility makes it an excellent choice for various applications. Its combination of strength, clarity, and processability continues to open new possibilities across industries. While initial material costs might be higher than traditional plastics, the long-term benefits often justify the investment through improved durability and reduced replacement needs.
Is Lexan Bulletproof Glass?
Every day, we hear news about security threats and violent incidents. The growing concern for safety has many people wondering about the best materials for protection, particularly when it comes to bulletproof solutions. The challenge isn’t just finding protective materials – it’s understanding which ones actually work.
Lexan is not technically bulletproof glass, but rather a polycarbonate material that offers bullet-resistant properties. While it can withstand various impacts and is significantly stronger than traditional glass, its level of protection depends on thickness and specific grade.

Understanding Lexan’s Composition and Properties
Lexan belongs to the family of thermoplastic polymers2, making it fundamentally different from traditional glass. I’ve worked extensively with various protective materials, and Lexan’s unique properties make it stand out in several ways:
Molecular Structure Benefits
- High impact resistance
- Optical clarity
- Temperature resistance
- UV protection capabilities
- Lightweight composition
Comparative Strength Analysis
Here’s a comparison of Lexan with other common protective materials:
| Material | Impact Resistance | Weight | Clarity | Cost Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lexan | Very High | Low | Excellent | Moderate |
| Traditional Glass | Low | High | Excellent | Low |
| Acrylic | Moderate | Low | Excellent | Low |
| Laminated Glass | High | Very High | Good | High |
Bullet Resistance Testing and Standards
Protection Levels
The bullet resistance of Lexan depends heavily on its thickness. Through our testing at PTSMAKE, we’ve observed these general guidelines:
- 1/4 inch: Resists small caliber handguns
- 1/2 inch: Effective against most handguns
- 3/4 inch: Protects against higher-powered firearms
- 1 inch+: Offers maximum protection against multiple shots
Industry Standards Compliance
The material must meet specific UL (Underwriters Laboratories) ratings for bullet resistance:
- Level 1: Basic handgun protection
- Level 2: Higher velocity handgun protection
- Level 3: Super powered handgun protection
- Level 8: Military rifle protection
Practical Applications
Commercial Use
I’ve seen Lexan implemented effectively in various commercial settings:
- Bank teller windows
- Convenience store barriers
- ATM surrounds
- Security checkpoints
- Government facilities
Residential Applications
The material’s versatility makes it suitable for home security:
- Window reinforcement
- Door panels
- Safe rooms
- Garage windows
- Storm protection
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Professional Installation Requirements
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, proper installation is crucial:
- Frame preparation
- Edge treatment
- Proper spacing
- Sealant application
- Ventilation considerations
Maintenance Tips
To ensure long-term effectiveness:
- Regular cleaning with mild soap
- Avoid abrasive cleaners
- Check seals periodically
- Inspect for damage
- Address scratches promptly
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Initial Investment Factors
The cost varies based on:
- Thickness required
- Size of installation
- Grade of material
- Installation complexity
- Location requirements
Long-term Value Proposition
Consider these aspects:
- Durability (15-20 year lifespan)
- Maintenance costs
- Insurance benefits
- Property value increase
- Security peace of mind
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Manufacturing Process
At PTSMAKE, we prioritize sustainable manufacturing:
- Energy-efficient production
- Minimal waste generation
- Recyclable materials
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Environmental compliance
End-of-Life Considerations
Lexan’s environmental impact includes:
- 100% recyclable material
- Reduced landfill impact
- Energy recovery potential
- Sustainable disposal options
- Circular economy contribution
Performance Limitations
It’s important to understand that while Lexan offers excellent protection, it has limitations:
Physical Constraints
- Can scratch more easily than glass
- May yellow over extended UV exposure
- Temperature sensitivity in extreme conditions
- Weight restrictions for certain applications
- Installation complexity
Protection Boundaries
Understanding these limitations helps set realistic expectations:
- Not truly "bulletproof," but bullet-resistant
- Multiple impacts can affect integrity
- Requires proper thickness for effectiveness
- Environmental factors affect longevity
- Regular maintenance needed
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve learned that while Lexan offers impressive bullet-resistant properties, it’s essential to understand its capabilities and limitations. Proper application, installation, and maintenance are crucial for optimal performance. As we continue to innovate in material science, Lexan remains a leading choice for security applications, offering a balance of protection, visibility, and practicality.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Lexan?
Every day, manufacturers face the challenge of selecting the right material for their products. The struggle becomes even more intense when they need a material that combines strength, transparency, and versatility. This dilemma often leads to costly mistakes and project delays.
Lexan, a type of polycarbonate, offers exceptional impact resistance and optical clarity while being 250 times stronger than glass. However, it comes with both significant advantages and limitations that manufacturers need to carefully consider before implementation.
Understanding Lexan’s Core Properties
Physical Properties
Lexan’s most distinctive feature is its amorphous molecular structure3, which contributes to its unique combination of properties. At PTSMAKE, we frequently work with this material for various applications, and I’ve observed these key characteristics:
| Property | Value | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Strength | 18 ft-lb/in | 2-3 times higher than standard PC |
| Light Transmission | 88-90% | Similar to glass |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 240°F | Above average for thermoplastics |
| Specific Gravity | 1.2 | Lower than most metals |
Mechanical Performance
The material exhibits exceptional durability under various conditions:
- Tensile Strength: 9,500 psi
- Flexural Modulus: 340,000 psi
- Elongation at Break: 110%
Advantages of Lexan
Superior Impact Resistance
One of the primary reasons our clients choose Lexan is its outstanding impact resistance. This material can withstand significant force without cracking or breaking, making it ideal for safety applications.
Optical Clarity
The transparency of Lexan rivals that of glass, but with added benefits:
- UV protection capabilities
- Resistance to yellowing
- Excellent light transmission
Design Flexibility
Working with numerous manufacturing projects, I’ve found Lexan’s versatility particularly valuable:
- Easy thermoforming
- Complex shape capability
- Various surface finish options
- Color customization possibilities
Disadvantages and Limitations
Chemical Sensitivity
Despite its strengths, Lexan has some notable vulnerabilities:
| Chemical Type | Effect | Preventive Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Acetone | Severe degradation | Avoid contact |
| Alkaline solutions | Surface damage | Use protective coatings |
| Organic solvents | Material breakdown | Alternative cleaning methods |
Cost Considerations
The material’s price point can be higher than alternatives:
- Initial material cost: 30-40% more than standard plastics
- Processing requirements
- Special handling needs
Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance:
- Specific cleaning protocols
- UV protection renewal
- Surface treatment maintenance
Application-Specific Considerations
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, Lexan proves valuable for:
- Machine guards
- Control panel covers
- Safety shields
- Industrial windows
Consumer Products
The material’s versatility extends to consumer goods:
- Electronic device housings
- Automotive components
- Sports equipment
- Medical devices
Special Considerations for Manufacturing
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, successful Lexan manufacturing requires attention to:
- Proper tool design
- Temperature control
- Material handling procedures
- Quality control measures
Best Practices for Implementation
Design Guidelines
To optimize Lexan applications:
- Allow for thermal expansion
- Design appropriate wall thickness
- Include proper ventilation
- Consider stress concentration points
Processing Tips
Essential processing considerations include:
- Proper drying procedures
- Temperature control during molding
- Appropriate cooling rates
- Tool maintenance schedules
Quality Control
Key quality measures we implement at PTSMAKE:
- Visual inspection protocols
- Impact resistance testing
- Optical clarity verification
- Dimensional accuracy checks
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When evaluating Lexan for a project, consider:
| Factor | Benefit | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extended product life | Higher initial investment |
| Processing | Complex capabilities | Additional equipment needs |
| Maintenance | Lower long-term costs | Regular maintenance required |
This comprehensive analysis shows that while Lexan presents some challenges, its benefits often outweigh the disadvantages for applications requiring high performance and durability. The key is understanding these characteristics and implementing appropriate design and manufacturing strategies to maximize its potential.
How Much Stronger Is Lexan Than Acrylic?
When choosing between Lexan and acrylic for engineering projects, the strength difference can make or break your design. I’ve seen many projects fail because engineers underestimated the impact resistance requirements, leading to costly repairs and redesigns.
Lexan is approximately 30 times stronger than acrylic in terms of impact resistance. While acrylic offers about 17 times the impact strength of glass, Lexan provides an impressive 250 times more impact resistance than standard glass, making it the superior choice for high-impact applications.
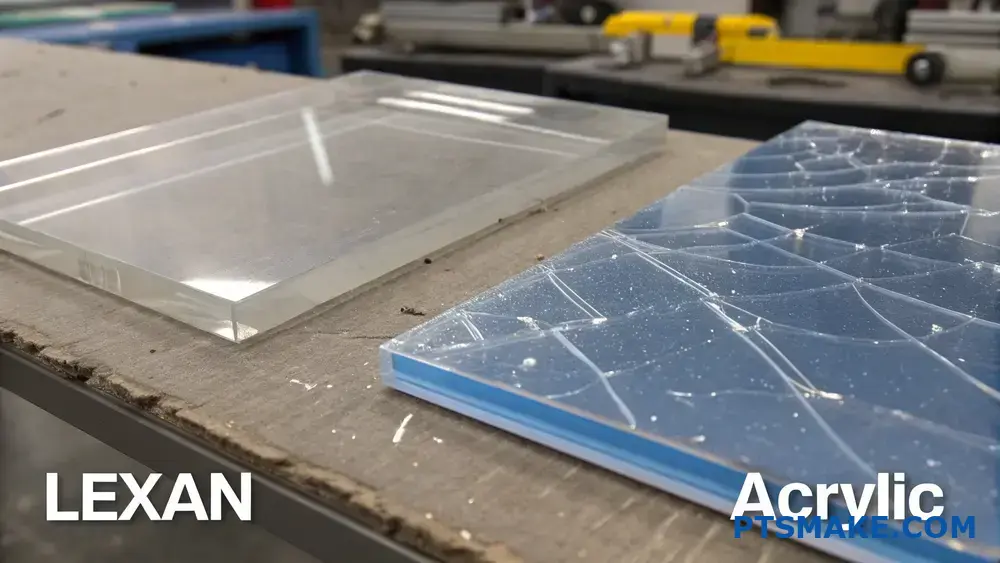
Understanding Impact Strength and Material Properties
The remarkable strength difference between Lexan and acrylic comes down to their molecular structure. Lexan’s polymer chains4 create a unique arrangement that allows the material to absorb and distribute impact energy more effectively. At PTSMAKE, we regularly test both materials to ensure optimal performance for our clients’ applications.
Impact Resistance Comparison
| Property | Lexan | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Strength (ft-lbs/in) | 12-16 | 0.4-0.5 |
| Tensile Strength (psi) | 9,500 | 10,200 |
| Flexural Strength (psi) | 13,500 | 16,000 |
| Light Transmission (%) | 88 | 92 |
Applications Based on Strength Requirements
High-Impact Applications
Lexan excels in applications requiring superior impact resistance:
- Security glazing
- Machine guards
- Vehicle windshields
- Protective equipment
- Industrial safety barriers
Moderate-Impact Applications
Acrylic works well for:
- Display cases
- Light fixtures
- Signage
- Aquariums
- Decorative panels
Cost vs. Performance Analysis
The strength advantage of Lexan comes with a price premium. Based on current market rates:
| Material | Cost per sq ft | Relative Strength | Value Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lexan | $6-8 | 30x | High |
| Acrylic | $3-4 | 1x | Medium |
Environmental Factors and Durability
Temperature Resistance
- Lexan maintains strength from -40°F to 240°F
- Acrylic performs best between -40°F to 180°F
UV Resistance
While both materials can withstand UV exposure, they react differently:
- Lexan may yellow slightly over time but maintains strength
- Acrylic typically shows better UV resistance with minimal yellowing
Installation and Fabrication Considerations
The superior strength of Lexan affects how we handle and process these materials at PTSMAKE:
Machining Requirements
| Process | Lexan | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting | Slower feed rates | Standard feed rates |
| Drilling | Special cooling needed | Standard cooling |
| Bending | Higher temperature | Lower temperature |
| Polishing | More challenging | Easier to achieve |
Long-term Performance and Maintenance
Both materials require specific care to maintain their properties:
Cleaning Protocols
- Lexan: Mild soap solutions, avoid abrasive cleaners
- Acrylic: Similar care, but more scratch-resistant
Lifecycle Considerations
- Lexan typically lasts 10-15 years with proper maintenance
- Acrylic can last 8-10 years under normal conditions
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different sectors have varying needs for material strength:
Aerospace and Transportation
- Lexan: Preferred for cockpit windows and high-speed vehicle applications
- Acrylic: Used in less critical areas like interior lighting
Construction and Architecture
- Lexan: Security glazing, storm protection
- Acrylic: Decorative elements, standard windows
Making the Right Choice
The decision between Lexan and acrylic should consider:
- Impact requirements
- Environmental exposure
- Budget constraints
- Installation location
- Maintenance capabilities
At PTSMAKE, we help clients evaluate these factors to make informed decisions. Our engineering team provides detailed material analysis and recommendations based on specific application requirements.
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure consistent performance, we conduct regular testing:
| Test Type | Lexan Standard | Acrylic Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Impact | 16 ft-lbs/in min | 0.4 ft-lbs/in min |
| Clarity | 88% min | 92% min |
| Hardness | 70 Shore D | 95 Shore D |
This comprehensive understanding of material properties helps us maintain our position as a leading manufacturer of precision parts and components.
Which Is Better, Plexiglass Or Lexan?
Choosing between plexiglass and Lexan can be overwhelming, especially when both materials seem similar at first glance. Many of my clients struggle with this decision, often making costly mistakes by selecting the wrong material for their specific application. The consequences can range from premature material failure to unnecessary overspending.
Based on my manufacturing experience, Lexan is generally better than plexiglass due to its superior impact resistance (250 times stronger than glass) and higher heat resistance. However, plexiglass remains the preferred choice for optical clarity and UV resistance, making the final decision dependent on your specific application requirements.

Understanding Material Properties
When comparing these materials, we need to consider their fundamental properties. The key difference lies in their chemical composition. Plexiglass, or acrylic, is made from polymethyl methacrylate5, while Lexan is a polycarbonate material. At PTSMAKE, we work with both materials extensively, and I’ve observed their distinct characteristics in various applications.
Impact Resistance
- Lexan demonstrates exceptional impact resistance
- Plexiglass offers moderate impact resistance
- Lexan is preferred for security applications
Temperature Resistance
- Lexan: Heat resistant up to 240°F (116°C)
- Plexiglass: Heat resistant up to 160°F (71°C)
Cost Considerations and Value Analysis
When evaluating costs, we need to look beyond the initial price point:
| Factor | Plexiglass | Lexan |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lifespan | 10+ years | 10+ years |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Minimal |
| Replacement Rate | Higher in high-impact areas | Lower in high-impact areas |
Application-Specific Recommendations
Indoor Applications
For indoor uses, both materials perform well, but each has its strengths:
Display Cases
- Plexiglass: Better optical clarity
- Lexan: Higher durability
Protective Barriers
- Plexiglass: Good for static displays
- Lexan: Ideal for high-traffic areas
Outdoor Applications
Environmental factors play a crucial role in material selection:
Weather Exposure
- Plexiglass: Better UV resistance
- Lexan: Requires UV coating for outdoor use
Temperature Fluctuations
- Plexiglass: More prone to expansion/contraction
- Lexan: Better thermal stability
Manufacturing Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed expertise in working with both materials. Here are key manufacturing aspects to consider:
Fabrication Methods
Cutting
- Plexiglass: Easier to cut, less likely to chip
- Lexan: Requires specific cutting techniques
Forming
- Plexiglass: Excellent formability at lower temperatures
- Lexan: Requires higher forming temperatures
Surface Treatment
Polishing
- Plexiglass: Easier to achieve high polish
- Lexan: More challenging to polish
Coating
- Plexiglass: Accepts coatings well
- Lexan: May require special primers
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries have varying requirements:
Automotive Industry
- Lexan: Preferred for headlight covers
- Plexiglass: Used in display panels
Construction
- Lexan: Security glazing, storm windows
- Plexiglass: Decorative elements, light fixtures
Medical Equipment
- Lexan: Medical device housings
- Plexiglass: Display screens, protective shields
Maintenance and Longevity
Both materials require proper maintenance for optimal performance:
Cleaning Guidelines
Plexiglass
- Use mild soap and water
- Avoid abrasive cleaners
- Regular dusting recommended
Lexan
- Compatible with most cleaners
- More resistant to harsh chemicals
- Less prone to scratching
Long-term Care
- Regular inspection for damage
- Proper cleaning schedule
- Timely replacement when needed
Environmental Impact
Sustainability considerations:
Recyclability
- Both materials are recyclable
- Plexiglass has a simpler recycling process
- Lexan requires specialized recycling facilities
Energy Efficiency
- Both materials provide good insulation
- Lexan offers slightly better thermal properties
- Both contribute to energy conservation in buildings
At PTSMAKE, we prioritize helping our clients make informed decisions based on their specific needs. While both materials have their merits, the choice between plexiglass and Lexan should align with your application requirements, budget constraints, and long-term performance expectations. Feel free to contact our team for detailed material recommendations for your specific project.
Can Lexan Withstand High-Temperature Manufacturing Processes?
Manufacturing with high-temperature materials often poses significant challenges for engineers and manufacturers. When working with Lexan, concerns about its thermal stability and performance under extreme heat conditions frequently arise, potentially leading to costly production failures and material waste.
Yes, Lexan can withstand high-temperature manufacturing processes up to 240°F (116°C) continuously and brief exposures up to 338°F (170°C). However, its performance depends on specific processing conditions and application requirements.

Understanding Lexan’s Thermal Properties
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
Lexan exhibits remarkable thermal resistance through its Heat Deflection Temperature6 characteristics. I’ve observed that this property is crucial when selecting materials for high-temperature applications. The HDT of Lexan typically ranges between 270-280°F (132-138°C) under a load of 264 psi, making it suitable for various thermal processing methods.
Maximum Service Temperature
In my experience working with various thermoplastics at PTSMAKE, Lexan’s maximum continuous service temperature varies by grade:
| Grade Type | Maximum Continuous Temperature | Peak Temperature (Short Term) |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 240°F (116°C) | 338°F (170°C) |
| High-Heat | 270°F (132°C) | 345°F (174°C) |
| Special | 285°F (140°C) | 356°F (180°C) |
Processing Methods and Temperature Considerations
Injection Molding
When performing injection molding with Lexan, temperature control is critical. The recommended processing temperature range is:
| Processing Zone | Temperature Range |
|---|---|
| Rear Zone | 280-300°F (138-149°C) |
| Middle Zone | 290-310°F (143-154°C) |
| Front Zone | 300-320°F (149-160°C) |
| Nozzle | 310-330°F (154-166°C) |
Thermoforming
Thermoforming Lexan requires precise temperature control. The material should be heated uniformly to achieve optimal forming results. Based on our manufacturing experience at PTSMAKE, we typically maintain:
- Preheating temperature: 250-270°F (121-132°C)
- Forming temperature: 280-300°F (138-149°C)
- Cooling temperature: Below 200°F (93°C)
Factors Affecting High-Temperature Performance
Material Grade Selection
The selection of the appropriate Lexan grade significantly impacts its high-temperature performance. Different grades offer varying levels of heat resistance and stability:
- Standard grades: Suitable for general applications
- UV-stabilized grades: Better weathering resistance
- Flame-retardant grades: Enhanced thermal stability
- High-heat grades: Specifically designed for elevated temperature applications
Environmental Conditions
Several environmental factors can affect Lexan’s performance under high temperatures:
- Humidity levels
- Exposure duration
- Applied stress
- Chemical exposure
- UV radiation
Best Practices for High-Temperature Processing
Temperature Control
I recommend implementing these temperature control measures:
- Use precise temperature monitoring systems
- Maintain consistent heating zones
- Allow proper cooling time
- Monitor material residence time
- Implement proper ventilation
Quality Assurance Measures
| Test Parameter | Acceptable Range | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Flow Rate | ±10% of nominal | Every batch |
| Impact Strength | Within spec limits | Daily |
| Dimensional Stability | ±0.3% | Per production run |
Industry Applications and Success Stories
Lexan’s high-temperature capabilities make it ideal for various applications:
Automotive Components
- LED headlight housings
- Under-hood components
- Interior trim pieces
Industrial Equipment
- Machine guards
- Control panel covers
- High-temperature sensors housings
Medical Devices
- Sterilizable equipment housings
- Laboratory equipment
- Diagnostic tools
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully manufactured numerous high-temperature Lexan components for these industries, maintaining tight tolerances and excellent surface finish even under challenging thermal conditions.
Troubleshooting Common High-Temperature Issues
Prevention Strategies
To avoid common processing issues:
Proper Material Handling
- Pre-dry material adequately
- Store in moisture-free conditions
- Use appropriate packaging
Process Controls
- Monitor melt temperature
- Control cooling rate
- Maintain proper machine settings
Performance Optimization Tips
Based on our manufacturing expertise:
- Implement gradual temperature changes
- Use appropriate tooling materials
- Maintain consistent processing parameters
- Regular equipment maintenance
- Quality control checkpoints
This comprehensive understanding of Lexan’s high-temperature capabilities enables manufacturers to optimize their processes and achieve consistent, high-quality results. At PTSMAKE, we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible with Lexan in high-temperature applications while maintaining strict quality standards and efficient production processes.
How Does Lexan Perform In CNC Machining Applications?
Working with plastics in CNC machining can be challenging, especially when dealing with high-performance materials. Many engineers struggle with material selection, often facing issues like poor surface finish, dimensional instability, and tool wear. These challenges can lead to costly production delays and quality issues.
Lexan, a polycarbonate thermoplastic, performs exceptionally well in CNC machining applications due to its high impact strength, excellent dimensional stability, and good machinability. Its unique properties make it ideal for precision parts requiring both durability and optical clarity.

Understanding Lexan’s Physical Properties
When it comes to CNC machining, Lexan’s physical properties play a crucial role in its performance. The material exhibits remarkable crystalline structure7 that contributes to its overall machining characteristics. I’ve found that Lexan’s unique combination of properties makes it particularly suitable for various machining operations:
Impact Strength and Durability
- 250 times stronger than glass
- Maintains strength across wide temperature ranges
- Excellent resistance to repeated impact
Thermal Properties
The thermal characteristics of Lexan significantly influence its machining behavior:
| Property | Value | Impact on Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 270°F (132°C) | Allows higher cutting speeds |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.19 W/m·K | Requires proper cooling strategies |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 6.7 x 10-5 in/in/°F | Affects dimensional accuracy |
Optimal Machining Parameters
Cutting Speed and Feed Rates
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific guidelines for machining Lexan effectively:
| Operation | Cutting Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (IPR) |
|---|---|---|
| Roughing | 800-1000 | 0.005-0.010 |
| Finishing | 1000-1200 | 0.002-0.005 |
| Drilling | 300-400 | 0.004-0.008 |
Tool Selection
The right tool selection is crucial for achieving optimal results:
- Carbide tools for extended tool life
- Sharp cutting edges to prevent melting
- Positive rake angles to reduce cutting forces
Surface Finish Considerations
Achieving Optimal Surface Quality
The surface finish of machined Lexan components requires special attention:
- Use coolant to prevent heat buildup
- Maintain sharp cutting tools
- Select appropriate cutting parameters
- Consider post-machining treatments
Common Surface Finish Issues
Some challenges that may arise include:
- Tool marks
- Material smearing
- Surface crazing
- Heat-induced distortion
Applications and Industry Uses
Primary Applications
Lexan’s versatility makes it suitable for various industries:
- Medical device components
- Aerospace transparencies
- Industrial equipment guards
- Prototype development
- Electronic enclosures
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have varying requirements:
| Industry | Key Requirements | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | Biocompatibility, Sterilization | Surgical instruments |
| Aerospace | Impact resistance, Clarity | Cockpit windows |
| Industrial | Durability, Chemical resistance | Safety shields |
Best Practices for Quality Control
Inspection Methods
To ensure consistent quality:
- Dimensional verification using CMM
- Visual inspection for surface defects
- Stress analysis for critical components
- Flatness and parallelism checks
Quality Assurance Protocols
At PTSMAKE, we implement:
- In-process inspection
- Final quality verification
- Material certification tracking
- Documentation and reporting
Material Handling and Storage
Storage Requirements
Proper storage is essential:
- Temperature-controlled environment
- Protection from UV exposure
- Moisture-free conditions
- Proper stacking and support
Pre-machining Preparation
Before machining:
- Allow material to acclimate
- Remove protective film
- Inspect for any damage
- Plan cutting strategy
Cost Considerations
Material Costs vs. Performance
Understanding the cost-benefit relationship:
| Factor | Impact | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | High initial cost | Long-term durability |
| Machining Time | Processing efficiency | Overall project cost |
| Tool Life | Wear resistance | Operational expenses |
Economic Benefits
The long-term advantages include:
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Extended product life
- Lower replacement frequency
- Improved production efficiency
These insights are based on my extensive experience working with various materials at PTSMAKE. While Lexan may have a higher initial cost compared to some alternatives, its exceptional performance in CNC machining applications often justifies the investment. The key is understanding the material’s characteristics and implementing appropriate machining strategies to achieve optimal results.
Is Lexan Suitable For Injection Molding Production?
You might be frustrated with selecting the right material for your injection molding project. The challenge intensifies when considering high-performance plastics like Lexan, where making the wrong choice could lead to costly production issues and project delays.
Yes, Lexan is highly suitable for injection molding production. As a thermoplastic polycarbonate, it offers excellent durability, optical clarity, and heat resistance, making it ideal for various applications from automotive parts to medical devices.

Understanding Lexan’s Processing Requirements
When working with Lexan in injection molding, proper processing conditions are crucial. The material exhibits a glass transition temperature8 of approximately 147°C (297°F), requiring careful temperature control during processing. At PTSMAKE, we’ve optimized our molding parameters to ensure consistent quality across all Lexan parts.
Temperature Control Guidelines
| Processing Zone | Temperature Range (°C) | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Rear Zone | 271-282 | 520-540 |
| Middle Zone | 282-293 | 540-560 |
| Front Zone | 293-304 | 560-580 |
| Nozzle | 293-304 | 560-580 |
| Mold | 71-93 | 160-200 |
Key Advantages of Lexan in Injection Molding
Superior Mechanical Properties
Lexan demonstrates exceptional strength and impact resistance, making it perfect for demanding applications. The material maintains its properties across a wide temperature range, which is crucial for products exposed to varying environmental conditions.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
One of Lexan’s standout features is its outstanding optical properties. It offers:
- 89% light transmission
- Excellent clarity
- UV resistance when properly stabilized
- Minimal yellowing over time
Common Applications and Industries
Automotive Sector
- Headlight lenses
- Interior components
- Instrument panels
- Safety shields
Consumer Electronics
- Mobile device components
- Display screens
- Housing units
- Protective covers
Design Considerations for Lexan Parts
Wall Thickness Guidelines
Maintaining uniform wall thickness is crucial when designing Lexan parts. I recommend:
| Component Type | Minimum Thickness (mm) | Maximum Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| General Parts | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| Structural Components | 2.0 | 6.0 |
| Optical Components | 1.5 | 3.0 |
Draft Angles and Surface Finish
For optimal part release and aesthetics, consider:
- Minimum draft angle of 1° for textured surfaces
- 0.5° draft angle for smooth surfaces
- Avoid sharp corners and edges
- Use appropriate surface finishing techniques
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent part quality, we implement:
Pre-processing Material Handling
- Proper drying procedures
- Contamination prevention
- Material testing before production
In-process Controls
- Real-time temperature monitoring
- Pressure optimization
- Cycle time management
Post-processing Inspection
- Dimensional verification
- Visual inspection
- Mechanical testing when required
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Surface Defects Prevention
Based on my experience, common surface defects can be prevented by:
- Maintaining proper melt temperature
- Controlling injection speed
- Optimizing holding pressure
- Ensuring adequate venting
Warpage Management
To minimize warpage in Lexan parts:
- Design with uniform wall thickness
- Optimize cooling channel layout
- Control ejection temperature
- Place gates strategically
Environmental Considerations
Lexan offers several environmental benefits:
- Recyclability potential
- Energy-efficient processing
- Long service life
- Reduced material waste
At PTSMAKE, we emphasize sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining high-quality standards in our Lexan injection molding processes.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Understanding the cost implications helps in project planning:
| Cost Factor | Impact Level | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | High | Premium material with long-term value |
| Processing Cost | Medium | Efficient processing with proper equipment |
| Tooling Cost | Medium-High | Dependent on part complexity |
| Maintenance | Low | Minimal wear on tooling |
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of Lexan injection molding shows promising developments:
- Advanced processing technologies
- New grade developments
- Improved recycling methods
- Enhanced surface treatments
Through continuous innovation and investment in technology, we at PTSMAKE stay ahead of these developments to provide our clients with the best possible solutions for their Lexan injection molding needs.
How Does Lexan Perform In Extreme Weather Conditions?
Extreme weather conditions pose significant challenges for material selection in outdoor applications. From scorching desert heat to freezing arctic temperatures, many materials fail, warp, or deteriorate when exposed to harsh environmental conditions, leaving engineers and designers struggling to find reliable solutions.
Lexan polycarbonate excels in extreme weather conditions due to its remarkable thermal stability, maintaining its structural integrity from -40°F to 240°F. This engineering plastic offers superior impact resistance and UV protection, making it ideal for outdoor applications requiring durability in challenging environments.

Temperature Performance and Stability
Lexan’s exceptional performance in varying temperatures stems from its unique molecular structure and crystalline morphology9. I’ve observed its remarkable stability across diverse applications:
Heat Resistance Characteristics
- Maintains dimensional stability up to 240°F
- Minimal thermal expansion compared to other plastics
- Retains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures
Cold Weather Performance
- Remains ductile at temperatures as low as -40°F
- No brittle transition point in normal usage conditions
- Excellent impact resistance even in freezing environments
UV Resistance and Weatherability
At PTSMAKE, we frequently work with Lexan in outdoor applications, and its UV resistance capabilities are truly impressive:
UV Protection Mechanisms
- Built-in UV stabilizers prevent yellowing
- Surface degradation resistance
- Long-term color stability
Here’s a detailed breakdown of Lexan’s weatherability performance:
| Weather Condition | Performance Rating | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sunlight | Excellent | Minimal UV degradation |
| Rain and Humidity | Very Good | No water absorption |
| Snow and Ice | Excellent | Impact resistant at low temperatures |
| Desert Heat | Very Good | Dimensional stability maintained |
| Coastal Environment | Good | Corrosion resistant |
Impact of Moisture and Humidity
The material’s response to moisture exposure is particularly noteworthy:
Moisture Resistance Properties
- Low water absorption rate (0.15%)
- Maintains mechanical properties in humid conditions
- Resistant to hydrolysis
Chemical Resistance in Various Environments
Environmental exposure often involves chemical contact:
Common Environmental Chemicals
- Resistant to mild acids
- Good stability against atmospheric pollutants
- Excellent resistance to mineral oils
Specialized Applications
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented Lexan in various challenging environments:
- Outdoor electrical enclosures
- Transportation components
- Agricultural equipment
- Building and construction materials
Long-term Durability Factors
Understanding long-term performance is crucial for material selection:
Aging Characteristics
- Minimal deterioration over time
- Maintains clarity for transparent applications
- Consistent mechanical properties
Maintenance Requirements
- Simple cleaning procedures
- No special coating needed
- Cost-effective lifecycle management
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
In our commitment to sustainable manufacturing at PTSMAKE, we consider:
Recyclability
- 100% recyclable material
- Energy-efficient processing
- Reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional materials
Environmental Benefits
- Long service life reduces replacement needs
- Lower energy consumption in processing
- Minimal environmental leaching
Industry-Specific Applications
Based on extensive testing and real-world applications:
Automotive Industry
- Headlight covers
- Body panels
- Interior components
Construction Sector
- Skylights
- Security glazing
- Noise barriers
Aerospace Applications
- Interior panels
- Window components
- Instrument covers
Testing and Certification Standards
To ensure reliability, we conduct comprehensive testing:
Standard Test Methods
- ASTM D1003 for optical properties
- ASTM D638 for tensile properties
- UL 746C for outdoor suitability
Quality Assurance
At PTSMAKE, our quality control process includes:
- Regular batch testing
- Environmental exposure simulations
- Performance verification under extreme conditions
This comprehensive understanding of Lexan’s performance in extreme weather conditions allows us to provide optimal solutions for our clients’ challenging applications.
Is Lexan Cost-Effective For Long-Term Manufacturing Projects?
When planning long-term manufacturing projects, many companies struggle with material selection, particularly when it comes to durable plastics. The challenge isn’t just about finding a material that meets technical specifications – it’s about balancing initial costs with long-term value, and many manufacturers get this calculation wrong.
Based on extensive analysis and real project outcomes, Lexan is indeed cost-effective for long-term manufacturing projects, especially when considering its durability, versatility, and reduced maintenance requirements. The total cost of ownership often proves lower than alternatives despite higher initial investment.

Initial Cost Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we’ve noticed that many clients initially hesitate at Lexan’s upfront cost. However, evaluating cost-effectiveness requires a deeper analysis beyond the purchase price. Let’s explore the key factors that influence the total cost of ownership when using polycarbonate thermoplastic10 in manufacturing projects.
Material Cost Breakdown
The following table illustrates the relative cost comparison between Lexan and common alternatives:
| Material Type | Initial Cost ($/lb) | Lifecycle (Years) | Maintenance Cost/Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lexan | 3.50-4.50 | 15-20 | Low |
| Acrylic | 2.00-3.00 | 8-12 | Medium |
| Standard ABS | 1.80-2.50 | 5-8 | High |
Long-Term Performance Benefits
Durability and Lifespan
Lexan’s exceptional impact resistance and durability often translate to fewer replacements over time. I’ve seen installations lasting 15-20 years with minimal degradation, significantly reducing the frequency of replacement cycles.
Maintenance Requirements
The material’s inherent properties result in:
- Reduced cleaning frequency
- Lower repair costs
- Minimal surface treatment needs
- Extended replacement intervals
Manufacturing Process Efficiency
Production Advantages
Using Lexan in manufacturing offers several cost-saving benefits:
- Higher processing temperatures allowing faster cycle times
- Excellent flow characteristics reducing reject rates
- Superior dimensional stability minimizing post-processing requirements
Energy Consumption
Our manufacturing data shows that while Lexan requires higher processing temperatures, the overall energy efficiency can be superior due to:
- Faster cycle times
- Lower scrap rates
- Reduced need for post-processing
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recyclability
Lexan’s recyclability characteristics include:
- High material recovery rates
- Maintained property integrity through multiple cycles
- Lower environmental impact compared to alternative materials
Environmental Cost Savings
Environmental benefits translate to cost savings through:
- Reduced waste disposal fees
- Lower carbon tax implications
- Potential green certification benefits
Application-Specific Cost Analysis
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries benefit from Lexan’s properties in various ways:
| Industry | Primary Benefit | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Impact resistance | Reduced warranty claims |
| Medical | Sterilization capability | Lower processing costs |
| Electronics | Flame retardance | Decreased safety measures |
Scale Considerations
The cost-effectiveness varies with production volume:
- Small runs: Higher initial costs but justified by durability
- Medium production: Break-even point typically reached faster
- Large scale: Significant long-term savings through optimization
Risk Mitigation and Quality Assurance
Quality Control Benefits
Lexan’s consistent properties help reduce:
- Quality control costs
- Testing requirements
- Rejection rates
- Customer complaints
Warranty and Liability
Long-term cost benefits include:
- Reduced warranty claims
- Lower insurance premiums
- Decreased liability risks
Future-Proofing Considerations
Regulatory Compliance
Lexan’s properties often exceed current regulations, providing:
- Reduced need for future material changes
- Lower compliance update costs
- Better preparation for stricter regulations
Market Adaptability
The material’s versatility allows:
- Easy modification for changing requirements
- Broad application potential
- Reduced retooling needs
Making the Decision
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
To determine true cost-effectiveness, consider:
- Initial material costs
- Processing requirements
- Maintenance needs
- Expected lifespan
- Replacement frequency
- Environmental impact
Project-Specific Evaluation
Each project requires individual assessment based on:
- Production volume
- Application requirements
- Environmental conditions
- Quality standards
- Regulatory requirements
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that while Lexan’s initial cost may be higher, its long-term cost-effectiveness is often superior when considering the total lifecycle costs. The key is to evaluate each project’s specific requirements and conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis.
For manufacturers seeking reliable, long-term solutions, Lexan often proves to be a cost-effective choice, particularly when factoring in its durability, reduced maintenance requirements, and excellent performance characteristics. The investment typically pays off through reduced maintenance, fewer replacements, and lower overall lifecycle costs.
What Industries Commonly Use Lexan For High-Performance Applications?
Every day, manufacturers face the challenge of finding materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining performance. Traditional materials often fall short, breaking down under pressure, heat, or impact, leading to costly replacements and potential safety risks.
Lexan, a high-performance polycarbonate material, is widely used across aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries. Its exceptional strength, transparency, and heat resistance make it ideal for demanding applications where traditional plastics fail.

Aerospace and Aviation Applications
The aerospace industry demands materials that can perform under extreme conditions. In my experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve provided numerous Lexan components for aerospace applications.
Cabin Windows and Cockpit Displays
Lexan’s optical clarity11 makes it perfect for aircraft windows and display covers. Its impact resistance exceeds that of traditional acrylic materials by 250 times, while maintaining excellent visibility.
Interior Components
- Overhead storage bins
- Seat components
- Cabin dividers
- Emergency exit signs
Automotive Industry Implementation
The automotive sector relies heavily on Lexan for both functional and aesthetic components. Here’s a breakdown of common applications:
| Component Type | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Headlight Lenses | UV resistance, clarity | Front/rear lighting systems |
| Body Panels | Impact resistance, lightweight | Fenders, spoilers |
| Interior Parts | Flame retardant, durability | Dashboard components |
| Windows | Safety, weight reduction | Side windows, sunroofs |
Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical field, Lexan’s properties make it invaluable for various applications:
Diagnostic Equipment
- Medical imaging device housings
- Laboratory equipment
- Analytical instruments
- Surgical tool components
Patient Care Equipment
The material’s ability to withstand sterilization processes while maintaining structural integrity is crucial for:
- IV equipment housings
- Respiratory devices
- Monitoring equipment enclosures
- Surgical lighting covers
Electronics and Consumer Devices
Protection and Enclosures
At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with electronics manufacturers who choose Lexan for:
- Smartphone cases
- Laptop housings
- Display screens
- Security equipment enclosures
Industrial Electronics
| Application | Key Requirements | Lexan Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Control Panels | Impact resistance | Maintains integrity under stress |
| Display Covers | Optical clarity | Clear viewing, scratch resistant |
| Equipment Housing | Heat resistance | Stable up to 240°F |
| Safety Shields | Durability | Long-lasting protection |
Construction and Architecture
The construction industry utilizes Lexan in various applications:
Structural Elements
- Skylights
- Greenhouse panels
- Sound barriers
- Security glazing
Safety Applications
- Bulletproof windows
- Security barriers
- Machine guards
- Safety shields
Sports and Recreation Equipment
Lexan’s durability makes it ideal for:
- Protective gear
- Sports eyewear
- Helmet visors
- Swimming pool enclosures
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial settings, Lexan serves multiple purposes:
Safety Equipment
- Machine guards
- Safety shields
- Protective barriers
- Emergency vehicle windows
Process Equipment
- Chemical processing vessels
- Sight glasses
- Control panel covers
- Industrial lighting fixtures
The versatility of Lexan in these industries stems from its unique combination of properties:
| Property | Benefit | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Strength | 250x stronger than glass | Reduced replacement costs |
| Temperature Resistance | -40°F to 240°F stability | Wide application range |
| UV Protection | Minimal yellowing | Extended product life |
| Chemical Resistance | Maintains properties | Reliable performance |
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed expertise in processing Lexan for various applications. Our advanced manufacturing capabilities ensure precise tolerances and consistent quality across all industries we serve. From prototype to production, we help clients leverage Lexan’s properties for their specific applications.
Regular maintenance and proper handling are essential for maximizing Lexan’s performance. Our technical team provides guidance on:
- Proper cleaning procedures
- Installation techniques
- Environmental considerations
- Performance optimization
Can Lexan Be Easily Machined For Custom Parts?
Many manufacturers struggle with machining Lexan parts due to its unique properties. I’ve seen countless projects derailed by warping, melting, and stress cracking during the machining process, leading to wasted materials and missed deadlines.
Yes, Lexan can be machined for custom parts, but it requires specific techniques and parameters. The key is maintaining proper cutting speeds, using sharp tools, and implementing adequate cooling to prevent thermal damage. With the right approach, Lexan machining can deliver excellent results.

Understanding Lexan’s Properties
Lexan, also known as polycarbonate, possesses unique characteristics that directly impact its machinability. The material’s viscoelastic behavior12 makes it both an opportunity and challenge for manufacturing professionals. I’ve found that understanding these properties is crucial for successful machining:
Physical Properties
- High impact resistance
- Optical clarity
- Heat resistance
- Dimensional stability
- UV resistance
Essential Machining Parameters
When machining Lexan at our PTSMAKE facility, we follow specific parameters that consistently deliver superior results:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 300-500 ft/min | Varies with thickness |
| Feed Rate | 0.005-0.015 in/rev | Adjust based on finish requirements |
| Tool Relief Angle | 5-15 degrees | Prevents material drag |
| Cooling Method | Air or mist | Avoid flood coolant |
Common Machining Operations
Milling
Milling Lexan requires careful attention to tool selection and cutting parameters. At PTSMAKE, we use specialized carbide end mills with specific geometries designed for plastics. Key considerations include:
- Using sharp, polished cutting edges
- Maintaining consistent chip load
- Implementing proper chip evacuation
- Monitoring heat generation
Drilling
Successful drilling of Lexan involves:
- Using specially designed plastic drilling bits
- Starting with pilot holes
- Implementing peck drilling for deeper holes
- Maintaining steady feed rates
Turning
When turning Lexan parts, consider:
- Using positive rake angles
- Maintaining sharp cutting tools
- Implementing proper chip breaking
- Controlling spindle speed
Common Challenges and Solutions
Heat Management
Excessive heat is one of the biggest challenges in Lexan machining. Solutions include:
- Using compressed air cooling
- Taking lighter cuts
- Implementing proper feed rates
- Allowing cooling periods between operations
Surface Finish
To achieve optimal surface finish:
- Select appropriate cutting tools
- Use proper cutting speeds
- Implement correct feed rates
- Consider post-machining treatments
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent quality in Lexan machining:
- Regular tool inspection and replacement
- Dimensional verification during machining
- Surface finish monitoring
- Stress testing when applicable
Material Handling and Storage
Proper material handling significantly impacts machining success:
- Store in climate-controlled environment
- Protect from UV exposure
- Handle with clean gloves
- Maintain proper storage orientation
Industry Applications
Lexan machined parts find applications in various industries:
Aerospace
- Instrument panels
- Window components
- Interior components
Medical
- Equipment housings
- Protective shields
- Diagnostic equipment components
Industrial
- Machine guards
- Control panels
- Protective barriers
Best Practices for Success
Based on our experience at PTSMAKE, following these best practices ensures successful Lexan machining:
- Always use sharp tools
- Maintain consistent cutting parameters
- Implement proper cooling methods
- Verify material condition before machining
- Monitor part temperature during operations
Cost Considerations
Several factors influence Lexan machining costs:
| Factor | Impact | Optimization Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Grade | High | Select appropriate grade |
| Tool Wear | Medium | Use optimal cutting parameters |
| Machine Time | High | Efficient programming |
| Setup Requirements | Medium | Standardize procedures |
Future Trends
The future of Lexan machining is evolving with:
- Advanced CNC technology integration
- Improved cutting tool materials
- Enhanced cooling systems
- Automated quality control
Project Planning
For successful Lexan machining projects:
- Define clear specifications
- Select appropriate tools and parameters
- Create detailed machining strategy
- Implement quality control measures
- Document process parameters
Through careful attention to these aspects and leveraging our expertise at PTSMAKE, we consistently achieve high-quality results in Lexan machining. The key is understanding the material’s unique properties and implementing appropriate machining strategies.
Learn how thermoplastic polymers enhance product durability and safety in various industries. ↩
Learn about thermoplastic polymers to understand their unique properties and applications in protective materials. ↩
Learn how Lexan’s molecular structure impacts its strength and versatility in various applications. ↩
Learn how polymer chains improve impact resistance in materials for enhanced engineering design. ↩
Learn about this material’s properties to make informed decisions for your projects. ↩
Learn about Lexan’s thermal resistance for effective material selection in high-temperature applications. ↩
Learn about Lexan’s crystalline structure for better machining outcomes and improved part durability. ↩
Understanding this helps ensure proper processing parameters for effective injection molding. ↩
Discover how crystalline morphology enhances Lexan’s performance in extreme conditions for better material choice. ↩
Learn about polycarbonate thermoplastic’s benefits for cost-effective long-term manufacturing solutions. ↩
Optical clarity refers to the material’s ability to transmit light with minimal distortion or loss, making it ideal for applications requiring clear visibility. ↩
Learn how viscoelastic behavior affects machining efficiency and material properties in Lexan. ↩