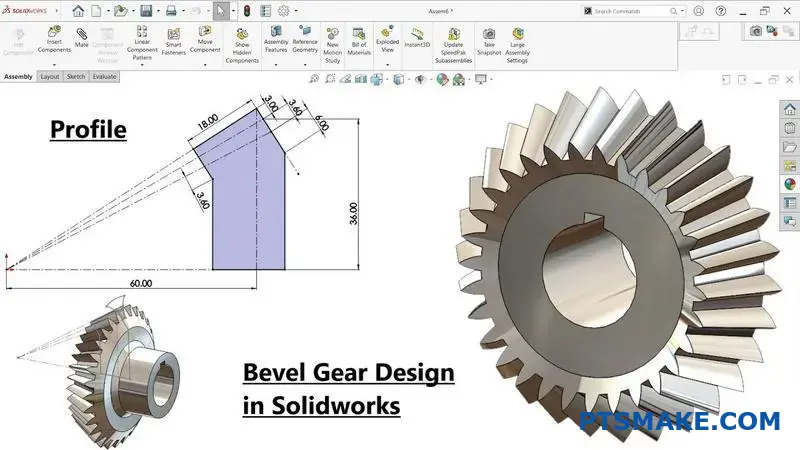
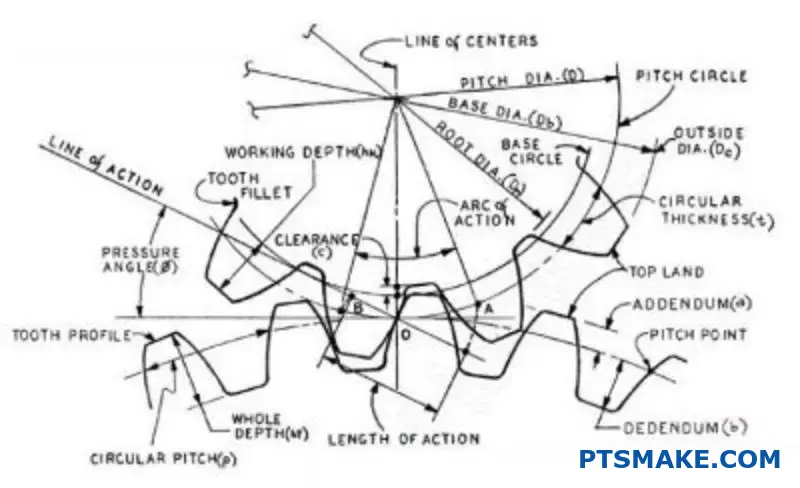
Have you ever struggled with complex part geometries that seem impossible to machine? I remember facing this exact challenge when a medical device company approached us with an intricate implant design.
5-axis CNC machining is an advanced manufacturing process that enables simultaneous movement across five different axes, allowing for complex geometries and superior surface finishes while reducing setup time and improving accuracy compared to traditional 3-axis machining.

After 15 years in precision manufacturing at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen how 5-axis machining has revolutionized production capabilities. Let me share my insights about this game-changing technology.
What are the 5 axis of machining?
If you’re new to 5-axis machining, you might wonder how these movements actually work. I faced the same question when we got our first 5-axis machine back in 2010.
The five axes consist of the three linear axes (X, Y, and Z) and two rotary axes (A and B or B and C), allowing the cutting tool or workpiece to move in multiple directions simultaneously for complex part creation.
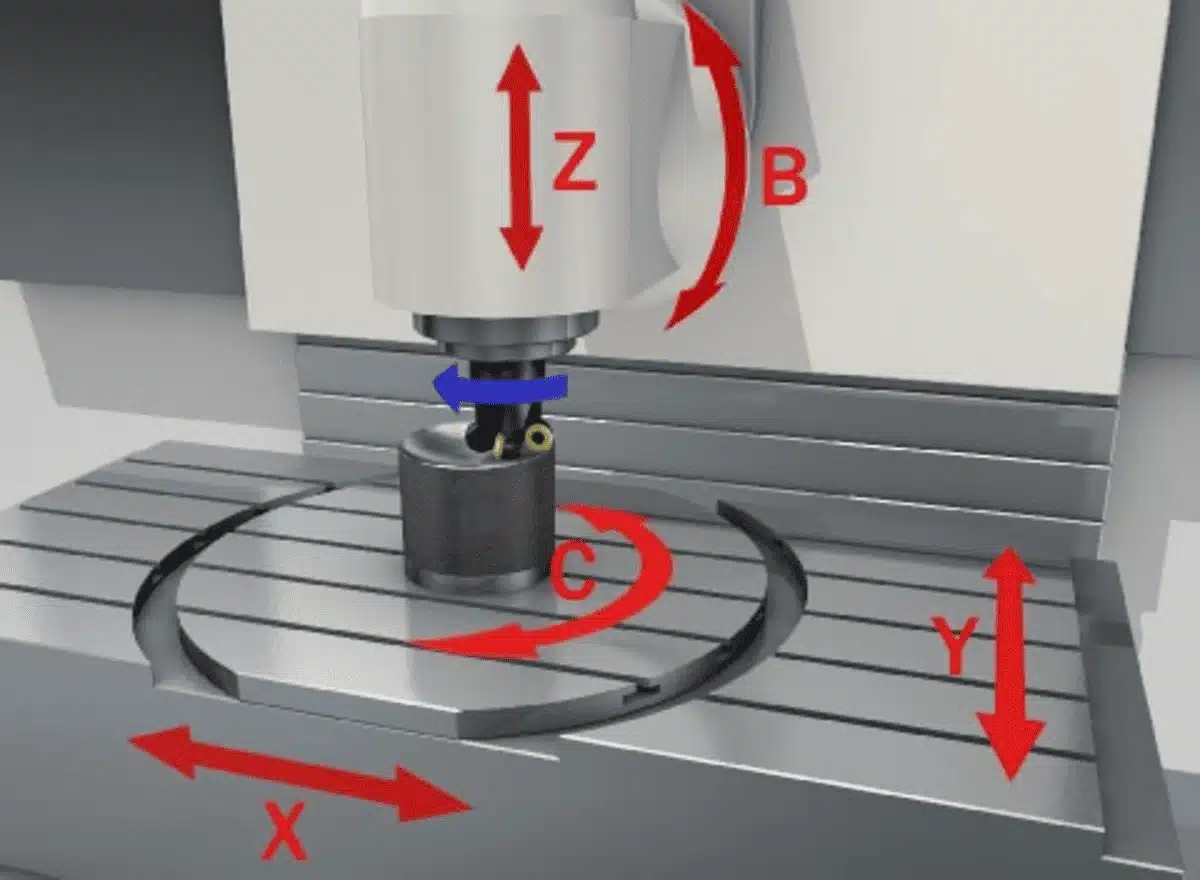
Understanding Each Axis in Detail
Linear Axes (X, Y, Z)
These are the fundamental movements that form the basis of all CNC machining:
| Axis | Movement Direction | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| X | Left to right | Horizontal cutting paths |
| Y | Front to back | Depth of cut adjustments |
| Z | Up and down | Vertical tool positioning |
Rotary Axes (A, B, C)
The rotary axes add the capability for angular movements:
| Axis | Rotation | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| A | Around X-axis | Tilting forward/backward |
| B | Around Y-axis | Tilting left/right |
| C | Around Z-axis | Rotating in horizontal plane |
Common Configurations
In my experience working with various 5-axis setups, I’ve found these common configurations:
Table-Table Configuration
- The workpiece moves in both rotary axes
- Ideal for smaller, lighter parts
- Offers excellent accuracy
Head-Head Configuration
- The tool moves in both rotary axes
- Better for larger workpieces
- Allows for more aggressive cutting
Table-Head Configuration
- Combines one rotating table with one tilting head
- Provides a good balance of capabilities
- Most versatile for mixed part sizes
What is the difference between 3 axis and 5 axis machining?
Many clients ask me this question when considering upgrading their manufacturing capabilities. It’s like comparing a regular car to a high-performance sports car – both will get you there, but the journey is very different.
The main difference is that 3-axis machining moves only in straight lines along X, Y, and Z axes, while 5-axis adds two rotary movements, enabling complex geometries, better surface finishes, and reduced setup time.
Key Differences in Capability
Tool Accessibility
In my years of experience, I’ve seen how tool accessibility dramatically affects part quality:
| Feature | 3-Axis | 5-Axis |
|---|---|---|
| Undercuts | Multiple setups required | Single setup possible |
| Deep pockets | Limited reach | Better access |
| Complex contours | Difficult to achieve | Easily machined |
Production Efficiency
Setup Time
- 3-axis often requires multiple setups
- 5-axis can complete parts in one setup
- We’ve seen setup time reductions of up to 60%
Surface Finish
- 3-axis leaves stepping on curved surfaces
- 5-axis maintains consistent tool engagement
- Results in superior surface quality
Accuracy
- 3-axis has cumulative errors from multiple setups
- 5-axis maintains better tolerances
- Critical for precision components
What is the difference between 5 axis and 6 axis CNC?
This question came up recently when a robotics company was deciding between our 5-axis and 6-axis services. The distinction is crucial for specific applications.
While 5-axis CNC machines use three linear (X, Y, Z) and two rotary axes, 6-axis adds another rotary axis, typically used in robotic arms for specialized applications like welding or assembly rather than traditional machining.
Detailed Comparison
Applications and Capabilities
| Feature | 5-Axis CNC | 6-Axis Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Material removal | Multi-purpose |
| Accuracy | Higher | Lower |
| Rigidity | Better | Limited |
| Flexibility | Process-specific | Multi-process |
Real-World Applications
From my experience managing both technologies:
5-Axis CNC
- Aerospace components
- Medical implants
- Complex mold making
- Precision mechanical parts
6-Axis Robots
- Welding operations
- Assembly tasks
- Material handling
- Surface finishing
How much does 5 axis CNC machining cost per hour?
As someone who manages pricing strategies for a manufacturing facility, I understand this is a crucial consideration for project planning.
5-axis CNC machining typically costs between $70-300 per hour in developed countries, varying based on machine type, complexity, and location. However, the higher hourly rate often results in lower total project costs due to reduced setup time and improved efficiency.

Cost Breakdown Analysis
Direct Costs
| Cost Component | Percentage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Machine depreciation | 25-30% | Based on $500K-1M investment |
| Labor | 20-25% | Skilled operator wages |
| Tooling | 15-20% | Including wear and replacement |
| Overhead | 25-30% | Facility and support costs |
Factors Affecting Hourly Rates
Geographic Location
- North America: $200-300/hour
- Western Europe: €180-280/hour
- Asia: $70-200/hour
Machine Specifications
- Entry-level: $70-150/hour
- High-end: $250-350/hour
- Ultra-precision: $400+/hour
Industry Requirements
- Aerospace: Higher rates due to certifications
- General manufacturing: Standard rates
- Prototyping: Premium rates for flexibility
What is the difference between 3 4 and 5 axis CNC?
Through my years of experience with various CNC configurations, I’ve helped numerous clients understand these differences to choose the right technology for their needs.
The main distinction lies in movement capabilities: 3-axis moves linearly in X, Y, and Z; 4-axis adds one rotary axis (usually A or B); and 5-axis adds two rotary axes, enabling complete tool orientation for complex geometries.
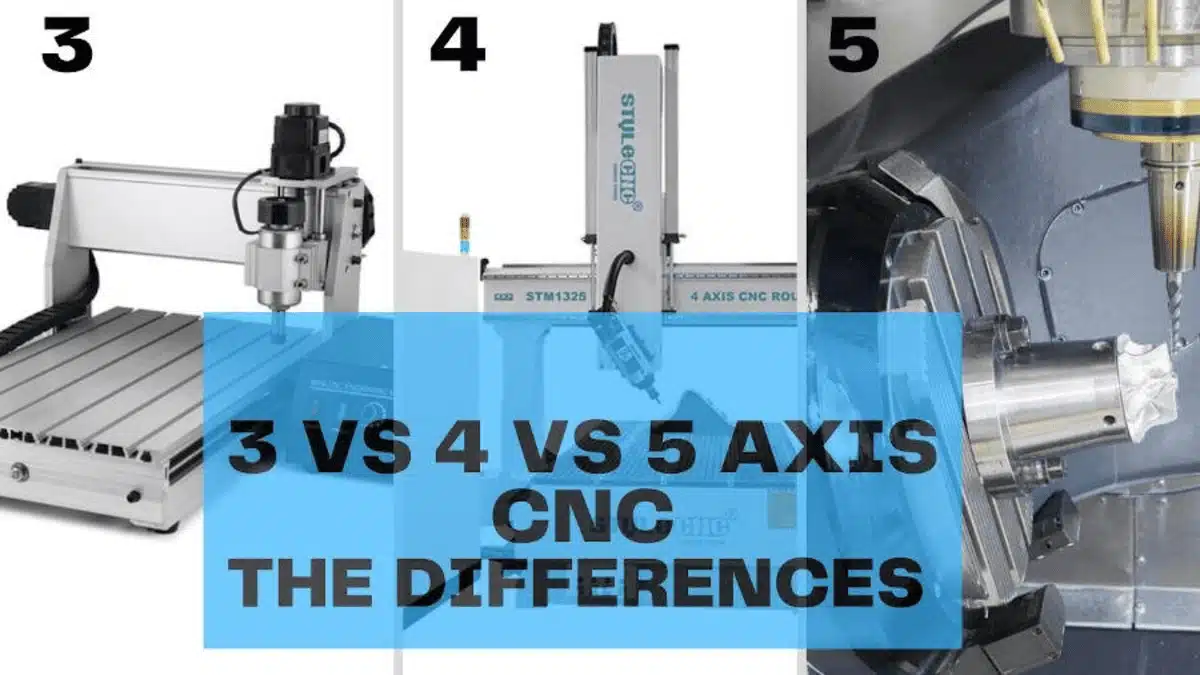
Comparative Analysis
Capability Overview
| Feature | 3-Axis | 4-Axis | 5-Axis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Setup time | Longest | Moderate | Shortest |
| Complex surfaces | Limited | Better | Best |
| Cost per hour | Lowest | Medium | Highest |
| Learning curve | Easy | Moderate | Steep |
Application-Specific Benefits
3-Axis Machining
- Simple prismatic parts
- 2.5D features
- Basic milling operations
- Lower investment cost
4-Axis Machining
- Cylindrical parts
- Indexed machining
- Basic contoured surfaces
- Moderate complexity
5-Axis Machining
- Complex geometries
- Aerospace components
- Medical implants
- High-end molds
How much does CNC machining cost per hour in China?
As the partner of PTSMAKE, operating in China since 2002, I can provide detailed insights into the local manufacturing cost structure.
CNC machining costs in China typically range from $15-40 per hour for standard operations, with 5-axis machining ranging from $80-150 per hour, significantly lower than Western rates while maintaining comparable quality with proper quality control systems.

Cost Structure Analysis
Rate Variations by Region
| Region | 3-Axis Rate | 5-Axis Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 cities | $25-40/hr | $100-150/hr |
| Tier 2 cities | $20-25/hr | $90-120/hr |
| Tier 3 cities | $13-20/hr | $60-90/hr |
Contributing Factors
Labor Costs
- Skilled operator wages: $5-10/hour
- Engineering support: $10-15/hour
- Quality control: $5-10/hour
Operating Expenses
- Equipment costs: Similar to global prices
- Facility overhead: 40-60% lower than West
- Utilities: 30-50% lower than West
Quality Considerations
- ISO certification requirements
- Quality control systems
- International standards compliance
Conclusion
After 20+ years in precision manufacturing, I’ve seen how 5-axis CNC machining transforms production capabilities, offering unmatched precision and efficiency. While the initial investment is higher, the benefits in reduced setup time, improved accuracy, and complex geometry capabilities make it invaluable for modern manufacturing.