Have you ever wondered why there are so many different types of pins in manufacturing? After 15+ years at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen how choosing the wrong pin can lead to costly project failures.
Pins come in several main types: dowel pins, spring pins, clevis pins, cotter pins, and taper pins. Each type serves specific purposes in mechanical assemblies, from alignment and fastening to securing components and transferring loads.

Through my years of experience working with global manufacturers, I’ve learned that understanding pin types is crucial for design success. Let me share what I’ve discovered about each type’s unique features and applications, which will help you make better decisions for your next project.
What Are Pins and Their Uses?
Have you ever wondered why something as simple as a pin plays such a crucial role in modern engineering? As a precision manufacturing expert, I’ve witnessed how these tiny components make a massive difference in product reliability and performance.
Pins are engineered fastening components designed to secure, align, or support various parts in mechanical assemblies. They come in different materials and designs, serving critical functions across industries from aerospace to medical devices, where precision and reliability are paramount.

Understanding Pin Fundamentals
In the manufacturing world, pins are far more sophisticated than they appear. At PTSMAKE, we produce various precision pins that serve different purposes. The most common functions include:
- Securing components together
- Maintaining precise alignment between parts
- Supporting structural loads
- Serving as pivot points
- Creating temporary or permanent connections
Types of Pins and Their Applications
Different industries require specific pin types for optimal performance. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown:
Dowel Pins
These cylindrical pins provide precise alignment and positioning. They’re commonly used in:
- Automotive engine assemblies
- Production equipment
- Precision machinery
- Tool and die applications
Roll Pins (Spring Pins)
These flexible, hollow pins provide excellent retention force through their spring action:
- Power transmission equipment
- Agricultural machinery
- Construction equipment
- Industrial machinery
Clevis Pins
Designed for applications requiring frequent assembly and disassembly:
- Heavy equipment
- Agricultural implements
- Construction machinery
- Material handling equipment
Material Selection for Pin Manufacturing
The choice of material significantly impacts pin performance. Here’s a detailed analysis:
| Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, good wear resistance | General machinery, automotive |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, moderate strength | Food processing, medical devices |
| Brass | Good machinability, corrosion resistant | Electrical components, decorative applications |
| Titanium | High strength-to-weight ratio, biocompatible | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Plastic | Lightweight, chemical resistant | Electronics, consumer products |
Manufacturing Techniques and Precision
The manufacturing process directly affects pin quality and performance. At PTSMAKE, we employ several techniques:
CNC Machining
- Offers tight tolerances (typically ±0.0005")
- Excellent for custom designs
- Suitable for all materials
- Ideal for prototype and small-batch production
Cold Forming
- Cost-effective for high volumes
- Excellent material strength properties
- Limited to certain materials
- Consistent quality in mass production
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes improve pin performance through:
- Enhanced hardness
- Better wear resistance
- Improved strength
- Stress relief
Quality Considerations
When selecting pins for specific applications, consider these critical factors:
Load Requirements
- Static load capacity
- Dynamic load handling
- Shear strength requirements
- Impact resistance needs
Environmental Conditions
- Temperature exposure
- Chemical exposure
- Moisture levels
- UV exposure
Installation Methods
- Press fit requirements
- Clearance fit needs
- Installation force
- Removal considerations
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have unique pin requirements:
Aerospace
- High precision tolerances
- Lightweight materials
- Superior strength
- Reliable performance in extreme conditions
Medical Devices
- Biocompatibility
- Sterilization capability
- High reliability
- Precise dimensions
Automotive
- Cost-effectiveness
- High volume production capability
- Consistent quality
- Durability under stress
Electronics
- Non-magnetic properties
- Electrical conductivity/insulation
- Clean room compatibility
- Temperature stability
By understanding these various aspects of pins, engineers and designers can make informed decisions about which type of pin best suits their specific application needs. The right pin choice ensures optimal performance, reliability, and longevity in the final product.
What Are Dowel Pins and Their Applications?
Have you ever wondered how precision machinery maintains perfect alignment? The secret often lies in a small but crucial component: the dowel pin. At PTSMAKE, I’ve seen these simple yet ingenious devices transform complex assembly challenges into seamless operations.
Dowel pins are cylindrical positioning components manufactured with precise tolerances, primarily used to align and secure mechanical assemblies. These hardened metal pins ensure exact component alignment, prevent lateral movement, and maintain consistent positioning in various applications.

Understanding Dowel Pin Construction
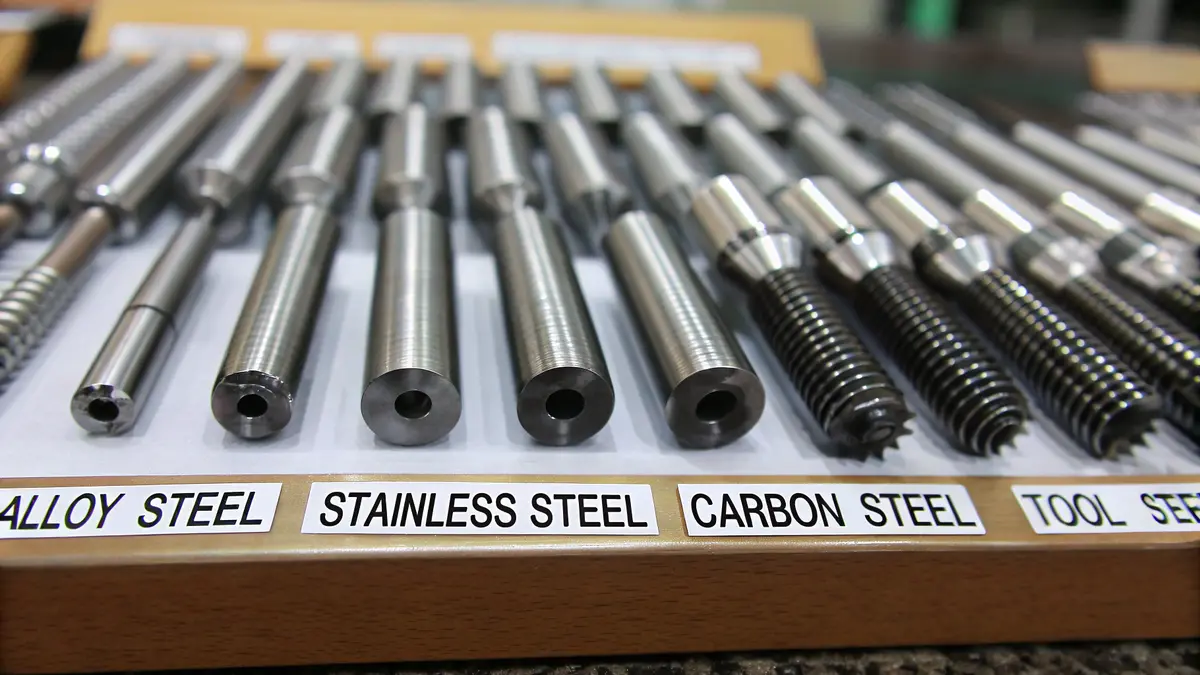
The effectiveness of dowel pins stems from their precise manufacturing process. As a precision manufacturing expert, I can tell you that the material selection and dimensional accuracy are crucial factors. The most common materials include:
| Material Type | Advantages | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steel | High strength, wear resistance | Heavy machinery, automotive |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, durability | Medical equipment, food processing |
| Carbon Steel | Cost-effective, good strength | General manufacturing, furniture |
| Tool Steel | Extreme hardness, heat resistance | Die making, industrial tools |
Critical Dimensional Characteristics
Dowel pins are manufactured to extremely tight tolerances, typically:
- Diameter tolerance: ±0.0002" to ±0.0005"
- Length tolerance: ±0.005" to ±0.010"
- Straightness: 0.001" per inch of length
- Surface finish: 16-32 microinches
Common Applications Across Industries
Automotive Manufacturing
In automotive assembly, dowel pins are essential for:
- Engine block alignment
- Transmission housing assembly
- Cylinder head positioning
- Clutch plate alignment
CNC Machining and Tooling
As a CNC machining service provider, we regularly use dowel pins for:
- Fixture positioning
- Workpiece alignment
- Tool holder setup
- Machine calibration
Furniture Manufacturing
The furniture industry relies on dowel pins for:
- Joint reinforcement
- Panel alignment
- Cabinet assembly
- Structural support
Design Considerations and Best Practices
Proper Sizing
The general rule for dowel pin sizing includes:
- Length should be 1.5-2 times the pin diameter
- Hole depth should allow for proper engagement
- Clearance holes should be sized according to fit requirements
Installation Methods
There are several proven installation techniques:
- Press-fit installation
- Light interference fit
- Transitional fit
- Clearance fit
Load-Bearing Capabilities
Dowel pins excel in high-load applications due to their:
- High shear strength
- Excellent wear resistance
- Superior fatigue resistance
- Minimal deformation under stress
Load Distribution Factors
When designing with dowel pins, consider:
- Shear force direction
- Number of pins needed
- Pin spacing requirements
- Material compatibility
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance:
- Visual inspection for wear
- Dimensional verification
- Surface finish evaluation
- Replacement scheduling
Industry-Specific Standards
Different industries have specific requirements:
- ISO standards for manufacturing
- ANSI/ASME specifications
- DIN standards for European applications
- JIS standards for Asian markets
Future Trends and Innovations
The evolution of dowel pin technology includes:
- Advanced material compositions
- Improved surface treatments
- Enhanced manufacturing processes
- Smart monitoring capabilities
At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented these innovations to provide superior dowel pin solutions that meet the evolving needs of modern manufacturing. Through careful material selection, precise manufacturing, and rigorous quality control, we ensure our dowel pins maintain the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Remember, while dowel pins may seem simple, their proper selection and implementation can significantly impact the success of your assembly project. Whether you’re working on a small furniture piece or a complex automotive component, understanding these fundamental aspects will help you make informed decisions in your manufacturing process.
What Are Taper Pins and Their Characteristics?
Have you ever wondered why some machinery components stay perfectly aligned for years without loosening? The secret often lies in a simple yet ingenious component – the taper pin. Let me share my insights about this fascinating fastener.
Taper pins are precision-engineered fasteners with a subtle conical shape, designed to create an interference fit that securely connects mechanical components. Their unique design allows for both temporary and permanent assembly solutions while maintaining precise alignment.
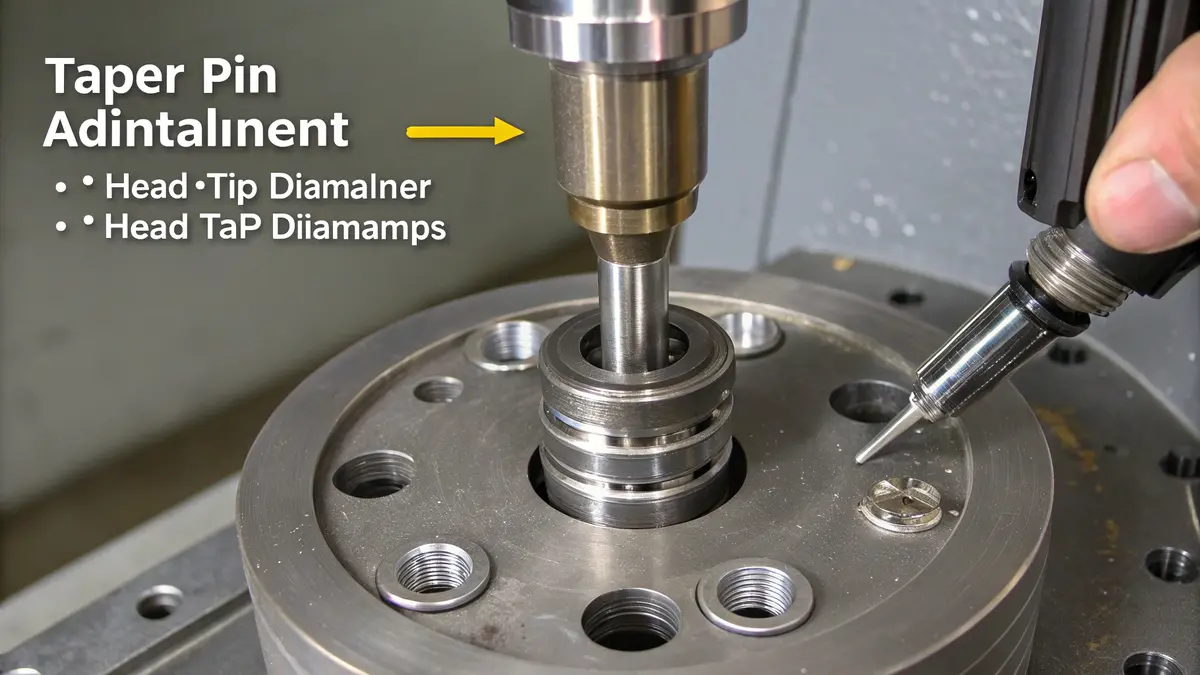
Understanding Taper Pin Design
The fundamental characteristic of taper pins is their gradual diameter reduction from head to tip. In my experience working with precision components, this subtle taper (typically 1:50) creates an exceptional holding force when properly installed. The design follows strict standards:
- Head diameter: Slightly larger than the hole entrance
- Tip diameter: Marginally smaller than the hole exit
- Surface finish: Smooth to ensure proper fit
- Length: Varies based on application requirements
Standard vs Metric Taper Pins
Working in international manufacturing, I’ve encountered both standard and metric taper pins. Here’s a comparative analysis:
| Feature | Standard Taper Pins | Metric Taper Pins |
|---|---|---|
| Taper Ratio | 1:48 | 1:50 |
| Size Range | #0 to #10 | 0.5mm to 50mm |
| Material Options | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel | Similar + Additional Alloys |
| Common Applications | US/UK Equipment | European/Asian Machinery |
| Standards | ASME B18.8.2 | ISO 8740 |
Material Selection Considerations
The choice of material significantly impacts pin performance. Common options include:
Carbon Steel
- Excellent strength
- Good wear resistance
- Cost-effective
- Suitable for most applications
Stainless Steel
- Corrosion resistant
- Higher cost
- Ideal for food processing equipment
- Medical device applications
Alloy Steel
- Enhanced strength
- Better wear characteristics
- Higher temperature applications
- Aerospace and automotive use
Installation and Removal Techniques
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance. The process typically involves:
Hole Preparation
- Reaming to exact size
- Ensuring proper alignment
- Clean, burr-free surfaces
Installation Steps
- Initial hand insertion
- Gentle tapping with appropriate hammer
- Monitoring insertion depth
- Checking for proper seating
Removal Procedures
- Using appropriate extraction tools
- Avoiding damage to surrounding material
- Maintaining hole integrity for reuse
Applications in Various Industries
In the precision manufacturing sector, I’ve seen taper pins used extensively across different applications:
Machine Tool Industry
- Alignment of major components
- Securing tool holders
- Position indexing mechanisms
Automotive Manufacturing
- Engine component alignment
- Transmission assembly
- Fixture and jig construction
Aerospace Applications
- Critical alignment requirements
- High-stress environments
- Safety-critical assemblies
Size Selection and Specifications
Choosing the correct pin size involves several factors:
Load Requirements
- Shear strength needed
- Expected stress patterns
- Safety factors
Installation Considerations
- Material thickness
- Access for installation
- Removal requirements
Environmental Factors
- Temperature variations
- Exposure to chemicals
- Vibration levels
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance ensures long-term reliability:
Periodic Checks
- Visual inspection for wear
- Checking for loosening
- Monitoring alignment
Replacement Criteria
- Visible wear or damage
- Loss of holding force
- Change in alignment
Documentation
- Installation dates
- Maintenance history
- Replacement schedule
Through my extensive work with precision components, I’ve found taper pins to be remarkably reliable when properly specified and installed. Their simplicity, combined with precise engineering, makes them an invaluable element in modern machinery design. Whether used for temporary alignment during assembly or permanent component fixing, taper pins continue to prove their worth in countless applications across industries.
What Are Cotter Pins and Split Pins?
Ever wondered about those small metal pins that keep crucial machinery parts from falling apart? In my manufacturing facility, these tiny components play a vital role in preventing catastrophic failures and ensuring equipment safety.
Cotter pins, also called split pins, are U-shaped metal fasteners with a head and two prongs that can be split and bent after insertion. They serve as mechanical locking devices to prevent nuts and bolts from loosening in various applications.
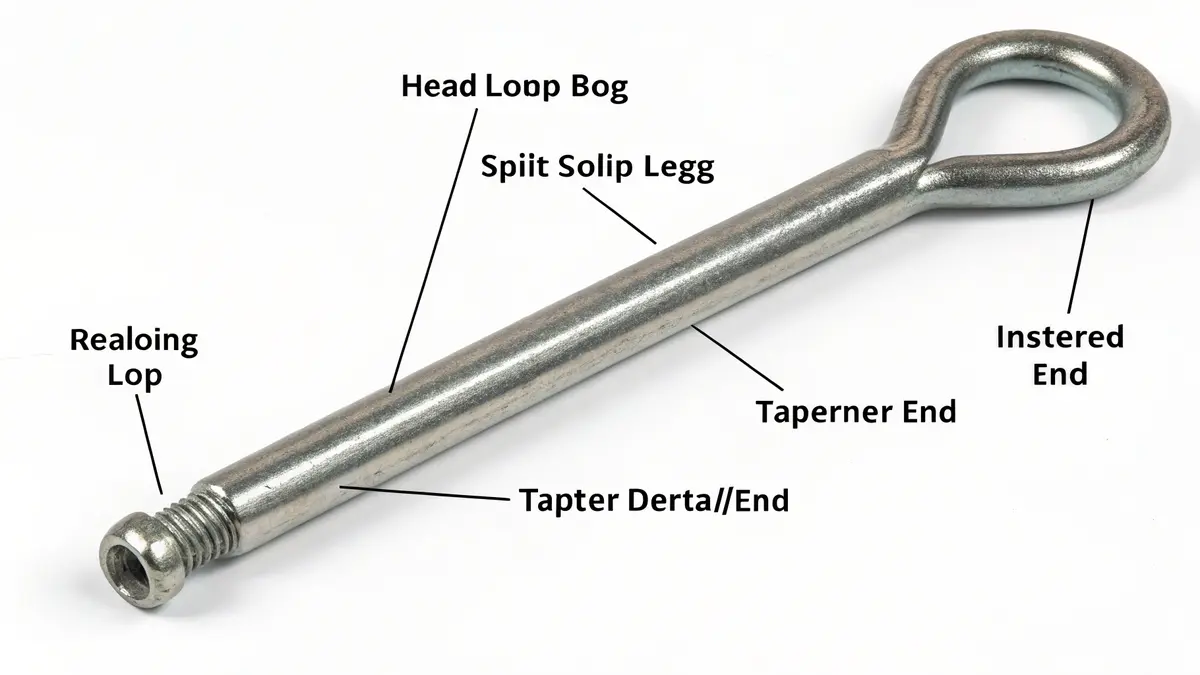
Basic Structure and Design
The design of cotter pins is brilliantly simple yet highly effective. The main components include:
- Head loop: Allows easy insertion and removal
- Split legs: Can be separated and bent after installation
- Tapered end: Facilitates smooth insertion through holes
The standard dimensions typically range from 1/16 inch to 3/8 inch in diameter, with lengths varying from 1/2 inch to 6 inches. At PTSMAKE, we often work with various sizes to meet different customer requirements.
Material Selection and Properties
Different applications require different materials. Here’s a breakdown of common cotter pin materials:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Economical, good formability | General purpose use |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, durable | Marine environments |
| Zinc-plated Steel | Enhanced rust protection | Outdoor equipment |
| Copper | Non-sparking, conductive | Electrical applications |
Installation Techniques
The installation process is straightforward but requires attention to detail:
- Insert the pin through the pre-drilled hole
- Spread the legs apart
- Bend each leg in opposite directions
- Verify secure installation
I always emphasize to our clients that proper installation is crucial for optimal performance. A poorly installed cotter pin can compromise the entire assembly’s safety.
Common Applications
Cotter pins find extensive use across various industries:
- Automotive: Securing castle nuts on tie rods and axle shafts
- Agriculture: Fastening implement pins and hitches
- Aviation: Safety backup for critical fasteners
- Industrial machinery: Securing rotating components
Safety Considerations
When working with cotter pins, several safety factors should be considered:
Size Selection
- Always choose the correct diameter for the hole
- Ensure sufficient length for proper bending
- Consider load requirements
Material Compatibility
- Match material to environmental conditions
- Account for thermal expansion
- Consider chemical exposure
Maintenance Protocol
- Regular inspection for wear or damage
- Replacement at scheduled intervals
- Documentation of maintenance activities
Industry Standards and Specifications
Various standards govern cotter pin manufacturing and usage:
- ASME B18.8.2: Dimensional specifications
- ISO 1234: International standards for split pins
- AS 1476: Australian standards for mechanical fastening
Cost-Effective Solutions
From my experience at PTSMAKE, cost optimization in cotter pin selection involves:
- Bulk purchasing strategies
- Material selection based on application
- Standardization across applications
- Quality vs. price considerations
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Some frequent challenges with cotter pins include:
Incorrect sizing
- Solution: Use manufacturer specifications
- Verify hole diameter before selection
Installation difficulties
- Solution: Use proper tools
- Follow installation guidelines
Premature failure
- Solution: Regular inspection
- Proper material selection
Corrosion issues
- Solution: Choose appropriate materials
- Consider environmental factors
Future Trends
The future of cotter pins involves:
Advanced Materials
- Composite materials
- Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Improved durability
Smart Features
- Integration with IoT sensors
- Wear indicators
- Enhanced traceability
Sustainable Manufacturing
- Eco-friendly materials
- Recyclable options
- Reduced waste production
By understanding these aspects of cotter pins, manufacturers and engineers can make informed decisions about their use in various applications. These simple yet crucial components continue to play a vital role in mechanical assemblies across industries.
What Are Spring Pins and Their Benefits?
Have you ever wondered why some mechanical components stay perfectly aligned even under intense vibration? The secret might lie in a small but mighty component – the spring pin. Let me share why these simple yet ingenious fasteners have become indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Spring pins are hollow, cylindrical fasteners that compress when inserted into holes, creating a secure fit through radial tension. Their unique design allows for easy installation while providing excellent resistance to vibration and wear, making them ideal for various industrial applications.
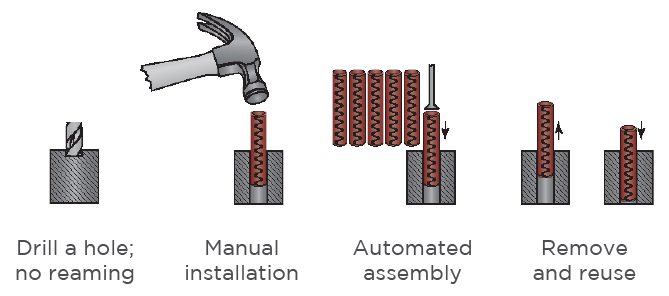
Understanding Spring Pin Design
The genius of spring pins lies in their seemingly simple design. As a manufacturing professional, I’ve seen how their hollow cylindrical structure allows for radial compression during installation. The pin’s diameter slightly exceeds the hole diameter, creating tension when inserted that ensures a secure fit.
Key design features include:
- Chamfered ends for smooth insertion
- Precision-engineered slots for controlled compression
- Calculated wall thickness for optimal spring tension
- Various diameter-to-length ratios for different applications
Material Selection and Properties
The choice of material significantly impacts a spring pin’s performance. Here’s a breakdown of common materials and their applications:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, economical | General purpose assembly |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, durable | Food processing, outdoor equipment |
| Spring Steel | Superior elasticity, fatigue resistant | High-stress applications |
| Beryllium Copper | Non-magnetic, corrosion resistant | Electronic equipment |
Installation Methods and Best Practices
The effectiveness of spring pins heavily depends on proper installation. From my experience working with precision components, I recommend these key practices:
Hole Preparation
- Ensure correct hole sizing (typically 0.2-0.5mm smaller than pin diameter)
- Maintain proper hole roundness
- Remove any burrs or debris
Installation Technique
- Use appropriate installation tools
- Apply even pressure during insertion
- Avoid hammering or forcing the pin
Applications Across Industries
Spring pins have proven their worth in various industrial applications:
Automotive Manufacturing
- Engine component alignment
- Door hinge assemblies
- Brake system components
- Transmission assemblies
Electronics Manufacturing
- Circuit board mounting
- Connector alignment
- Equipment housing assembly
- Panel fastening
Heavy Machinery
- Equipment frame assembly
- Safety mechanism retention
- Guide rail alignment
- Tool holder securing
Advantages Over Traditional Fasteners
Spring pins offer several benefits compared to conventional fastening methods:
Cost Efficiency
- Reduced installation time
- Lower material costs
- Minimal maintenance requirements
Performance Benefits
- Superior vibration resistance
- Self-locking capabilities
- Uniform load distribution
- Extended service life
Design Flexibility
- Various size options
- Multiple material choices
- Easy modification for specific applications
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance:
Visual Inspection
- Check for surface wear
- Look for deformation
- Examine for corrosion
Performance Testing
- Verify retention force
- Check alignment
- Test for proper movement
Future Trends and Innovations
The spring pin industry continues to evolve with:
- Advanced materials development
- Improved coating technologies
- Enhanced design optimization
- Automated installation systems
- Smart monitoring capabilities
Through my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed how spring pins have become increasingly crucial in precision manufacturing. Their reliability, combined with cost-effectiveness, makes them an excellent choice for many applications. When selecting spring pins for your project, consider factors like load requirements, environmental conditions, and installation method to ensure optimal performance.
Remember, while spring pins might seem simple, their proper selection and installation are crucial for successful application. Whether you’re designing new equipment or improving existing assemblies, understanding these fundamentals will help you make informed decisions about using spring pins in your projects.
## What Are Clevis Pins and Hitch Pins?
Have you ever wondered why some mechanical connections stay perfectly secure even under extreme stress? The secret often lies in two simple yet ingenious components: clevis pins and hitch pins. These small but mighty fasteners are the unsung heroes of industrial machinery.
**Clevis pins and hitch pins are specialized fastening devices designed for quick-release connections in high-stress applications. Clevis pins feature a cylindrical body with a hole for a cotter pin, while hitch pins come with built-in locking mechanisms, both ensuring secure mechanical joints.**
%[Clevis And Hitch Pins In Various Sizes And Styles](https://ptsmake.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ptsmake2025-02-04T091216.056Z-.webp "Various Types Of Clevis And Hitch Pins")
### Understanding Clevis Pins
Clevis pins are fundamental components in mechanical connections. At PTSMAKE, we manufacture these pins with precision because their design is crucial for safety-critical applications. The typical clevis pin consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end and a hole at the other end for inserting a cotter pin or other retaining device.
The basic structure includes:
- A flat or domed head
- A precisely machined shaft
- A cross-hole for the retaining device
- Optional grooves for improved retention
### Hitch Pin Configurations
Based on my manufacturing experience, hitch pins represent a more modern approach to quick-connect solutions. They typically feature:
| Feature | Purpose | Common Applications |
|---------|----------|-------------------|
| Spring-loaded balls | Quick locking mechanism | Agricultural equipment |
| L-shaped design | Easy grip and removal | Trailer hitches |
| Bridge pin style | Heavy-duty applications | Construction machinery |
| Swivel designs | Flexible connections | Mobile equipment |
### Material Selection Considerations
The choice of materials significantly impacts pin performance. Here's what we consider when manufacturing these components:
- Steel Alloys: Most common for general applications
- Stainless Steel: For corrosive environments
- Heat-treated variants: For exceptional strength requirements
- Zinc or chrome plating: For enhanced corrosion resistance
### Critical Applications
In my manufacturing practice, I've observed these pins being crucial in:
1. Agricultural Equipment
- Implement attachments
- Three-point hitches
- Power take-off shields
2. Construction Machinery
- Bucket attachments
- Boom connections
- Safety linkages
3. Transportation Systems
- Trailer couplings
- Towing equipment
- Safety chains
### Design Variations
Modern manufacturing allows for various design modifications:
#### Head Styles
- Button head for low-profile applications
- T-handled for easy manipulation
- Flanged head for load distribution
- Ring-top for quick access
#### Retention Methods
1. Traditional cotter pins
2. Lynch pins
3. R-clips
4. Bridge pins with internal springs
### Installation and Maintenance Tips
For optimal performance, consider these factors:
1. Proper Sizing
- Diameter tolerance within ±0.005"
- Length allowing for full engagement
- Head clearance requirements
2. Regular Inspection
- Check for wear patterns
- Monitor retention device condition
- Verify proper alignment
### Safety Considerations
When implementing these components:
1. Load Ratings
- Always verify weight capacity
- Consider dynamic loads
- Factor in safety margins
2. Environmental Factors
- Temperature extremes
- Exposure to elements
- Chemical compatibility
3. Replacement Schedules
- Regular inspection intervals
- Wear indicator monitoring
- Preventive maintenance timing
### Advanced Manufacturing Aspects
At PTSMAKE, we focus on several critical manufacturing elements:
1. Surface Finish
- Specific roughness requirements
- Plating considerations
- Corrosion protection
2. Tolerance Control
- Precise diameter control
- Straightness specifications
- Roundness requirements
3. Quality Testing
- Material certification
- Dimensional verification
- Load testing protocols
This comprehensive understanding of clevis and hitch pins ensures optimal performance in various applications. The key is selecting the right combination of design, material, and retention method for your specific needs.
## What Are Grooved Pins and Their Applications?
Having worked extensively with precision components, I've noticed that grooved pins often get overlooked despite their crucial role in modern assembly applications. These small but mighty fasteners deserve more attention than they typically receive.
**Grooved pins are cylindrical fasteners with longitudinal grooves pressed into their surface, designed to provide superior holding power in assemblies. They excel in applications requiring reliable fastening without the complexity of threaded connections.**
%[Grooved Pins Structure And Applications](https://ptsmake.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ptsmake2025-02-04T091328.925Z-.webp "Grooved Pins In Manufacturing")
### Understanding Grooved Pin Design
The distinctive feature of grooved pins lies in their unique surface structure. These pins have several longitudinal grooves pressed into their surface, typically ranging from 3 to 6 grooves depending on the pin diameter. The grooves create slight material displacement when inserted into a hole, generating retention force through elastic deformation of both the pin and hole material.
### Material Composition and Properties
The choice of material significantly impacts a grooved pin's performance. Here's a detailed breakdown of common materials:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Best Applications |
|--------------|----------------|-------------------|
| Carbon Steel | High strength, economical, good wear resistance | General purpose assemblies, automotive components |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, moderate strength | Food equipment, outdoor applications, marine use |
| Hardened Steel | Superior wear resistance, highest strength | High-stress applications, precision machinery |
| Brass | Non-magnetic, good conductivity | Electronic equipment, sensitive instruments |
### Applications Across Industries
In my manufacturing experience, I've seen grooved pins excel in various applications:
1. Automotive Assembly
- Door hinge components
- Seat adjustment mechanisms
- Dashboard assembly fixtures
2. Electronics Manufacturing
- Circuit board mounting
- Connector alignment
- Housing assemblies
3. Furniture Production
- Joint reinforcement
- Panel alignment
- Hardware mounting
### Installation Considerations
Proper installation is crucial for optimal performance. The key factors include:
1. Hole Preparation
- Correct diameter sizing (typically H7 tolerance)
- Proper surface finish
- Appropriate depth calculation
2. Installation Method
- Press-fit installation
- Light hammer installation
- Automated insertion systems
### Performance Advantages
Grooved pins offer several distinct advantages:
1. Retention Strength
- Superior holding power compared to smooth pins
- Consistent performance over time
- Resistance to vibration loosening
2. Cost Efficiency
- Simple design reduces manufacturing costs
- Quick installation saves labor time
- Minimal maintenance requirements
### Design Guidelines
When incorporating grooved pins into assemblies, consider these critical factors:
1. Load Requirements
- Shear force calculations
- Tensile strength needs
- Dynamic load considerations
2. Environmental Factors
- Temperature exposure
- Chemical exposure
- Moisture presence
3. Assembly Parameters
- Material thickness
- Access for installation
- Maintenance requirements
### Troubleshooting Common Issues
Understanding potential problems helps ensure successful implementation:
1. Installation Problems
- Misalignment during insertion
- Improper hole preparation
- Wrong pin size selection
2. Performance Issues
- Insufficient holding power
- Premature wear
- Corrosion concerns
3. Solutions
- Proper tool selection
- Regular maintenance checks
- Material compatibility verification
### Innovation and Future Trends
The grooved pin industry continues to evolve with:
1. Advanced Materials
- Composite materials integration
- Enhanced coating technologies
- Smart material applications
2. Manufacturing Improvements
- Precision grinding techniques
- Automated quality control
- Sustainable production methods
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I've observed that successful grooved pin applications require careful consideration of all these factors. The key lies in understanding not just the component itself, but how it integrates into the larger assembly system. When properly specified and installed, grooved pins provide a reliable, cost-effective fastening solution for a wide range of applications.
## How Are Specialty and Custom Pins Designed?
Have you ever wondered why some industries require pins that can't be found in any catalog? In aerospace, medical devices, and robotics, standard pins often fall short. The demand for specialized pins that meet exact specifications has never been higher.
**Custom pins are designed through a precise collaboration between engineers and manufacturers, utilizing advanced CNC machining and injection molding. The process involves detailed requirement analysis, material selection, prototyping, and rigorous testing to ensure each pin meets specific industry standards.**
%[Custom Pin Manufacturing Process](https://ptsmake.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ptsmake2025-02-04T091437.000Z-.webp "Advanced CNC Machining For Custom Pins")
### Understanding Custom Pin Requirements
The journey of creating specialty pins begins with a thorough understanding of application requirements. At PTSMAKE, we analyze several critical factors:
- Operating environment conditions
- Load-bearing requirements
- Material compatibility needs
- Assembly and installation specifications
- Industry-specific regulations
### Material Selection Process
Material selection is crucial for custom pins. Here's a breakdown of common materials and their applications:
| Material Type | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|--------------|----------------|---------------------|
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistant, high strength | Medical devices, food processing |
| Titanium | Lightweight, biocompatible | Aerospace, medical implants |
| Engineering Plastics | Chemical resistant, cost-effective | Electronics, consumer products |
| Tool Steel | Wear resistant, high hardness | Industrial machinery, robotics |
### Design Considerations for Different Industries
The design process varies significantly across industries:
#### Medical Industry Requirements
Medical pins require exceptional precision and biocompatibility. We focus on:
- Sterilization compatibility
- Surface finish requirements
- Material traceability
- FDA compliance documentation
#### Aerospace Applications
Aerospace pins demand the highest level of reliability:
- Extreme temperature resistance
- Specific strength-to-weight ratios
- Fatigue resistance properties
- AS9100 certification compliance
#### Robotics and Automation
Robotics applications require pins with:
- Precise dimensional accuracy
- Wear resistance properties
- Dynamic load capabilities
- Smooth operation characteristics
### Manufacturing Techniques
Our manufacturing approach combines various techniques:
#### CNC Machining Process
- High-precision turning operations
- Multi-axis milling capabilities
- Micro-machining for intricate features
- Advanced surface finishing options
#### Quality Control Measures
Quality assurance is integral to custom pin manufacturing:
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) inspection
- Material certification verification
- Surface roughness testing
- Dimensional tolerance checking
- Functional testing protocols
### Design Optimization Strategies
We employ several strategies to optimize custom pin designs:
1. Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- Stress distribution analysis
- Deformation prediction
- Fatigue life estimation
2. Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
- Cost optimization
- Production efficiency
- Material utilization
3. Prototype Development
- Rapid prototyping options
- Functional testing
- Design iteration capabilities
### Industry-Specific Certifications
Different industries require various certifications:
| Industry | Required Certifications | Quality Standards |
|----------|------------------------|-------------------|
| Medical | ISO 13485, FDA | GMP compliance |
| Aerospace | AS9100D | NADCAP |
| Automotive | IATF 16949 | PPAP requirements |
| Industrial | ISO 9001 | Industry standards |
### Production Scaling Considerations
When moving from prototype to production, we consider:
1. Volume Requirements
- Batch size optimization
- Production scheduling
- Inventory management
2. Cost Management
- Material selection optimization
- Process efficiency improvements
- Quality control automation
3. Documentation
- Production process documentation
- Quality control records
- Material traceability
The design and manufacturing of specialty and custom pins requires a comprehensive understanding of industry requirements, material properties, and manufacturing capabilities. At PTSMAKE, we combine our expertise in CNC machining and injection molding with rigorous quality control to deliver pins that meet the most demanding specifications. Through continuous innovation and adherence to industry standards, we ensure that each custom pin solution provides optimal performance for its intended application.
## How To Choose the Right Type of Pin?
Selecting the wrong pin type can lead to product failure, safety hazards, and costly recalls. In my role at PTSMAKE, I've seen how this seemingly simple component can make or break a product's success.
**The right pin choice depends on four key factors: application requirements, material compatibility, environmental conditions, and manufacturing specifications. A systematic evaluation of these elements ensures optimal performance and reliability.**
%[Pin Types Manufacturing Process](https://ptsmake.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/ptsmake2025.02.04-1836.webp "Various Types Of Industrial Pins")
### Understanding Pin Application Requirements
The first step in pin selection is clearly defining your application needs. This involves analyzing several critical factors:
- Load requirements
- Installation method
- Space constraints
- Assembly/disassembly frequency
- Cost considerations
I recommend creating a detailed requirements checklist before proceeding with pin selection. This helps prevent overlooking crucial factors that could affect performance.
### Material Selection Guidelines
Material choice significantly impacts pin performance. Here's a comprehensive comparison of common pin materials:
| Material Type | Strength | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Best Applications |
|--------------|----------|---------------------|-------|-------------------|
| Stainless Steel | High | Excellent | Moderate | Medical, food processing |
| Carbon Steel | Very High | Poor | Low | Heavy machinery |
| Brass | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Electrical components |
| Aluminum | Low | Good | Low | Light-duty applications |
| Titanium | Very High | Excellent | High | Aerospace, medical |
### Size and Tolerance Considerations
Proper sizing is crucial for pin functionality. Consider these aspects:
1. Diameter tolerances
2. Length requirements
3. Head size (if applicable)
4. Hole fit specifications
At PTSMAKE, we maintain tight tolerances of ±0.01mm for precision applications. This level of accuracy ensures proper fit and function across various applications.
### Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions significantly influence pin performance:
- Temperature range
- Exposure to chemicals
- Moisture levels
- Vibration intensity
- UV exposure
For example, in outdoor applications, I always recommend using corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel or applying appropriate surface treatments.
### Manufacturing Process Selection
The manufacturing method affects both quality and cost:
1. CNC Machining
- Best for complex geometries
- Excellent for small batches
- Higher cost per unit
2. Cold Forming
- Ideal for high volume
- More economical
- Limited to simpler designs
3. Swiss Turning
- Perfect for long, thin pins
- High precision capability
- Moderate cost
### Quality Assurance Measures
To ensure pin reliability, implement these quality checks:
1. Dimensional inspection
2. Material certification
3. Surface finish verification
4. Hardness testing
5. Load testing (when applicable)
### Cost Optimization Strategies
Balance quality and cost through:
- Material selection optimization
- Production volume analysis
- Manufacturing process selection
- Secondary operation reduction
- Supplier partnership development
### Supplier Selection Criteria
Choose manufacturers based on:
1. Technical capabilities
2. Quality certifications
3. Production capacity
4. Communication effectiveness
5. Delivery reliability
### Common Challenges and Solutions
Address typical pin-related issues:
1. Quality Inconsistencies
- Solution: Implement robust QC processes
- Regular supplier audits
- Clear specification documentation
2. Delivery Delays
- Solution: Buffer stock management
- Multiple supplier relationships
- Clear lead time agreements
3. Communication Issues
- Solution: Regular progress updates
- Dedicated project management
- Clear documentation requirements
### Working with PTSMAKE
Our approach to pin manufacturing includes:
1. Technical Consultation
- Material selection guidance
- Design optimization support
- Manufacturing process recommendation
2. Quality Assurance
- ISO 9001:2015 certified processes
- Advanced inspection equipment
- 100% quality verification
3. Production Efficiency
- Automated manufacturing systems
- Lean production practices
- Quick changeover capabilities
By following these guidelines and working with experienced manufacturers, you can ensure the selection of the right pin type for your application. The key is to thoroughly evaluate all requirements and maintain clear communication with your manufacturing partner throughout the process.






