In my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen many clients confused about overmolding and 2K injection molding. It’s like choosing between a sandwich and a burger – they might look similar, but each serves different needs.
Overmolding involves injecting material over an existing part in two separate processes, while 2K (two-shot) injection molding creates multi-material products in a single machine cycle. They differ in process steps, cost, and end applications.


Let me share what I’ve learned from working with hundreds of clients at PTSMAKE. Both these processes can create amazing multi-material products, but choosing the right one can save you time and money. I’ll explain the key differences, show you real examples, and help you decide which process fits your project best.
What is Overmolding?
Have you ever wondered how your phone case combines hard plastic with soft, grippy surfaces? Or why modern medical devices feel both sturdy and comfortable? The secret lies in overmolding technology.
Overmolding is a manufacturing process where we inject a second material over an existing first material to create a single, multi-material component. This technique combines different materials’ properties to enhance product functionality, durability, and user experience.
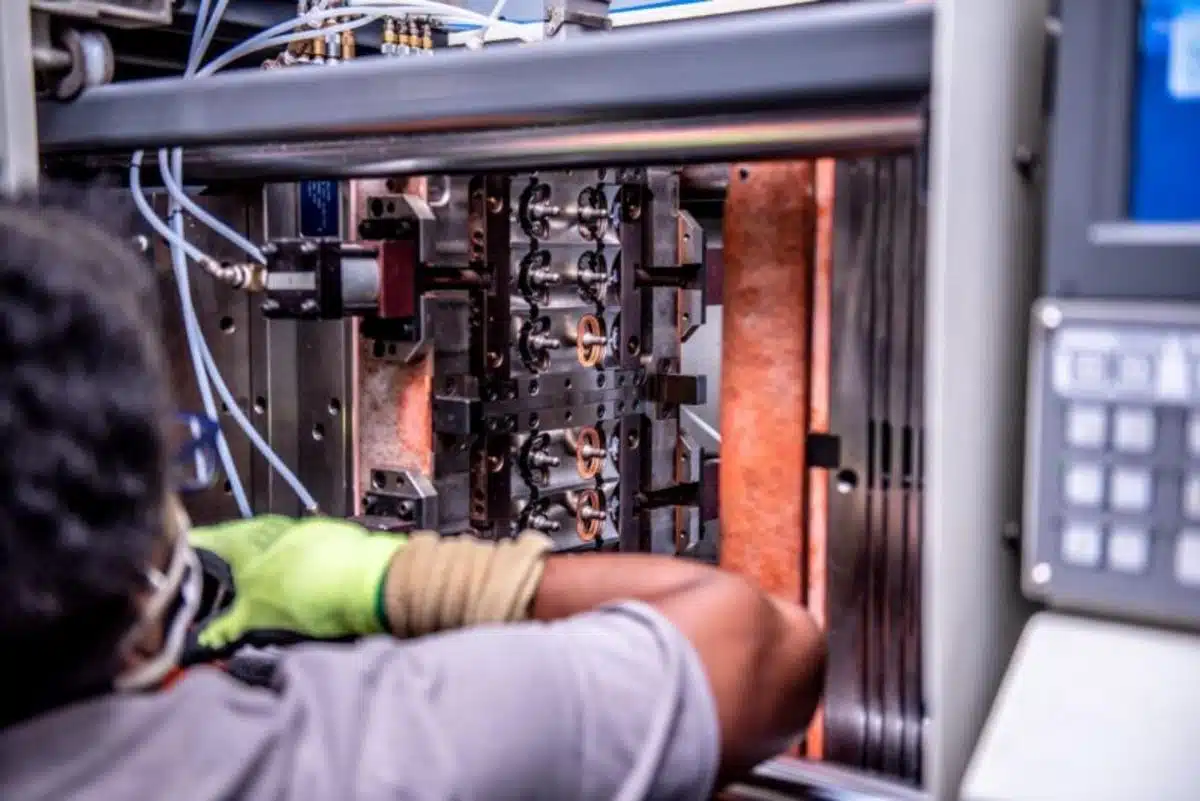

Understanding the Basics of Overmolding
In my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve witnessed overmolding revolutionize product design across various industries. This process typically involves two main components: a rigid substrate (usually a thermoplastic) and an overmolded material (often a softer, more flexible material like TPE or rubber).
The process works in two stages:
- First, we create the base component through traditional injection molding
- Then, we inject the second material over specific areas of the base component
Key Benefits of Overmolding
Based on our extensive experience working with clients across different industries, I’ve identified several crucial advantages:
| Benefit | Description | Real-world Example |
|---|---|---|
| Enhanced Ergonomics | Soft-touch surfaces improve grip and user comfort | Power tool handles |
| Improved Durability | Shock absorption and vibration dampening | Electronic device cases |
| Design Flexibility | Multiple color and material combinations | Consumer product housings |
| Cost Efficiency | Eliminates assembly steps and reduces parts | Medical device components |
| Environmental Sealing | Creates waterproof and dustproof barriers | Outdoor equipment |
Material Combinations and Compatibility
One of the most critical aspects I’ve learned in overmolding is material selection. Here are the most common combinations we use at PTSMAKE:
Hard Substrate Materials:
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
- PC (Polycarbonate)
- Nylon
- PP (Polypropylene)
Overmolding Materials:
- TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer)
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
- Silicone
- Soft PVC
Industry Applications
During my career, I’ve seen overmolding transform various industries:
Medical Devices
- Surgical instruments with improved grip
- Wearable devices combining rigid housings with comfortable skin contact surfaces
- Medical equipment handles with antimicrobial properties
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphone and tablet cases
- Gaming controller grips
- Waterproof electronic enclosures
Automotive Components
- Dashboard controls
- Interior trim pieces
- Gear shift knobs
Design Considerations
When designing for overmolding, I always advise our clients to consider:
Material Compatibility
- Chemical bonding properties
- Thermal expansion rates
- Processing temperature requirements
Geometric Features
- Wall thickness variations
- Undercuts and draft angles
- Gate locations
Production Requirements
- Volume expectations
- Cost constraints
- Quality standards
Common Challenges and Solutions
Through my experience, I’ve encountered several challenges in overmolding:
| Challenge | Solution | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Adhesion | Material compatibility testing | Improved product durability |
| Flash Formation | Optimized tool design | Better aesthetic quality |
| Dimensional Stability | Proper cooling time calculation | Enhanced precision |
| Cost Management | Strategic material selection | Improved profitability |
Quality Control in Overmolding
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous quality control measures:
Pre-production Testing
- Material compatibility verification
- Mold flow analysis
- Prototype evaluation
In-process Controls
- Temperature monitoring
- Pressure verification
- Cycle time optimization
Post-production Inspection
- Visual inspection
- Adhesion testing
- Dimensional verification
Through my years of experience in the industry, I’ve seen overmolding evolve from a niche process to a mainstream manufacturing solution. Its ability to combine different materials in a single component while reducing assembly costs and improving product performance makes it an invaluable tool in modern manufacturing.
What is 2K Injection Molding?
Have you ever wondered how those sleek smartphone cases with soft-grip sections are made in one piece? Or how your car’s dashboard combines hard plastic with soft-touch materials seamlessly?
2K injection molding is an advanced manufacturing process that injects two different materials or colors into a single mold sequentially, creating complex parts with multiple properties in one production cycle, eliminating the need for assembly.
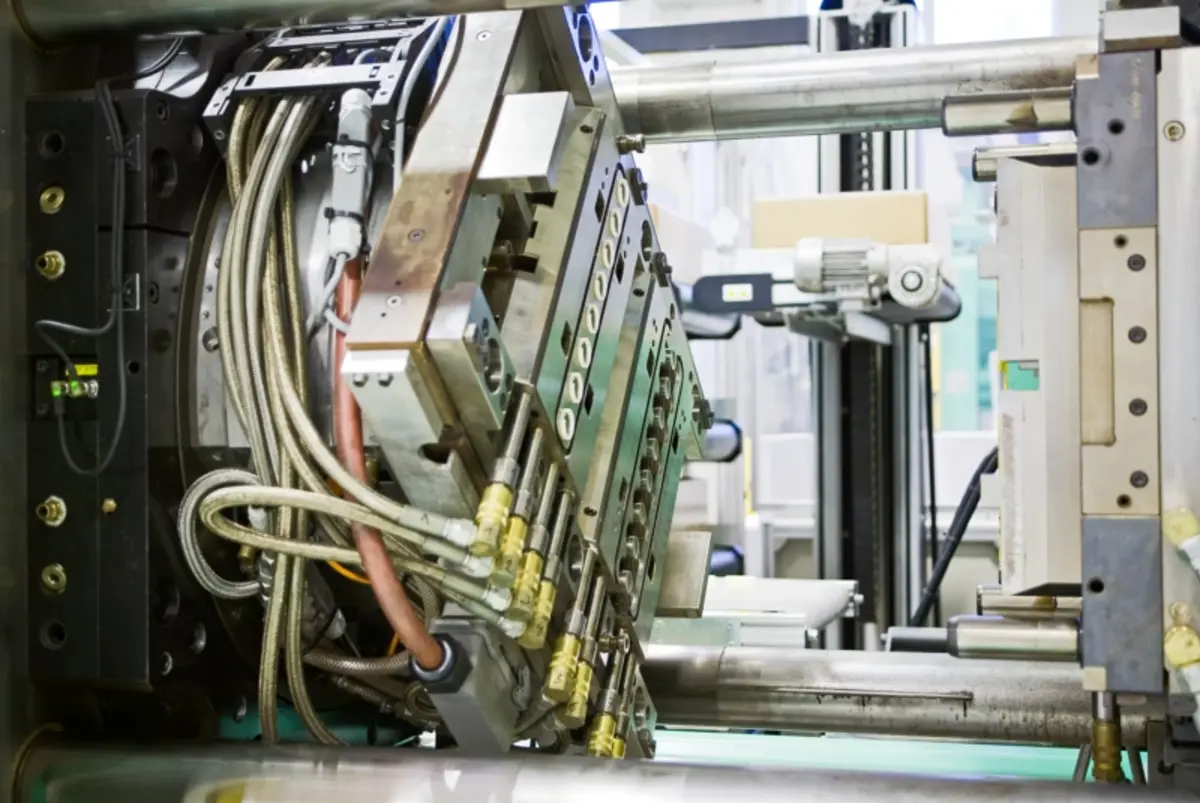

The Basic Mechanism of 2K Molding
In my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve overseen countless 2K injection molding projects. The process starts with injecting the first material (usually a rigid plastic) into the mold cavity. Then, either by rotating the mold or using a robot, we inject the second material into another cavity. The two materials bond chemically or mechanically during the cooling process.
Key Components of 2K Injection Molding
| Component | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Injection Unit | Processes first material | Forms base structure |
| Secondary Injection Unit | Processes second material | Adds functional/aesthetic features |
| Rotating Mold System | Enables material transfer | Ensures precise alignment |
| Control System | Manages timing and sequence | Maintains quality consistency |
Material Compatibility and Selection
One crucial aspect I always emphasize to our clients is material compatibility. Not all materials bond well together. Through our experience, we’ve developed a comprehensive material pairing guide:
| Primary Material | Compatible Secondary Materials | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PC | TPE, TPU, Silicone | Electronics housings |
| ABS | TPE, TPU, SEBS | Automotive components |
| PA | TPE, TPU | Tool handles |
| PP | TPE, TPU, SEBS | Consumer goods |
Advantages Over Traditional Molding
From my experience working with global manufacturers, 2K injection molding offers several distinct benefits:
Production Efficiency
- Eliminates assembly steps
- Reduces labor costs
- Shortens production cycles by 25-40%
Quality Improvements
- Better material bonding
- Reduced defect rates
- Consistent part quality
Design Flexibility
- Complex geometries possible
- Multiple color combinations
- Varying material properties in one part
Industry Applications
Based on our work at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen 2K injection molding excel in various sectors:
Automotive Industry
- Dashboard components
- Gear shifters
- Interior trim pieces
- Light housings
Consumer Electronics
- Smartphone cases
- Remote controls
- Gaming controllers
- Wearable devices
Medical Devices
- Surgical instruments
- Drug delivery devices
- Diagnostic equipment
- Medical device housings
Technical Considerations
When implementing 2K injection molding, several factors require careful attention:
Process Parameters
- Injection pressure control
- Material temperature management
- Cycle time optimization
- Cooling time coordination
Design Guidelines
- Wall thickness ratios
- Gate locations
- Material flow paths
- Bonding surface area
Quality Control Measures
- Visual inspection protocols
- Bond strength testing
- Dimensional accuracy checks
- Surface finish evaluation
Cost Implications
Through our years of experience, I’ve observed that while initial tooling costs for 2K molding are higher, the long-term benefits often justify the investment:
| Cost Factor | Impact | ROI Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Tooling | 30-50% higher than traditional | 6-12 months |
| Labor | 40-60% lower | Immediate |
| Material Waste | 20-30% reduction | 3-6 months |
| Quality Control | 25-35% lower rejection rates | 3-6 months |
Process Limitations and Solutions
Even with its advantages, 2K injection molding has certain limitations that we’ve learned to address:
Material Constraints
- Limited material combinations
- Temperature compatibility issues
- Bonding strength variations
Design Restrictions
- Minimum wall thickness requirements
- Gate location limitations
- Part size constraints
Cost Considerations
- Higher initial investment
- Complex mold design
- Specialized equipment needs
Through careful planning and material selection, these limitations can be effectively managed to achieve optimal results.
How Does Overmolding Differ from 2K Injection Molding?
After 15+ years in plastic injection molding, I’ve seen countless clients confused between overmolding and 2K injection molding, often leading to costly project delays and rework.
Overmolding and 2K injection molding are distinct manufacturing processes. Overmolding uses two separate molding steps in sequence, while 2K injection molding combines both steps into a single cycle using specialized equipment.
Process Workflow Differences
In my daily operations at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that understanding the workflow is crucial. Let me break down the key differences:
Overmolding Process
- First step: Create the base component (substrate)
- Second step: Transfer to another mold or machine
- Final step: Mold the second material over the substrate
- Total time: Usually 20-45 minutes for the complete cycle
2K Injection Molding Process
- Single machine operation
- Automated rotation between shots
- Continuous molding cycle
- Total time: Typically 30-60 seconds per part
Equipment Requirements
Based on my experience managing both processes, here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Type | Standard injection molding machine | Specialized multi-component machine |
| Tool Complexity | Simple, separate molds | Complex, integrated mold system |
| Setup Time | Longer, multiple setups | Shorter, single setup |
| Investment Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher machine and tooling costs |
Material Compatibility Considerations
I’ve helped numerous clients select the right materials for their projects. Here’s what you need to know:
Overmolding Material Options
- More flexible material combinations
- Better for incompatible materials
- Allows time for proper bonding
- Can use adhesion promoters
2K Molding Material Requirements
- Materials must be chemically compatible
- Similar processing temperatures needed
- Limited material combination options
- Faster bonding requirements
Design Considerations
Through my years of project management, I’ve identified these critical design factors:
Overmolding Design Benefits
- More complex geometries possible
- Better control over interface thickness
- Easier to modify designs
- More forgiving tolerance requirements
2K Molding Design Limitations
- Restricted by tool movement
- Need for precise gate locations
- Limited undercuts possible
- Tighter tolerance requirements
Cost Implications
Let me share some insights from our pricing discussions:
Overmolding Costs
- Lower tooling investment
- Higher labor costs
- Increased handling costs
- Better for lower volumes
2K Molding Costs
- Higher initial investment
- Lower labor costs
- Reduced handling costs
- More economical for high volumes
Quality Considerations
In my quality control experience:
Overmolding Quality Aspects
- Better control over each layer
- Easier inspection between steps
- More consistent bonding
- Lower reject rates in complex parts
2K Molding Quality Factors
- Faster cycle times can affect bonding
- More difficult to inspect interfaces
- Higher consistency in simple parts
- Better for high-volume consistency
Application Selection Guide
Based on thousands of projects I’ve overseen:
Best for Overmolding
- Medical devices requiring certified materials
- Complex electronic enclosures
- Soft-touch handles and grips
- Low to medium production volumes
Best for 2K Molding
- Automotive components
- High-volume consumer products
- Simple two-color applications
- Parts requiring fast production cycles
Through my extensive experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve learned that choosing between overmolding and 2K injection molding isn’t just about technical capabilities – it’s about understanding your specific project needs, production volumes, and quality requirements. Each process has its unique advantages, and success lies in making an informed choice based on your particular application.
What are the Advantages and Limitations of Overmolding?
As a manufacturing expert with 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen countless projects where overmolding seemed perfect on paper but brought unexpected challenges in reality.
Overmolding is a manufacturing process that combines multiple materials into a single part, offering benefits like improved grip and reduced assembly needs, but it also comes with challenges such as longer production cycles and material bonding issues.

Key Advantages of Overmolding
Enhanced Product Functionality
In my experience working with major electronics manufacturers, overmolding has proven invaluable for improving product grip and feel. Here’s what I’ve observed:
- Soft-touch grips on power tools
- Non-slip surfaces on medical devices
- Ergonomic handles on consumer products
Reduced Assembly Requirements
One of the most significant benefits I’ve seen is the elimination of multiple assembly steps:
- No need for mechanical fasteners
- Fewer individual components
- Reduced labor costs
- Lower risk of assembly errors
Improved Product Protection
The sealing capabilities of overmolding are remarkable:
- Water-resistant barriers
- Protection against dust and debris
- Vibration dampening
- Enhanced durability in harsh environments
| Protection Type | Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Seal | Prevents water ingress | Outdoor electronics |
| Impact Protection | Absorbs shock | Mobile devices |
| Chemical Resistance | Guards against corrosion | Industrial equipment |
| Thermal Insulation | Temperature management | Hand tools |
Limitations and Challenges
Extended Production Cycles
From my manufacturing floor experience:
- Setup times are longer
- Additional quality checks needed
- Multiple material handling requirements
- Cooling time between shots
Cost Considerations
The financial impact includes:
- Higher initial tooling investment
- Secondary operation costs
- Material compatibility testing
- Increased quality control measures
Technical Challenges
Material Bonding Issues
I’ve encountered these common problems:
- Poor adhesion between materials
- Thermal expansion mismatches
- Chemical compatibility concerns
- Surface preparation requirements
Design Limitations
Key restrictions include:
- Material thickness constraints
- Gate location limitations
- Complex geometry challenges
- Tool design considerations
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Material Compatibility | Risk of delamination | Extensive material testing |
| Tool Design | Higher complexity | Advanced CAD simulation |
| Quality Control | Increased inspection needs | Automated vision systems |
| Production Speed | Longer cycle times | Process optimization |
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Consumer Electronics
In our work with major electronics manufacturers:
- Soft-touch buttons on remote controls
- Waterproof seals for outdoor devices
- Impact-resistant casings for mobile phones
Medical Devices
Our medical device projects demonstrate:
- Ergonomic surgical tool handles
- Chemical-resistant equipment housings
- Sterilization-compatible components
Automotive Applications
Common automotive uses include:
- Interior trim components
- Weatherproof electrical connectors
- Vibration-dampening mounts
Best Practices for Successful Overmolding
Based on my experience managing thousands of projects:
Material Selection
- Thorough compatibility testing
- Temperature resistance verification
- Chemical resistance evaluation
Design Optimization
- Proper gate location planning
- Wall thickness consideration
- Draft angle implementation
Process Control
- Temperature monitoring
- Pressure optimization
- Cycle time management
Quality Assurance
- Visual inspection protocols
- Bond strength testing
- Dimensional verification
Through my years at PTSMAKE, I’ve learned that successful overmolding requires careful balance between these advantages and limitations. While the benefits can be substantial, careful planning and expertise are essential for achieving optimal results. I always advise our clients to thoroughly evaluate their specific requirements against these factors before committing to an overmolding solution.
What are the Advantages and Limitations of 2K Injection Molding?
Are you struggling to decide if 2K injection molding is right for your project? After 15+ years in the industry, I’ve seen both the incredible benefits and challenging limitations of this technology.
2K injection molding offers fast production cycles and strong material bonding, but comes with high initial equipment costs and is best suited for high-volume production. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making informed manufacturing decisions.
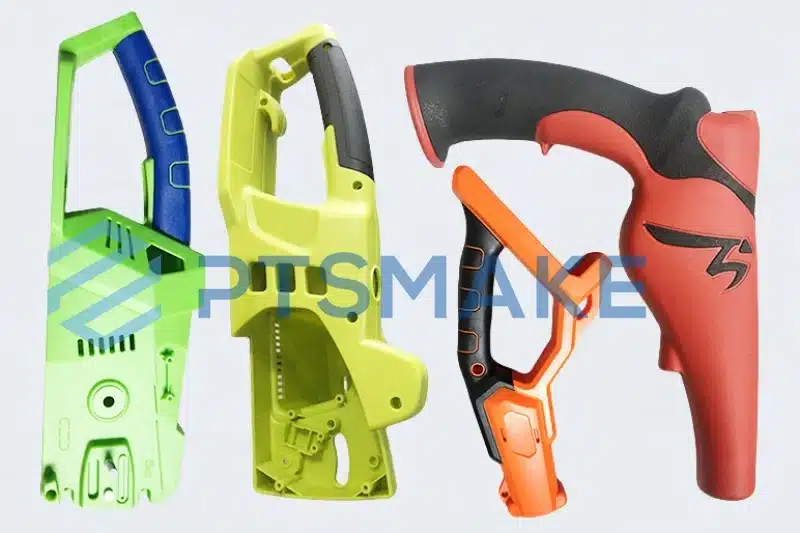

Key Advantages of 2K Injection Molding
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve identified several significant benefits that make 2K injection molding stand out:
Efficient Production Cycles
The integration of two materials in a single molding cycle significantly reduces production time. In our facility, we’ve achieved:
| Traditional Process | 2K Molding Process | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|
| 45-60 seconds/part | 25-35 seconds/part | Up to 40% |
Superior Material Bonding
Unlike traditional assembly methods, 2K molding creates a molecular bond between materials. This results in:
- Higher structural integrity
- Better resistance to environmental factors
- Reduced risk of component separation
- Improved product longevity
Enhanced Design Flexibility
The ability to combine different materials opens up new design possibilities:
- Multi-color combinations
- Soft-touch overlays
- Integrated seals and gaskets
- Complex geometries
Limitations and Challenges
High Initial Investment
From my experience managing production lines, the initial costs can be substantial:
| Investment Category | Approximate Cost Range |
|---|---|
| 2K Molding Machine | $150,000 – $500,000 |
| Custom Tooling | $25,000 – $100,000 |
| Setup and Training | $10,000 – $30,000 |
Volume Requirements
2K molding becomes cost-effective primarily in high-volume production:
- Minimum recommended annual volume: 100,000+ units
- Optimal production range: 250,000+ units
- Break-even point typically requires significant production runs
Technical Complexities
In my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed several technical challenges:
- Material compatibility requirements
- Complex tool design needs
- Precise process control demands
- Specialized operator training requirements
Real-World Applications
Automotive Industry
We’ve successfully implemented 2K molding for:
- Dashboard components with soft-touch surfaces
- Multi-color indicator lights
- Integrated seals in electrical connectors
- Weather-resistant exterior trim
Consumer Electronics
Our experience includes:
- Smartphone cases with rubber grips
- Gaming controller components
- Waterproof device housings
- Multi-color indicator lights
Medical Devices
Critical applications include:
- Surgical instruments with ergonomic grips
- Medical device housings with integrated seals
- Drug delivery devices with multiple materials
- Laboratory equipment components
Process Optimization Strategies
Based on our manufacturing experience, I recommend:
Material Selection
- Conduct thorough material compatibility testing
- Consider shrinkage rates of both materials
- Evaluate cost-effectiveness of material combinations
Tool Design
- Implement proper venting and cooling channels
- Design optimal gate locations
- Account for material flow patterns
Quality Control
- Implement automated inspection systems
- Establish clear quality parameters
- Maintain strict process documentation
Cost Management
- Optimize cycle times
- Minimize material waste
- Implement predictive maintenance
- Train operators effectively
Through years of working with various clients at PTSMAKE, I’ve learned that success in 2K injection molding requires careful consideration of these factors. While the technology offers remarkable advantages in terms of production efficiency and product quality, it’s essential to carefully evaluate whether the benefits justify the initial investment and ongoing operational requirements for your specific application.
The key is to thoroughly analyze your production requirements, material specifications, and long-term manufacturing strategy before committing to 2K injection molding. In many cases, the technology’s advantages can provide a significant competitive edge, but only when properly aligned with your manufacturing goals and production volumes.
Which Industries Benefit Most from Overmolding?
Are you wondering which industries can truly maximize the potential of overmolding? After 15+ years in manufacturing, I’ve seen remarkable transformations across various sectors.
Overmolding technology primarily benefits four key industries: medical devices, consumer electronics, automotive, and handheld tools. These sectors leverage overmolding to enhance product functionality, improve user experience, and increase durability while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
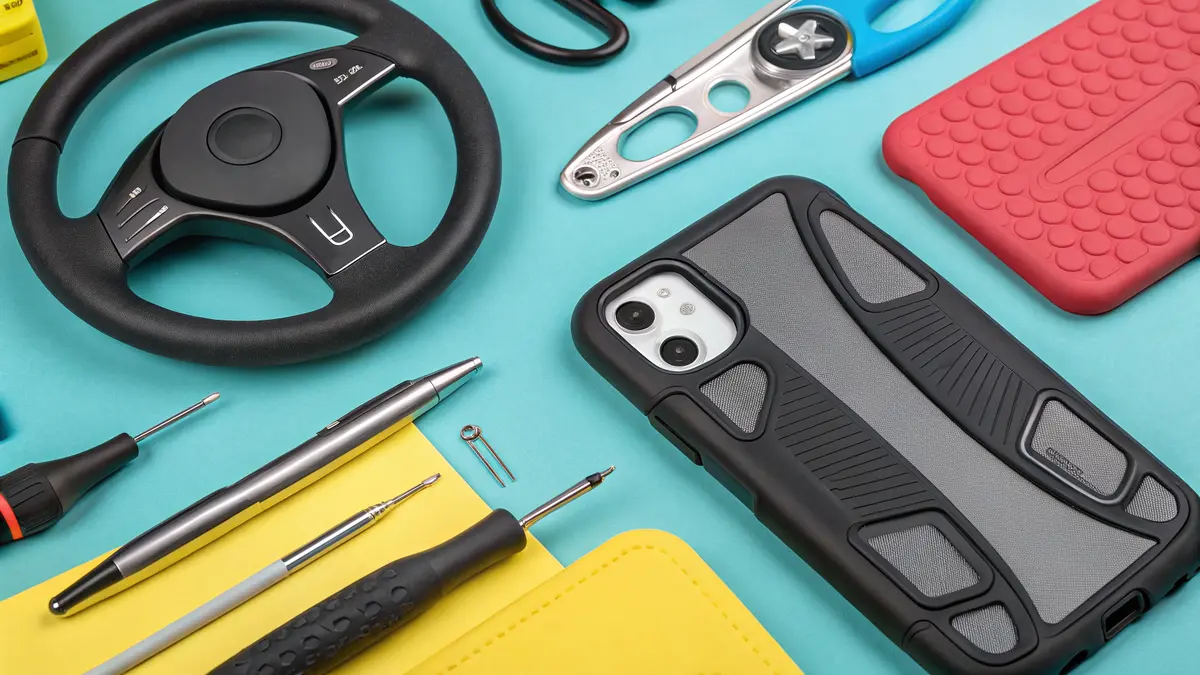

Medical Industry Applications
In my experience working with medical device manufacturers, overmolding has revolutionized medical equipment design. Medical devices require precise grip, comfort, and sterilization capabilities. Here are some key applications:
- Surgical instruments with ergonomic handles
- Medical syringes with enhanced grip
- Dental tools with comfortable grips
- Medical device enclosures with sealing properties
The medical industry particularly values overmolding because it creates seamless, bacteria-resistant surfaces that are easy to clean and sterilize.
Consumer Electronics Impact
The consumer electronics sector has embraced overmolding for both protective and aesthetic purposes. I’ve seen countless examples where this technology has improved product durability and user experience:
| Product Category | Overmolding Benefits |
|---|---|
| Smartphone Cases | Impact resistance, grip enhancement |
| Earbuds | Comfort, water resistance |
| Remote Controls | Durability, shock absorption |
| Gaming Controllers | Ergonomic grip, sweat resistance |
Automotive Industry Integration
The automotive sector represents one of the largest markets for overmolding. From my collaboration with major automotive manufacturers, I’ve observed these critical applications:
Interior Components
- Dashboard controls
- Door handles
- Center console elements
- Steering wheel grips
External Parts
- Weather seals
- Gaskets
- Cable connectors
- Trim components
Handheld Tools Revolution
Working with tool manufacturers has shown me how overmolding has transformed the power and hand tool industry:
Power Tools
- Drill handles with vibration dampening
- Saw grips with enhanced safety features
- Impact driver housings with improved durability
- Electric screwdriver handles with better control
Hand Tools
- Screwdriver handles with ergonomic design
- Plier grips with comfort features
- Wrench handles with non-slip properties
- Hammer grips with shock absorption
Cross-Industry Benefits
Through my years at PTSMAKE, I’ve identified several universal advantages that overmolding brings to these industries:
Enhanced Functionality
- Better grip and control
- Improved sealing properties
- Vibration dampening
- Impact resistance
Aesthetic Improvements
- Custom color options
- Texture variations
- Brand differentiation
- Premium look and feel
Cost Efficiency
- Reduced assembly steps
- Lower labor costs
- Decreased production time
- Minimal waste
User Experience
- Improved ergonomics
- Better tactile feedback
- Enhanced safety features
- Greater comfort
Manufacturing Considerations
Based on our extensive experience with diverse clients, I’ve found these key factors crucial for successful overmolding implementation:
| Consideration | Impact |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Determines bond strength and performance |
| Design Optimization | Affects manufacturing efficiency |
| Quality Control | Ensures consistent results |
| Cost Management | Influences market competitiveness |
Through working with various industries, I’ve learned that successful overmolding applications require careful consideration of:
- Material Compatibility
- Design Requirements
- Production Volume
- Environmental Conditions
- Regulatory Compliance
The success of overmolding in these industries demonstrates its versatility and effectiveness. Having overseen countless projects, I can confidently say that when properly implemented, overmolding provides significant competitive advantages in terms of product quality, user satisfaction, and manufacturing efficiency.
Which Industries Benefit Most from 2K Injection Molding?
Are you wondering which industries are leading the 2K injection molding revolution? After 15+ years in manufacturing, I’ve seen remarkable transformations across various sectors.
2K injection molding has become a game-changer in automotive, consumer electronics, and medical industries. These sectors benefit from reduced assembly costs, enhanced product functionality, and improved production efficiency through this advanced manufacturing process.
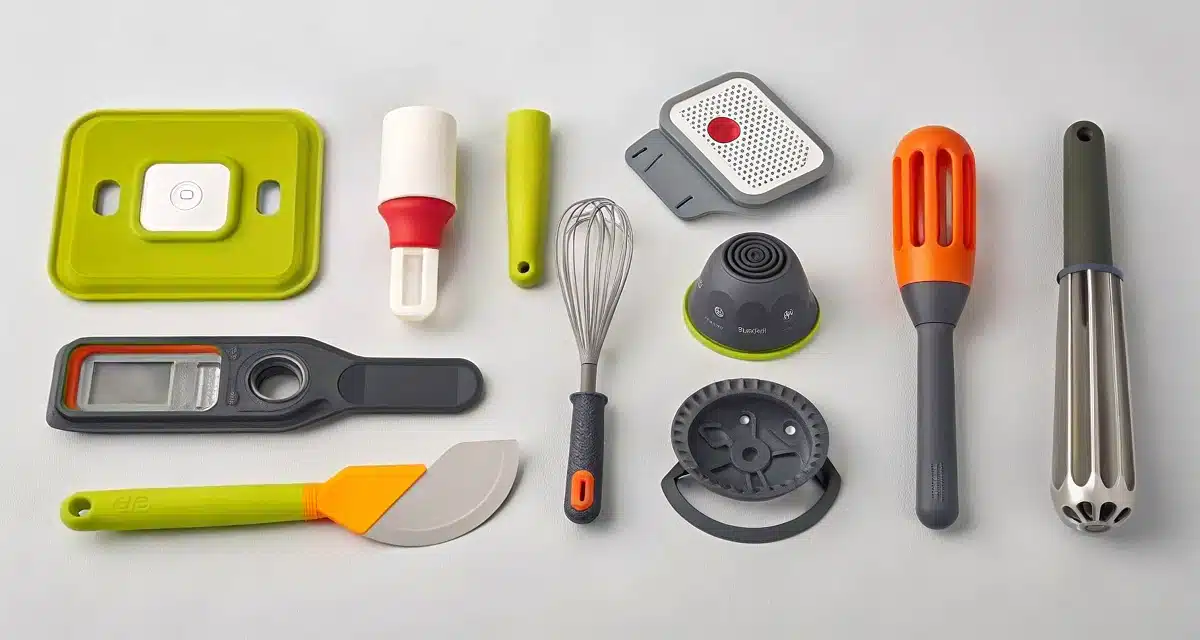

Automotive Industry Applications
In my experience working with major automotive manufacturers, 2K injection molding has revolutionized interior component production. The automotive sector benefits from:
- Multi-material dashboard components
- Soft-touch steering wheel controls
- Illuminated button assemblies
- Weather-resistant exterior trim
The integration of hard and soft materials in a single process has significantly reduced assembly time and improved part quality. For example, a door handle with integrated soft-grip material now takes 40% less time to produce compared to traditional methods.
Consumer Electronics Evolution
The electronics industry has embraced 2K molding for:
| Component Type | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Button Assemblies | Multi-color options, improved tactile feel | Mobile phones, remote controls |
| Device Housings | Waterproof sealing, aesthetic appeal | Smart devices, wearables |
| Control Panels | Enhanced durability, integrated displays | Home appliances, gaming consoles |
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical sector particularly benefits from 2K molding’s ability to create:
- Ergonomic surgical instruments with soft-grip handles
- Multi-component diagnostic devices
- Sealed medical housings with integrated gaskets
I’ve seen sterilization-compatible materials combined with comfortable grip surfaces, reducing manufacturing steps while improving product safety.
Home Appliance Innovations
Modern appliances utilize 2K molding for:
- Control panel interfaces
- Sealed water-resistant components
- Ergonomic handles and grips
- Decorative elements with functional properties
Personal Care Products
The personal care industry leverages 2K molding for:
- Toothbrush handles with grip zones
- Razor handles combining rigid structure with soft touch
- Cosmetic packaging with multiple material properties
Cost Benefits Across Industries
From my manufacturing experience, I’ve observed these key advantages:
Reduced Assembly Costs
- Elimination of secondary operations
- Lower labor requirements
- Decreased inventory management needs
Production Efficiency
- Faster cycle times
- Reduced scrap rates
- Improved quality consistency
Design Freedom
- Integration of multiple functions
- Enhanced aesthetic options
- Better ergonomic solutions
Quality and Performance Improvements
The implementation of 2K molding has led to:
| Aspect | Traditional Molding | 2K Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Assembly Steps | 3-4 steps | 1 step |
| Cycle Time | 45-60 seconds | 25-35 seconds |
| Defect Rate | 2-3% | <1% |
| Material Bond Strength | Moderate | High |
Environmental Impact
2K injection molding offers environmental benefits through:
- Reduced waste from eliminated assembly steps
- Lower energy consumption in production
- Decreased transportation needs for components
- Improved product longevity
When I work with clients across these industries, I consistently see 15-20% cost savings compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The ability to combine materials in a single process not only improves efficiency but also enables innovative design solutions that weren’t previously possible.
Through my years at PTSMAKE, I’ve witnessed the transformation of manufacturing processes across these sectors. The adoption of 2K injection molding continues to grow as more industries recognize its benefits in reducing costs, improving quality, and enabling innovative design solutions.
For companies considering 2K injection molding, it’s crucial to understand that success depends on proper material selection, tool design, and process control. The initial investment in 2K technology is often offset by long-term savings in production costs and improved product quality.
What Material Combinations Are Possible in Overmolding?
Have you ever wondered why your toothbrush handle feels soft while the head remains rigid? Or how your power tool has that perfect grippy surface? That’s overmolding magic at work.
Overmolding allows for various material combinations, primarily including thermoplastic-elastomer pairs, metal-plastic combinations, and multi-thermoplastic assemblies. The success depends on material compatibility, surface preparation, and proper bonding techniques.
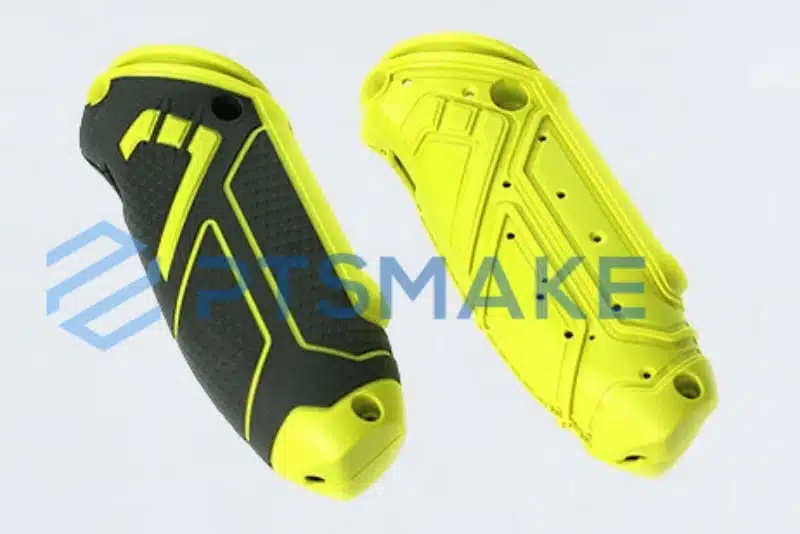

Common Material Combinations
Based on my 15+ years of experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve worked with numerous material combinations. Here are the most common ones:
Thermoplastic-Elastomer Combinations
The most popular combination we use is thermoplastic substrates with thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). These pairs offer excellent bonding properties and versatility. Here’s a typical compatibility table we use:
| Substrate Material | Compatible TPE | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PP | TPE-S, TPV | Consumer products, automotive parts |
| ABS | TPE-S, TPU | Electronic housings, handles |
| PC | TPE-U, TPE-E | Medical devices, tools |
| PA | TPE-E, TPU | Industrial components |
| PBT | TPE-E, TPU | Electrical connectors |
Metal-Plastic Combinations
When combining metals with plastics, surface treatment becomes crucial. I’ve seen many projects fail due to poor surface preparation. The key materials we commonly use include:
- Aluminum with engineered thermoplastics
- Stainless steel with high-performance polymers
- Brass with specialty grades of nylon
Multi-Thermoplastic Systems
This is where things get interesting. We can combine different thermoplastics to achieve specific properties:
- PC/ABS combinations for improved impact resistance
- PBT/PET blends for enhanced chemical resistance
- PA/PP systems for cost-effective strength
Critical Factors for Successful Bonding
Material Compatibility
From my experience, chemical compatibility is the foundation of successful overmolding. Here’s what we consider:
- Chemical structure similarity
- Melting temperature ranges
- Molecular chain interaction potential
- Surface energy characteristics
Surface Preparation Techniques
I’ve learned that proper surface preparation can make or break an overmolding project:
| Preparation Method | Best For | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Treatment | Metals, high-performance plastics | Excellent |
| Corona Treatment | Most thermoplastics | Very Good |
| Chemical Etching | Metals, difficult-to-bond plastics | Good |
| Mechanical Abrasion | Metal substrates | Moderate |
Advanced Bonding Solutions
In my work at PTSMAKE, we’ve developed several approaches to enhance bonding:
Primer Applications
- Use of specialized primers for incompatible materials
- Development of custom primer formulations
- Application of surface-specific treatments
Mechanical Interlocking
- Design of undercuts and channels
- Creation of micro-texture patterns
- Implementation of dovetail features
Process Parameters
Based on our manufacturing data:- Mold temperature control within ±5°C
- Injection pressure optimization
- Cycle time adjustments for different material combinations
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Over my years in the industry, I’ve encountered various challenges:
Delamination Prevention
To prevent separation between layers:
Material Selection Considerations
- Check compatibility charts
- Verify temperature resistance
- Test chemical resistance
Process Control
- Monitor injection speeds
- Control cooling rates
- Maintain consistent pressure
Quality Control Measures
We implement strict quality controls:
| Test Method | Parameter Measured | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Pull Test | Bond strength | Every batch |
| Cross-section Analysis | Interface quality | Weekly |
| Environmental Testing | Long-term durability | Monthly |
| Chemical Resistance | Material integrity | Per project |
Through my experience, I’ve found that successful overmolding requires a deep understanding of material properties and processing parameters. At PTSMAKE, we continuously update our material combination database and processing parameters to ensure optimal results for our clients.
This comprehensive approach to material selection and processing has helped us achieve a 98% success rate in our overmolding projects, with minimal instances of bond failure or quality issues. Remember, the key is not just selecting compatible materials, but also understanding how to process them correctly.
What Material Combinations Are Possible in 2K Injection Molding?
After 15+ years in injection molding, I’ve seen countless clients struggle with choosing the right material combinations for their 2K projects. Let me share what actually works.
Two-component (2K) injection molding allows specific material combinations like rigid-to-soft plastics or multi-colored hard materials. Common pairings include ABS with TPE, PC with ABS, and various other compatible thermoplastics that create strong chemical bonds.
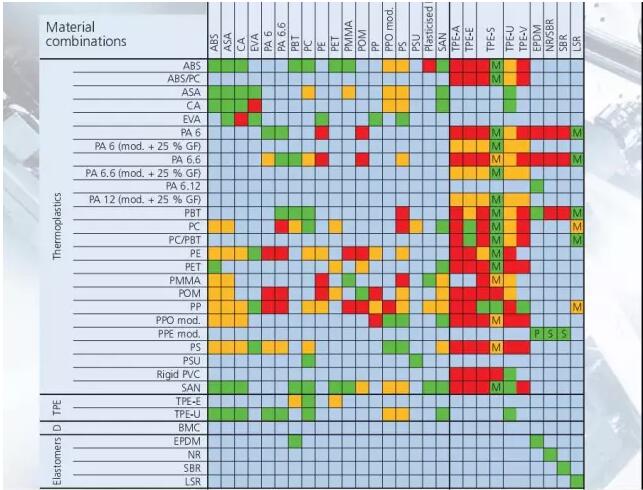
Common Compatible Material Combinations
In my daily work at PTSMAKE, I frequently recommend these proven material combinations to our clients:
| Base Material | Compatible Overmold Material | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | TPE/TPU | Power tool grips, consumer electronics |
| PC | ABS | Automotive parts, electronics housings |
| PA | TPE/TPU | Mechanical components, sports equipment |
| PP | TPE/TPU | Consumer products, medical devices |
| PBT | TPE/TPU | Electrical connectors, automotive parts |
Hard-Hard Material Combinations
When working with hard-hard combinations, I’ve found these pairings particularly effective:
PC/ABS Combination
- Excellent mechanical properties
- High impact resistance
- Good chemical resistance
- Common in automotive and electronics industries
PA/PBT Combination
- Superior strength characteristics
- Good dimensional stability
- Enhanced thermal resistance
- Widely used in mechanical components
Soft-Hard Material Combinations
Based on my experience with hundreds of projects, these combinations offer the best results:
ABS/TPE Configuration
- Strong bond strength
- Excellent surface finish
- Good flexibility in the soft component
- Perfect for ergonomic applications
PC/TPU Setup
- High durability
- Superior impact resistance
- Excellent wear properties
- Ideal for outdoor applications
Chemical Bonding Considerations
Through my years of experience, I’ve learned that successful 2K molding relies heavily on proper chemical bonding:
Material Compatibility
- Molecular structure alignment
- Similar melting temperatures
- Compatible chemical properties
Processing Parameters
- Melt temperature control
- Injection pressure optimization
- Cooling time management
Design Optimization Strategies
Here are key strategies I’ve developed over my career:
Interface Design
- Maximize contact area
- Create mechanical interlocks
- Ensure proper material flow
Part Geometry
- Consider shrinkage rates
- Plan for differential thermal expansion
- Design appropriate wall thickness transitions
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement these essential quality checks:
Physical Testing
- Bond strength evaluation
- Impact resistance testing
- Environmental stress testing
Visual Inspection
- Surface finish quality
- Color consistency
- Part dimension verification
Industry-Specific Applications
Different sectors require specific material combinations:
Automotive Industry
- PC/ABS for interior components
- PA/TPE for exterior trim
- PBT/TPU for functional parts
Consumer Electronics
- ABS/TPE for handheld devices
- PC/ABS for housings
- PA/TPE for protective components
Medical Devices
- PP/TPE for ergonomic handles
- PC/TPU for equipment housings
- PBT/TPE for device components
Through my extensive experience with 2K injection molding, I’ve learned that successful material combination selection requires careful consideration of:
- End-use requirements
- Environmental conditions
- Manufacturing constraints
- Cost considerations
- Regulatory compliance
The key to successful 2K injection molding lies in understanding not just the material properties, but also how these materials interact during the molding process. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed extensive expertise in optimizing these material combinations to achieve the best possible results for our clients’ specific applications.
What Are the Key Design Considerations for Overmolding?
In my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen countless overmolding projects fail due to poor design considerations. One recent project taught me that success lies in the details of initial design planning.
Successful overmolding design requires careful attention to draft angles, material thickness consistency, and shrinkage rates. The key is creating proper mechanical interlocks while ensuring material compatibility between the substrate and overmold components.
Essential Draft Angles and Wall Thickness
After working with thousands of overmolding projects, I’ve learned that proper draft angles are crucial. I recommend a minimum draft angle of 1-2° for most applications, but complex geometries may require up to 5°. The right draft angle ensures:
- Easy part ejection from the mold
- Reduced wear on tooling
- Consistent part quality
- Lower production costs
Wall thickness uniformity is equally important. I always advise my clients to maintain a consistent wall thickness ratio between the substrate and overmold material, typically between 1:1 and 1:3.
Material Selection and Shrinkage Management
Here’s a breakdown of common material combinations and their shrinkage rates:
| Substrate Material | Overmold Material | Typical Shrinkage Rate | Compatibility Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | TPE | 0.004-0.006 in/in | Excellent |
| PC | TPU | 0.005-0.007 in/in | Very Good |
| PP | TPE | 0.015-0.025 in/in | Good |
| Nylon | TPV | 0.008-0.012 in/in | Moderate |
| PBT | LSR | 0.002-0.004 in/in | Excellent |
Mechanical Interlocking Strategies
Based on my experience, successful mechanical interlocking requires three key elements:
- Undercuts – I typically design these at 0.5-1.0mm depth
- Surface texturing – Using 0.1-0.3mm deep patterns
- Dovetail features – With 15-30° angles for optimal grip
Chemical Bonding Optimization
Material adhesion is critical for durability. I’ve developed this process for optimal bonding:
Surface preparation
- Plasma treatment
- Chemical primers when needed
- Clean, contamination-free surfaces
Processing parameters
- Temperature control within ±5°C
- Proper pressure settings
- Optimal cycle times
Geometric Design Constraints
When designing overmolded parts, I always consider these geometric limitations:
- Corner radii – Minimum 0.5mm for internal corners
- Gate location – At least 1.5x material thickness from critical features
- Parting line placement – Away from cosmetic surfaces
- Venting requirements – 0.02-0.03mm depth for proper air escape
Processing Window Considerations
From my years of experience, I’ve found these processing parameters crucial:
Temperature control
- Substrate material temperature
- Overmold material temperature
- Mold temperature
Pressure settings
- Injection pressure
- Hold pressure
- Back pressure
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent quality, I implement these checks:
Visual inspection
- Complete coverage
- No voids or gaps
- Surface finish quality
Physical testing
- Adhesion strength
- Impact resistance
- Environmental stress testing
Design Optimization Tips
Here are my proven strategies for optimal design:
Material flow analysis
- Use simulation software
- Identify potential problems
- Optimize gate locations
Prototype testing
- Validate design concepts
- Test mechanical properties
- Verify assembly fit
Production considerations
- Tool maintenance access
- Cycle time optimization
- Cost-effective manufacturing
The success of overmolding design depends on understanding and implementing these key considerations. Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve learned that paying attention to these details early in the design phase prevents costly issues during production and ensures high-quality, durable parts that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Remember, successful overmolding isn’t just about following design rules – it’s about understanding how these elements work together to create a superior product. By carefully considering each aspect I’ve outlined, you’ll be well-equipped to design successful overmolded components that deliver both functionality and value.
What Are the Key Design Considerations for 2K Injection Molding?
Have you ever wondered why some 2K molded products fail while others succeed? After 15+ years in injection molding, I’ve seen how proper design can make or break a project.
Two-component (2K) injection molding requires careful consideration of material compatibility, part geometry, gating location, and mold design. Success depends on understanding these critical factors and implementing proper design strategies from the start.
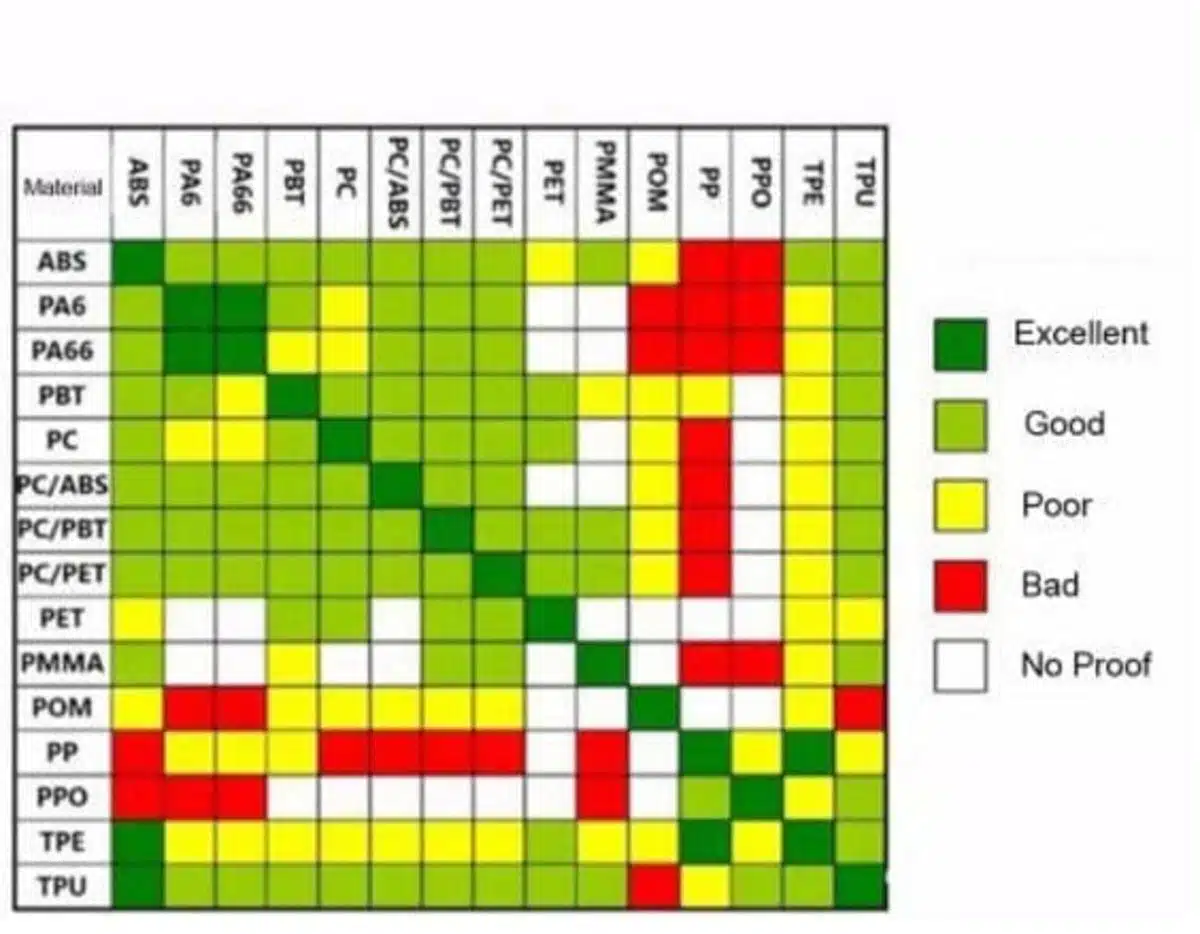
Material Compatibility Considerations
From my experience working with countless 2K projects at PTSMAKE, material selection is the foundation of successful 2K molding. The two materials must have:
- Compatible melting temperatures
- Similar shrinkage rates
- Good adhesion properties
- Chemical compatibility
Here’s a detailed compatibility table I’ve developed over years of testing:
| Material 1 | Material 2 | Compatibility Level | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PC | TPE | Excellent | Consumer electronics |
| ABS | TPE | Very Good | Automotive parts |
| PA | TPE | Good | Tool handles |
| PP | TPE | Fair | Consumer goods |
| POM | TPE | Poor | Not recommended |
Design Guidelines for Interlocking Features
When designing interlocking features, I always emphasize these key points to our clients:
- Minimum wall thickness ratio between materials should be 1:1.5
- Avoid sharp corners in interface areas
- Design proper mechanical interlocks
- Include sufficient overlap between materials
Gate Location and Flow Analysis
Based on my extensive experience, proper gate location is crucial for 2K molding success. I recommend:
Primary material gate location:
- Place gates in thick sections
- Maintain balanced flow paths
- Consider weld line locations
Secondary material considerations:
- Ensure complete filling of cavities
- Minimize pressure drops
- Account for material viscosity differences
Part Ejection Strategy
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific guidelines for successful part ejection:
Draft angles:
- Primary material: minimum 1.5°
- Secondary material: minimum 2°
Surface texture considerations:
- Smooth surfaces: increase draft angles by 1°
- Textured surfaces: increase draft angles by 2°
Cycle Time Optimization
To achieve efficient cycle times, I always focus on:
Temperature control:
- Optimize cooling channel layout
- Balance cooling between materials
- Monitor interface temperature
Process parameters:
- Adjust injection speeds
- Control holding pressures
- Optimize cooling times
Cost Reduction Strategies
Based on my experience managing hundreds of 2K projects, here are effective ways to reduce costs:
Design optimization:
- Minimize material usage
- Simplify part geometry
- Reduce cycle time
Material selection:
- Choose cost-effective materials
- Consider regrind usage
- Optimize material properties
Manufacturing Considerations
When designing for 2K injection molding, I always consider these manufacturing aspects:
Mold design:
- Proper venting
- Efficient runner systems
- Balanced filling
Process control:
- Temperature monitoring
- Pressure optimization
- Quality control measures
Over my 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that successful 2K injection molding requires a holistic approach. Each aspect – from material selection to manufacturing considerations – plays a crucial role in achieving high-quality parts. The key is to address these design considerations early in the development process.
Design validation through simulation and prototyping is essential. We always recommend conducting flow analysis and testing different material combinations before full production. This approach has helped us achieve consistent quality while minimizing costs for our clients.
Remember, 2K injection molding is a complex process that requires expertise and attention to detail. By following these design considerations and working with experienced manufacturers, you can maximize the chances of project success and achieve optimal results.
Which Process is Better for Your Project?
Are you struggling to choose between overmolding and 2K injection molding for your next project? After 15+ years in manufacturing, I’ve helped countless clients make this crucial decision.
Both overmolding and 2K injection molding offer unique advantages, but your choice should depend on specific factors like production volume, part complexity, material compatibility, and budget. Let me guide you through making the right decision.
Production Volume Considerations
In my experience working with various clients at PTSMAKE, production volume is often the first factor to consider. Here’s how both processes compare:
| Production Volume | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Low Volume (<10,000 units) | More cost-effective | Higher initial costs |
| Medium Volume (10,000-100,000) | Moderate efficiency | Good efficiency |
| High Volume (>100,000) | Labor-intensive | Most cost-effective |
Part Complexity Analysis
When it comes to part complexity, I’ve observed some clear distinctions between these processes:
| Complexity Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Complexity | Limited by manual handling | Highly complex possible |
| Material Combinations | Wide range possible | Limited to compatible materials |
| Surface Details | Excellent | Very good |
| Internal Features | Limited | Advanced capabilities |
Material Requirements and Compatibility
Based on my 15+ years of manufacturing experience, material selection plays a crucial role:
| Material Aspect | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Range | Broader selection | Limited to compatible pairs |
| Bond Strength | Variable | Excellent |
| Chemical Resistance | Depends on materials | Generally better |
| Temperature Resistance | Good | Excellent |
Cost Structure Breakdown
Let me share what I’ve learned about the financial aspects of both processes:
| Cost Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Tooling | Lower | Higher |
| Per-Part Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Labor Costs | Higher | Lower |
| Material Waste | Moderate | Minimal |
Production Time and Efficiency
In my time at PTSMAKE, I’ve noticed significant differences in production efficiency:
| Time Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Cycle Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Setup Time | Shorter | Longer |
| Changeover Time | Moderate | Longer |
| Overall Efficiency | Moderate | High |
Quality and Consistency
Quality control is crucial, and here’s what I’ve observed:
| Quality Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Part Consistency | Good | Excellent |
| Defect Rate | Higher | Lower |
| Bond Strength | Variable | Consistent |
| Surface Finish | Excellent | Very good |
Design Flexibility
From my experience working with various projects:
| Design Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Design Changes | More flexible | Less flexible |
| Material Combinations | More options | Limited options |
| Geometry Freedom | Moderate | High |
| Prototype Options | Better | Limited |
Environmental Impact
Sustainability is increasingly important:
| Environmental Factor | Overmolding | 2K Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Material Waste | More | Less |
| Energy Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Recyclability | Variable | Better |
| Process Emissions | Higher | Lower |
Making Your Decision
Based on my extensive experience, here’s a simplified decision framework:
Choose Overmolding when:
- You need maximum material combination flexibility
- Your production volume is lower
- You require frequent design changes
- Budget for initial tooling is limited
Choose 2K Injection Molding when:
- You have high production volumes
- Part consistency is crucial
- You need shorter cycle times
- Long-term cost efficiency is priority
I recently helped a client choose between these processes for their medical device component. They initially leaned toward overmolding due to lower upfront costs. However, after analyzing their annual production volume of 500,000 units, we determined that 2K injection molding would reduce their per-part cost by 40% and improve consistency, making it the better choice despite higher initial tooling costs.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. At PTSMAKE, we evaluate each project individually, considering all these factors to recommend the most suitable process for our clients’ specific needs.
Future Trends in Overmolding and 2K Injection Molding?
As a manufacturing expert with 15+ years in injection molding, I’ve seen dramatic changes. But what’s coming next will revolutionize how we think about overmolding and 2K molding processes.
The future of overmolding and 2K injection molding is moving towards smart manufacturing, with integrated sensors, sustainable materials, and AI-driven process optimization. These advances will enable faster production times and more complex designs while reducing environmental impact.
Sustainable Material Innovation
In my experience at PTSMAKE, material innovation is rapidly changing. We’re seeing new developments that were unimaginable just a few years ago:
- Bio-based polymers from renewable sources
- Recycled materials with enhanced properties
- Self-healing polymers for longer product life
- Smart materials that respond to environmental changes
Our team has successfully tested several new sustainable materials, showing promising results for both performance and environmental impact.
Smart Manufacturing Integration
The integration of smart technology is transforming traditional molding processes:
| Technology | Current Application | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|
| IoT Sensors | Process monitoring | Predictive maintenance |
| AI Systems | Quality control | Autonomous operation |
| Digital Twins | Design optimization | Real-time adjustments |
| Cloud Computing | Data collection | Complete process automation |
Advanced Mold Design Evolution
Modern mold design is becoming more sophisticated:
- Conformal cooling channels
- Topology-optimized structures
- 3D-printed mold inserts
- Dynamic venting systems
I’ve personally overseen projects where these advances reduced cycle times by 35% while improving part quality.
Industry 4.0 Implementation
The integration of Industry 4.0 principles is reshaping our approach:
- Real-time process monitoring
- Automated quality control systems
- Digital workflow management
- Predictive maintenance schedules
Hybrid Manufacturing Solutions
At PTSMAKE, we’re exploring combinations of traditional and new technologies:
- Additive + injection molding
- In-mold assembly solutions
- Multi-material combinations
- Automated post-processing
Enhanced Design Capabilities
New design possibilities are emerging:
- Complex geometries
- Integrated electronics
- Variable material properties
- Micro-feature molding
Eco-friendly Process Innovations
Sustainability is becoming central to molding operations:
- Energy-efficient systems
- Closed-loop material recycling
- Water conservation methods
- Waste reduction strategies
Last year, our facility reduced energy consumption by 25% through these innovations.
Production Speed Optimization
Several factors are driving faster production:
| Factor | Impact | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| AI-driven cycle optimization | 30% faster | 1-2 years |
| Advanced cooling systems | 40% reduction | 6-12 months |
| Automated part handling | 50% efficiency gain | 3-6 months |
| Smart material flow control | 20% improvement | 1 year |
Quality Control Advancement
Modern quality control is evolving with:
- In-mold sensors
- Computer vision systems
- AI-powered defect detection
- Real-time process adjustment
Cost Efficiency Improvements
New technologies are making production more cost-effective:
- Reduced material waste
- Lower energy consumption
- Decreased labor costs
- Minimal quality issues
We’ve seen ROI periods shrink from 24 months to just 12 months with these improvements.
Industry-Specific Adaptations
Different sectors are driving unique innovations:
- Medical: Clean room integration
- Automotive: Lightweight solutions
- Electronics: EMI shielding
- Aerospace: High-performance materials
After working with various industries, I’ve noticed each sector pushes technology in different directions, creating a rich ecosystem of innovations.
These trends represent my observations from 15+ years in the industry and our ongoing work at PTSMAKE. The future of overmolding and 2K injection molding is bright, with continuous improvements in efficiency, sustainability, and capability. The key to success will be staying adaptable and embracing these new technologies while maintaining focus on quality and customer needs.
I believe the next decade will bring even more dramatic changes, and companies that prepare now will be best positioned to benefit from these advances. At PTSMAKE, we’re already implementing many of these innovations, ensuring we stay at the forefront of manufacturing technology.







