Have you ever experienced sudden hydraulic system failures that brought your entire production line to a halt? These breakdowns often trace back to failing end caps, leading to fluid leaks, pressure loss, and costly downtime. Without proper understanding of these critical components, you’re essentially gambling with your equipment’s reliability and your operation’s efficiency.
Hydraulic cylinder end caps are specialized mechanical components that seal both ends of a hydraulic cylinder. They play a crucial role in containing hydraulic fluid, maintaining system pressure, and providing structural support for the entire cylinder assembly.
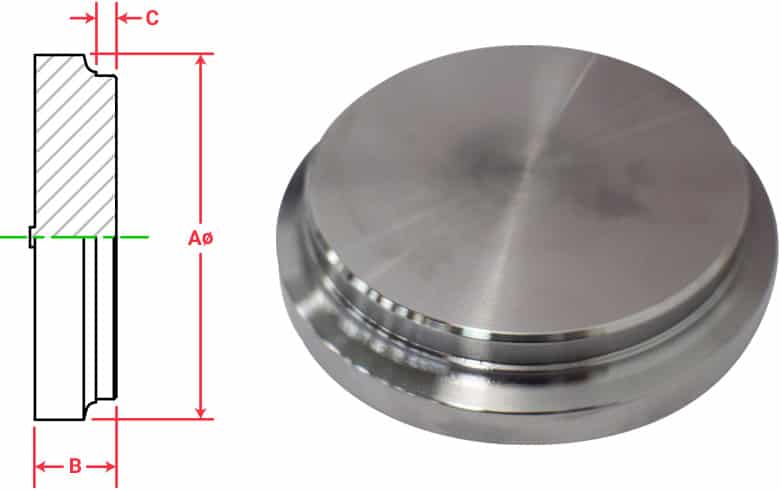

Understanding the Basic Structure
End caps are more complex than they might appear at first glance. The main body typically includes mounting points, fluid ports, and precision-machined surfaces for sealing elements. In my experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve found that the metallurgical composition1 of these components significantly impacts their performance and longevity.
These components usually feature:
- Threaded or bolted mounting points
- Precision-machined sealing surfaces
- Port connections for hydraulic fluid
- Internal grooves for sealing elements
Types of End Cap Designs
Different applications require different end cap configurations. Here are the main types we commonly manufacture:
Threaded End Caps
- Most common in medium-pressure applications
- Offers excellent sealing capabilities
- Easy maintenance and replacement
- Cost-effective manufacturing process
Bolted End Caps
- Preferred for high-pressure systems
- Superior structural integrity
- Better load distribution
- Enhanced safety features
Welded End Caps
- Permanent installation
- Maximum pressure rating
- Minimal maintenance required
- Highest sealing reliability
Critical Design Considerations
| Design Factor | Impact | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Determines strength and durability | High |
| Surface Finish | Affects sealing performance | Critical |
| Port Configuration | Influences flow characteristics | Medium |
| Mounting Method | Impacts maintenance accessibility | High |
| Temperature Rating | Determines operational limits | Critical |
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process significantly influences end cap performance. At PTSMAKE, we employ various techniques:
-
CNC Machining
- Ensures precise dimensional accuracy
- Creates smooth sealing surfaces
- Allows for complex port configurations
- Maintains consistent quality
-
Surface Treatment
- Enhances wear resistance
- Improves corrosion protection
- Extends service life
- Optimizes sealing performance
Performance Factors and Testing
Quality assurance is crucial for end cap reliability. Key testing parameters include:
Pressure Testing
- Static pressure hold tests
- Dynamic cycle testing
- Burst pressure verification
- Leak detection procedures
Material Verification
- Hardness testing
- Chemical composition analysis
- Dimensional inspection
- Surface finish measurement
Common Applications
End caps serve various industries:
- Heavy Construction Equipment
- Mining Machinery
- Agricultural Equipment
- Industrial Manufacturing
- Marine Systems
- Aerospace Applications
Maintenance Considerations
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance:
-
Inspection Points
- Check for external leakage
- Monitor mounting security
- Examine seal condition
- Verify port integrity
-
Preventive Measures
- Regular torque verification
- Seal replacement schedule
- Surface cleaning procedures
- Port protection methods
Industry Standards and Specifications
End caps must meet various standards:
- ISO hydraulic standards
- NFPA guidelines
- SAE specifications
- Industry-specific requirements
These standards ensure:
- Safety compliance
- Performance reliability
- Interchangeability
- Quality consistency
Through my experience in precision manufacturing, I’ve learned that successful hydraulic system operation heavily depends on end cap quality. The key lies in understanding not just the component itself, but how it integrates into the larger system. Proper material selection, precise manufacturing, and regular maintenance are essential for optimal performance and longevity.
What Materials Are Used for End Caps?
Choosing the wrong material for hydraulic cylinder end caps can lead to catastrophic system failures and costly downtimes. I’ve witnessed many cases where improper material selection resulted in premature wear, corrosion issues, and even complete system breakdowns. These problems often surface at the most inconvenient times, causing production delays and safety concerns.
End caps for hydraulic cylinders are primarily manufactured using aluminum, stainless steel, cast iron, or composite materials. Each material offers specific advantages in terms of strength, corrosion resistance, weight, and cost-effectiveness, making material selection crucial for optimal performance.

Traditional Metal Materials
Cast Iron End Caps
Cast iron remains one of the most widely used materials for end caps due to its excellent compression strength and vibration dampening properties. At PTSMAKE, we often recommend cast iron for heavy-duty applications where stability is crucial. The material’s metallurgical structure2 provides superior wear resistance and thermal stability.
Key benefits include:
- Excellent vibration absorption
- High compressive strength
- Cost-effective for large-scale production
- Good thermal conductivity
Stainless Steel Options
Stainless steel end caps offer exceptional corrosion resistance and strength. They are particularly suitable for harsh environments and applications requiring strict hygiene standards. The material’s durability makes it ideal for:
- Marine applications
- Food processing equipment
- Chemical processing systems
- High-pressure systems
Modern Alternatives
Aluminum Solutions
Aluminum end caps have gained popularity due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. These components offer:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lightweight | Reduced overall system weight |
| Corrosion Resistant | Minimal maintenance requirements |
| Heat Dissipation | Better thermal management |
| Cost-Effective | Lower transportation costs |
Composite Materials
Modern composite materials represent the cutting edge in end cap manufacturing. These materials combine:
- High strength
- Lightweight properties
- Chemical resistance
- Design flexibility
Material Selection Criteria
Environmental Considerations
The operating environment plays a crucial role in material selection:
| Environment | Recommended Material |
|---|---|
| Marine | Stainless Steel |
| Industrial | Cast Iron |
| Aerospace | Aluminum |
| Chemical Plants | Composite/Stainless Steel |
Pressure Requirements
Material selection must account for system pressure:
- Low Pressure (<1000 psi): Aluminum or composites
- Medium Pressure (1000-3000 psi): Cast iron
- High Pressure (>3000 psi): Stainless steel or high-grade cast iron
Temperature Factors
Different materials handle temperature variations differently:
| Temperature Range | Suitable Materials |
|---|---|
| -40°C to 0°C | Stainless Steel |
| 0°C to 100°C | All Materials |
| >100°C | Cast Iron, Special Alloys |
Cost Considerations
Material costs vary significantly:
- Cast Iron: Most economical for large volumes
- Aluminum: Mid-range pricing, good value
- Stainless Steel: Higher initial cost, excellent longevity
- Composites: Premium pricing, specialized applications
Performance Optimization
To maximize end cap performance:
- Match material properties to application requirements
- Consider the entire system’s operating conditions
- Factor in maintenance requirements
- Evaluate life-cycle costs versus initial investment
The key to successful material selection lies in understanding the specific application requirements and environmental conditions. For instance, a food processing plant might require stainless steel for sanitary reasons, while a construction equipment manufacturer might opt for cast iron due to its durability and cost-effectiveness.
I always advise our clients to consider future operating conditions and potential system upgrades when selecting materials. This forward-thinking approach helps prevent costly modifications later. By carefully evaluating these factors, we can ensure that the end caps not only meet current requirements but also provide reliable service throughout their expected lifetime.
How Are Hydraulic Cylinder End Caps Manufactured?
Manufacturing hydraulic cylinder end caps with inconsistent quality can lead to catastrophic system failures, causing expensive downtime and safety hazards. Many manufacturers struggle with choosing the right production method, often resulting in components that don’t meet precise specifications or fail prematurely.
Hydraulic cylinder end caps are manufactured through various processes including CNC machining, casting, forging, and injection molding. Each method offers unique advantages for different production requirements, with CNC machining being the most common for its precision and flexibility.
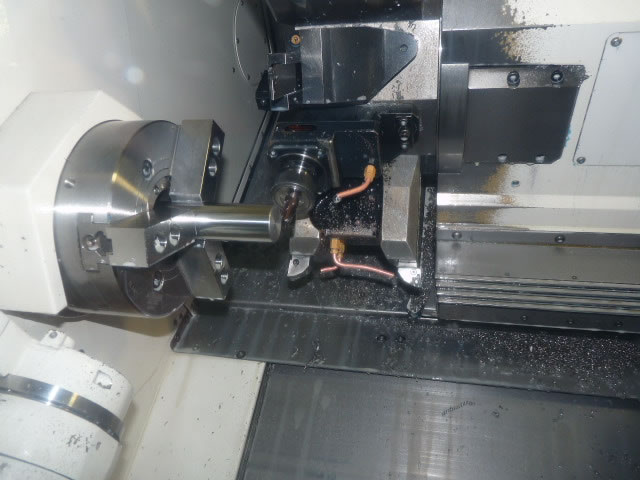

CNC Machining Process
CNC machining remains the primary method for producing hydraulic cylinder end caps. This process utilizes computer-controlled cutting tools to remove material from metal blocks, creating precise components. At PTSMAKE, we frequently employ multi-axis machining3 for complex end cap geometries.
The process typically involves:
- Material selection (usually steel or aluminum)
- CAD/CAM programming
- Initial rough cutting
- Precision finishing
- Quality inspection
Key advantages include:
- Exceptional dimensional accuracy (±0.002")
- Excellent surface finish
- No tooling costs
- Suitable for both prototypes and production
Casting Methods
Die casting and sand casting offer cost-effective solutions for high-volume production. The process involves:
| Casting Type | Advantages | Limitations | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High production rate, Good surface finish | Higher tooling costs | Large volume production |
| Sand Casting | Lower tooling costs, Design flexibility | Rougher surface finish | Complex geometries |
| Investment Casting | Excellent detail, Smooth finish | Higher unit cost | Precision components |
Forging Techniques
Forging produces end caps with superior strength characteristics through controlled deformation of metal. The process includes:
- Heating the metal billet
- Shaping using dies
- Heat treatment
- Final machining
Benefits of forging:
- Enhanced material strength
- Improved grain structure
- Better fatigue resistance
- Reduced material waste
Injection Molding Applications
For specific applications requiring lightweight materials, injection molding offers:
- Consistent part quality
- High production rates
- Cost-effective for large volumes
- Excellent surface finish
The process requires:
- Material selection (engineering plastics)
- Mold design and fabrication
- Process parameter optimization
- Quality control
Quality Control Measures
Ensuring end cap quality involves multiple inspection steps:
-
Dimensional Verification
- CMM measurements
- Laser scanning
- Thread gauge testing
-
Material Testing
- Hardness testing
- Chemical composition analysis
- Non-destructive testing
-
Performance Validation
- Pressure testing
- Leak testing
- Load capacity verification
Material Selection Guidelines
| Material | Pressure Rating | Cost Factor | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High | Low | Moderate |
| Stainless Steel | High | High | Excellent |
| Aluminum | Medium | Medium | Good |
| Engineering Plastics | Low | Low | Excellent |
Manufacturing Cost Considerations
Several factors influence end cap manufacturing costs:
-
Production Volume
- Low volume: CNC machining preferred
- High volume: Casting or forging optimal
-
Material Costs
- Raw material selection
- Processing requirements
- Waste reduction strategies
-
Equipment Investment
- Machine capabilities
- Tooling requirements
- Maintenance costs
Quality control is crucial throughout the manufacturing process. We implement statistical process control (SPC) to monitor key parameters and ensure consistent quality. Regular calibration of measuring equipment and operator training are essential components of our quality system.
The choice of manufacturing method depends on several factors:
- Production volume requirements
- Cost constraints
- Performance specifications
- Material requirements
- Surface finish needs
- Dimensional accuracy requirements
For optimal results, manufacturers should consider:
- Application requirements
- Production volumes
- Budget constraints
- Quality specifications
- Delivery timelines
Each manufacturing method has its place in end cap production, and often a combination of processes may be used to achieve the desired results. The key is selecting the right process for specific application requirements while maintaining quality and cost-effectiveness.
The future of hydraulic cylinder end cap manufacturing continues to evolve with advancing technologies, including:
- Advanced materials development
- Improved machining capabilities
- Enhanced quality control methods
- Automated inspection systems
These advancements help ensure higher quality, more consistent products while maintaining competitive pricing in the global market.
What Are the Key Functions of End Caps?
Have you ever experienced sudden hydraulic system failures that brought your entire production line to a halt? These breakdowns often trace back to one critical component – the end caps. When end caps fail, they don’t just affect one part of the system; they can lead to catastrophic pressure loss, fluid leakage, and even safety hazards.
End caps in hydraulic cylinders serve three essential functions: maintaining system pressure, housing vital sealing components, and providing a secure mounting surface. These components act as the foundation of hydraulic system integrity, directly impacting operational efficiency and safety.
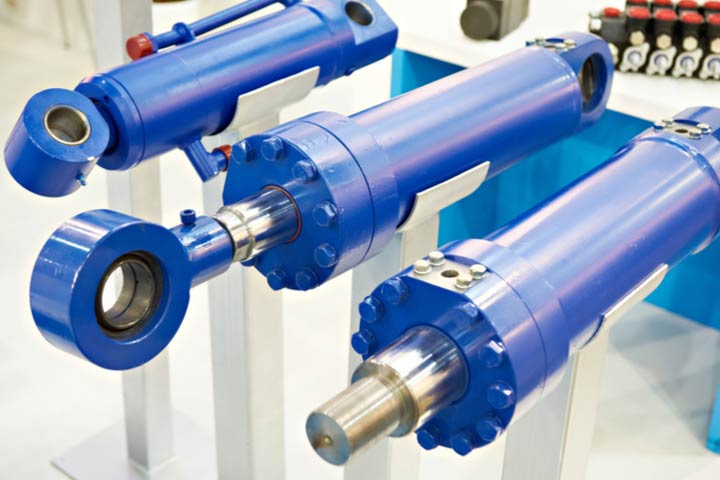

Primary Pressure Maintenance Function
The most crucial role of end caps is maintaining system pressure. I’ve designed countless end caps at PTSMAKE, and I’ve learned that proper pressure containment requires precise engineering of the radial stress distribution4 within the end cap structure.
Key aspects of pressure maintenance include:
- Structural integrity to withstand high-pressure operations
- Even distribution of force across the cap surface
- Prevention of pressure loss through proper material selection
- Strategic reinforcement at high-stress points
Sealing Component Housing
End caps serve as protective housings for critical sealing elements. This function requires careful consideration of:
Seal Groove Design
- Proper depth and width specifications
- Surface finish requirements
- Material compatibility considerations
Component Protection
| Protection Aspect | Design Requirement | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Seal Grove Depth | 0.120" – 0.150" | Prevents seal extrusion |
| Surface Finish | 16-32 RMS | Ensures optimal seal contact |
| Material Hardness | 28-32 RC | Reduces wear and extends life |
| Concentricity | 0.002" TIR max | Maintains uniform sealing |
Mounting Surface Functionality
The mounting surface function of end caps is critical for system integration. Based on my experience, successful mounting design must address:
Alignment Requirements
- Precise bolt hole patterns
- Perpendicularity to cylinder axis
- Surface flatness specifications
Load Distribution
- Even stress distribution across mounting points
- Adequate material thickness at connection points
- Proper torque specifications for mounting hardware
Design Considerations for Reliability
To ensure optimal performance, end cap design must account for:
Material Selection
- High-strength alloys for pressure resistance
- Corrosion-resistant materials for harsh environments
- Heat-treated options for enhanced durability
Manufacturing Precision
- Tight tolerancing for critical dimensions
- Superior surface finish requirements
- Proper heat treatment processes
Common Issues and Solutions
Understanding potential problems helps prevent failures:
Design-Related Issues
- Insufficient material thickness leading to deformation
- Poor seal groove design causing leakage
- Improper mounting hole placement affecting alignment
Manufacturing Defects
- Out-of-specification dimensions
- Poor surface finish quality
- Heat treatment inconsistencies
Preventive Measures
- Regular inspection protocols
- Proper installation procedures
- Scheduled maintenance routines
Impact on System Performance
The relationship between end cap quality and system performance is direct:
Efficiency Factors
- Pressure retention capability
- Seal life expectancy
- System alignment stability
Reliability Indicators
- Leak-free operation
- Consistent pressure maintenance
- Stable mounting configuration
Through my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that properly designed and manufactured end caps can significantly extend system life and reduce maintenance costs. The key is understanding the interplay between these various functions and ensuring each aspect receives appropriate attention during design and manufacturing.
A well-designed end cap isn’t just about meeting basic functional requirements; it’s about optimizing each aspect to create a component that enhances overall system performance. This includes considering factors like:
- Material selection based on operating conditions
- Manufacturing processes that ensure consistent quality
- Quality control measures that verify specifications
- Installation procedures that maintain design integrity
End caps might seem simple at first glance, but their role in hydraulic system performance cannot be overstated. Whether you’re designing a new system or maintaining existing equipment, understanding these key functions is crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability.
What Are the Different Types of Hydraulic Cylinder End Caps?
Selecting the right end cap for hydraulic cylinders often becomes a challenging task for engineers and manufacturers. I’ve noticed many clients struggling with premature system failures and costly maintenance issues due to improper end cap selection. The consequences of choosing the wrong type can lead to devastating hydraulic system breakdowns and production delays.
Hydraulic cylinder end caps come in three main types: threaded, welded, and bolted designs. Each type serves specific purposes and offers unique advantages in terms of pressure ratings, serviceability, and installation methods. The choice depends on factors like operating pressure, maintenance requirements, and application environment.
Threaded End Caps
Threaded end caps are among the most common types I work with at PTSMAKE. These caps feature precise thread pitch5 patterns that screw directly into the cylinder barrel. They excel in applications where:
- Regular maintenance access is required
- Space constraints exist
- Medium pressure ratings are acceptable
The installation process involves carefully threading the cap into the cylinder barrel with proper torque specifications. I’ve found that the success rate of threaded end caps largely depends on:
- Thread quality and precision
- Proper installation torque
- Regular maintenance checks
Welded End Caps
In my experience with high-pressure applications, welded end caps provide superior strength and reliability. These caps are permanently attached to the cylinder barrel through precision welding processes. Key advantages include:
- Maximum pressure capability
- Excellent seal integrity
- Reduced risk of leakage
However, they come with certain limitations:
- No maintenance access
- Cannot be easily replaced
- Require specialized welding expertise
Bolted End Caps
For versatility and serviceability, bolted end caps offer an excellent middle ground. They utilize multiple bolts to secure the cap to the cylinder barrel. The design features:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Multiple bolt pattern | Even pressure distribution |
| Removable design | Easy maintenance access |
| Replaceable seals | Extended service life |
| Variable bolt sizes | Customizable strength |
Selection Criteria Table
| End Cap Type | Pressure Rating | Maintenance Access | Cost | Installation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threaded | Medium | Good | Low | Medium |
| Welded | High | None | Medium | High |
| Bolted | Medium-High | Excellent | High | Low |
Application Considerations
When helping clients select the appropriate end cap type, I consider several crucial factors:
Operating Pressure
- Low Pressure (<1000 psi): Threaded caps often suffice
- Medium Pressure (1000-3000 psi): Bolted caps recommended
- High Pressure (>3000 psi): Welded caps typically required
Maintenance Requirements
The frequency and type of maintenance needed significantly influence the selection:
- Regular maintenance: Choose bolted or threaded
- Minimal maintenance: Consider welded options
- Emergency access needs: Avoid welded designs
Environmental Factors
Different environments demand specific considerations:
- Corrosive environments: Special material selection
- Temperature extremes: Proper seal selection
- Vibration exposure: Additional securing methods
Cost Considerations
Budget constraints often play a crucial role:
- Initial cost vs. long-term maintenance
- Installation expenses
- Replacement part availability
Manufacturing Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we emphasize several key aspects during end cap manufacturing:
-
Material Selection
- Carbon steel for standard applications
- Stainless steel for corrosive environments
- Specialized alloys for extreme conditions
-
Quality Control
- Precision machining tolerances
- Surface finish requirements
- Thread quality verification
-
Testing Procedures
- Pressure testing protocols
- Seal integrity verification
- Material certification
Through our manufacturing process, we ensure each end cap meets specific industry standards and client requirements. This attention to detail has helped us maintain our reputation for reliability and quality in hydraulic component manufacturing.
How to Ensure Proper Sealing in End Caps?
In my manufacturing experience, improper sealing in hydraulic cylinder end caps is a persistent challenge that plagues many engineers and manufacturers. When sealing fails, it leads to fluid leaks, reduced system efficiency, and potential equipment failure. These issues not only compromise performance but also result in costly downtime and repairs.
To ensure proper sealing in end caps, it’s essential to implement a comprehensive approach that combines the right sealing materials, precise installation techniques, and regular maintenance procedures. This systematic method guarantees optimal performance and prevents premature system failures.
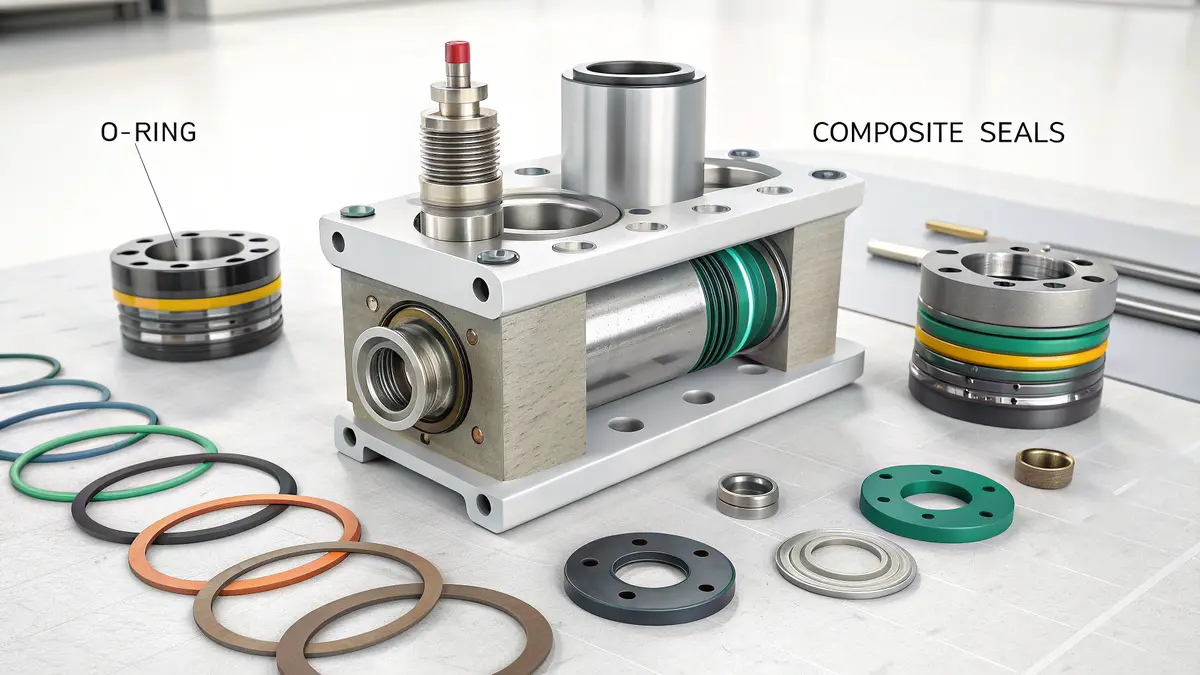

Understanding Sealing Materials and Their Applications
The selection of appropriate sealing materials is crucial for achieving optimal performance. I’ve found that different applications require specific sealing solutions based on their operating conditions. The elastomeric composition6 of sealing materials plays a vital role in determining their effectiveness and longevity.
O-Ring Selection Criteria
O-rings are among the most common sealing elements used in end caps. Here’s a detailed breakdown of selection factors:
| Parameter | Consideration | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Durometer | 70-90 Shore A | Affects compression set and wear resistance |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +100°C | Influences material degradation |
| Chemical Compatibility | Based on fluid type | Determines seal longevity |
| Pressure Rating | Up to 5000 PSI | Affects seal design and material choice |
| Size Tolerance | ±0.07mm | Critical for proper fit and function |
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is as crucial as material selection. I recommend following these key steps:
-
Surface Preparation
- Clean all sealing surfaces thoroughly
- Remove any burrs or sharp edges
- Verify surface finish requirements
- Apply appropriate lubricant
-
Alignment Verification
- Check concentricity of components
- Ensure proper groove dimensions
- Verify end cap alignment with cylinder bore
Maintenance and Inspection Protocols
Regular maintenance is essential for prolonged seal life. I’ve developed a comprehensive inspection schedule:
Daily Checks
- Visual inspection for leaks
- Monitoring system pressure
- Temperature monitoring
- Unusual noise detection
Monthly Maintenance
- Torque verification of end cap bolts
- Seal condition assessment
- Cleaning of external surfaces
- Documentation of findings
Advanced Sealing Technologies
Modern manufacturing has introduced several innovative sealing solutions:
-
Composite Seals
- Enhanced temperature resistance
- Improved pressure handling
- Better wear characteristics
- Extended service life
-
Smart Sealing Systems
- Integrated sensors for condition monitoring
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
- Real-time performance data
- Early warning indicators
Environmental Considerations
Operating environment significantly impacts seal performance:
Temperature Effects
- High temperatures can cause material degradation
- Low temperatures may reduce flexibility
- Thermal cycling requires special consideration
- Material selection must account for temperature range
Pressure Considerations
- Static pressure limits
- Dynamic pressure capabilities
- Pressure spikes and their impact
- System pressure monitoring
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent sealing performance, implement these quality control steps:
-
Material Testing
- Hardness verification
- Dimensional accuracy
- Chemical composition analysis
- Performance testing
-
Installation Verification
- Torque specification compliance
- Alignment verification
- Pressure testing
- Leak detection procedures
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When sealing problems occur, follow this systematic approach:
-
Problem Identification
- Visual inspection
- Pressure testing
- Performance monitoring
- Leak detection
-
Root Cause Analysis
- Material failure assessment
- Installation error verification
- Operating condition review
- Maintenance history evaluation
This comprehensive approach to end cap sealing ensures reliable performance and extended service life. By following these guidelines and maintaining proper documentation, you can significantly reduce the risk of seal failures and associated downtime.
What Are Common Failures in End Caps?
Ever faced unexpected hydraulic system breakdowns due to end cap failures? These critical components can suddenly fail, leading to costly production delays and safety hazards. When an end cap fails, it doesn’t just affect one part – it can cascade into complete system failure, potentially causing thousands of dollars in damage and dangerous fluid leaks.
End cap failures typically occur due to five main issues: material fatigue, excessive pressure, improper installation, corrosion, and seal deterioration. Understanding these failure modes helps prevent catastrophic system breakdowns and ensures optimal hydraulic performance.
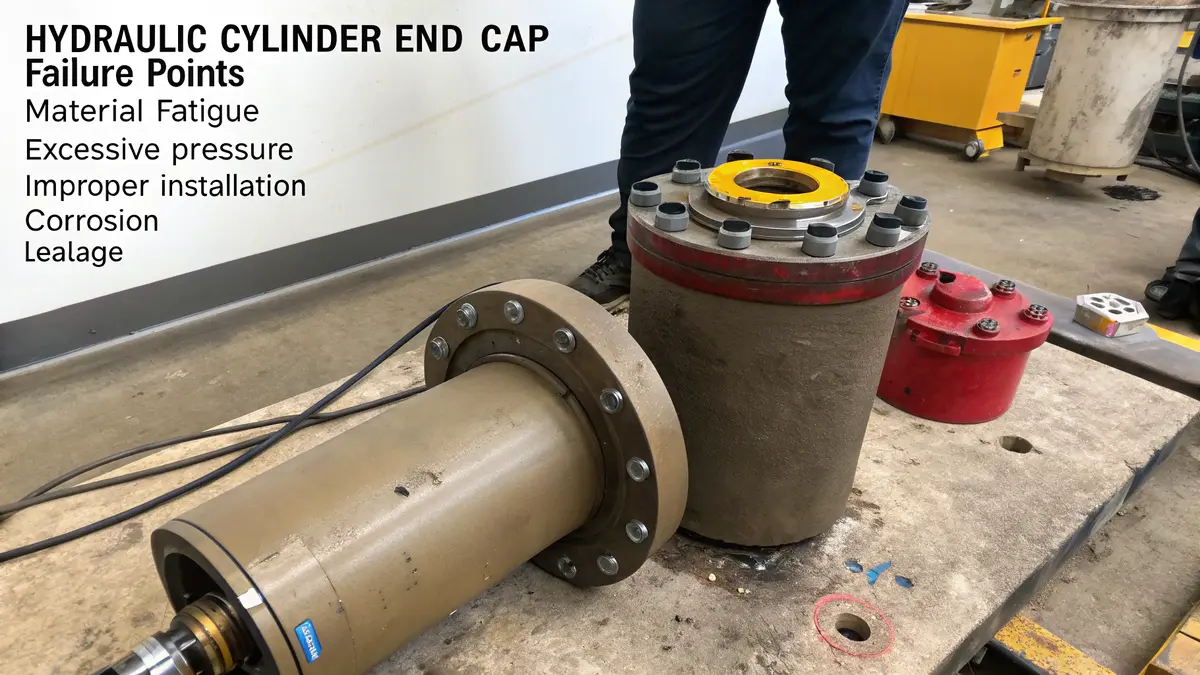

Material Fatigue and Stress Analysis
In my experience at PTSMAKE, material fatigue remains one of the most prevalent causes of end cap failures. This occurs when the metal undergoes repeated stress cycles, leading to microscopic crack propagation7. I’ve observed that end caps made from lower-grade materials are particularly susceptible to this issue.
Key indicators of material fatigue include:
- Visible surface cracks
- Deformation around mounting points
- Metal discoloration
- Unusual vibration during operation
Pressure-Related Failures
Excessive pressure can cause immediate or gradual end cap damage. Here’s what typically happens:
| Pressure Issue | Consequences | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Sudden pressure spikes | Immediate cap rupture | Install pressure relief valves |
| Constant overpressure | Progressive deformation | Regular pressure monitoring |
| Pressure cycling | Material weakening | Implement proper system controls |
| Uneven pressure distribution | Localized stress points | Ensure proper cap alignment |
Installation and Maintenance Problems
Poor installation practices often lead to premature failures. Common issues include:
- Misaligned mounting holes
- Incorrect torque specifications
- Damaged threads during assembly
- Improper cleaning before installation
Corrosion Effects and Prevention
Corrosion severely impacts end cap integrity. I recommend focusing on these areas:
-
External Corrosion
- Environmental exposure
- Chemical contamination
- Protective coating damage
- Surface treatment wear
-
Internal Corrosion
- Fluid contamination
- Chemical incompatibility
- Water ingress
- pH imbalance
Seal System Failures
The seal system plays a crucial role in end cap performance:
-
Primary Seal Issues
- Wear and tear
- Chemical degradation
- Temperature damage
- Improper sizing
-
Secondary Seal Problems
- Backup ring failures
- O-ring compression set
- Incorrect material selection
- Installation damage
Preventive Measures and Maintenance
To extend end cap life and prevent failures:
-
Regular Inspection Schedule
- Weekly visual checks
- Monthly pressure tests
- Quarterly seal inspection
- Annual comprehensive assessment
-
Proper Installation Procedures
- Use calibrated torque tools
- Follow manufacturer guidelines
- Verify alignment before tightening
- Document installation steps
-
Material Selection Guidelines
- Consider operating pressure
- Evaluate environmental conditions
- Account for fluid compatibility
- Factor in temperature ranges
Troubleshooting Techniques
When investigating end cap failures:
-
Visual Inspection
- Look for visible cracks
- Check for deformation
- Examine seal condition
- Inspect mounting surfaces
-
Pressure Testing
- Static pressure checks
- Dynamic load testing
- Leak detection
- Pressure cycle analysis
-
Material Analysis
- Hardness testing
- Surface finish evaluation
- Dimensional checking
- Metallurgical examination
Performance Optimization
To maximize end cap performance:
-
Design Considerations
- Proper material selection
- Adequate safety factors
- Optimal geometry
- Stress distribution analysis
-
Operating Parameters
- Pressure limitations
- Temperature ranges
- Fluid compatibility
- Maintenance intervals
This comprehensive approach to end cap failure analysis has helped me identify and prevent numerous potential failures. By understanding these common issues and implementing proper maintenance procedures, you can significantly reduce the risk of hydraulic system failures and extend the service life of your equipment.
How to Maintain and Replace End Caps?
Maintaining hydraulic cylinder end caps is a critical challenge that many manufacturers face. When these components fail, entire production lines can grind to a halt, causing costly delays and potential safety hazards. I’ve witnessed companies lose thousands of dollars due to improper end cap maintenance and unexpected failures.
The key to maintaining and replacing end caps lies in regular inspection, proper cleaning, and following manufacturer-specified replacement procedures. By implementing a systematic maintenance schedule and using the right tools, you can significantly extend the life of your hydraulic cylinder end caps and prevent unexpected failures.

Regular Inspection Procedures
The first step in maintaining end caps is establishing a consistent inspection routine. I recommend checking for signs of wear, including material fatigue8, corrosion, and seal degradation. Here’s a detailed inspection checklist I’ve developed:
-
Visual Inspection
- Check for visible cracks or damage
- Look for signs of fluid leakage
- Examine seal condition
- Inspect mounting surfaces
-
Physical Assessment
- Test for unusual movement
- Check tightness of fasteners
- Verify alignment
- Measure wear patterns
Cleaning and Maintenance Guidelines
Proper cleaning is essential for extending end cap life. I’ve found that following these steps helps prevent premature wear:
Cleaning Process
- Remove surface debris
- Apply appropriate cleaning solution
- Clean seal grooves carefully
- Dry thoroughly before reassembly
| Cleaning Agent | Best Used For | Precautions |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral Spirits | General cleaning | Use in ventilated area |
| Isopropyl Alcohol | Removing oils | Avoid prolonged contact |
| Specialized Cleaners | Heavy contamination | Follow manufacturer guidelines |
End Cap Replacement Steps
When replacement becomes necessary, following these steps ensures safe and effective installation:
-
Preparation
- Depressurize the system
- Gather necessary tools
- Document original configuration
- Clean work area
-
Removal Process
- Mark orientation
- Remove mounting hardware
- Extract old end cap carefully
- Clean mounting surface
-
Installation
- Verify new end cap specifications
- Apply recommended lubricant
- Install new seals
- Align properly
- Torque fasteners to specification
Preventive Maintenance Schedule
I recommend implementing this maintenance schedule:
| Frequency | Task | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Visual Check | Look for leaks and damage |
| Weekly | Basic Inspection | Check mounting hardware |
| Monthly | Detailed Check | Clean and inspect seals |
| Quarterly | Full Assessment | Complete system review |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Based on my experience, these are the most frequent end cap problems and solutions:
-
Leakage
- Check seal condition
- Verify proper torque
- Inspect surface finish
- Replace damaged components
-
Misalignment
- Verify mounting accuracy
- Check cylinder straightness
- Adjust as needed
- Replace if severely worn
-
Excessive Wear
- Analyze operating conditions
- Check for contamination
- Review maintenance history
- Upgrade materials if needed
Best Practices for Long-Term Reliability
To maximize end cap life, I always emphasize these key points:
- Use proper tools
- Follow torque specifications
- Maintain clean operating conditions
- Document all maintenance activities
- Train maintenance personnel properly
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be the top priority. Essential safety measures include:
-
System Shutdown
- Verify power is off
- Release stored energy
- Lock out/tag out procedures
- Confirm zero pressure
-
Personal Protection
- Wear appropriate PPE
- Use proper lifting techniques
- Follow safety protocols
- Maintain clear work area
Cost-Effective Management Strategies
To optimize your maintenance budget:
- Keep detailed records
- Stock critical spares
- Train staff effectively
- Use quality replacement parts
- Implement predictive maintenance
This comprehensive approach to end cap maintenance and replacement has helped me reduce downtime and extend component life significantly. By following these guidelines, you can maintain optimal performance while minimizing operational costs and preventing unexpected failures.
What Are the Latest Innovations in End Cap Technology?
Keeping up with the latest end cap technology innovations has become increasingly challenging for manufacturing professionals. As hydraulic systems become more complex, traditional end caps often fall short in meeting modern performance demands. The pressure to find more efficient, durable, and intelligent solutions grows stronger every day.
The latest innovations in end cap technology focus on smart integration, material advancement, and enhanced sealing capabilities. Key developments include sensor-equipped end caps for real-time monitoring, lightweight composite materials for improved efficiency, and advanced sealing solutions that significantly reduce fluid leakage and system downtime.
Smart Sensor Integration
The integration of smart sensors into end caps represents one of the most significant advances in hydraulic system monitoring. These intelligent components enable:
- Real-time pressure monitoring
- Temperature tracking
- Wear detection
- Predictive maintenance capabilities
The implementation of piezoelectric sensors9 in modern end caps has revolutionized how we monitor hydraulic system performance. These sensors provide crucial data that helps prevent system failures and optimize maintenance schedules.
Advanced Material Technologies
Modern end cap manufacturing has embraced innovative materials that offer superior performance:
| Material Type | Benefits | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Fiber Composites | Lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio | High-performance systems |
| Nano-engineered Polymers | Enhanced durability, better thermal properties | Extreme environment operations |
| Ceramic-Metal Hybrids | Superior wear resistance, thermal stability | Heavy-duty industrial systems |
Enhanced Sealing Solutions
Recent developments in sealing technology have significantly improved end cap performance:
-
Multi-layer Sealing Systems
- Primary seal for standard operation
- Secondary seal for backup protection
- Tertiary seal for catastrophic failure prevention
-
Dynamic Sealing Technology
- Self-adjusting seal compression
- Temperature-responsive materials
- Pressure-activated sealing mechanisms
Digital Manufacturing Integration
Modern end cap production has evolved with Industry 4.0 principles:
-
Automated Quality Control
- 3D scanning for dimensional accuracy
- Automated surface finish inspection
- Real-time production monitoring
-
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
- Precision CNC machining
- Additive manufacturing for complex geometries
- Hybrid manufacturing solutions
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable end cap solutions have become increasingly important:
-
Eco-friendly Materials
- Recyclable components
- Biodegradable sealing elements
- Reduced carbon footprint manufacturing
-
Energy Efficiency
- Optimized fluid flow design
- Reduced friction coefficients
- Improved thermal management
Future Trends and Developments
The evolution of end cap technology continues with several emerging trends:
-
AI-Enhanced Design
- Topology optimization
- Performance prediction
- Automated design iterations
-
Connected Systems
- IoT integration
- Remote monitoring capabilities
- Cloud-based analytics
-
Customization Capabilities
- Application-specific designs
- Rapid prototyping
- On-demand manufacturing
System Integration Improvements
Modern end caps are designed with better system integration in mind:
-
Modular Design Approaches
- Standardized interfaces
- Plug-and-play capabilities
- Easy maintenance access
-
Performance Optimization
- Reduced pressure drops
- Improved flow characteristics
- Enhanced thermal management
Testing and Validation
New testing methodologies ensure reliable performance:
-
Advanced Testing Protocols
- Accelerated life testing
- Environmental stress screening
- Digital twin simulation
-
Quality Assurance
- Non-destructive testing
- Real-time monitoring
- Performance validation
The evolution of end cap technology represents a significant leap forward in hydraulic system performance and reliability. These innovations not only improve system efficiency but also contribute to reduced maintenance costs and extended service life. As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in hydraulic systems, the role of advanced end cap technology becomes increasingly crucial in meeting the demands of modern industrial applications.
How to Choose the Right End Caps for Your Application?
Choosing the wrong end caps for hydraulic cylinders can lead to catastrophic system failures and costly downtime. I’ve seen numerous cases where improper end cap selection resulted in leakage, premature wear, and even complete system breakdowns, putting both equipment and operator safety at risk.
The right end cap selection requires careful consideration of operating pressure, environmental conditions, material compatibility, and mounting requirements. Key factors include pressure rating, temperature resistance, sealing design, and installation method to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
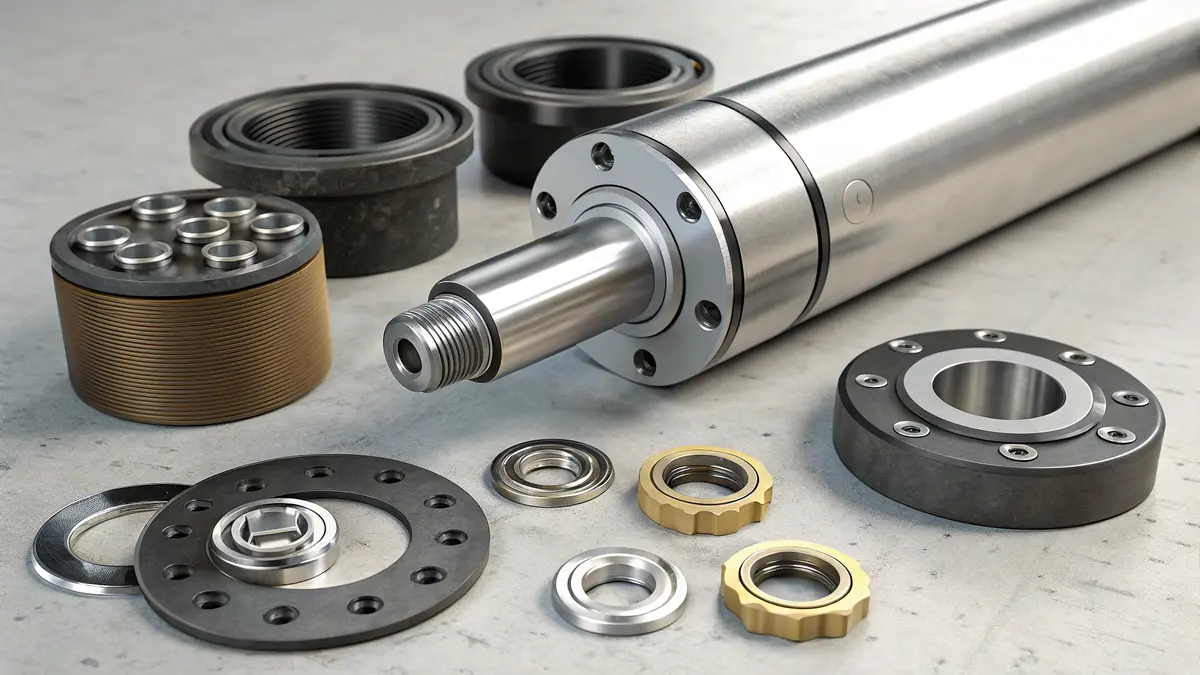

Understanding Operating Pressure Requirements
Operating pressure is the most critical factor in end cap selection. The yield strength10 of the end cap material must withstand the maximum system pressure with an appropriate safety margin. I recommend using this pressure rating guide:
| Operating Pressure (PSI) | Recommended Material | Safety Factor |
|---|---|---|
| 0-1,500 | Cast Iron | 4:1 |
| 1,500-3,000 | Carbon Steel | 4:1 |
| 3,000-5,000 | Alloy Steel | 5:1 |
| 5,000+ | High-Strength Steel | 6:1 |
Environmental Considerations
The operating environment significantly impacts end cap performance and longevity. Here are key environmental factors to evaluate:
- Temperature Range: Select materials that maintain structural integrity within your system’s temperature range
- Chemical Exposure: Consider resistance to hydraulic fluids, cleaners, and environmental contaminants
- Moisture Exposure: Choose corrosion-resistant materials or appropriate protective coatings
- UV Exposure: For outdoor applications, ensure materials won’t degrade under sun exposure
Mounting Configuration Options
End cap mounting methods affect both installation and maintenance procedures:
-
Threaded Mount
- Best for smaller cylinders
- Provides excellent sealing
- Easier maintenance access
- Limited to specific pressure ranges
-
Tie-Rod Mount
- Superior for high-pressure applications
- Even load distribution
- Multiple attachment points
- Better stability under dynamic loads
-
Welded Mount
- Permanent installation
- Highest pressure capability
- Reduced maintenance access
- Requires specialized manufacturing
Material Selection Criteria
Material choice impacts both performance and cost-effectiveness:
-
Cast Iron
- Excellent vibration dampening
- Good wear resistance
- Cost-effective for low-pressure applications
- Limited pressure capability
-
Carbon Steel
- Better pressure handling than cast iron
- Good machinability
- Moderate cost
- Requires surface protection
-
Stainless Steel
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Excellent for food-grade applications
- Higher material cost
- Better temperature resistance
Sealing System Design
Proper sealing is crucial for preventing leakage and maintaining system efficiency:
-
O-Ring Grooves
- Must meet precise dimensional specifications
- Require proper surface finish
- Need correct groove depth for compression
- Should include backup rings for high pressure
-
Surface Finish Requirements
- Ra 16-32 microinches for dynamic seals
- Ra 32-63 microinches for static seals
- Proper chamfer angles for seal installation
- No sharp edges that could damage seals
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Proper installation and maintenance procedures ensure optimal performance:
-
Installation Requirements
- Proper alignment during assembly
- Correct torque specifications
- Clean installation environment
- Proper tool usage
-
Maintenance Access
- Easy seal replacement
- Inspection points
- Lubrication access
- Monitoring capabilities
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When selecting end caps, consider these cost factors:
-
Initial Investment
- Material costs
- Manufacturing complexity
- Quality requirements
- Quantity needed
-
Long-term Considerations
- Expected service life
- Maintenance requirements
- Replacement costs
- Downtime impact
Quality Assurance Measures
Implement these quality checks:
-
Material Certification
- Chemical composition verification
- Physical properties testing
- Heat treatment validation
- Traceability documentation
-
Dimensional Inspection
- Critical dimension verification
- Surface finish measurement
- Roundness checking
- Thread quality inspection
Remember, selecting the right end cap is crucial for system reliability and safety. By carefully considering these factors and consulting with experienced manufacturers, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your hydraulic system components.
-
Understand how material choices enhance hydraulic end caps’ performance and lifespan. ↩
-
Learn about the best materials for hydraulic cylinder end caps for performance and durability. ↩
-
Discover how multi-axis machining enhances precision and efficiency in hydraulic cylinder end cap manufacturing. ↩
-
Explore how radial stress impacts pressure maintenance for better hydraulic system reliability. ↩
-
Understanding thread pitch ensures proper engagement and sealing for effective hydraulic applications. ↩
-
Learn about elastomeric composition for better sealing performance and longevity in hydraulic applications. ↩
-
Learn about crack propagation to enhance maintenance strategies and prevent hydraulic system failures. ↩
-
Understanding material fatigue helps prevent failures and extend the lifespan of hydraulic components. ↩
-
Piezoelectric sensors are devices that use the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, strain, or force by converting them to an electrical charge. These sensors are crucial for modern end cap monitoring systems. ↩
-
Understand material limits to prevent failures, ensuring safety and system reliability. ↩