Many manufacturers struggle with PP injection molding, facing issues like warping, shrinkage, and inconsistent part quality. I’ve seen these problems cause significant production delays and costly material waste, particularly when molding complex PP parts.
The key factors in PP injection molding are mold temperature (40-80°C), melt temperature (200-280°C), injection pressure (10,000-15,000 PSI), and cooling time. These parameters directly impact part quality, cycle time, and production efficiency.
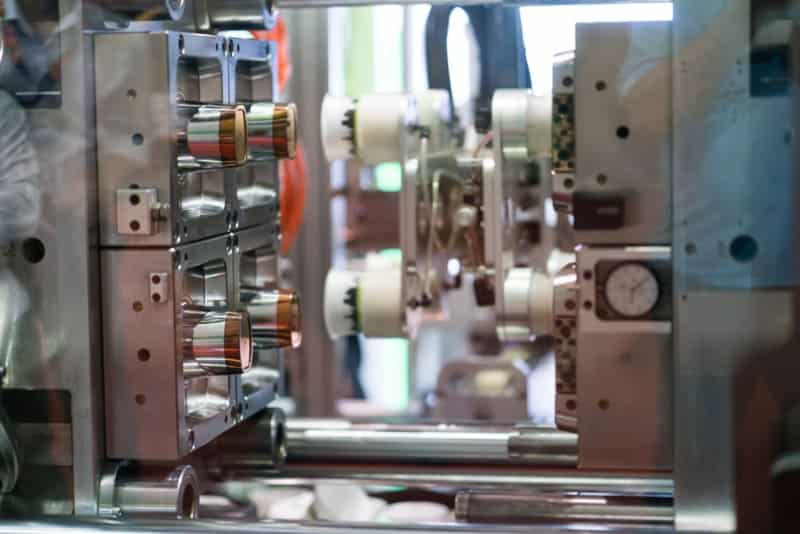

Let me share what I’ve learned about optimizing these key factors at PTSMAKE. We’ll explore each parameter in detail, and I’ll show you how proper control can significantly improve your PP molding results. From material preparation to final part ejection, every step matters in achieving consistent quality.
What Is PP Injection Molding?
Have you ever wondered why some plastic products feel inconsistent in quality or fail prematurely? Many manufacturers struggle with plastic part production, facing issues like warping, shrinkage, and poor surface finish. These problems not only lead to costly production delays but can also damage brand reputation.
PP injection molding is a manufacturing process that transforms polypropylene (PP) plastic pellets into solid parts by heating them until molten, then injecting the material into a mold cavity under high pressure. This versatile process creates everything from automotive parts to consumer goods.

Understanding PP Material Properties
PP, or polypropylene, stands out in the world of plastics for its unique combination of properties. This semi-crystalline1 polymer offers exceptional benefits that make it ideal for injection molding:
Chemical and Physical Properties
- Melting point: 130-171°C
- Density: 0.895-0.92 g/cm³
- Chemical resistance: Excellent against acids and bases
- Moisture absorption: Very low
Mechanical Properties
- High flexural strength
- Good fatigue resistance
- Excellent impact strength
- Low friction coefficient
The PP Injection Molding Process Steps
At PTSMAKE, we follow a precise sequence of steps to ensure optimal results:
Material Preparation
- Drying PP pellets (if necessary)
- Adding colorants or additives
- Setting up the injection molding machine
Plasticization
- Heating PP to melting temperature
- Maintaining consistent melt temperature
- Controlling screw speed and back pressure
Injection Phase
- Filling the mold cavity
- Applying holding pressure
- Cooling and solidification
Part Ejection
- Opening the mold
- Removing the finished part
- Quality inspection
Key Process Parameters
Success in PP injection molding depends on precise control of various parameters:
| Parameter | Typical Range | Impact on Part Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 200-280°C | Affects flow and surface finish |
| Injection Pressure | 500-1500 bar | Determines part filling |
| Mold Temperature | 20-60°C | Influences cooling and warpage |
| Cooling Time | 10-30 seconds | Controls dimensional stability |
Common Applications
PP injection molding serves various industries with its versatile applications:
Automotive Components
- Interior trim parts
- Battery cases
- Bumper components
- Fluid reservoirs
Consumer Goods
- Food containers
- Household items
- Toys and recreational products
- Garden furniture
Industrial Applications
- Material handling containers
- Industrial equipment housings
- Chemical storage tanks
- Protective covers
Design Considerations for PP Injection Molding
To achieve optimal results, consider these design principles:
Wall Thickness
- Maintain uniform wall thickness
- Recommended range: 1.0-3.0mm
- Gradual transitions between sections
Draft Angles
- Minimum 1-2 degrees for textured surfaces
- 0.5-1 degree for smooth surfaces
- Increased angles for deep draws
Gate Location
- Strategic placement for flow patterns
- Multiple gates for large parts
- Consideration of weld line locations
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement comprehensive quality control:
Visual Inspection
- Surface finish evaluation
- Color consistency check
- Flash and sink mark detection
Dimensional Verification
- Critical dimension measurements
- Warpage assessment
- Shrinkage compensation
Performance Testing
- Impact resistance tests
- Environmental stress testing
- Load-bearing capacity verification
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, here are solutions to common problems:
Warpage
- Optimize cooling time
- Adjust mold temperature
- Review gate locations
Sink Marks
- Modify wall thickness
- Adjust holding pressure
- Review cooling system design
Short Shots
- Increase injection pressure
- Check material temperature
- Verify gate size adequacy
Cost Optimization Strategies
To maintain competitive pricing while ensuring quality:
Material Selection
- Grade optimization
- Regrind usage consideration
- Bulk purchasing strategies
Process Efficiency
- Cycle time reduction
- Energy consumption optimization
- Automation implementation
Tool Maintenance
- Preventive maintenance scheduling
- Regular cleaning procedures
- Wear monitoring
What Are the Benefits and Disadvantages of Polypropylene?
Have you ever struggled with choosing the right plastic material for your products? Many manufacturers face this challenge daily, often feeling overwhelmed by the numerous options available. The wrong choice can lead to product failures, increased costs, and project delays.
Polypropylene (PP) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer that offers an excellent balance of properties, including high chemical resistance, good mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness. However, it also has limitations such as UV sensitivity and limited low-temperature performance.
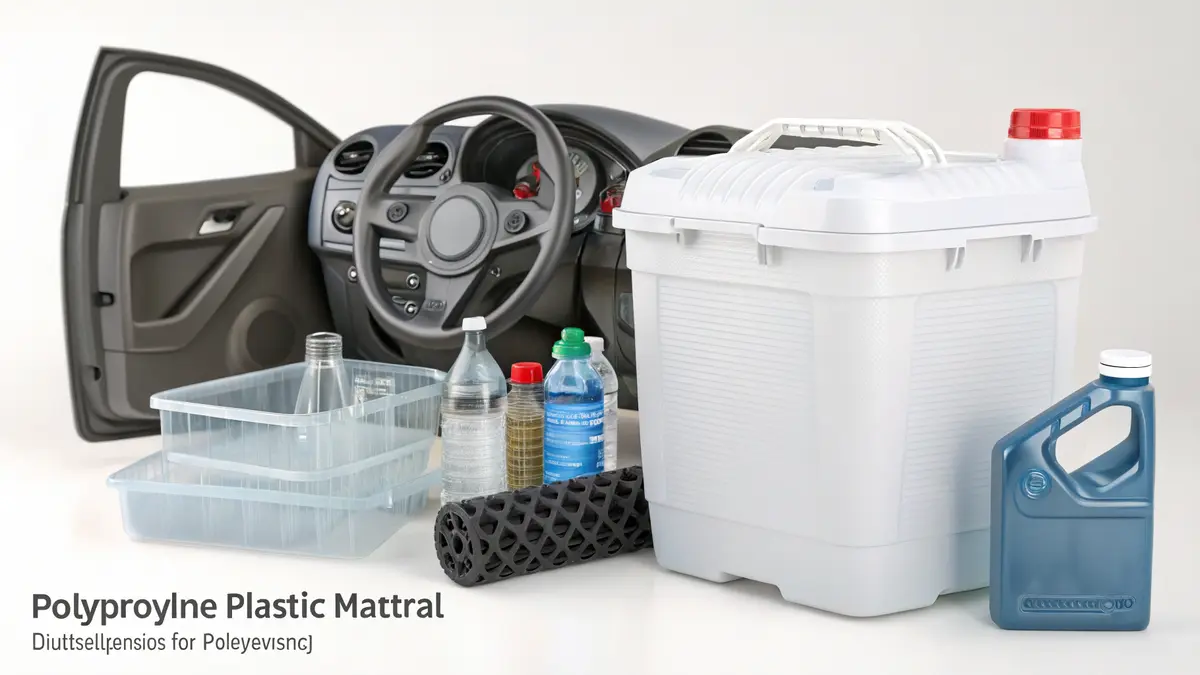

Chemical Properties and Molecular Structure
The unique properties of polypropylene stem from its molecular structure. PP consists of carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in a specific pattern, creating a tacticity that significantly influences its characteristics. I’ve observed that different grades of PP can be engineered to meet specific requirements, making it highly adaptable for various applications.
Chemical Resistance
PP demonstrates excellent resistance to:
- Acids and bases
- Chemical solvents
- Common household chemicals
- Industrial cleaning agents
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve worked with numerous PP applications. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its mechanical properties:
| Property | Value Range | Industry Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 32-43 MPa | ASTM D638 |
| Flexural Modulus | 1.14-1.55 GPa | ISO 178 |
| Impact Strength | 2.5-7.0 kJ/m² | ASTM D256 |
| Density | 0.90-0.91 g/cm³ | ASTM D792 |
Key Benefits
Cost-Effectiveness
PP is one of the most economical polymers available. At PTSMAKE, we often recommend it to clients seeking budget-friendly solutions without compromising quality.
Processing Versatility
The material offers:
- Easy processing in injection molding
- Good flow characteristics
- Short cycle times
- Minimal warpage
Environmental Advantages
- 100% recyclable
- Lower energy consumption during processing
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Minimal waste generation
Notable Limitations
Temperature Sensitivity
PP shows limitations in:
- Low-temperature environments (below 0°C)
- High-temperature applications (above 120°C)
- Thermal cycling conditions
UV and Oxidation Vulnerability
Without proper additives, PP can experience:
- Color fading
- Surface degradation
- Reduced mechanical properties
- Shortened lifespan
Industry Applications
Automotive Sector
PP finds extensive use in:
- Interior trim components
- Battery cases
- Bumper systems
- Under-hood components
Consumer Goods
Common applications include:
- Food containers
- Household items
- Packaging materials
- Textile products
Medical Industry
PP is crucial for:
- Syringes
- Medical containers
- Laboratory equipment
- Diagnostic tools
Material Selection Considerations
When helping clients at PTSMAKE choose between PP and other materials, I consider several factors:
Environmental Conditions
- Operating temperature range
- UV exposure
- Chemical exposure
- Mechanical stress requirements
Processing Requirements
- Production volume
- Cycle time needs
- Surface finish requirements
- Dimensional stability
Cost Factors
- Material price
- Processing costs
- Tool maintenance
- Product lifecycle
Design Optimization Tips
For successful PP applications, consider:
Wall Thickness
- Maintain uniform wall thickness
- Avoid thick sections
- Design appropriate ribs and gussets
Gate Location
- Optimize for flow pattern
- Consider weld line placement
- Account for shrinkage behavior
Surface Finish
- Plan for texture requirements
- Consider post-processing needs
- Account for aesthetic expectations
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous quality control procedures:
Material Testing
- Melt flow index verification
- Moisture content analysis
- Contamination checks
Process Monitoring
- Temperature control
- Pressure monitoring
- Cycle time optimization
Product Validation
- Dimensional inspection
- Performance testing
- Visual inspection
The success of PP applications largely depends on understanding both its capabilities and limitations. Through careful material selection, proper design considerations, and appropriate quality control measures, manufacturers can effectively leverage PP’s benefits while mitigating its disadvantages.
What Temperature Is Needed for Polypropylene Injection Molding?
Setting the wrong temperature for PP injection molding can lead to serious quality issues and production delays. I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with warped parts, incomplete fills, and material degradation simply because they couldn’t nail down the right temperature settings.
For polypropylene injection molding, the optimal melt temperature typically ranges from 380°F to 480°F (193°C to 249°C), while the mold temperature should be maintained between 80°F to 120°F (27°C to 49°C). These temperatures ensure proper material flow and part quality.

Understanding Temperature Zones in PP Injection Molding
Barrel Temperature Profile
The thermal gradient2 across different heating zones plays a crucial role in achieving optimal material flow. At PTSMAKE, we typically set up our barrel temperatures in multiple zones:
| Zone | Temperature Range (°F) | Temperature Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Zone | 360-380 | 182-193 |
| Compression Zone | 400-420 | 204-216 |
| Metering Zone | 440-460 | 227-238 |
| Nozzle | 460-480 | 238-249 |
Critical Factors Affecting Temperature Selection
Material Grade Considerations
Different PP grades require specific temperature settings:
- Homopolymer PP: Generally processes at lower temperatures
- Copolymer PP: Requires slightly higher temperatures
- Glass-filled PP: Needs higher temperatures to ensure proper fiber orientation
Part Design Impact
The complexity of your part design directly influences temperature requirements:
- Thin-walled parts need higher temperatures for better flow
- Thick sections can use lower temperatures to prevent sink marks
- Complex geometries may require varied temperature profiles
Temperature-Related Processing Issues and Solutions
Common Problems
Short Shots
- Cause: Too low melt temperature
- Solution: Gradually increase barrel temperature by 10°F increments
Burning
- Cause: Excessive melt temperature
- Solution: Reduce barrel temperature while maintaining proper fill
Warpage
- Cause: Improper mold temperature
- Solution: Adjust mold temperature for uniform cooling
Temperature Control Best Practices
Startup Procedures
- Begin with lower temperature settings
- Gradually increase to operating temperature
- Allow sufficient soak time
- Verify temperature uniformity across zones
Production Monitoring
- Use infrared temperature guns for surface temperature checks
- Monitor power consumption of heating elements
- Regular calibration of temperature sensors
Advanced Temperature Considerations
Material Specific Adjustments
Different PP formulations require specific temperature considerations:
| PP Type | Melt Temperature (°F) | Mold Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|---|
| Recycled PP | 380-420 | 80-100 |
| Medical Grade | 420-460 | 90-110 |
| Flame Retardant | 440-480 | 100-120 |
Environmental Factors
Temperature control must account for:
- Ambient temperature fluctuations
- Humidity levels
- Cooling system efficiency
- Machine location
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement strict temperature monitoring protocols:
- Continuous temperature logging
- Regular quality checks
- Process parameter documentation
- Statistical process control
Optimization Strategies
Fine-Tuning Process
Initial Setup
- Start with manufacturer’s recommended temperatures
- Document baseline parameters
- Perform short-run trials
Parameter Adjustment
- Make single variable changes
- Allow sufficient stabilization time
- Document all changes and results
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Proper temperature management affects energy consumption:
- Insulate barrel and hot runner systems
- Maintain optimal cooling water temperature
- Regular maintenance of heating elements
- Use energy-efficient heating systems
We at PTSMAKE place significant emphasis on energy efficiency while maintaining precise temperature control. Our advanced monitoring systems ensure consistent temperature profiles throughout production runs, resulting in high-quality PP parts for our clients in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods.
What Is PP Filler Used For?
Have you ever struggled with high material costs in plastic manufacturing while trying to maintain product quality? Many manufacturers face this challenge, especially when working with polypropylene (PP). The rising costs of raw materials and increasing pressure to reduce production expenses can feel overwhelming.
PP fillers are additives mixed with pure polypropylene to enhance specific properties while reducing overall material costs. These materials, including calcium carbonate, talc, and glass fibers, can improve strength, stiffness, and heat resistance while making production more cost-effective.
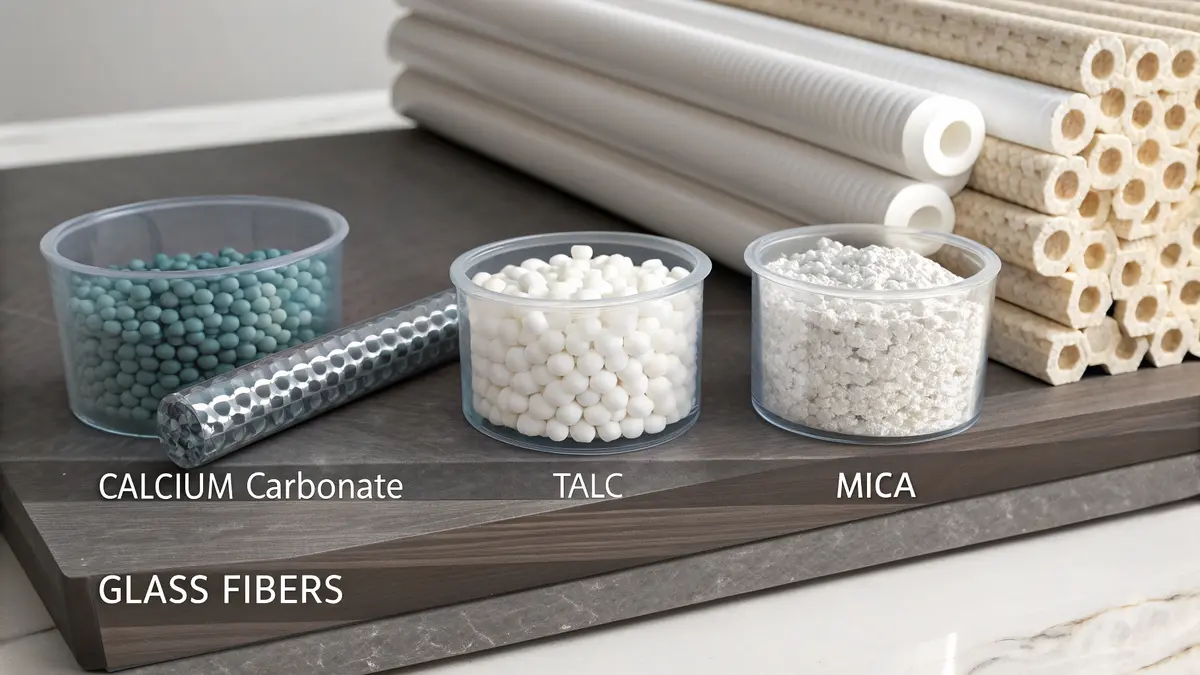

Common Types of PP Fillers
At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with various PP fillers to meet different manufacturing requirements. Here are the most common types:
Mineral Fillers
- Calcium Carbonate
- Talc
- Mica
- Kaolin
These mineral reinforcements3 provide unique benefits to PP compounds. I’ve found that each type offers distinct advantages for specific applications.
Glass-Based Fillers
- Glass Fibers
- Glass Beads
- Glass Flakes
Properties Enhanced by PP Fillers
Different fillers improve various properties of PP materials. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Filler Type | Primary Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Carbonate | Cost reduction, Impact resistance | Automotive parts, Consumer goods |
| Talc | Stiffness, Heat resistance | Appliance components |
| Glass Fiber | Strength, Dimensional stability | Structural parts |
| Mica | Electrical properties, Heat resistance | Electronic housings |
Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive Industry
In my experience at PTSMAKE, automotive manufacturers frequently request PP with specific fillers for:
- Interior trim components
- Under-hood parts
- Exterior body panels
- Battery housings
The automotive sector demands materials that can withstand various environmental conditions while maintaining structural integrity.
Consumer Goods
For consumer products, we often recommend filled PP for:
- Appliance housings
- Furniture components
- Storage containers
- Garden equipment
Industrial Applications
The industrial sector benefits from filled PP in:
- Chemical storage tanks
- Industrial containers
- Material handling equipment
- Structural components
Cost-Benefit Analysis
When implementing PP fillers, consider these factors:
Material Cost Reduction
- Raw material savings: 15-30%
- Processing efficiency improvements
- Reduced waste management costs
Performance Improvements
- Enhanced mechanical properties
- Better thermal stability
- Improved dimensional accuracy
Production Considerations
- Equipment requirements
- Processing parameters
- Quality control measures
Environmental Impact
The use of PP fillers can contribute to sustainability in several ways:
Reduced Carbon Footprint
- Lower energy consumption during processing
- Decreased raw material usage
- More efficient transportation due to weight reduction
Recycling Considerations
The presence of fillers can affect recycling processes. At PTSMAKE, we carefully select fillers that maintain recyclability while meeting performance requirements.
Best Practices for PP Filler Implementation
Based on our experience at PTSMAKE, here are key considerations:
Material Selection
- Identify specific application requirements
- Consider environmental conditions
- Evaluate cost constraints
- Assess processing capabilities
Processing Guidelines
- Proper drying procedures
- Temperature control
- Mixing ratios
- Quality control measures
Performance Testing
To ensure optimal results, we conduct:
Mechanical Testing
- Tensile strength
- Impact resistance
- Flexural properties
- Heat deflection
Quality Assurance
- Dimensional stability
- Surface finish
- Color consistency
- Long-term durability
Future Trends
The PP filler industry continues to evolve with:
Advanced Hybrid Fillers
- Combinations of different filler types
- Engineered particle sizes
- Surface-modified variants
Sustainable Options
- Bio-based fillers
- Recycled content
- Biodegradable alternatives
Smart Materials
- Conductive fillers
- Thermal management additives
- Sensor-compatible compounds
Technical Considerations
When working with filled PP, consider:
Processing Parameters
- Melt temperature control
- Injection pressure adjustments
- Cooling time modifications
- Screw design requirements
Quality Control Measures
- Regular material testing
- Process monitoring
- Product validation
- Documentation requirements
Through careful selection and implementation of PP fillers, manufacturers can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining or improving product performance. At PTSMAKE, we continually explore new filler technologies and applications to provide our customers with optimal solutions for their specific needs.
What Destroys Polypropylene?
Have you ever noticed your polypropylene products deteriorating unexpectedly? This common plastic, found in everything from food containers to automotive parts, can mysteriously degrade, leaving many manufacturers and users puzzled and frustrated by premature failures.
Polypropylene (PP) primarily degrades through oxidation, UV exposure, extreme temperatures, and certain chemical exposures. These factors can break down the polymer chains, leading to brittleness, discoloration, and eventual material failure, significantly reducing the product’s lifespan.
Understanding the Chemical Degradation Process
The deterioration of polypropylene involves complex chemical reactions. When exposed to various environmental factors, PP undergoes chain scission4, which breaks down the long polymer chains into shorter segments. This process typically manifests in several ways:
Oxidative Degradation
- Free radical formation
- Chain breaking reactions
- Formation of carbonyl groups
- Reduced molecular weight
Thermal Effects on PP Structure
Thermal degradation occurs through different mechanisms:
| Temperature Range (°C) | Effect on PP | Visible Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Below 0 | Becomes brittle | Surface cracking |
| 0-100 | Generally stable | Minimal change |
| Above 100 | Softening begins | Deformation |
| Above 160 | Severe degradation | Melting, discoloration |
Environmental Factors Affecting PP Stability
UV Radiation Impact
In my experience working with injection molding at PTSMAKE, UV radiation is one of the most significant threats to PP stability. The process typically follows these stages:
- Initial photon absorption
- Free radical formation
- Progressive chain breakdown
- Surface deterioration
Chemical Exposure Effects
Different chemicals affect PP in various ways:
| Chemical Type | Impact Level | Prevention Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Strong acids | Severe | Special additives required |
| Strong bases | Moderate | Surface treatment |
| Organic solvents | Mild to severe | Material grade selection |
| Oxidizing agents | Severe | Antioxidant addition |
Prevention Strategies in Manufacturing
As a manufacturer specializing in PP injection molding, I’ve implemented several strategies to enhance PP stability:
Material Selection and Modification
- Using high-quality PP grades
- Adding appropriate stabilizers:
- Antioxidants
- UV stabilizers
- Heat stabilizers
- Process stabilizers
Processing Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we focus on these critical aspects during PP injection molding:
- Temperature control
- Moisture management
- Processing speed optimization
- Cooling rate regulation
Real-World Applications and Solutions
Industrial Applications
Different industries require specific approaches:
| Industry | Common Issues | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | UV exposure | UV stabilizers + carbon black |
| Medical | Sterilization damage | Special PP grades |
| Packaging | Chemical resistance | Barrier layers |
| Electronics | Heat exposure | Thermal stabilizers |
Maintenance and Storage
To maximize PP product lifespan:
- Store in controlled environments
- Avoid direct sunlight
- Maintain moderate temperatures
- Prevent chemical exposure
Testing and Quality Control
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous testing protocols:
Physical Testing
- Impact strength
- Tensile strength
- Flexural properties
- Dimensional stability
Chemical Analysis
- Oxidation induction time
- Molecular weight distribution
- Crystallinity assessment
- Thermal analysis
Future Developments in PP Protection
The field of PP protection continues to evolve:
- New stabilizer technologies
- Advanced processing methods
- Improved additive packages
- Enhanced testing protocols
Based on my manufacturing experience, the key to preventing PP degradation lies in understanding these destructive factors and implementing appropriate preventive measures. At PTSMAKE, we continuously update our injection molding processes to incorporate the latest developments in PP protection technology, ensuring our clients receive products with optimal durability and performance.
Remember, successful PP product manufacturing requires a comprehensive approach combining material science, processing expertise, and quality control. By understanding what destroys polypropylene, we can better protect and enhance this versatile material’s performance across various applications.
What Is the Difference Between PLA and PP Injection Molding?
When manufacturers need to choose between PLA and PP for injection molding, they often struggle with understanding their distinct characteristics. Making the wrong material choice can lead to product failures, wasted resources, and costly production delays.
Both PLA and PP are popular materials for injection molding, but they serve different purposes. PLA is a biodegradable polymer ideal for eco-friendly applications, while PP offers superior durability and chemical resistance, making it perfect for long-lasting consumer products.
Material Properties and Processing Requirements
Physical Properties Comparison
PLA (Polylactic Acid) and PP (Polypropylene) have distinct physical characteristics that affect their crystallization behavior5 during the molding process. At PTSMAKE, we’ve observed that these differences significantly impact the final product quality.
| Property | PLA | PP |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 150-180°C | 160-170°C |
| Density | 1.24 g/cm³ | 0.90 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Medium | High |
Processing Parameters
The success of injection molding with either material depends heavily on proper processing parameters:
Temperature Control
- PLA requires precise temperature control (180-220°C)
- PP offers more flexibility (200-280°C)
- Mold temperature for PLA: 20-30°C
- Mold temperature for PP: 20-60°C
Injection Speed and Pressure
- PLA needs moderate injection speeds to prevent degradation
- PP tolerates higher injection speeds
- Both materials require different holding pressures
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biodegradability
PLA stands out for its biodegradable properties, breaking down in industrial composting facilities within 3-6 months. PP, being a conventional plastic, can take hundreds of years to decompose.
Carbon Footprint
PLA production generally results in:
- Lower carbon emissions
- Reduced fossil fuel dependency
- Renewable resource utilization
PP manufacturing involves:
- Higher carbon emissions
- Petroleum-based resources
- Non-renewable material consumption
Application Considerations
Industry-Specific Uses
| Industry | PLA Applications | PP Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Medical | Surgical implants, Drug delivery systems | Medical equipment, Syringes |
| Packaging | Food containers, Disposable cutlery | Reusable containers, Bottle caps |
| Consumer Goods | Eco-friendly products, Disposable items | Durable goods, Automotive parts |
| Electronics | Temporary components, Prototypes | Long-term housing, Electrical parts |
Cost Analysis
The economic aspects of choosing between PLA and PP include:
Material Costs
- PLA: Generally higher cost per kg
- PP: More economical for large-scale production
- Volume considerations affect overall costs
Processing Costs
- PLA requires more precise control, potentially increasing setup time
- PP offers more forgiving processing windows
- Equipment maintenance requirements differ
Quality Control and Testing
Common Quality Issues
For PLA:
- Warping due to crystallization
- Moisture sensitivity
- Limited heat resistance
- Surface finish variations
For PP:
- Shrinkage control
- Weld line strength
- Color consistency
- Flow mark prevention
Testing Methods
Quality assurance procedures include:
- Dimensional accuracy testing
- Impact resistance evaluation
- Environmental stress testing
- Chemical resistance assessment
Expert Tips for Material Selection
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, here are key considerations for choosing between PLA and PP:
Project Requirements Analysis:
- Expected product lifespan
- Environmental conditions
- Mechanical stress levels
- Cost constraints
Production Considerations:
- Volume requirements
- Equipment capabilities
- Quality control measures
- Post-processing needs
Environmental Factors:
- Regulatory compliance
- End-of-life disposal
- Carbon footprint goals
- Customer preferences
Economic Aspects:
- Initial investment
- Running costs
- Material availability
- Market demands
In my daily work with clients at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that successful material selection comes from understanding these differences and aligning them with specific project requirements. The key is not just knowing the technical aspects but also considering the practical implications for your specific application.
Is PLA Better Than PP?
Choosing between PLA and PP can be confusing for many product designers and engineers. I often see professionals struggling to decide which material best suits their applications, especially when considering environmental impact versus performance requirements.
The answer isn’t straightforward – PLA and PP each have their unique advantages. PLA excels in biodegradability and printing ease, while PP offers superior durability and chemical resistance. Your specific application requirements should guide your choice.
Material Properties Comparison
When comparing PLA and PP, we need to examine several key properties. At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with both materials in our injection molding processes, and I’ve observed their distinct characteristics firsthand.
Mechanical Properties
The crystallinity6 of these materials significantly affects their performance. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Property | PLA | PP |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 50-70 MPa | 30-40 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Medium | High |
| Flexibility | Limited | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 60°C | Up to 120°C |
Environmental Impact
Biodegradability
PLA offers clear advantages in terms of environmental impact:
- Biodegrades in industrial composting conditions
- Made from renewable resources
- Lower carbon footprint during production
PP, while not biodegradable, has its own environmental benefits:
- Highly recyclable
- Durable, meaning less frequent replacement
- Lower energy consumption during processing
Cost Considerations
The cost analysis extends beyond just material prices:
| Factor | PLA | PP |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Processing Cost | Medium | Low |
| End-of-Life Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |
Application Scenarios
Industrial Applications
PP generally performs better in industrial settings due to:
- Better chemical resistance
- Higher temperature tolerance
- Superior fatigue resistance
- Greater impact strength
I’ve seen numerous successful implementations of PP in automotive parts, chemical containers, and medical devices at PTSMAKE.
Consumer Products
PLA shows strengths in:
- Food packaging
- Disposable items
- Low-stress applications
- Products requiring biodegradability
Processing Considerations
Injection Molding Parameters
Both materials require different processing approaches:
| Parameter | PLA | PP |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Temperature | 20-25°C | 20-60°C |
| Melt Temperature | 180-210°C | 200-250°C |
| Injection Pressure | Higher | Lower |
| Cooling Time | Longer | Shorter |
Quality Control Challenges
Some common challenges we encounter:
PLA:
- Moisture sensitivity
- Narrow processing window
- Thermal degradation risks
PP:
- Shrinkage control
- Warpage issues
- Surface finish variations
Performance in Different Environments
Temperature Performance
- PLA becomes soft around 60°C
- PP maintains stability up to 120°C
- Temperature cycling affects PLA more significantly
Chemical Resistance
PP demonstrates superior resistance to:
- Acids and bases
- Common solvents
- Cleaning agents
- Oil and grease
Moisture Sensitivity
PLA requires more careful handling due to:
- Higher moisture absorption
- Potential degradation during storage
- Need for pre-drying before processing
Making the Right Choice
Consider these factors when choosing between PLA and PP:
Application Requirements:
- Operating temperature
- Chemical exposure
- Mechanical stress levels
- Environmental conditions
Production Considerations:
- Volume requirements
- Cost constraints
- Processing capabilities
- Quality specifications
Environmental Impact:
- End-of-life disposal
- Recycling requirements
- Carbon footprint goals
- Regulatory compliance
At PTSMAKE, we help clients navigate these decisions by conducting detailed material analysis and running test runs to ensure optimal material selection for each application.
Future Developments
The landscape of plastic materials continues to evolve:
- New PLA grades with improved heat resistance
- Enhanced PP formulations for specific applications
- Hybrid materials combining benefits of both
- Advanced recycling technologies
I believe both materials will continue to play important roles in different applications, with improvements in properties and processing capabilities further expanding their use cases.
What Is the Best Plastic for Injection Molding?
When selecting plastics for injection molding, many engineers and product designers face overwhelming choices. With hundreds of plastic materials available, making the wrong choice can lead to project delays, quality issues, and unnecessary costs.
The best plastic for injection molding depends on your specific application requirements. Generally, thermoplastics like PP, ABS, and POM are popular choices due to their excellent balance of mechanical properties, processability, and cost-effectiveness.

Understanding Material Properties for Injection Molding
In my experience at PTSMAKE, the key to selecting the right plastic material lies in understanding its fundamental properties. The material’s molecular weight distribution7 significantly affects its processing characteristics and final part performance.
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile strength
- Impact resistance
- Flexural modulus
- Wear resistance
- Hardness
Thermal Properties
- Heat deflection temperature
- Melting point
- Thermal expansion
- Thermal conductivity
Chemical Properties
- Chemical resistance
- UV stability
- Moisture absorption
- Environmental stress crack resistance
Common Thermoplastics and Their Applications
Let me break down the most popular thermoplastic materials we frequently use at PTSMAKE:
Polypropylene (PP)
PP remains one of our most requested materials due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. It offers:
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Good fatigue resistance
- Low density
- High strength-to-weight ratio
Common applications include:
- Consumer products
- Automotive components
- Medical devices
- Food containers
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS provides excellent impact resistance and surface finish:
- High impact strength
- Good dimensional stability
- Easy to paint and plate
- Excellent aesthetic properties
Polyoxymethylene (POM/Acetal)
POM is ideal for precision engineering components:
- High stiffness
- Excellent dimensional stability
- Low friction coefficient
- Good wear resistance
Material Selection Guide
Here’s a comparative table of common thermoplastics based on key properties:
| Material | Strength | Cost | Chemical Resistance | Heat Resistance | Processability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | Medium | Low | Excellent | Medium | Excellent |
| ABS | High | Medium | Good | Medium | Good |
| POM | High | High | Good | High | Good |
| PA | High | Medium | Medium | High | Medium |
| PC | Very High | High | Poor | High | Medium |
Industry-Specific Considerations
Automotive Industry
For automotive applications, we often recommend:
- Glass-filled PP for structural components
- ABS/PC blends for exterior parts
- POM for mechanical components
- PA66 for under-hood applications
Medical Industry
Medical applications require:
- USP Class VI or ISO 10993 compliance
- Sterilization resistance
- Chemical compatibility
- Biocompatibility
Consumer Electronics
Electronics housings need:
- Flame retardancy (UL94 ratings)
- EMI shielding capabilities
- Good aesthetic properties
- Impact resistance
Cost Considerations and Material Economics
The total cost of material selection includes:
- Raw material cost
- Processing requirements
- Tooling considerations
- Production cycle times
- Scrap rates
- Secondary operations
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
At PTSMAKE, we’re increasingly focusing on sustainable materials:
- Recycled content options
- Bio-based alternatives
- Energy-efficient processing
- End-of-life considerations
Quality Control and Testing
To ensure material performance:
- Material certification
- Incoming material testing
- Process parameter validation
- Final part testing
- Long-term stability assessment
Advanced Material Options
For specialized applications, we offer:
- Custom compound formulations
- Reinforced materials
- Special additive packages
- High-performance blends
The best plastic for injection molding ultimately depends on balancing:
- Application requirements
- Processing considerations
- Economic factors
- Environmental impact
- Quality standards
Through careful material selection and our advanced manufacturing capabilities at PTSMAKE, we help clients optimize their injection molding projects for success. We consider not just the immediate performance requirements but also long-term durability, cost-effectiveness, and environmental responsibility.
How to Optimize PP Injection Molding for Better Results?
Achieving consistent quality in PP injection molding can be challenging. I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with issues like warping, sink marks, and dimensional instability, leading to high scrap rates and production delays. These problems not only impact product quality but also significantly increase production costs and delivery times.
To optimize PP injection molding, focus on four key areas: proper material handling, precise temperature control, optimized injection parameters, and effective cooling strategies. These elements, combined with regular process monitoring and adjustments, ensure high-quality PP parts production.

Understanding Material Properties and Preparation
PP (Polypropylene) exhibits unique crystallization behavior8 during processing, which directly impacts part quality. At PTSMAKE, we always emphasize proper material preparation before molding:
Drying Requirements
- Pre-drying temperature: 70-80°C
- Drying time: 2-3 hours
- Moisture content: < 0.05%
Material Storage Guidelines
| Storage Parameter | Recommended Value | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 20-25°C | Prevents moisture absorption |
| Relative Humidity | < 50% | Maintains material stability |
| Container Type | Sealed container | Protects from contamination |
| Storage Duration | Max 6 months | Ensures material properties |
Temperature Control Optimization
Barrel Temperature Profile
| Zone | Temperature Range (°C) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Feed Zone | 190-200 | Initial material softening |
| Compression Zone | 200-220 | Material plastification |
| Metering Zone | 220-230 | Final melt preparation |
| Nozzle | 220-230 | Optimal flow condition |
Injection Parameters Settings
Critical Process Parameters
Injection Speed
- Fast enough to prevent premature freezing
- Slow enough to avoid burning or shear damage
- Typical range: 50-100 mm/s
Injection Pressure
- Initial pressure: 600-800 bar
- Hold pressure: 40-60% of injection pressure
- Duration: Based on gate freeze time
Mold Temperature
- Core side: 20-30°C
- Cavity side: 20-30°C
- Temperature differential: < 5°C
Cooling Strategy Implementation
Cooling System Design
Channel Layout
- Uniform cooling channel distribution
- Optimal channel diameter: 8-12mm
- Channel spacing: 2.5-3 times diameter
Cooling Time Calculation
- Based on wall thickness
- Typical range: 10-30 seconds
- Monitor part temperature at ejection
Quality Control Measures
Process Monitoring
| Parameter | Monitoring Frequency | Acceptable Variation |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | Every 2 hours | ±5°C |
| Injection Pressure | Every shot | ±2% |
| Cooling Time | Every setup | ±1 second |
| Part Weight | Every hour | ±0.1% |
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Surface Defects Prevention
Sink Marks
- Increase packing pressure
- Optimize cooling system
- Adjust wall thickness design
Flow Lines
- Increase melt temperature
- Adjust injection speed
- Modify gate location
Warpage
- Balance cooling
- Optimize packing parameters
- Review part design
Process Documentation and Control
Parameter Recording
- Document all process settings
- Track changes and results
- Maintain historical data
Quality Metrics
- First article inspection
- In-process checks
- Final quality verification
Advanced Optimization Techniques
Scientific Molding Approach
- Systematic process development
- Data-driven optimization
- Continuous improvement
Design of Experiments (DOE)
- Identify critical parameters
- Optimize parameter combinations
- Validate results
At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented these optimization strategies across numerous PP injection molding projects. Our systematic approach has consistently delivered superior results, with typical improvements including:
- 30% reduction in scrap rate
- 25% decrease in cycle time
- 40% improvement in surface quality
- 50% reduction in defect rates
By following these guidelines and continuously monitoring and adjusting the process, you can achieve optimal results in PP injection molding. Remember that successful optimization is an ongoing process that requires attention to detail and regular evaluation of results.
What Are Common Defects in PP Injection Molding?
Manufacturing PP parts through injection molding can be challenging. I’ve seen many clients struggle with quality issues, facing production delays and increased costs due to defects. These issues not only affect product quality but also impact their business reputation and bottom line.
Common defects in PP injection molding include sink marks, warping, burn marks, short shots, and flow lines. These issues typically arise from incorrect processing parameters, poor mold design, or material handling problems. However, with proper knowledge and control measures, most defects can be prevented or minimized.
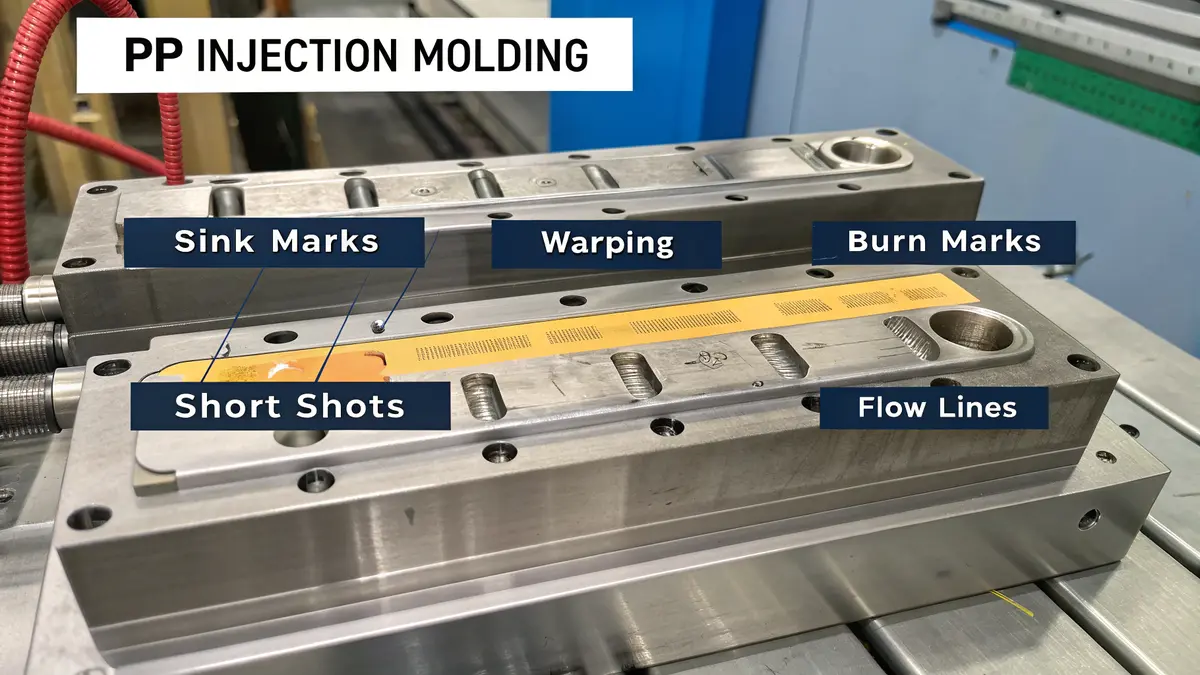
Understanding Sink Marks and Prevention
Sink marks are one of the most common defects I encounter in PP injection molding. These depressions occur when thicker sections of the part cool and shrink unevenly. The volumetric shrinkage9 of PP during cooling can lead to these unsightly surface depressions.
To prevent sink marks:
- Maintain uniform wall thickness
- Optimize cooling channel design
- Adjust holding pressure and time
- Consider using a higher injection pressure
Warping: Causes and Solutions
Warping occurs when different sections of the PP part cool at different rates, causing internal stresses. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed several strategies to minimize warping:
Design Considerations
- Uniform wall thickness
- Proper rib design
- Strategic gate location
- Balanced cooling system design
Processing Parameters
- Optimal melt temperature
- Balanced cooling time
- Appropriate holding pressure
- Controlled ejection temperature
Flow Lines and Their Prevention
Flow lines appear as wavy patterns or lines on the surface of PP parts. These visual defects often occur in areas far from the gate or around obstacles.
Key Prevention Measures
| Factor | Control Method | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | Increase within range | Improves flow characteristics |
| Injection Speed | Optimize for material | Reduces visible flow patterns |
| Gate Design | Proper sizing and location | Ensures uniform filling |
| Material Selection | Grade selection | Affects flow behavior |
Burn Marks: Identification and Resolution
Burn marks appear as brownish or black discolorations on PP parts. They result from trapped air being compressed and heated during injection.
Prevention Strategies
- Optimize venting system
- Adjust injection speed
- Control melt temperature
- Verify material moisture content
Short Shots and Their Solutions
Short shots occur when the mold cavity isn’t completely filled. Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, several factors contribute to this defect:
Material-Related Factors
- Incorrect PP grade selection
- Improper drying
- Contamination
- Degraded material
Process-Related Solutions
| Parameter | Adjustment | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Pressure | Increase | Better cavity filling |
| Melt Temperature | Optimize | Improved flow |
| Gate Size | Enlarge if needed | Enhanced material flow |
| Runner System | Balance design | Uniform filling |
Flash Formation Control
Flash appears as excess material at the parting line or other areas. To control flash in PP molding:
Prevention Methods
- Regular mold maintenance
- Proper clamp force calculation
- Optimized processing parameters
- Mold surface quality inspection
Jetting Prevention
Jetting creates snake-like patterns on the part surface. At PTSMAKE, we prevent jetting through:
Design Solutions
- Gate design optimization
- Runner system improvements
- Wall thickness adjustments
- Flow leader implementation
Color and Pigment Issues
Inconsistent coloring can affect PP parts’ appearance. Control measures include:
- Proper masterbatch percentage
- Uniform material mixing
- Temperature control
- Residence time management
- Screw design optimization
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent PP part quality, we implement:
Inspection Procedures
| Stage | Check Points | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Process parameters | Each setup |
| Production | Visual inspection | Hourly |
| Post-molding | Dimensional check | Per batch |
| Final | Quality validation | Per lot |
Material Handling Guidelines
Proper PP material handling is crucial for defect prevention:
- Moisture control through proper drying
- Contamination prevention
- Regrind percentage management
- Storage condition monitoring
- Material rotation system
Through implementing these comprehensive control measures, we at PTSMAKE consistently achieve high-quality PP injection molded parts. Our systematic approach to defect prevention has helped numerous clients maintain their production quality while reducing costs associated with rejections and rework.
Learn about semi-crystalline polymers and their benefits for better material choices in manufacturing. ↩
Learn about temperature variations in molding for optimal material processing. ↩
Discover how these reinforcements enhance performance and reduce costs in PP applications. ↩
Learn about chain scission to understand polypropylene degradation and improve material durability. ↩
Learn how crystallization affects polymer properties and impacts product quality in injection molding. ↩
Learn how crystallinity affects material performance for better design choices. ↩
Learn about how molecular weight impacts processing and performance in injection molding materials. ↩
Learn how polymer arrangement affects the quality and properties of molded parts. ↩
Learn about volumetric shrinkage to prevent sink marks and ensure better PP part quality. ↩







