In today’s manufacturing landscape, engineers and designers often struggle to find materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity. Many conventional stainless steels either lack the necessary strength or fail to provide adequate corrosion resistance, leading to premature part failures and increased maintenance costs.
17-4 PH stainless steel is a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel that combines exceptional strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good hardness properties. Its unique composition, featuring chromium, nickel, copper, and other alloying elements, makes it ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors.
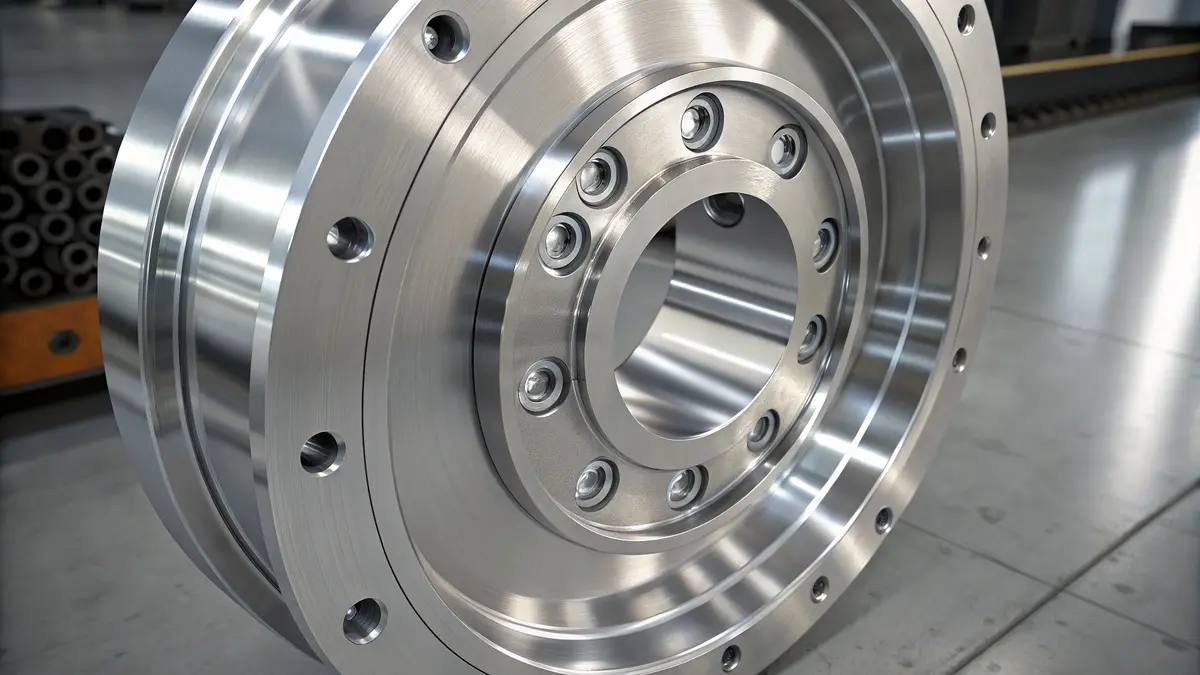

Chemical Composition and Structure
The exceptional properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel stem from its carefully balanced chemical composition. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its main components:
| Element | Percentage Range |
|---|---|
| Chromium | 15.0-17.5% |
| Nickel | 3.0-5.0% |
| Copper | 3.0-5.0% |
| Carbon | Max 0.07% |
| Silicon | Max 1.0% |
| Manganese | Max 1.0% |
| Phosphorus | Max 0.04% |
| Sulfur | Max 0.03% |
| Iron | Balance |
Key Properties and Characteristics
I’ve worked with various grades of stainless steel, and 17-4 PH stands out for several reasons:
Mechanical Properties:
- Ultimate Tensile Strength: 170,000 PSI (1,170 MPa)
- Yield Strength: 150,000 PSI (1,030 MPa)
- Hardness: 35-45 HRC (after heat treatment)
Corrosion Resistance:
- Excellent resistance to atmospheric corrosion
- Good resistance to many chemical environments
- Superior performance in marine environments
Heat Treatment Options
The versatility of 17-4 PH comes from its various heat treatment conditions:
- Condition A: Solution treated
- Condition H900: Peak hardness and strength
- Condition H1025: Better ductility with good strength
- Condition H1150: Maximum ductility
Industry Applications
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen 17-4 PH used effectively in:
Aerospace:
- Aircraft fittings
- Landing gear components
- Structural parts
Medical:
- Surgical instruments
- Dental tools
- Medical device components
Industrial:
- Pump shafts
- Valve components
- Chemical processing equipment
Manufacturing Considerations
When working with 17-4 PH stainless steel, several factors require attention:
Machining:
- Use sharp, coated carbide tools
- Maintain steady feeds and speeds
- Provide adequate cooling during machining
Welding:
- Preheating recommended
- Post-weld heat treatment often necessary
- Use matching filler metals
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While 17-4 PH might have a higher initial cost compared to standard stainless steels, its benefits often justify the investment:
Long-term advantages:
- Reduced maintenance costs
- Extended service life
- Better performance in critical applications
Value considerations:
- Lower replacement frequency
- Improved safety margins
- Enhanced reliability
Quality Control
At PTSMAKE, we implement strict quality control measures for 17-4 PH components:
Material verification:
- Chemical composition testing
- Mechanical property validation
- Heat treatment certification
Manufacturing inspection:
- Dimensional accuracy checks
- Surface finish verification
- Non-destructive testing when required
Comparison with Other Stainless Steels
17-4 PH offers distinct advantages over other stainless steel grades:
Versus 316 Stainless:
- Higher strength
- Better wear resistance
- Similar corrosion resistance
Versus 440C Stainless:
- Better corrosion resistance
- More uniform properties
- Superior toughness
This comprehensive understanding of 17-4 PH stainless steel helps ensure optimal material selection and application success. The material’s unique combination of properties continues to make it a preferred choice in demanding applications where reliability and performance are crucial.
What are the Chemical and Mechanical Properties?
Understanding the chemical and mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel can be overwhelming. Many engineers struggle with selecting the right material for their projects due to the complex relationship between composition, heat treatment, and final properties. This complexity often leads to costly mistakes in material selection and processing.
17-4 PH stainless steel is a precipitation-hardening martensitic stainless steel that combines high strength, good corrosion resistance, and excellent mechanical properties. Its unique chemical composition and response to heat treatment make it ideal for demanding applications in aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors.
Chemical Composition
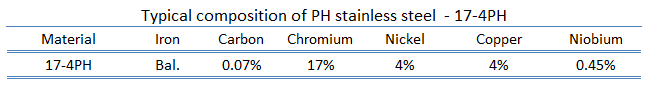
The chemical composition of 17-4 PH stainless steel is carefully balanced to achieve its remarkable properties. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its elemental composition:
| Element | Percentage Range (%) |
|---|---|
| Chromium | 15.0 – 17.5 |
| Nickel | 3.0 – 5.0 |
| Copper | 3.0 – 5.0 |
| Niobium + Tantalum | 0.15 – 0.45 |
| Carbon | 0.07 max |
| Manganese | 1.0 max |
| Silicon | 1.0 max |
| Phosphorus | 0.04 max |
| Sulfur | 0.03 max |
| Iron | Balance |
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel vary significantly depending on the heat treatment condition. I’ve seen remarkable differences in performance across various heat treatment states:
Condition A (Solution Annealed)
- Tensile Strength: 1000 MPa
- Yield Strength: 760 MPa
- Elongation: 10%
- Hardness: 33 HRC
Condition H900 (Peak Aged)
- Tensile Strength: 1380 MPa
- Yield Strength: 1280 MPa
- Elongation: 10%
- Hardness: 45 HRC
Heat Treatment Effects
The heat treatment process significantly influences the final properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel. From my experience working with various manufacturers, I’ve observed these critical aspects:
Solution Treatment
- Temperature: 1038°C (1900°F)
- Cooling: Air cool or oil quench
- Results: Creates supersaturated martensitic structure
Aging Treatments
Different aging temperatures produce various property combinations:
| Condition | Temperature (°C) | Time (Hours) | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | 482 | 1 | Maximum strength |
| H925 | 496 | 4 | High strength with better ductility |
| H1025 | 552 | 4 | Improved toughness |
| H1150 | 621 | 4 | Maximum ductility |
Corrosion Resistance
The corrosion resistance of 17-4 PH stainless steel comes from its high chromium content and is comparable to Type 304 stainless steel. Key characteristics include:
- Excellent resistance to atmospheric corrosion
- Good resistance to many chemical environments
- Enhanced resistance in the aged condition
- Suitable for marine environments
Application-Specific Properties
Based on my daily interactions with clients across different industries, I’ve noticed these industry-specific requirements:
Aerospace Applications
- High fatigue strength
- Excellent stress corrosion resistance
- Good dimensional stability
Medical Industry
- Bio-compatibility
- High cleanliness
- Consistent mechanical properties
Industrial Applications
- Wear resistance
- Impact strength
- Thermal stability
Temperature Effects
The material’s behavior at different temperatures is crucial for many applications:
| Temperature Range | Property Changes |
|---|---|
| -73°C to 24°C | Maintains toughness |
| 24°C to 316°C | Stable strength |
| 316°C to 427°C | Gradual strength decrease |
| Above 427°C | Significant property changes |
Processing Considerations
For optimal results when working with 17-4 PH stainless steel, these factors require attention:
- Proper solution treatment before aging
- Controlled cooling rates
- Precise aging temperature control
- Surface preparation methods
- Post-processing heat treatment requirements
This comprehensive understanding of 17-4 PH stainless steel’s properties helps ensure successful application in various industries. The material’s versatility and reliability make it an excellent choice for demanding applications requiring high strength and good corrosion resistance.
How is the Heat Treatment Process Performed?
Heat treating 17-4 PH stainless steel can be tricky and confusing for many manufacturers. I’ve seen countless projects fail due to improper heat treatment processes, resulting in parts that don’t meet specifications and costly production delays. This is especially frustrating when dealing with high-precision components where material properties are critical.
The heat treatment process for 17-4 PH stainless steel involves two main steps: solution annealing at 1900°F (1038°C) followed by precipitation hardening at specific temperatures ranging from 900°F to 1150°F (482-621°C) to achieve desired mechanical properties.
Solution Annealing: The Foundation
Solution annealing is the crucial first step in the heat treatment process. We heat the material to 1900°F (1038°C) and hold it at this temperature for about 30 minutes per inch of thickness. This process dissolves all precipitates into the austenitic matrix, creating a homogeneous structure. After heating, we rapidly cool the material to below 90°F (32°C) using forced air or oil quenching, which transforms the austenite to martensite.
Precipitation Hardening Conditions
The second phase involves aging treatments at different temperatures, each producing unique mechanical properties. Here’s a detailed breakdown of common conditions:
| Condition | Temperature | Time | Typical Hardness (HRC) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (ksi) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | 900°F (482°C) | 1 hour | 44-46 | 190-210 |
| H925 | 925°F (496°C) | 4 hours | 40-42 | 170-190 |
| H1025 | 1025°F (552°C) | 4 hours | 35-37 | 155-170 |
| H1075 | 1075°F (579°C) | 4 hours | 31-33 | 145-160 |
| H1150 | 1150°F (621°C) | 4 hours | 28-32 | 135-150 |
Temperature Control and Monitoring
Precise temperature control is essential during both solution annealing and aging treatments. We use calibrated thermocouples and modern heat treatment furnaces with temperature uniformity of ±10°F (±5.6°C). The heating rate should be controlled to prevent thermal shock, typically around 400°F (204°C) per hour.
Microstructural Changes During Heat Treatment
During precipitation hardening, copper-rich precipitates form within the martensitic matrix. The size and distribution of these precipitates directly influence the material’s mechanical properties:
- Lower aging temperatures (H900-H925): Produces fine, closely spaced precipitates resulting in maximum strength and hardness
- Higher aging temperatures (H1075-H1150): Creates larger, more widely spaced precipitates leading to improved ductility and toughness
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent heat treatment results, we implement several quality control measures:
- Regular furnace calibration and temperature mapping
- Hardness testing after heat treatment
- Tensile testing for critical applications
- Microstructure examination when required
Common Heat Treatment Challenges
The heat treatment process can face several challenges that need careful attention:
- Warping and distortion during rapid cooling
- Incomplete transformation during solution annealing
- Non-uniform heating in large or complex parts
- Surface oxidation during high-temperature exposure
Optimizing Heat Treatment Parameters
The selection of heat treatment parameters depends on the application requirements:
High Strength Applications (H900-H925):
- Aerospace components
- High-pressure valve parts
- Surgical instruments
Balanced Properties (H1025):
- General industrial components
- Pump shafts
- Fasteners
Maximum Toughness (H1075-H1150):
- Impact-resistant parts
- Heavy-duty machinery components
- Marine applications
Being in the manufacturing industry for over 15 years, I’ve found that heat treatment is as much an art as it is a science. Understanding the relationship between processing parameters and final properties is crucial for achieving consistent results. At PTSMAKE, we maintain detailed process documentation and continuously monitor our heat treatment operations to ensure reliable and repeatable outcomes for our clients.
What are the Common Applications?
Have you ever wondered why some industries seem to consistently choose certain materials over others? In the world of manufacturing, selecting the wrong material can lead to catastrophic failures, especially in critical applications where lives and millions of dollars are at stake. The challenge of finding a material that combines exceptional strength with superior corrosion resistance has long puzzled engineers and designers.
17-4 PH stainless steel has emerged as a versatile solution across multiple industries, from aerospace to medical devices. Its unique combination of high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good machinability makes it ideal for critical components in demanding applications.

Aerospace Industry Applications
The aerospace sector relies heavily on 17-4 PH stainless steel for critical components. I’ve worked with numerous aerospace clients who choose this material for its exceptional properties:
- Landing gear components
- Turbine blades
- Fasteners and structural elements
- Actuator shafts
- Engine mounts
The material’s high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to extreme temperatures make it particularly valuable in aircraft applications. Many of our aerospace clients specifically request 17-4 PH for parts that require both strength and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures.
Automotive Sector Implementation
In the automotive industry, 17-4 PH stainless steel finds applications in:
| Component | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Transmission parts | High torque resistance |
| Valve components | Temperature stability |
| Steering mechanisms | Excellent wear resistance |
| Performance racing parts | Superior strength |
| Suspension components | Durability under stress |
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical industry values 17-4 PH stainless steel for its:
- Biocompatibility
- Sterilization capability
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- High strength-to-weight ratio
Common medical applications include:
- Surgical instruments
- Dental tools
- Medical implants
- Laboratory equipment
- Sterilization containers
Energy Sector Usage
The energy industry relies on 17-4 PH stainless steel for various critical components:
| Application | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Turbine blades | High fatigue resistance |
| Pump shafts | Superior corrosion resistance |
| Valve stems | Excellent wear properties |
| Pressure vessels | High strength retention |
| Heat exchanger parts | Temperature stability |
Marine Industry Implementation
In marine applications, 17-4 PH stainless steel proves invaluable due to its exceptional corrosion resistance in saltwater environments. Common uses include:
- Propeller shafts
- Underwater fasteners
- Marine pumps
- Valve components
- Structural supports
Chemical Processing Equipment
The chemical processing industry benefits from 17-4 PH stainless steel’s properties in:
- Reaction vessels
- Pump components
- Valve bodies
- Mixing equipment
- Process piping
Oil and Gas Applications
The oil and gas sector utilizes 17-4 PH stainless steel in various applications:
| Component | Critical Feature |
|---|---|
| Wellhead components | Corrosion resistance |
| Valve bodies | High pressure capability |
| Downhole tools | Strength retention |
| Pump components | Wear resistance |
| Fasteners | Environmental durability |
Food Processing Equipment
The food industry values 17-4 PH stainless steel for:
- Mixing equipment
- Processing vessels
- Cutting tools
- Storage containers
- Transport equipment
The material’s ability to maintain cleanliness and resist corrosion makes it ideal for food-grade applications.
Nuclear Power Applications
In nuclear power plants, 17-4 PH stainless steel is used in:
- Reactor components
- Fuel handling equipment
- Pressure vessels
- Valve bodies
- Structural supports
The material’s stability under radiation exposure and high temperatures makes it particularly suitable for nuclear applications.
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that the versatility of 17-4 PH stainless steel continues to expand into new applications. Its unique combination of properties – high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good machinability – makes it an ideal choice for critical components across various industries. We regularly work with clients to optimize their designs and manufacturing processes to take full advantage of this remarkable material’s capabilities.
How Does 17-4 PH Compare to Other Stainless Steels?
Choosing between different stainless steel grades can be overwhelming. With so many options available, engineers often struggle to determine which grade will best suit their specific application. Making the wrong choice can lead to premature part failure, increased maintenance costs, and project delays.
17-4 PH stainless steel offers a unique combination of high strength, good corrosion resistance, and excellent heat treatment response. While it excels in many applications, it may not always be the best choice compared to grades like 304, 316, or 15-5 PH, depending on specific requirements.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
When it comes to corrosion resistance, each stainless steel grade has its strengths. I’ve found that 17-4 PH offers good overall corrosion resistance, but it’s not always the top performer. Here’s how it compares:
- 316 Stainless Steel: Provides superior corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments and against chemical attack
- 304 Stainless Steel: Offers excellent general corrosion resistance in non-chloride environments
- 17-4 PH: Good general corrosion resistance, but may be susceptible to pitting in high-chloride environments
- 15-5 PH: Similar to 17-4 PH, with slightly better corrosion resistance in some conditions
Mechanical Properties and Hardness
The mechanical properties of these grades vary significantly:
| Property | 17-4 PH | 304 | 316 | 15-5 PH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 1070-1310 | 515-620 | 485-620 | 1070-1270 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 1000-1170 | 205-310 | 170-310 | 1000-1140 |
| Hardness (HRC) | 35-45 | 88 HRB | 95 HRB | 35-45 |
Machinability Characteristics
I’ve worked with various machine shops, and their feedback consistently shows that machinability varies between these grades:
- 17-4 PH: Good machinability, especially in the annealed condition
- 304: Moderate machinability, tends to work harden during machining
- 316: Similar to 304 but slightly more difficult to machine
- 15-5 PH: Comparable to 17-4 PH in terms of machinability
Cost Considerations
The cost difference between these grades can significantly impact project budgets:
| Grade | Relative Cost | Cost Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH | High | Alloying elements, heat treatment |
| 304 | Low | Common grade, widely available |
| 316 | Medium | Higher molybdenum content |
| 15-5 PH | High | Similar to 17-4 PH |
Typical Applications
Each grade has found its niche in specific industries:
17-4 PH Applications
- Aerospace components
- Surgical instruments
- Valve components
- Nuclear reactor parts
304 Applications
- Food processing equipment
- Kitchen equipment
- General purpose fabrication
- Architectural applications
316 Applications
- Marine equipment
- Chemical processing equipment
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing
- Outdoor installations
15-5 PH Applications
- Aircraft components
- High-strength fasteners
- Pump shafts
- Nuclear applications
Heat Treatment Response
The heat treatment capabilities of these grades differ significantly:
- 17-4 PH: Excellent response to aging treatments, can achieve various strength levels
- 304: Non-heat treatable, work hardening only
- 316: Non-heat treatable, work hardening only
- 15-5 PH: Similar to 17-4 PH, slightly different aging responses
Fabrication Considerations
When it comes to fabrication methods:
- Welding: All grades are weldable, but 17-4 PH and 15-5 PH require special procedures
- Forming: 304 and 316 offer better formability than precipitation hardening grades
- Cold Working: 304 and 316 respond well to cold working, while 17-4 PH is typically used in heat-treated conditions
Surface Finish Capabilities
The ability to achieve and maintain surface finish varies:
| Grade | Polishability | Surface Finish Retention |
|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH | Good | Excellent |
| 304 | Excellent | Very Good |
| 316 | Excellent | Excellent |
| 15-5 PH | Good | Excellent |
Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, I recommend 17-4 PH when high strength and moderate corrosion resistance are required, particularly in aerospace and medical applications. However, for marine environments or applications requiring maximum corrosion resistance, 316 stainless steel might be a better choice. 304 remains the most cost-effective option for general-purpose applications where high strength isn’t critical.
What are the Advantages and Limitations?
Selecting the right material for precision manufacturing can feel overwhelming. Many engineers struggle to balance between material properties, cost, and performance requirements. I’ve seen projects fail simply because of poor material selection, leading to costly repairs and production delays.
17-4 PH stainless steel offers an excellent combination of high strength, good corrosion resistance, and ease of fabrication. However, it also has limitations like stress corrosion cracking in certain environments that need careful consideration during material selection.

Key Advantages of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel
Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio
17-4 PH stainless steel delivers exceptional mechanical properties while maintaining a relatively low weight. The material achieves ultimate tensile strengths up to 200,000 psi after heat treatment, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications where high strength and minimal weight are crucial.
Excellent Corrosion Resistance
The high chromium content (15-17.5%) creates a protective oxide layer that provides outstanding resistance to:
- General atmospheric corrosion
- Most acids and alkaline solutions
- Salt water environments
- Industrial chemicals
Versatile Heat Treatment Options
One of the most valuable features of 17-4 PH is its heat treatment flexibility:
| Condition | Temperature Range (°F) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| H900 | 900°F | Maximum strength and hardness |
| H1025 | 1025°F | Balanced strength and ductility |
| H1150 | 1150°F | Maximum ductility and toughness |
Easy Fabrication Properties
The material offers excellent machinability and weldability compared to other high-strength steels. I recommend it for complex geometries and precision components because:
- Good dimensional stability during heat treatment
- Minimal warpage and distortion
- Compatible with standard machining processes
- Excellent surface finish capability
Notable Limitations to Consider
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) Susceptibility
The material can be vulnerable to SCC under specific conditions:
- High tensile stress environments
- Presence of chlorides
- Elevated temperatures
- Certain heat treatment conditions
Cost Considerations
While not a technical limitation, 17-4 PH is more expensive than conventional stainless steels. However, its superior properties often justify the higher initial cost through:
- Extended service life
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Better performance in demanding applications
Temperature Limitations
The material shows some restrictions in extreme temperature applications:
- Maximum service temperature around 600°F
- Reduced mechanical properties at cryogenic temperatures
- Potential phase transformations at elevated temperatures
Application-Specific Considerations
Industry-Specific Requirements
Different industries have varying requirements that affect material selection:
| Industry | Key Considerations | Recommended Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | High strength, fatigue resistance | Landing gear components |
| Medical | Biocompatibility, sterilization | Surgical instruments |
| Oil & Gas | Corrosion resistance, strength | Valve components |
| Automotive | Cost-effectiveness, durability | High-stress components |
Environmental Factors
When selecting 17-4 PH, consider the operating environment:
- Chemical exposure levels
- Temperature cycles
- Mechanical stress patterns
- Humidity and atmospheric conditions
Quality and Certification Requirements
Different applications may require specific certifications:
- AMS specifications for aerospace
- ASTM standards for general engineering
- NACE requirements for oil and gas
- FDA compliance for medical applications
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that successful implementation of 17-4 PH stainless steel requires careful consideration of both its advantages and limitations. We regularly work with customers to evaluate their specific requirements and help them make informed decisions about material selection. The key is to balance the material’s exceptional properties against its limitations within the context of each unique application.
How is 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Machined?
Machining 17-4 PH stainless steel can be a daunting challenge for many manufacturers. The material’s high strength and hardness, especially in the H900 condition, often lead to rapid tool wear and inconsistent surface finishes. I’ve seen many shops struggle with premature tool failures and dimensional accuracy issues when working with this demanding alloy.
The key to successfully machining 17-4 PH stainless steel lies in selecting the right cutting tools, maintaining proper speeds and feeds, and implementing specific cooling strategies. With correct machining parameters and proper tool selection, you can achieve excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances while maximizing tool life.
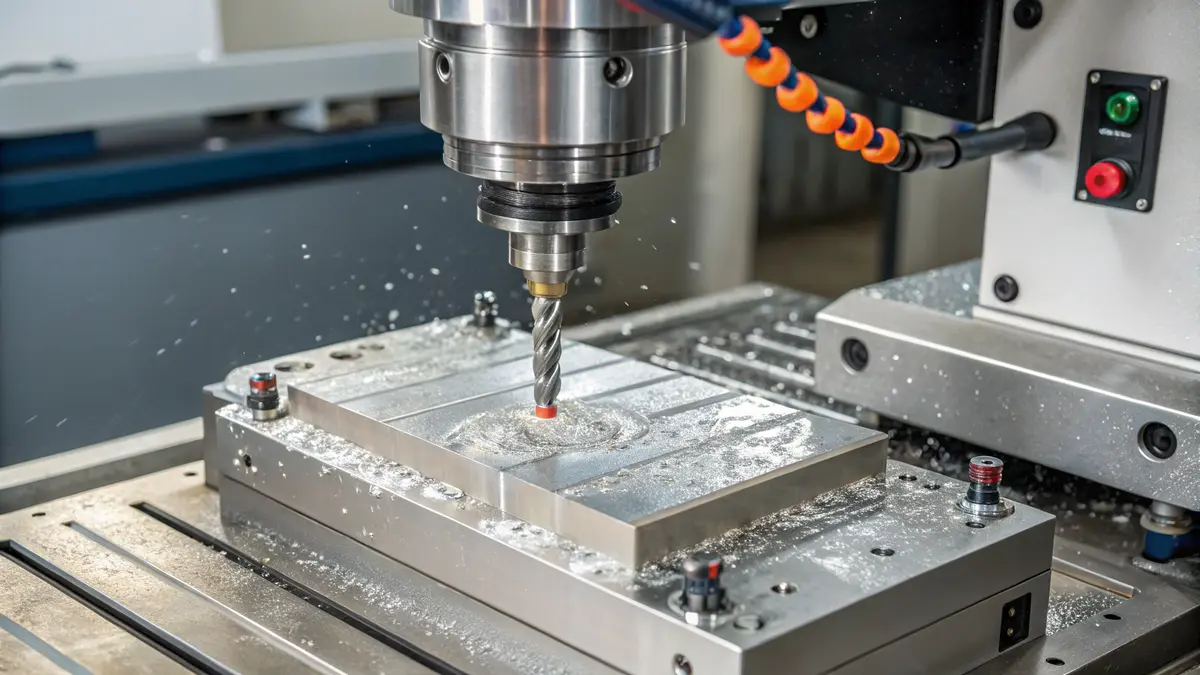

Tool Selection Guidelines
Selecting the right cutting tools is crucial for machining 17-4 PH stainless steel effectively. I recommend using carbide tools with specialized coatings for optimal performance. The most effective options include:
- Multilayer TiAlN coated carbide tools
- PVD-coated grades with enhanced wear resistance
- Tools with positive rake angles to reduce cutting forces
For turning operations, I’ve found that ceramic-coated inserts perform exceptionally well, especially when machining H900 condition material. The coating helps dissipate heat and extends tool life significantly.
Recommended Cutting Parameters
Based on my experience, these cutting parameters work well for most 17-4 PH machining operations:
| Operation Type | Cutting Speed (SFM) | Feed Rate (IPR) | Depth of Cut (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Roughing | 200-250 | 0.008-0.012 | 0.060-0.120 |
| Finishing | 250-300 | 0.004-0.006 | 0.010-0.030 |
| Drilling | 150-200 | 0.004-0.008 | – |
| Threading | 100-150 | Pitch-dependent | 0.002-0.005 |
Cooling Strategies
Proper cooling is essential when machining 17-4 PH stainless steel. I always recommend:
- Using high-pressure coolant (1000 PSI minimum)
- Directing coolant precisely at the cutting edge
- Maintaining consistent coolant flow throughout the operation
- Considering cryogenic cooling for challenging applications
Surface Finish Optimization
To achieve optimal surface finishes when machining 17-4 PH:
- Maintain rigid tool setup with minimal overhang
- Use tools with nose radii appropriate for the finish requirements
- Implement climb milling whenever possible
- Monitor tool wear regularly to prevent surface degradation
Tool Wear Management
Tool wear management is critical for successful machining of 17-4 PH stainless steel. I recommend:
- Regular tool inspection intervals
- Implementing tool wear prediction systems
- Using tool wear monitoring technology
- Having backup tools readily available
Special Considerations for H900 Condition
The H900 condition presents unique challenges due to its increased hardness:
- Reduce cutting speeds by 20-25% compared to annealed material
- Increase coolant pressure and flow
- Use more rigid tooling setups
- Consider specialized coating technologies
Process Optimization Tips
To optimize your machining process:
- Start with conservative cutting parameters
- Monitor cutting forces and adjust accordingly
- Document successful parameter combinations
- Maintain consistent tool geometries across setups
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Some common mistakes to watch out for include:
- Using inadequate coolant pressure
- Exceeding recommended cutting speeds
- Neglecting tool wear monitoring
- Using inappropriate tool geometries
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent quality:
- Implement regular in-process inspections
- Monitor tool wear patterns
- Track surface finish measurements
- Document process parameters for repeatability
Machining 17-4 PH stainless steel requires attention to detail and proper planning. By following these guidelines and maintaining consistent processes, you can achieve excellent results while maximizing tool life and maintaining part quality. Remember that successful machining of this material is a balance between productivity and tool life – finding the right combination of parameters for your specific application is key to long-term success.
What Welding Techniques are Used?
Welding 17-4 PH stainless steel can be tricky, and I’ve seen many manufacturers struggle with cracking and distortion issues. The wrong welding technique can lead to weakened joints, compromised corrosion resistance, and parts that fail quality control. These problems become even more critical in aerospace and medical applications where safety is paramount.
The most effective welding techniques for 17-4 PH stainless steel are TIG (GTAW) and MIG (GMAW) welding, combined with proper pre-heating and post-weld heat treatment. These methods, when executed correctly, maintain the material’s strength and corrosion resistance while minimizing distortion.
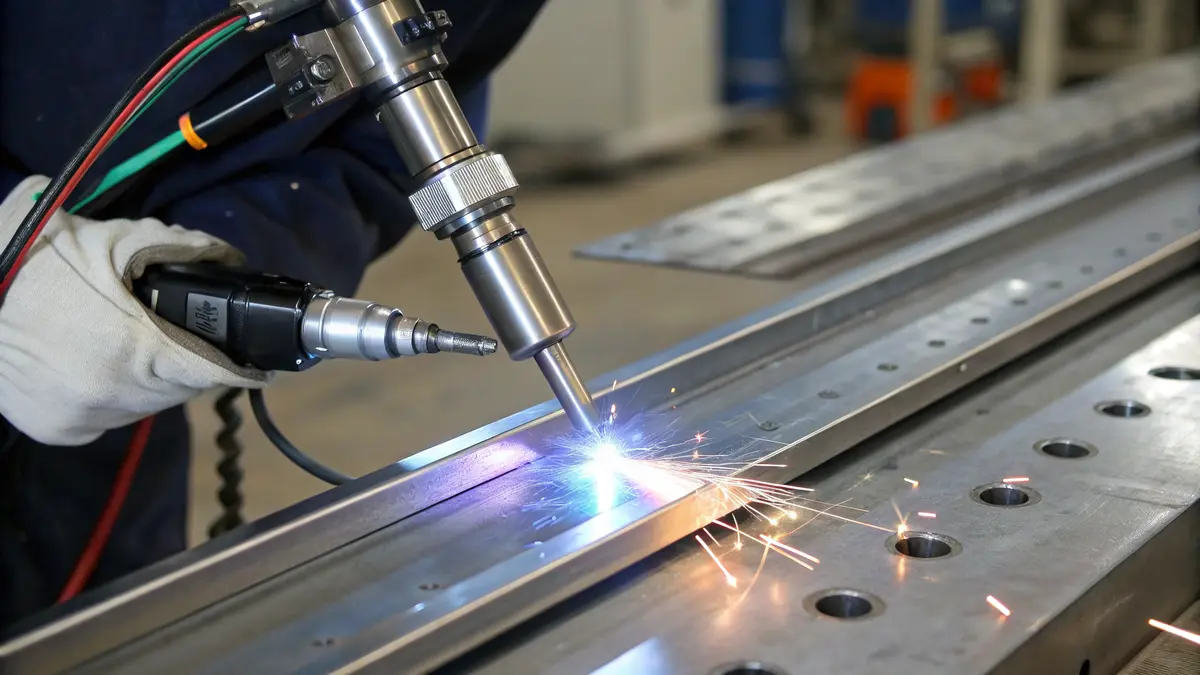

TIG Welding (GTAW) Process
TIG welding stands out as the preferred method for 17-4 PH stainless steel, especially for precision work. I recommend this technique for several key reasons:
- Superior control over the weld pool
- Excellent weld bead appearance
- Minimal spatter and clean welds
- Better suited for thin sections
The success of TIG welding depends heavily on proper parameter selection. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the optimal parameters I’ve found work best:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Current | 100-150 Amps | Adjust based on thickness |
| Voltage | 12-15 V | Keep consistent |
| Travel Speed | 3-5 inches/min | Slower for thicker sections |
| Shielding Gas | 100% Argon | 20-25 CFH flow rate |
| Filler Metal | ER630 or matching composition | Must match base metal |
MIG Welding (GMAW) Considerations
MIG welding offers higher deposition rates and is particularly useful for thicker sections. The key advantages include:
- Faster welding speeds
- Better gap bridging ability
- Higher productivity
- Suitable for automated processes
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Feed Speed | 200-300 IPM | Based on wire diameter |
| Voltage | 22-26 V | Adjust for arc stability |
| Current | 160-200 Amps | Thickness dependent |
| Stick Out | 1/2 – 3/4 inch | Maintain consistency |
| Gas Flow | 35-45 CFH | 98% Ar/2% O2 mix |
Pre-Welding Preparation
Proper preparation is crucial for successful welding of 17-4 PH stainless steel:
Surface Cleaning
- Remove all oils, greases, and contaminants
- Use acetone or similar solvents
- Avoid chlorinated cleaners
Joint Preparation
- Proper fit-up with minimal gap
- Bevel angles typically 60-75 degrees
- Root face of 1/16 inch recommended
Pre-heating
- Heat to 300-400°F (149-204°C)
- Use temperature-indicating crayons
- Maintain throughout welding process
Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)
This is arguably the most critical step in welding 17-4 PH stainless steel. The PWHT process:
- Relieves residual stresses
- Restores mechanical properties
- Prevents distortion and cracking
- Ensures dimensional stability
The recommended PWHT schedule I use is:
| Step | Temperature | Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating | 1100°F (593°C) | 1-2 hours | Slow ramp up |
| Holding | 1100°F (593°C) | 4 hours | Maintain temperature |
| Cooling | Room temperature | Air cool | No quenching |
Quality Control Measures
To ensure weld quality, implement these inspection methods:
Visual Inspection
- Check for surface defects
- Verify bead appearance
- Look for color uniformity
Non-Destructive Testing
- Dye penetrant testing
- X-ray inspection
- Ultrasonic testing
Mechanical Testing
- Tensile strength
- Hardness testing
- Bend tests
Common Challenges and Solutions
Based on my experience, here are the most frequent issues and their solutions:
Hot Cracking
- Solution: Reduce heat input
- Maintain proper interpass temperature
- Use appropriate filler metal
Distortion
- Solution: Use proper fixturing
- Apply balanced welding sequence
- Control heat input
Loss of Corrosion Resistance
- Solution: Proper post-weld cleaning
- Maintain proper shielding
- Apply correct PWHT
The success of welding 17-4 PH stainless steel relies heavily on following these established procedures and maintaining strict control over all parameters. In my work with aerospace and medical device manufacturers, I’ve found that attention to detail in each step of the process is crucial for achieving consistent, high-quality welds that meet stringent industry standards.
How Does It Perform in Corrosive Environments?
I’ve noticed many engineers struggle with material selection for corrosive environments. Their components fail prematurely due to rust and corrosion, leading to costly replacements and production delays. Even worse, these failures often happen without warning, causing unexpected downtime and safety risks.
17-4 PH stainless steel shows excellent corrosion resistance in most environments, particularly after proper heat treatment. It maintains its structural integrity in marine atmospheres and mild acid conditions, though it may be vulnerable to strong acids and chloride-rich environments.

Understanding Corrosion Resistance Properties
The corrosion resistance of 17-4 PH comes from its chromium content (15-17.5%) and the passive oxide layer it forms. In my manufacturing experience, this material consistently outperforms standard stainless steels in several key aspects:
| Environment Type | Corrosion Resistance Level | Performance Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Marine Atmosphere | Excellent | Minimal surface pitting |
| Mild Acids | Good | Suitable for pH > 4 |
| Strong Acids | Fair | Not recommended for long-term exposure |
| Chloride Solutions | Moderate | May experience stress corrosion cracking |
Environmental Factor Effects
Temperature plays a crucial role in how 17-4 PH responds to corrosive environments. I’ve observed these patterns:
Room Temperature (20-25°C)
- Maintains excellent corrosion resistance
- Passive layer remains stable
- Minimal material degradation
Elevated Temperatures (>150°C)
- Increased susceptibility to pitting
- Accelerated corrosion in acidic environments
- Requires additional protective measures
Comparison with Other Stainless Steels
When comparing 17-4 PH to other stainless steels, several factors stand out:
| Steel Grade | Corrosion Resistance | Strength Level | Cost Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17-4 PH | High | Very High | 1.5x |
| 316L | Very High | Moderate | 1.3x |
| 304 | Moderate | Moderate | 1.0x |
| 440C | Low | High | 1.2x |
Stress Corrosion Cracking Resistance
I’ve found that the heat treatment condition significantly affects stress corrosion cracking (SCC) resistance:
H900 Condition
- Higher strength but reduced SCC resistance
- Best suited for mild environments
- Regular inspection recommended
H1150 Condition
- Improved SCC resistance
- Lower strength properties
- Better for aggressive environments
Practical Applications in Corrosive Settings
Based on my experience with various manufacturing projects, here are the best practices for using 17-4 PH in corrosive environments:
Marine Applications
- Use H1150 condition for better corrosion resistance
- Apply protective coatings in splash zones
- Regular maintenance schedule required
Chemical Processing
- Avoid direct contact with strong acids
- Monitor temperature exposure carefully
- Implement periodic thickness measurements
Outdoor Industrial Use
- Consider atmospheric corrosion factors
- Plan for seasonal maintenance
- Use appropriate surface treatments
Surface Treatment Options
To enhance corrosion resistance, several surface treatments prove effective:
| Treatment Type | Protection Level | Cost Impact | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Passivation | Moderate | Low | 1-2 years |
| Electropolishing | High | Medium | 2-3 years |
| Nitriding | Very High | High | 3-5 years |
Preventive Measures and Maintenance
For optimal performance in corrosive environments, I recommend:
Regular Inspection Protocols
- Visual examinations every 3 months
- Annual thickness measurements
- Documentation of any surface changes
Cleaning Procedures
- Remove surface contaminants promptly
- Use appropriate cleaning agents
- Avoid abrasive cleaning methods
Environmental Controls
- Monitor temperature and humidity
- Control exposure to corrosive substances
- Implement proper ventilation systems
Through this comprehensive analysis of 17-4 PH’s performance in corrosive environments, I’ve aimed to provide practical insights for engineers and designers. The key is understanding both the material’s capabilities and limitations, then implementing appropriate measures to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What Surface Treatments and Finishing Options are Available?
Selecting the right surface treatment for 17-4 PH stainless steel can be overwhelming. Many manufacturers struggle with balancing corrosion resistance, aesthetic requirements, and cost considerations. Without proper surface finishing, even the highest quality 17-4 PH components can fail prematurely or fall short of appearance expectations.
Surface treatments for 17-4 PH stainless steel include passivation, electropolishing, and various coating options. These processes enhance corrosion resistance, improve aesthetic appearance, and optimize component performance in specific applications. Each treatment method offers unique benefits and considerations.
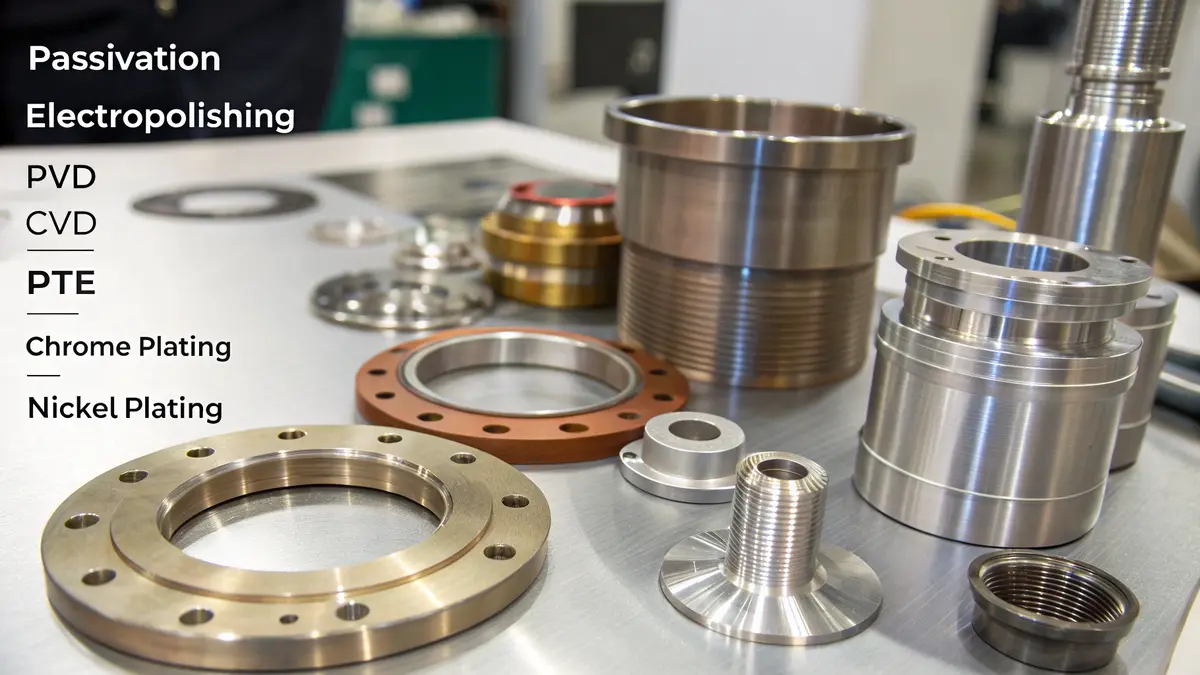

Understanding Passivation
Passivation is the most fundamental surface treatment for 17-4 PH stainless steel. This chemical process removes free iron from the surface and creates a protective oxide layer. At PTSMAKE, we typically use citric acid or nitric acid passivation methods, depending on the component requirements. The process takes 20-30 minutes and provides excellent corrosion resistance without changing the part dimensions.
Common benefits of passivation include:
- Enhanced corrosion resistance
- Removal of surface contaminants
- No dimensional changes
- Cost-effective treatment option
- Improved surface cleanliness
Electropolishing Benefits and Applications
Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes material from the surface, creating a smooth, bright finish. This treatment is particularly valuable for medical devices and food processing equipment made from 17-4 PH stainless steel. The process reduces surface roughness and removes microscopic peaks and valleys.
Key advantages of electropolishing:
- Superior corrosion resistance
- Improved cleanability
- Reduced product adhesion
- Enhanced aesthetic appearance
- Decreased bacterial attachment
Coating Options and Selection Criteria
| Coating Type | Primary Benefits | Typical Applications | Thickness Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVD | High hardness, wear resistance | Cutting tools, decorative parts | 2-5 μm |
| CVD | Excellent adhesion, uniform coverage | High-stress components | 3-10 μm |
| PTFE | Low friction, chemical resistance | Food processing equipment | 15-25 μm |
| Chrome plating | Wear resistance, appearance | Automotive parts | 10-50 μm |
| Nickel plating | Corrosion protection, conductivity | Electronic components | 5-25 μm |
Heat Treatment Considerations
The timing of surface treatments relative to heat treatment is crucial for 17-4 PH stainless steel. We recommend performing most surface treatments after final heat treatment to maintain optimal material properties. However, some coatings may require specific heat treatment modifications:
- Pre-treatment cleaning
- Heat treatment cycle
- Surface preparation
- Coating application
- Post-coating heat treatment (if required)
Surface Roughness Requirements
Different applications demand specific surface roughness values. We measure surface roughness using Ra (arithmetic average) values:
- Medical implants: Ra ≤ 0.2 μm
- Fluid handling components: Ra ≤ 0.8 μm
- General industrial parts: Ra ≤ 1.6 μm
- Structural components: Ra ≤ 3.2 μm
Quality Control and Testing Methods
To ensure surface treatment effectiveness, we employ various testing methods:
- Salt spray testing for corrosion resistance
- Adhesion testing for coatings
- Surface roughness measurements
- Hardness testing
- Visual inspection for aesthetic quality
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Modern surface treatment processes must consider environmental impacts. We implement several measures to minimize environmental footprint:
- Closed-loop chemical recovery systems
- Water recycling programs
- VOC-free coating options
- Energy-efficient equipment
- Waste minimization protocols
Cost Considerations and ROI Analysis
Surface treatment costs vary significantly based on process complexity and volume:
- Basic passivation: $0.5-2 per square inch
- Electropolishing: $2-5 per square inch
- PVD coating: $5-15 per square inch
- Complex coating systems: $15-30 per square inch
The investment typically pays off through:
- Extended component life
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Improved performance
- Enhanced product value
- Lower warranty claims
Application-Specific Recommendations
Based on industry experience, here are optimal surface treatments for common applications:
Medical Devices
- Primary: Electropolishing
- Secondary: Passivation
- Optional: Antimicrobial coatings
Aerospace Components
- Primary: PVD coating
- Secondary: Passivation
- Optional: Dry film lubricants
Food Processing Equipment
- Primary: Electropolishing
- Secondary: PTFE coating
- Optional: Antimicrobial treatments
Marine Applications
- Primary: Multiple-layer coating systems
- Secondary: Passivation
- Optional: Sacrificial anodes
Understanding these surface treatment options helps optimize component performance and longevity. The key is selecting the right combination of treatments based on application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints.
How is 17-4 PH Used in Aerospace and Defense?
In aerospace and defense manufacturing, selecting the wrong material for critical components can lead to catastrophic failures. When aircraft parts fail during operation, the consequences are often devastating. The margin for error in these industries is literally zero, making material selection one of the most crucial decisions.
17-4 PH stainless steel is extensively used in aerospace and defense applications due to its unique combination of high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good dimensional stability. It’s commonly found in aircraft landing gear, missile components, and structural fasteners where reliability is paramount.
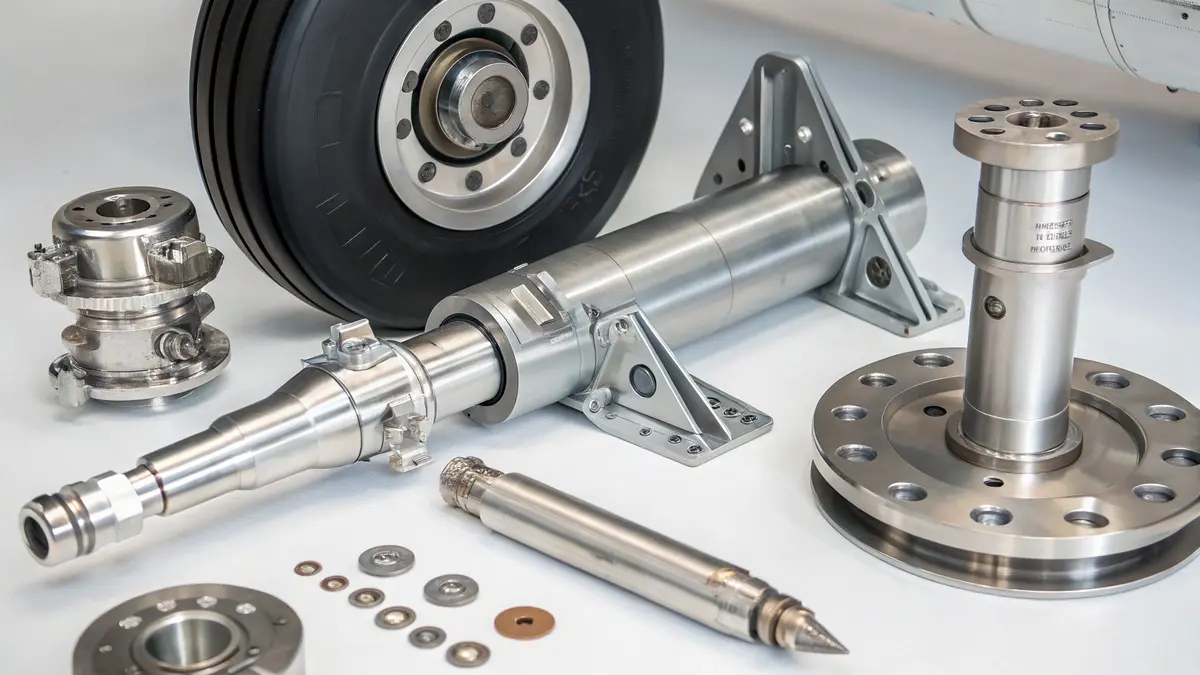

Critical Applications in Aircraft Systems
17-4 PH stainless steel has become indispensable in modern aircraft systems. Based on my manufacturing experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed its widespread use in:
- Landing gear components
- Control surface actuators
- Structural fasteners
- Engine mounts
- Wing attachments
The material’s high strength-to-weight ratio makes it particularly valuable in these applications where weight reduction is crucial for fuel efficiency.
Key Properties for Defense Applications
The defense sector demands materials that can withstand extreme conditions. Here’s why 17-4 PH excels:
| Property | Benefit in Defense Applications |
|---|---|
| High Tensile Strength | Withstands extreme mechanical stress |
| Excellent Corrosion Resistance | Maintains integrity in harsh environments |
| Good Fatigue Properties | Ensures long-term reliability |
| Dimensional Stability | Maintains precision in varying conditions |
| Heat Resistance | Performs well at elevated temperatures |
Missile Component Manufacturing
In missile systems, 17-4 PH is crucial for several components:
- Guidance System Housing
- Propulsion Components
- Structural Support Elements
- Control Surface Mechanisms
The material’s ability to maintain its properties under high-speed conditions and extreme temperatures makes it ideal for these applications.
Aircraft Landing Gear Requirements
Landing gear systems face unique challenges:
- High Impact Loads
- Frequent Stress Cycles
- Exposure to Various Weather Conditions
- Chemical Exposure (hydraulic fluids, de-icing agents)
17-4 PH’s combination of properties addresses these challenges effectively. At PTSMAKE, we regularly machine landing gear components that require tight tolerances and superior surface finish.
Manufacturing Considerations
When working with 17-4 PH for aerospace applications, several factors require attention:
Heat Treatment Protocols
- Solution treatment temperature control
- Aging process monitoring
- Proper cooling rates
Machining Parameters
- Optimal cutting speeds
- Appropriate tool selection
- Coolant requirements
Quality Control
- Dimensional inspection
- Material certification
- Non-destructive testing
Surface Treatment and Finishing
The performance of 17-4 PH components often depends on proper surface treatment:
Surface Preparation
- Cleaning procedures
- Surface roughness requirements
- Pre-treatment processes
Coating Applications
- Chromate conversion coating
- Anodizing options
- Specialized aerospace coatings
Final Inspection
- Surface finish measurement
- Coating thickness verification
- Adhesion testing
Certification and Quality Standards
Aerospace and defense applications require strict adherence to industry standards:
- AS9100 certification
- NADCAP compliance
- Material traceability
- Documentation requirements
- Testing protocols
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Despite its higher initial cost compared to conventional stainless steels, 17-4 PH offers long-term benefits:
- Extended Service Life
- Reduced Maintenance Requirements
- Lower Replacement Frequency
- Better Performance Reliability
In my experience at PTSMAKE, clients often find that the total cost of ownership is lower with 17-4 PH components due to these factors.
Future Trends
The aerospace and defense industries continue to evolve, affecting how 17-4 PH is used:
Advanced Manufacturing Methods
- Additive manufacturing applications
- Improved machining techniques
- Novel heat treatment processes
Enhanced Quality Control
- Advanced inspection methods
- Real-time monitoring systems
- Improved documentation processes
Sustainable Manufacturing
- Material efficiency
- Waste reduction
- Energy-efficient processing
The use of 17-4 PH in aerospace and defense applications represents a perfect balance of performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. As manufacturing technologies advance, we continue to discover new ways to optimize its use in these critical applications.
What Role Does It Play in Medical Equipment?
In the medical industry, the choice of materials for equipment and instruments can literally mean the difference between life and death. Many healthcare facilities struggle with instruments that corrode quickly, lose their precision, or raise concerns about patient safety due to material incompatibility. The stakes couldn’t be higher when it comes to selecting materials for medical applications.
17-4 PH stainless steel has emerged as a cornerstone material in medical equipment manufacturing, offering an optimal blend of strength, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Its unique properties make it particularly suitable for surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental tools, ensuring both patient safety and instrument longevity.
The Critical Properties for Medical Applications
When we talk about medical equipment, three key properties stand out for 17-4 PH stainless steel:
Biocompatibility
- Low nickel content reduces allergic reactions
- Minimal ion release into surrounding tissues
- Excellent compatibility with sterilization processes
Mechanical Properties
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Superior hardness after heat treatment
- Exceptional wear resistance
Corrosion Resistance
- Resistant to bodily fluids
- Withstands repeated sterilization
- Maintains surface integrity over time
Common Medical Applications
Based on my manufacturing experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed several key applications where 17-4 PH stainless steel excels:
Surgical Instruments
- Scalpels and surgical scissors
- Forceps and clamps
- Needle holders
- Retractors
These instruments require precise edges and maintaining their sharpness through multiple sterilization cycles.
Orthopedic Implants
- Bone screws
- Plates
- Surgical guides
- Temporary fixation devices
The material’s strength and biocompatibility make it ideal for these load-bearing applications.
Comparative Analysis with Other Medical-Grade Materials
Here’s a detailed comparison of 17-4 PH with other common medical materials:
| Property | 17-4 PH | 316L SS | Ti-6Al-4V | CoCr Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 1070 | 485 | 860 | 655 |
| Hardness (HRC) | 40-47 | 95 (HRB) | 36 | 35 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Very Good | Excellent | Good |
| Cost Effectiveness | High | Moderate | Low | Low |
| Machinability | Good | Excellent | Fair | Poor |
Manufacturing Considerations
The manufacturing process for medical equipment using 17-4 PH requires specific considerations:
Heat Treatment
- Solution treatment at 1900°F (1038°C)
- Age hardening at various temperatures
- Careful control of cooling rates
Surface Finishing
- Electropolishing for enhanced corrosion resistance
- Passivation to create protective oxide layer
- Mirror finishing for specific applications
Quality Control
- Strict dimensional tolerances
- Surface roughness measurements
- Material certification requirements
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Medical equipment manufacturers must adhere to:
FDA Requirements
- 21 CFR Part 820
- Material traceability
- Process validation
ISO Standards
- ISO 13485 for medical devices
- ISO 10993 for biocompatibility
- ISO 14971 for risk management
Cost-Benefit Analysis
The investment in 17-4 PH stainless steel for medical equipment often proves economical when considering:
Long-term Benefits
- Extended service life
- Reduced replacement frequency
- Lower maintenance costs
Performance Advantages
- Consistent mechanical properties
- Reliable sterilization capability
- Reduced risk of material failure
Future Trends and Innovations
The medical industry continues to evolve, and with it, the applications of 17-4 PH stainless steel:
Advanced Manufacturing Methods
- 3D printing capabilities
- Hybrid manufacturing processes
- Improved surface treatments
New Medical Applications
- Minimally invasive surgical tools
- Custom patient-specific instruments
- Advanced dental implements
I’ve seen how crucial material selection is in medical equipment manufacturing. 17-4 PH stainless steel has proven itself time and again as a reliable choice that meets the demanding requirements of the medical industry. Its combination of strength, durability, and biocompatibility makes it an invaluable material for creating safe and effective medical devices.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
An often-overlooked aspect of medical equipment is its environmental impact:
Recyclability
- High recycling potential
- Minimal material waste
- Energy-efficient processing
Lifecycle Considerations
- Extended service life reduces waste
- Minimal environmental impact during use
- Sustainable manufacturing practices
The medical field demands materials that can meet stringent requirements while ensuring patient safety and device longevity. 17-4 PH stainless steel continues to prove its worth in this challenging environment, making it an indispensable material for modern medical equipment manufacturing.
How is It Used in Oil, Gas, and Energy Industries?
In the oil, gas, and energy sectors, equipment failure can lead to catastrophic consequences. Harsh chemicals, extreme pressures, and temperature fluctuations constantly threaten to compromise system integrity. When critical components fail, it not only disrupts operations but also poses serious safety and environmental risks.
17-4 PH stainless steel plays a crucial role in oil, gas, and energy applications due to its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions. It’s commonly used in valves, pumps, and pressure vessels where reliability is paramount.

Critical Applications in Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on 17-4 PH stainless steel for various critical components. I’ve seen this material excel in:
- Downhole Tools
- Wellhead Components
- Safety Valves
- Flow Control Equipment
- Pressure Vessels
These applications demand materials that can withstand corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity. I’ve noticed that 17-4 PH’s combination of strength and corrosion resistance makes it particularly valuable for these demanding applications.
Performance in Harsh Environments
The performance of 17-4 PH in extreme conditions is remarkable. Here’s a breakdown of its capabilities:
| Environmental Factor | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -50°C to 300°C |
| Pressure Tolerance | Up to 15,000 PSI |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in H2S environments |
| Chemical Compatibility | Resistant to most hydrocarbon compounds |
| Wear Resistance | Superior surface hardness after heat treatment |
Applications in Power Generation
In the power generation sector, 17-4 PH finds extensive use in:
Steam Turbines
The material’s high strength and excellent fatigue resistance make it ideal for turbine blades and rotors. I’ve observed that components made from 17-4 PH consistently deliver reliable performance even under high-speed rotation and steam exposure.
Heat Exchangers
The combination of good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance makes 17-4 PH an excellent choice for heat exchanger components. These properties ensure efficient heat transfer while maintaining structural integrity.
Renewable Energy Applications
In renewable energy systems, 17-4 PH proves valuable in:
- Wind turbine shaft components
- Geothermal well equipment
- Tidal energy systems
- Solar thermal power plants
Material Selection Considerations
When selecting 17-4 PH for oil, gas, and energy applications, several factors need consideration:
- Operating Temperature
- Pressure Requirements
- Chemical Environment
- Mechanical Loads
- Service Life Expectations
I recommend conducting thorough material compatibility analysis before finalizing the selection. This helps ensure optimal performance and longevity of components in specific operating conditions.
Maintenance and Inspection Requirements
Regular maintenance practices for 17-4 PH components include:
- Visual inspections for surface degradation
- Non-destructive testing for crack detection
- Monitoring of operating parameters
- Periodic hardness testing
- Corrosion monitoring
Cost-Benefit Analysis
While 17-4 PH may have a higher initial cost compared to conventional materials, its long-term benefits often justify the investment:
- Extended service life
- Reduced maintenance requirements
- Lower risk of catastrophic failure
- Improved safety performance
- Better operational reliability
Future Trends
The energy sector continues to evolve, and with it, the applications of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Emerging trends include:
- Integration in hydrogen energy systems
- Advanced surface treatments for enhanced performance
- Development of optimized heat treatment protocols
- Implementation in new renewable energy technologies
Based on my experience, I’ve noticed increasing demand for 17-4 PH in emerging energy technologies, particularly where traditional materials fail to meet performance requirements. The material’s versatility and reliability continue to make it a preferred choice in these challenging applications.
What are the Challenges in Using 17-4 PH?
Working with 17-4 PH stainless steel seems straightforward until you encounter its hidden complexities. I’ve noticed many engineers underestimate the challenges this material presents, leading to costly production issues and project delays. The combination of its unique properties and specific processing requirements can make it particularly tricky to handle.
Despite its excellent strength and corrosion resistance, 17-4 PH stainless steel presents several manufacturing challenges including brittleness, stress corrosion cracking, and precision machining difficulties. However, these challenges can be managed through proper material selection and advanced processing techniques.

Brittleness and Material Behavior
The brittleness of 17-4 PH is one of its most significant challenges. This material exhibits different behavior patterns depending on its heat treatment condition:
- H900 condition: Maximum strength but increased brittleness
- H1150 condition: Better ductility but lower strength
- Solution annealed: Most machinable but requires subsequent heat treatment
During my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve developed specific approaches for handling these conditions:
| Heat Treatment Condition | Brittleness Level | Machining Difficulty | Recommended Cutting Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| H900 | High | Very Challenging | 60-90 SFM |
| H1150 | Medium | Moderate | 90-120 SFM |
| Solution Annealed | Low | Easier | 100-150 SFM |
Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) Risks
Stress corrosion cracking in 17-4 PH presents a serious concern that requires careful consideration:
Environmental Factors
- Chloride exposure
- High temperatures
- Acidic conditions
Stress-Related Issues
- Residual stresses from machining
- Applied loads during service
- Thermal cycling effects
To minimize SCC risks, we implement these preventive measures:
- Proper heat treatment sequences
- Controlled machining parameters
- Surface treatment considerations
Precision Machining Difficulties
The precision machining of 17-4 PH presents several unique challenges:
Tool Wear and Selection
- Rapid tool wear due to material hardness
- Need for specialized cutting tools
- Regular tool condition monitoring
Cutting Parameters
Tool life in 17-4 PH machining largely depends on proper cutting parameters:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Impact on Tool Life |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | 80-120 SFM | High |
| Feed Rate | 0.004-0.008 IPR | Medium |
| Depth of Cut | 0.020-0.100 inches | Medium |
Temperature Control
Temperature management is crucial during machining:
- Use of proper coolant strategies
- Prevention of work hardening
- Maintaining dimensional stability
Advanced Manufacturing Solutions
To address these challenges, we employ several advanced techniques:
Optimized Machining Strategies
- High-pressure coolant systems
- Rigid machine setups
- Advanced tool holding systems
Material Handling Protocols
- Proper storage conditions
- Controlled material flow
- Regular quality checks
Process Monitoring
- In-process inspection
- Tool wear monitoring
- Statistical process control
Quality Control Considerations
Maintaining quality while working with 17-4 PH requires:
Dimensional Stability
- Regular calibration checks
- Temperature-controlled environment
- Proper fixturing methods
Surface Finish Requirements
- Appropriate cutting tool selection
- Optimized finishing parameters
- Surface treatment considerations
Material Properties Verification
- Hardness testing
- Microstructure analysis
- Mechanical property validation
In my experience at PTSMAKE, the key to successful 17-4 PH machining lies in understanding these challenges and implementing appropriate countermeasures. This includes:
- Proper tool selection and cutting parameters
- Regular monitoring and adjustment of processes
- Comprehensive quality control procedures
- Advanced machining strategies
By carefully considering these aspects and implementing appropriate solutions, we can effectively manage the challenges associated with 17-4 PH machining while maintaining high quality and productivity standards.
How to Select the Right Supplier?
Finding a reliable supplier for 17-4 PH stainless steel components can be a daunting challenge. Many manufacturers have experienced costly delays, quality issues, and production setbacks due to working with the wrong supplier. When dealing with mission-critical applications, even minor defects in material quality or heat treatment can lead to catastrophic failures.
The key to selecting the right supplier lies in evaluating five crucial aspects: material certification, heat treatment consistency, machining capabilities, quality assurance systems, and track record in similar projects. A thorough assessment of these factors helps ensure reliable sourcing for critical components.

Material Certification Requirements
Proper material certification is the foundation of quality assurance for 17-4 PH components. I always require suppliers to provide:
- Mill Test Reports (MTR) for each batch
- Chemical composition analysis
- Physical property documentation
- Material traceability documentation
Our validation process includes cross-referencing all certification documents with international standards like ASTM A564/A564M. This ensures the material meets exact specifications for aerospace and medical applications.
Heat Treatment Process Control
The heat treatment process significantly influences the final properties of 17-4 PH components. When evaluating suppliers, I focus on:
| Heat Treatment Aspect | Key Requirements | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | ±5°F accuracy | Ensures consistent material properties |
| Process Documentation | Detailed records for each batch | Enables traceability and troubleshooting |
| Equipment Calibration | Regular certification | Maintains process reliability |
| Cooling Rate Control | Documented procedures | Affects final hardness and strength |
Machining Capabilities Assessment
Advanced machining capabilities are crucial for producing precise 17-4 PH components. I evaluate:
Equipment Infrastructure
- 5-axis CNC machines for complex geometries
- Modern measurement and inspection tools
- Regular maintenance schedules
- Equipment calibration records
Technical Expertise
- Operator training programs
- Experience with similar components
- Understanding of material-specific machining parameters
- Process optimization capabilities
Quality Assurance Standards
A robust quality management system is non-negotiable. The following elements must be present:
Quality Management System
- ISO 9001:2015 certification
- AS9100D certification for aerospace applications
- Documented quality procedures
- Regular internal audits
Inspection Capabilities
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) equipment
- Surface roughness testing
- Hardness testing facilities
- Non-destructive testing capabilities
Performance Track Record
Past performance often indicates future reliability. I assess:
Historical Data
- On-time delivery rates
- Quality rejection rates
- Response time to quality issues
- Customer references
Project Experience
- Similar component manufacturing history
- Industry-specific experience
- Problem-solving capabilities
- Technical support quality
Financial Stability Assessment
A supplier’s financial health directly impacts their ability to maintain quality and delivery commitments:
- Company financial statements
- Credit ratings
- Investment in new technology
- Market reputation
Communication and Support
Effective communication is crucial for successful partnerships:
Response Capability
- Technical query response time
- Quality issue resolution process
- Engineering support availability
- Documentation management
Collaboration Tools
- Online portal access
- Real-time production tracking
- Document sharing systems
- Quality reporting mechanisms
Price and Cost Structure
While price shouldn’t be the primary factor, it’s important to understand:
- Material cost breakdown
- Processing costs
- Quality control costs
- Overhead allocation
Finding the right supplier requires a systematic evaluation of all these factors. The initial investment in thorough supplier assessment pays off through reliable quality, consistent delivery, and reduced long-term costs. Based on my experience managing critical component sourcing, suppliers who excel in these areas typically become valuable long-term partners, contributing significantly to product success and reliability.
Remember, the goal isn’t just finding a supplier who can make the parts – it’s finding one who can consistently deliver quality components that meet all specifications and maintain that performance over time. This comprehensive evaluation approach helps ensure you select a supplier capable of meeting both current and future needs for your 17-4 PH stainless steel components.







