Many manufacturers struggle with choosing the right material for their plastic parts. The endless options and technical specifications can be overwhelming, often leading to costly mistakes in material selection. I’ve seen companies waste thousands of dollars on failed projects simply because they picked the wrong plastic.
ABS injection molding is a manufacturing process that combines acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene polymers to create durable plastic parts. This process uses heat and pressure to melt ABS plastic and inject it into molds, producing strong, impact-resistant components.

I want to share some critical insights about ABS injection molding that could save you time and money. As someone who oversees numerous ABS molding projects at PTSMAKE, I understand the importance of getting this process right. Let me walk you through the essential aspects that make ABS injection molding a preferred choice for many industries.
Is ABS Material Easy To Mold?
Have you ever experienced warped or deformed ABS plastic parts? Many manufacturers struggle with ABS molding issues, from unsightly sink marks to frustrating part failures. These challenges can lead to costly production delays and wasted materials, leaving you wondering if you’ve chosen the right material.
ABS is generally easy to mold due to its wide processing window and good flow characteristics. However, success depends on proper molding parameters, equipment setup, and material handling. With the right expertise and preparation, ABS can be molded efficiently and consistently.
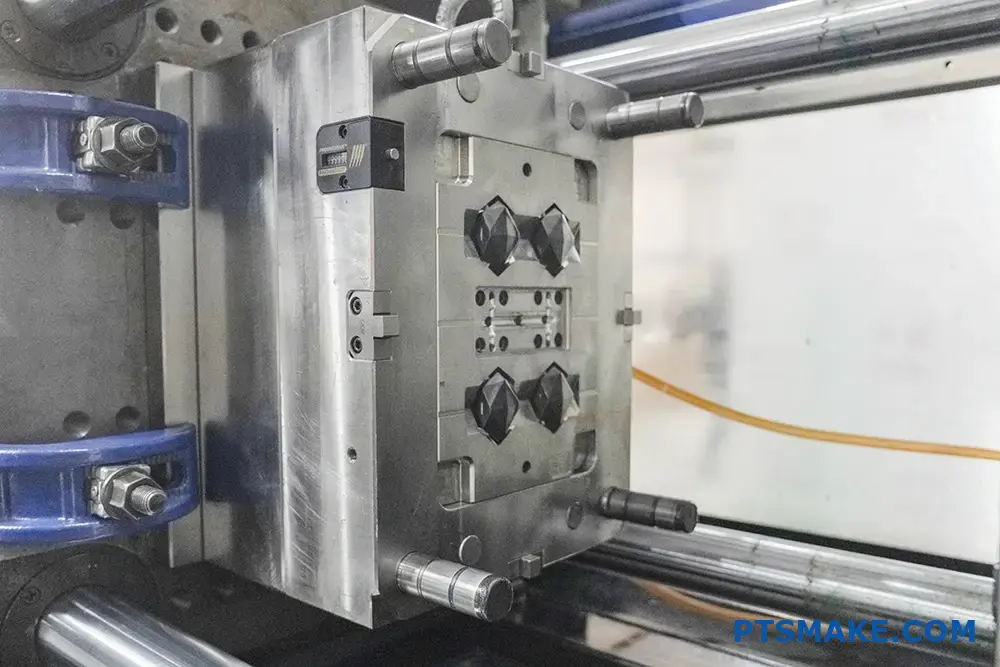
Understanding ABS Material Properties
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a versatile thermoplastic that offers a unique combination of properties. The material’s glass transition temperature1 plays a crucial role in its moldability. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found that understanding these properties is essential for successful molding:
Chemical Structure Benefits
- Acrylonitrile: Provides chemical resistance
- Butadiene: Enhances impact strength
- Styrene: Offers good processability
Key Physical Properties
| Property | Typical Range | Impact on Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Flow Index | 1-36 g/10min | Affects fill ability |
| Shrinkage | 0.4-0.7% | Influences part accuracy |
| Processing Temperature | 220-260°C | Determines melt behavior |
Critical Molding Parameters
Success in ABS molding relies heavily on controlling several key parameters:
Temperature Control
The proper temperature management is crucial for ABS molding. Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, we recommend:
- Barrel Temperature: 220-260°C
- Mold Temperature: 60-80°C
- Nozzle Temperature: 230-250°C
Pressure Settings
Proper pressure control ensures part quality:
- Injection Pressure: 70-120 MPa
- Hold Pressure: 50-80% of injection pressure
- Back Pressure: 2.5-5 MPa
Common Molding Challenges
Moisture Sensitivity
ABS requires proper drying before processing:
- Recommended moisture content: <0.1%
- Drying temperature: 80-85°C
- Drying time: 2-4 hours
Surface Defects Prevention
Common issues and solutions:
| Defect | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Sink Marks | Insufficient packing | Increase hold pressure |
| Flow Lines | Poor melt temperature | Adjust barrel temperature |
| Warpage | Uneven cooling | Balance cooling channels |
Material Handling Best Practices
Storage Requirements
- Store in sealed containers
- Maintain relative humidity below 50%
- Keep away from direct sunlight
Pre-Processing Steps
- Material testing
- Proper drying
- Equipment cleaning
- Parameter verification
Advanced Molding Techniques
Multi-Shot Molding
At PTSMAKE, we’ve successfully implemented multi-shot molding with ABS:
- Allows for complex designs
- Reduces assembly steps
- Improves part functionality
Scientific Molding Approach
Using scientific molding principles ensures consistency:
- Systematic process development
- Data-driven parameter selection
- Continuous monitoring and adjustment
Industry-Specific Considerations
Automotive Applications
- High impact resistance requirements
- Temperature stability needs
- Surface finish specifications
Consumer Electronics
- Tight dimensional tolerances
- Aesthetic requirements
- EMI shielding capabilities
Quality Control Measures
In-Process Controls
- Regular visual inspections
- Dimensional verification
- Weight checks
- Surface quality assessment
Post-Molding Testing
| Test Type | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Testing | Strength verification | Per batch |
| Dimensional Analysis | Size compliance | Per setup |
| Visual Inspection | Surface quality | 100% |
Cost Optimization Strategies
Material Selection
- Grade selection based on application
- Regrind usage optimization
- Supply chain management
Process Efficiency
- Cycle time optimization
- Energy consumption reduction
- Scrap rate minimization
Through implementing these comprehensive approaches at PTSMAKE, we’ve achieved consistent success in ABS molding. While the material presents some challenges, proper preparation and control make it one of the more forgiving engineering plastics to work with.
Can ABS Plastic Be Compression Molded?
When manufacturers consider compression molding ABS plastic, they often face a critical dilemma. The process seems straightforward, but the potential for material degradation and inconsistent results creates significant uncertainty. I’ve witnessed many clients struggle with failed attempts, wasting both time and resources.
While ABS plastic can technically be compression molded, it’s not recommended due to its thermoplastic nature. The material’s molecular structure makes it better suited for injection molding processes, where the controlled heating and cooling cycles can preserve its properties and ensure consistent quality.

Understanding ABS Material Properties
The success of any molding process heavily depends on understanding the material’s characteristics. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) has specific properties that influence its processing behavior:
Thermal Properties
- Glass transition temperature: 105°C
- Processing temperature range: 190-250°C
- Heat deflection temperature: 85-98°C
The material exhibits viscoelastic behavior2 during processing, which affects how it responds to compression forces.
Why Compression Molding Isn’t Ideal for ABS
Material Flow Characteristics
At PTSMAKE, we’ve extensively tested various molding methods for ABS. The material’s flow behavior presents several challenges during compression molding:
- Uneven material distribution
- Air entrapment risks
- Inconsistent density across the part
Temperature Control Issues
The following table illustrates the key differences between compression molding and injection molding for ABS:
| Parameter | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Limited | Precise |
| Cycle Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Part Consistency | Variable | High |
| Tool Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Production Volume | Low-Medium | Medium-High |
Better Alternatives for ABS Processing
Injection Molding Benefits
Based on our manufacturing experience, injection molding offers superior results for ABS:
- Better material flow control
- More consistent part quality
- Higher production efficiency
- Reduced waste
- Better surface finish
Process Parameters Optimization
For optimal results with ABS, we recommend the following injection molding parameters:
- Melt temperature: 220-260°C
- Mold temperature: 50-80°C
- Injection pressure: 70-120 MPa
- Holding pressure: 40-80% of injection pressure
Quality Considerations
Surface Finish and Aesthetics
The surface quality differences between compression and injection molded ABS parts are significant:
Injection molding provides:
- Smoother surfaces
- Better gloss retention
- More consistent texture
- Superior detail reproduction
Compression molding typically results in:
- Variable surface finish
- Potential for flow lines
- Less consistent appearance
- Limited detail capability
Structural Integrity
My team has conducted extensive testing on both compression and injection molded ABS parts. The structural integrity comparison reveals:
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile strength
- Impact resistance
- Dimensional stability
- Warpage resistance
Long-term Performance
- Weather resistance
- UV stability
- Chemical resistance
- Heat resistance
Cost Analysis and Production Efficiency
Production Volume Considerations
The choice between compression and injection molding often comes down to economics:
Low Volume Production (< 1,000 parts)
- Tool costs
- Setup time
- Material waste
- Labor requirements
High Volume Production (> 1,000 parts)
- Cycle time efficiency
- Automation potential
- Quality consistency
- Overall cost per part
Investment and ROI
When considering ABS processing methods, these factors influence the return on investment:
| Factor | Compression Molding | Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower | Higher |
| Operating Costs | Higher per part | Lower per part |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Scrap Rate | Higher | Lower |
| Labor Costs | Higher | Lower |
Environmental and Sustainability Impact
The manufacturing method choice affects environmental sustainability:
Material Waste
- Compression molding typically generates more waste
- Injection molding offers better material efficiency
- Recycling potential varies by process
Energy Consumption
- Process efficiency
- Equipment requirements
- Production cycle duration
At PTSMAKE, we prioritize sustainable manufacturing practices while maintaining high-quality standards. Our injection molding processes for ABS materials achieve material utilization rates above 98%, significantly reducing waste and environmental impact.
What Are The Different Grades Of ABS Injection Molding?
Choosing the right ABS grade for injection molding can be overwhelming. With hundreds of options available and each having distinct properties, many engineers and product designers struggle to make the optimal choice for their specific application. This decision directly impacts product quality and performance.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) grades for injection molding are categorized based on their specific properties and applications. The main categories include general-purpose, heat-resistant, high-impact, flame-retardant, and specialized grades, each offering unique characteristics for different manufacturing needs.

Understanding General-Purpose ABS Grades
General-purpose ABS grades are the most commonly used variants in injection molding. These grades offer a balanced combination of properties that make them suitable for a wide range of applications. At PTSMAKE, we frequently recommend these grades for products that don’t require extreme performance characteristics.
The key properties include:
- Moderate impact strength
- Good surface finish
- Decent heat resistance
- Cost-effective pricing
Common applications for general-purpose grades include:
- Consumer electronics housings
- Automotive interior components
- Household appliance parts
- Toys and recreational products
High-Impact ABS Grades
High-impact grades contain a higher percentage of butadiene rubber3 content, which significantly enhances impact resistance. These grades are essential when producing parts that need to withstand repeated impact or harsh conditions.
Performance Characteristics
- Superior impact strength
- Enhanced toughness
- Good low-temperature performance
- Slightly lower heat resistance
Typical Applications
- Protective equipment
- Tool housings
- Automotive exterior parts
- Industrial enclosures
Heat-Resistant ABS Grades
For applications requiring better thermal stability, heat-resistant ABS grades offer enhanced performance at elevated temperatures.
| Property | Standard Value | Enhanced Value |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 85°C | Up to 110°C |
| Vicat Softening Point | 100°C | Up to 120°C |
| Continuous Service Temperature | 75°C | Up to 95°C |
Flame-Retardant ABS Grades
Safety regulations often require materials with specific flame-retardant properties. These specialized grades incorporate flame-retardant additives while maintaining core ABS characteristics.
Key Features
- UL94 V-0, V-1, or V-2 ratings
- Minimal smoke emission
- Self-extinguishing properties
- Maintained mechanical properties
Plating-Grade ABS
These specialized grades are designed specifically for applications requiring metal plating. I’ve seen remarkable results with these grades in creating high-end decorative parts.
Critical Properties
- Enhanced surface quality
- Excellent platability
- Good adhesion to metal layers
- Consistent performance
Medical-Grade ABS
Medical applications require specific grades that meet stringent regulatory requirements. These grades offer:
- Biocompatibility
- FDA compliance
- USP Class VI certification
- Sterilization resistance
Transparent ABS Grades
While not as transparent as PC or PMMA, these grades offer improved clarity compared to standard ABS:
Applications Include
- Light guides
- Display windows
- Decorative elements
- Semi-transparent covers
Color-Specific Grades
Different colorability requirements need specific ABS grades:
| Color Type | Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Natural | Excellent colorability | Custom-colored parts |
| Pre-colored | Consistent color | Mass production |
| White | High brightness | Appliance housings |
| Black | UV resistant | Outdoor applications |
Recycled ABS Grades
As sustainability becomes increasingly important, recycled ABS grades are gaining popularity. At PTSMAKE, we offer several options:
- Post-industrial recycled grades
- Post-consumer recycled grades
- Blend grades (virgin + recycled)
Selection Criteria for ABS Grades
When helping clients choose the right ABS grade, I consider several factors:
Application Requirements
- Operating temperature
- Impact resistance needs
- Chemical exposure
- UV exposure
Processing Conditions
- Mold design
- Cycle time requirements
- Equipment capabilities
- Production volume
Economic Considerations
- Material cost
- Processing efficiency
- Part quality requirements
- Production scale
Regulatory Requirements
- Industry standards
- Environmental regulations
- Safety certifications
- Regional compliance
Quality Control Considerations
Each ABS grade requires specific quality control measures:
Testing Parameters
- Melt flow index
- Impact strength
- Heat deflection temperature
- Color consistency
- Surface quality
Process Controls
- Drying parameters
- Temperature profiles
- Injection pressure
- Cooling time
- Part removal
Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve found that understanding these different grades and their applications is crucial for successful injection molding projects. When you work with us, our team of experts helps you select the optimal ABS grade for your specific application, ensuring both performance and cost-effectiveness.
What Temperature Does ABS Plastic Mold At?
Every day, I encounter manufacturers struggling with ABS molding temperatures. They either end up with warped parts due to incorrect temperatures or face issues with material degradation. These temperature-related problems not only waste valuable materials but also lead to costly production delays.
For optimal results, ABS plastic typically molds at a temperature range of 440-500°F (227-260°C). The specific temperature within this range depends on the grade of ABS, part geometry, and molding conditions. Maintaining proper melt and mold temperatures is crucial for achieving high-quality parts.

Understanding ABS Molding Temperature Parameters
Melt Temperature Zones
The success of ABS injection molding heavily depends on maintaining proper temperatures across different zones. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed a comprehensive approach to temperature control that ensures consistent part quality. The thermal degradation4 of ABS can occur if temperatures exceed recommended limits.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of typical temperature zones:
| Zone | Temperature Range (°F) | Temperature Range (°C) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feed Zone | 380-420 | 193-216 | Material preparation |
| Compression Zone | 420-460 | 216-238 | Material melting |
| Metering Zone | 440-500 | 227-260 | Final melt homogenization |
Mold Temperature Control
The mold temperature plays a crucial role in part quality and cycle time. Based on my experience working with various ABS grades, I recommend the following mold temperature ranges:
| Part Type | Mold Temperature (°F) | Mold Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Thin-walled parts | 150-170 | 66-77 |
| Standard parts | 170-190 | 77-88 |
| Thick-walled parts | 190-210 | 88-99 |
Critical Factors Affecting Molding Temperature
Material Grade Considerations
Different grades of ABS require specific temperature settings:
- High-impact grades: Generally require lower temperatures
- Heat-resistant grades: Need higher processing temperatures
- Flame-retardant grades: Require precise temperature control
Part Design Impact
The part geometry significantly influences the optimal molding temperature:
- Wall thickness variations
- Presence of complex features
- Flow length requirements
- Surface finish specifications
Temperature-Related Defects and Solutions
Common Issues
Short Shots
- Cause: Too low melt temperature
- Solution: Increase temperature by 10°F increments
Burning
- Cause: Excessive melt temperature
- Solution: Reduce temperature gradually while monitoring part quality
Surface Defects
- Cause: Incorrect mold temperature
- Solution: Adjust mold temperature based on surface requirements
Quality Control Measures
To maintain consistent part quality, we at PTSMAKE implement:
- Real-time temperature monitoring
- Regular calibration of temperature sensors
- Documentation of optimal parameters
- Quality checks at specified intervals
Advanced Temperature Control Strategies
Process Optimization
To achieve optimal results:
- Start with manufacturer-recommended temperatures
- Make small, incremental adjustments
- Document all changes and outcomes
- Monitor part quality after each adjustment
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Proper temperature control also affects energy consumption:
- Insulate barrel and hot runner systems
- Use efficient heating elements
- Implement energy recovery systems
- Optimize cycle times
Special Applications and Considerations
High-Performance Parts
For demanding applications:
- Use precise temperature control systems
- Implement adaptive process control
- Monitor material residence time
- Validate part quality with enhanced testing
Multi-Material Applications
When molding ABS with other materials:
- Consider compatibility of processing temperatures
- Use appropriate temperature transitions
- Monitor material interface quality
- Implement proper purging procedures
Through careful temperature control and monitoring, we consistently achieve high-quality ABS parts. The key is understanding the relationship between material properties, processing conditions, and part requirements. At PTSMAKE, we’ve refined these processes to deliver exceptional results for our clients, whether they need prototype parts or high-volume production runs.
How To Optimize Part Design For ABS Injection Molding?
Designing parts for ABS injection molding can be challenging. Many engineers struggle with issues like warping, sink marks, and inconsistent wall thickness, leading to rejected parts and costly production delays.
The key to optimizing ABS injection molding design lies in following essential guidelines: maintaining uniform wall thickness, incorporating proper draft angles, designing appropriate rib structures, and positioning gate locations strategically. These elements ensure part quality and manufacturability.
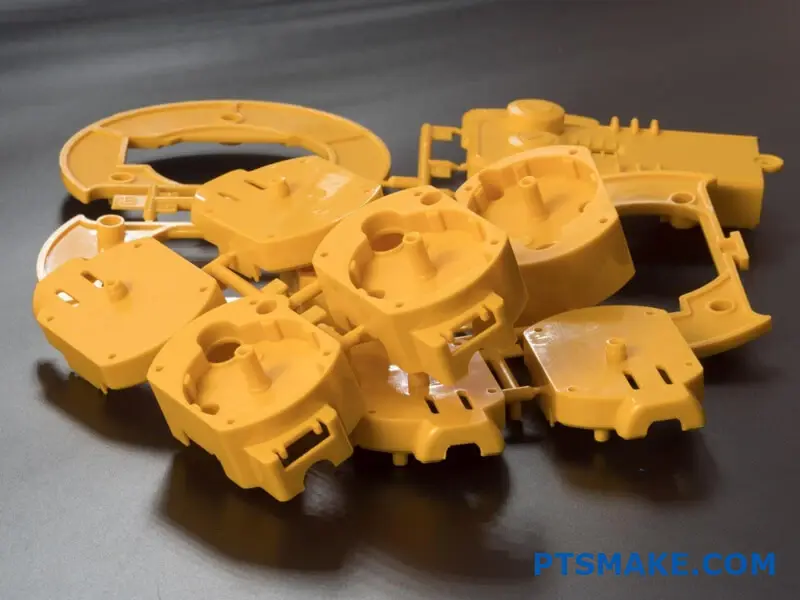

Understanding Wall Thickness Requirements
One of the most critical aspects of ABS part design is wall thickness. The rheological behavior5 of ABS during the molding process requires careful consideration of wall dimensions. I recommend following these guidelines:
Recommended Wall Thickness Range
| Part Size | Minimum Thickness | Maximum Thickness | Optimal Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small Parts (<4 inches) | 1.0 mm | 3.0 mm | 2.0 mm |
| Medium Parts (4-8 inches) | 1.2 mm | 3.5 mm | 2.5 mm |
| Large Parts (>8 inches) | 1.5 mm | 4.0 mm | 3.0 mm |
Wall Thickness Transitions
When designing transitions between different wall thicknesses, maintain a gradual change using a ratio of 3:1 or less. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found that abrupt changes often lead to stress concentrations and potential part failures.
Draft Angle Implementation
Draft angles are essential for easy part ejection. Based on my experience working with various ABS parts, I suggest:
- Minimum draft angle: 1° for textured surfaces
- Recommended draft angle: 2-3° for smooth surfaces
- Optimal draft angle: 3-5° for deep ribs and bosses
Rib Design Optimization
Ribs provide structural support while minimizing material usage. Follow these guidelines:
Rib Dimensions
- Thickness: 50-75% of adjacent wall thickness
- Height: Maximum 3 times the base wall thickness
- Spacing: Minimum 2 times the wall thickness between ribs
Gate Location Strategy
Gate placement significantly impacts part quality. Consider these factors:
Critical Gate Considerations
Flow Length
- Maximum flow length for ABS: 150-200 mm
- Multiple gates for larger parts
Gate Types
- Pin gates: Small parts, precise control
- Fan gates: Wide parts, even flow
- Submarine gates: Automatic degating
Corner and Edge Design
Proper corner design prevents stress concentration and ensures uniform filling:
Internal Corners
- Minimum radius: 0.5 times wall thickness
- Recommended radius: 1.0-1.5 times wall thickness
External Corners
- Minimum radius: 0.3 times wall thickness
- Recommended radius: 0.75 times wall thickness
Boss Design Requirements
In my work at PTSMAKE, I’ve found these boss design guidelines crucial:
Outer Diameter
- Maximum: 2 times inner diameter
- Minimum wall thickness: 60% of adjacent walls
Support Structure
- Use gussets for tall bosses
- Maximum height: 3 times outer diameter
Living Hinge Considerations
When designing living hinges for ABS parts:
Thickness Requirements
- Hinge section: 0.3-0.5 mm
- Transition zones: Gradual taper over 2-3 mm
Flex Radius
- Minimum: 1.5 times material thickness
- Optimal: 2.0-2.5 times material thickness
Material Flow Optimization
Proper material flow ensures part quality:
Flow Path Design
- Balanced flow paths to all sections
- Avoid dead spots and air traps
Venting Requirements
- Vent depth: 0.02-0.03 mm
- Location: End of flow paths and meeting points
Structural Support Elements
To maintain part integrity:
Reinforcement Options
- Strategic rib placement
- Core-out sections for large flat areas
- Honeycomb structures for lightweight strength
Load-Bearing Features
- Distribute loads across multiple points
- Incorporate support structures near high-stress areas
I’ve implemented these design principles in numerous projects at PTSMAKE, consistently achieving excellent results. Remember that successful ABS injection molding starts with thoughtful design consideration of these elements. The key is balancing theoretical design principles with practical manufacturing constraints.
What Are The Cost Factors In ABS Injection Molding Production?
Many manufacturers struggle with unpredictable costs in ABS injection molding projects. I’ve seen clients face budget overruns and unexpected expenses, leading to project delays and strained relationships with their suppliers.
The cost of ABS injection molding production is influenced by material selection, tooling expenses, production volume, part complexity, and manufacturing overhead. Each factor contributes differently to the final cost, requiring careful consideration during project planning.
Material Costs and Selection Impact
Raw Material Pricing
The cost of ABS resin significantly impacts the overall production expenses. At PTSMAKE, we carefully track market prices and maintain relationships with reliable suppliers to ensure competitive material costs for our clients. The material grade6 selection affects both the final product quality and production costs.
Material Waste Considerations
We implement efficient material handling systems to minimize waste. This includes:
- Runner system optimization
- Proper material storage
- Regrind usage management
- Quality control procedures
Tooling Investment Analysis
Initial Mold Design Costs
The complexity of your part directly influences mold design costs. Important factors include:
| Design Element | Cost Impact |
|---|---|
| Surface Finishes | Medium to High |
| Undercuts | High |
| Side Actions | Very High |
| Texture Requirements | Medium |
Mold Maintenance Expenses
Regular mold maintenance ensures consistent part quality and extends tool life. This includes:
- Preventive maintenance schedules
- Wear part replacement
- Surface treatment renewal
- Cooling system maintenance
Production Volume Considerations
Setup and Startup Costs
Initial setup costs are spread across the total production volume. Higher volumes typically result in lower per-unit costs. These costs include:
| Setup Element | Fixed/Variable |
|---|---|
| Machine Programming | Fixed |
| Material Loading | Variable |
| Quality Setup | Fixed |
| Test Runs | Variable |
Economy of Scale Benefits
Larger production runs offer several advantages:
- Reduced per-unit material costs
- Lower setup cost allocation
- Improved production efficiency
- Better negotiating power
Part Complexity Factors
Design Features Impact
Complex part designs require more sophisticated tooling and longer cycle times. Key considerations include:
- Wall thickness variations
- Internal features
- Surface finish requirements
- Assembly requirements
Quality Control Requirements
More complex parts often need additional quality checks, increasing overall costs:
- Dimensional inspections
- Material testing
- Visual inspections
- Functional testing
Manufacturing Overhead
Labor Costs
Labor expenses vary based on:
| Labor Type | Cost Factor |
|---|---|
| Machine Operations | Medium |
| Quality Control | High |
| Material Handling | Low |
| Packaging | Low |
Equipment and Facility Costs
Operating costs include:
- Machine depreciation
- Facility maintenance
- Utility expenses
- Insurance costs
Production Optimization Strategies
Cycle Time Reduction
At PTSMAKE, we focus on optimizing cycle times through:
- Advanced cooling system design
- Process parameter optimization
- Automation implementation
- Regular maintenance schedules
Quality Management
Effective quality control reduces costly defects:
- In-process monitoring
- Statistical process control
- Regular operator training
- Documentation systems
Cost Reduction Through Technology
Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
We utilize modern technologies to reduce costs:
- Smart manufacturing systems
- Automated material handling
- Process monitoring equipment
- Energy-efficient machines
Process Automation Benefits
Automation helps reduce costs through:
- Consistent product quality
- Reduced labor requirements
- Faster production cycles
- Lower material waste
Project Planning Considerations
Timeline Management
Effective project planning helps control costs by:
- Realistic scheduling
- Resource allocation
- Risk management
- Communication planning
Resource Allocation
Proper resource management ensures efficient production:
- Equipment utilization
- Labor scheduling
- Material inventory
- Quality control resources
This comprehensive understanding of cost factors in ABS injection molding production enables better project planning and cost control. At PTSMAKE, we work closely with our clients to optimize each factor, ensuring cost-effective production while maintaining high quality standards. Our experience in handling various project sizes and complexities allows us to provide valuable insights and solutions for managing production costs effectively.
How Does ABS Injection Molding Compare To PC Or PP Molding?
Manufacturers often struggle to choose between ABS, PC, and PP for their injection molding projects. The wrong material choice can lead to product failures, increased costs, and production delays. These challenges become even more critical when dealing with high-volume orders or complex part designs.
ABS injection molding offers a balanced combination of strength, processability, and cost-effectiveness compared to PC and PP molding. While PC excels in impact resistance and optical clarity, and PP provides chemical resistance and flexibility, ABS delivers good mechanical properties with easier processing conditions.
Material Properties and Processing Characteristics
When comparing these materials, we need to consider several key aspects. At PTSMAKE, we regularly work with all three materials, and each has its unique crystallization behavior7 that affects processing conditions and final part properties.
Processing Temperature Requirements
The processing temperature requirements vary significantly among these materials:
| Material | Melt Temperature (°C) | Mold Temperature (°C) | Drying Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | 220-260 | 60-80 | 80-85 |
| PC | 280-320 | 80-120 | 120-125 |
| PP | 200-250 | 20-60 | Not Required |
Mechanical Properties Comparison
The mechanical properties of these materials differ substantially:
| Property | ABS | PC | PP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 40-50 | 55-75 | 30-40 |
| Impact Strength (J/m) | 200-400 | 600-850 | 20-100 |
| Heat Deflection (°C) | 90-105 | 130-140 | 50-65 |
Cost Considerations and Production Efficiency
I’ve observed that material costs play a crucial role in project planning. ABS typically offers a middle-ground price point:
- ABS: $2.5-3.5/kg
- PC: $3.5-5.0/kg
- PP: $1.5-2.5/kg
Processing Efficiency Factors
Each material presents different processing challenges:
Cycle Time
- ABS: Moderate cycle times (20-30 seconds)
- PC: Longer cycle times (30-40 seconds)
- PP: Shorter cycle times (15-25 seconds)
Energy Consumption
- ABS: Moderate energy usage
- PC: Higher energy requirements due to higher processing temperatures
- PP: Lower energy consumption
Application-Specific Considerations
Consumer Electronics
ABS dominates this sector due to:
- Excellent surface finish
- Good dimensional stability
- Cost-effective production
Automotive Components
The choice depends on specific requirements:
- ABS: Interior trim, dashboard components
- PC: Headlight housings, transparent components
- PP: Bumpers, fluid reservoirs
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental aspects of these materials differ significantly:
Recyclability
- ABS: Good recyclability, maintains properties
- PC: Recyclable but with some property degradation
- PP: Excellent recyclability
Energy Footprint
- ABS: Moderate energy footprint
- PC: Higher energy footprint
- PP: Lower energy footprint
Quality Control and Testing Requirements
Quality control procedures vary for each material:
Common Quality Issues
ABS
- Warpage control
- Surface finish consistency
- Color matching
PC
- Moisture sensitivity
- Stress cracking
- Yellowing prevention
PP
- Shrinkage control
- Weld line strength
- Flow mark prevention
At PTSMAKE, we maintain strict quality control protocols for all materials, using advanced testing equipment and procedures to ensure consistent part quality.
Design Considerations for Different Materials
Each material requires specific design considerations:
Wall Thickness Guidelines
| Material | Recommended Wall Thickness (mm) | Maximum Wall Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | 1.2-3.5 | 4.0 |
| PC | 1.5-3.8 | 4.5 |
| PP | 0.8-3.0 | 3.5 |
Draft Angle Requirements
- ABS: 1-2 degrees
- PC: 1-3 degrees
- PP: 0.5-1.5 degrees
Practical Tips for Material Selection
When helping clients choose between these materials, I consider:
End-use requirements
- Temperature exposure
- Chemical resistance needs
- Mechanical load requirements
Production volume
- Tool life expectations
- Cycle time requirements
- Cost constraints
Aesthetic requirements
- Surface finish needs
- Color requirements
- Transparency needs
The decision between ABS, PC, and PP injection molding ultimately depends on balancing these various factors. While ABS offers a good middle-ground solution for many applications, specific requirements might make PC or PP more suitable for certain projects.
What Post-Processing Options Exist For ABS Molded Parts?
Many manufacturers struggle with the raw appearance of their ABS molded parts straight from the mold. The surface finish often shows visible gate marks, parting lines, and an inconsistent texture that doesn’t meet their product requirements. This can significantly impact product aesthetics and market acceptance.
Post-processing for ABS molded parts offers various solutions including surface finishing, painting, plating, and assembly operations. These techniques can enhance both the appearance and functionality of molded components, making them suitable for their intended applications.
Understanding Surface Preparation Techniques
Before applying any finishing treatments, proper surface preparation is crucial. The success of any post-processing method largely depends on how well the surface is prepared. At PTSMAKE, we employ several surface preparation techniques:
Mechanical Surface Treatment
- Sanding and polishing
- Bead blasting
- Tumbling
- Vibratory finishing
These methods help remove parting lines, gate vestiges, and create a uniform surface texture. The choice depends on the part geometry and final requirements.
Decorative Finishing Options
When it comes to enhancing the visual appeal of ABS parts, several anisotropic finishing8 techniques are available:
Painting Systems
The painting process typically involves:
| Step | Purpose | Common Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Cleaning | Remove contaminants | Solvent wiping, ultrasonic cleaning |
| Priming | Improve paint adhesion | Spray primer, adhesion promoter |
| Base coat | Main color application | Spray painting, dipping |
| Top coat | Protection and gloss | Clear coat, UV-resistant finish |
Metallic Finishing
Chrome plating and other metallic finishes can give ABS parts a premium appearance:
- Chemical etching
- Electroless plating
- Electroplating
- PVD coating
Functional Post-Processing
Beyond aesthetics, certain post-processing operations improve part functionality:
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment can:
- Relieve internal stresses
- Improve dimensional stability
- Enhance mechanical properties
Assembly Operations
Many ABS parts require additional operations:
| Operation Type | Purpose | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic welding | Join components | Electronic enclosures |
| Hot plate welding | Create strong bonds | Automotive parts |
| Adhesive bonding | Complex assemblies | Consumer products |
| Mechanical fastening | Removable joints | Serviceable items |
Surface Texturing Options
Surface texturing can dramatically change the appearance and feel of ABS parts:
Chemical Texturing
- Acid etching
- Chemical matting
- Selective surface modification
Physical Texturing
- Laser texturing
- Media blasting
- Pattern transfer
Quality Control Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we implement strict quality control measures for post-processed parts:
Visual Inspection
- Surface finish uniformity
- Color consistency
- Defect identification
Physical Testing
- Adhesion testing for coatings
- Impact resistance
- Environmental exposure testing
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Post-processing operations must consider:
Environmental Impact
- VOC emissions from painting
- Waste treatment requirements
- Material recycling possibilities
Safety Measures
- Personal protective equipment
- Ventilation requirements
- Chemical handling procedures
Cost Considerations
Different post-processing options vary significantly in cost:
| Process Type | Relative Cost | Production Volume Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Basic finishing | Low | All volumes |
| Painting | Medium | Medium to high volumes |
| Plating | High | High volumes |
| Texturing | Medium-High | Medium to high volumes |
Industry-Specific Applications
Post-processing requirements vary by industry:
Automotive
- High-gloss finishes
- Scratch resistance
- UV stability
Consumer Electronics
- Soft-touch coatings
- EMI shielding
- Aesthetic consistency
Medical Devices
- Biocompatibility
- Sterilization compatibility
- Chemical resistance
Through this comprehensive exploration of post-processing options for ABS molded parts, I’ve covered the essential techniques and considerations. At PTSMAKE, we work closely with our clients to determine the most appropriate post-processing methods based on their specific requirements, helping them achieve both functional and aesthetic goals efficiently and cost-effectively.
How To Prevent Warping In ABS Injection Molded Components?
Warping in ABS injection molded parts is a persistent challenge that can turn a perfect design into a costly nightmare. I’ve seen countless manufacturers struggle with warped components, leading to high scrap rates, production delays, and frustrated customers who demand perfection in their parts.
To prevent warping in ABS injection molded components, focus on optimizing mold design, maintaining uniform wall thickness, controlling cooling rates, and setting proper processing parameters. These factors, combined with careful material selection and handling, significantly reduce warping issues.

Understanding the Root Causes of Warping
When it comes to preventing warping in ABS components, understanding the fundamental causes is crucial. The primary reason for warping is uneven cooling, which creates internal stresses in the molded part. This occurs due to the volumetric shrinkage9 that happens as the material cools and solidifies.
Key Factors Contributing to Warping:
Design-Related Factors
- Inconsistent wall thickness
- Sharp corners and transitions
- Improper rib design
- Lack of draft angles
Process-Related Factors
- Incorrect melt temperature
- Unsuitable injection pressure
- Improper cooling time
- Uneven cooling channel layout
Implementing Design Solutions
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed comprehensive strategies to combat warping issues. Here are the proven design solutions we implement:
Optimal Wall Thickness Design
The key is maintaining uniform wall thickness throughout the part. Here’s a practical guide:
| Wall Thickness Range (mm) | Application Type | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 – 2.0 | Small components | Low |
| 2.0 – 3.0 | Medium-sized parts | Medium |
| 3.0 – 4.0 | Large components | High |
Draft Angle Considerations
Proper draft angles are essential for easy part removal and reduced stress:
| Component Size | Recommended Draft Angle | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Small (< 50mm) | 0.5° – 1° | Minimal ejection force |
| Medium (50-150mm) | 1° – 2° | Reduced warping risk |
| Large (> 150mm) | 2° – 3° | Optimal release |
Process Optimization Techniques
Temperature Control
Maintaining proper temperature throughout the molding cycle is critical:
Melt Temperature Range
- ABS optimal range: 220-260°C
- Monitor using thermal sensors
- Adjust based on part thickness
Mold Temperature Control
- Maintain 60-80°C for ABS
- Use efficient cooling channels
- Implement temperature monitoring systems
Injection Parameters
Proper injection parameters significantly impact warping:
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Impact on Warping |
|---|---|---|
| Injection Speed | 50-100 mm/s | Moderate |
| Hold Pressure | 40-60% of injection pressure | High |
| Cooling Time | 20-40 seconds | Critical |
Material Handling and Storage
Proper Material Preparation
Drying Requirements
- Temperature: 80-85°C
- Time: 2-4 hours
- Moisture content: < 0.1%
Storage Conditions
- Temperature: 20-25°C
- Humidity: < 50%
- Protected from direct sunlight
Advanced Solutions and Technologies
Smart Cooling System Design
At PTSMAKE, we utilize advanced cooling channel designs:
Conformal Cooling
- Follows part contour
- Reduces cycle time by 20-30%
- Improves part quality
Balanced Cooling
- Multiple cooling zones
- Temperature monitoring
- Adaptive control systems
Quality Control Measures
In-Process Monitoring
- Real-time warpage detection
- Automated parameter adjustment
- Quality documentation
Post-Process Inspection
- Dimensional verification
- Stress analysis
- Warpage measurement
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When warping occurs, follow this systematic approach:
Analysis Phase
- Document the warpage pattern
- Measure the deviation
- Review process parameters
Corrective Actions
- Adjust cooling time
- Modify hold pressure
- Fine-tune mold temperature
Cost-Effective Solutions
To minimize warping while maintaining cost-effectiveness:
Design Optimization
- Simulate before tooling
- Optimize material usage
- Reduce cycle time
Process Efficiency
- Implement automatic controls
- Maintain preventive maintenance
- Train operators properly
Through these comprehensive measures, we at PTSMAKE consistently achieve high-quality ABS injection molded components with minimal warping. Our approach combines technical expertise with practical experience to deliver reliable solutions for our clients’ most challenging projects.
What Industries Benefit Most From ABS Injection Molding?
In today’s manufacturing landscape, many industries struggle to find the perfect material for their products. They face challenges with durability, cost-effectiveness, and meeting strict quality standards. The complexity of material selection often leads to costly mistakes and production delays.
ABS injection molding stands out as a versatile manufacturing solution, benefiting industries from automotive to consumer electronics. Its combination of strength, heat resistance, and cost-effectiveness makes it particularly valuable for manufacturers seeking reliable, high-quality plastic components.

Automotive Industry Applications
The automotive sector represents one of the largest users of ABS injection molding. I’ve observed how this technology revolutionizes vehicle manufacturing through:
Interior Components
- Dashboard assemblies
- Door panels and handles
- Center console parts
- Instrument panel housing
Exterior Parts
- Mirror housings
- Grille components
- Wheel covers
- Bumper components
The thermoplastic elasticity10 of ABS makes it particularly suitable for parts that need to withstand varying temperatures and mechanical stress.
Consumer Electronics Manufacturing
At PTSMAKE, we regularly produce ABS components for consumer electronics. This industry benefits from:
Device Housings
- Smartphone cases
- Laptop shells
- Tablet enclosures
- Gaming console bodies
Internal Components
- Cable management systems
- Connector housings
- Switch mechanisms
- Battery compartments
Medical Device Industry
The medical sector demands exceptional material properties, which ABS delivers through:
| Medical Application | Key Benefits | Common Products |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Equipment | Chemical Resistance | Testing Device Housings |
| Surgical Tools | Sterilization Capability | Instrument Handles |
| Patient Care Items | Durability | Bed Controls |
| Laboratory Equipment | Precision Molding | Analysis Device Cases |
Home Appliance Sector
The appliance industry leverages ABS injection molding for:
Large Appliances
- Refrigerator components
- Washing machine panels
- Dishwasher parts
- Air conditioner housings
Small Appliances
- Coffee maker housings
- Blender bases
- Vacuum cleaner parts
- Food processor components
Toy Manufacturing Industry
The toy industry particularly benefits from ABS properties through:
Safety Features
- Impact resistance for durability
- Non-toxic material composition
- Smooth surface finish
- Color stability
Design Advantages
- Complex shape capability
- Tight tolerance maintenance
- Cost-effective production
- Consistent quality
Industrial Equipment Manufacturing
In industrial applications, ABS injection molding serves:
| Application Area | Component Types | Key Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Safety Equipment | Protective Covers | Impact Resistance |
| Control Systems | Housing Units | Electrical Insulation |
| Machine Parts | Operating Panels | Dimensional Stability |
| Tool Components | Ergonomic Handles | Durability |
Construction Industry Applications
The construction sector utilizes ABS for:
Interior Fixtures
- Light switch plates
- Electrical outlet covers
- HVAC components
- Door hardware
Plumbing Components
- Pipe fittings
- Valve housings
- Drainage systems
- Water management parts
Sports and Recreation Equipment
The sporting goods industry benefits from:
Protection Equipment
- Helmet components
- Protective gear shells
- Safety equipment housing
- Impact-resistant parts
Recreational Items
- Exercise equipment parts
- Sports accessory components
- Gaming equipment
- Outdoor activity gear
At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed extensive expertise in ABS injection molding across these industries. Our advanced manufacturing capabilities enable us to meet precise specifications while maintaining cost-effectiveness. We work closely with clients from various sectors to ensure their ABS components meet both industry standards and specific application requirements.
The versatility of ABS injection molding continues to expand its applications across industries. From automotive components to medical devices, this manufacturing process provides reliable solutions for diverse production needs. Our commitment to quality and precision at PTSMAKE ensures that each industry receives components that meet their unique specifications and performance requirements.
How To Ensure Quality Control In ABS Injection Molding?
Quality control issues in ABS injection molding can lead to costly production delays and material waste. I’ve witnessed many manufacturers struggle with inconsistent part quality, high rejection rates, and customer complaints, creating significant operational headaches and financial strain.
To ensure quality control in ABS injection molding, implement a comprehensive system that includes material testing, process parameter monitoring, and regular equipment maintenance. This approach, combined with trained operators and proper documentation, helps maintain consistent part quality throughout production.
Material Selection and Testing
The foundation of quality control begins with proper material selection. When working with ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), we pay special attention to the melt flow index11 of the material. At PTSMAKE, we conduct rigorous testing of incoming materials, including:
Material Certification Verification
- Checking material certificates
- Verifying material specifications
- Confirming batch numbers and storage conditions
Pre-processing Tests
- Moisture content analysis
- Melt flow rate testing
- Color consistency check
Process Parameter Control
Maintaining stable process parameters is crucial for consistent quality. The key parameters we monitor include:
| Parameter | Acceptable Range | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 220-260°C | Affects flow and surface finish |
| Injection Pressure | 500-1500 bar | Influences part filling |
| Holding Pressure | 40-70% of injection pressure | Controls shrinkage |
| Mold Temperature | 50-80°C | Affects surface quality |
Equipment Maintenance Protocol
Regular maintenance ensures machine reliability and part quality. Our maintenance schedule includes:
Daily Checks
- Hydraulic oil levels
- Heating system functionality
- Screw and barrel wear inspection
- Mold cleaning and lubrication
Weekly Maintenance
- Calibration verification
- Safety system testing
- Filter cleaning
- Cooling system inspection
Quality Inspection Methods
Quality inspection should be systematic and comprehensive:
In-process Inspection
- Visual inspection for defects
- Dimensional checking
- Weight consistency monitoring
- Surface finish evaluation
Final Quality Control
- Functional testing
- Impact resistance testing
- Environmental stress testing
- Batch sampling inspection
Documentation and Traceability
Proper documentation is essential for quality control:
Required Documentation
- Material certificates
- Process parameters records
- Inspection results
- Non-conformance reports
- Corrective action records
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
At PTSMAKE, we implement SPC to monitor and control the injection molding process:
Key SPC Tools
- Control charts
- Capability studies
- Trend analysis
- Root cause investigation
Operator Training and Certification
Quality control depends heavily on skilled operators. Our training program includes:
Basic Training
- Material handling
- Machine operation
- Quality inspection
- Safety procedures
Advanced Training
- Troubleshooting
- Process optimization
- Quality tools usage
- Documentation systems
Environmental Control
Environmental factors significantly impact ABS molding quality:
Critical Factors
- Temperature control (20-25°C)
- Humidity control (40-50%)
- Dust-free environment
- Proper material storage
Continuous Improvement
We maintain quality through ongoing improvement:
Improvement Activities
- Regular quality meetings
- Process optimization reviews
- Customer feedback analysis
- Technology updates
Defect Prevention Strategies
Prevention is more effective than correction:
Key Prevention Methods
- Design review meetings
- Process FMEA implementation
- Preventive maintenance
- Regular calibration
What Are The Environmental Considerations For ABS Injection Molding?
The increasing environmental concerns in plastic manufacturing have put ABS injection molding under scrutiny. Many manufacturers struggle with balancing production efficiency and environmental responsibility, facing challenges like proper waste management and reducing carbon footprint. These issues are becoming more critical as environmental regulations tighten globally.
ABS injection molding has significant environmental implications, from material selection to waste management. The key considerations include energy consumption, recycling capabilities, emissions control, and sustainable production practices. Implementing proper environmental measures can reduce ecological impact while maintaining production quality.

Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Energy usage in ABS injection molding is a crucial environmental factor. At PTSMAKE, we’ve implemented several energy-saving measures that I believe are essential for sustainable manufacturing:
Temperature Management
- Optimizing heating zones
- Using proper insulation
- Maintaining efficient cooling systems
Machine Efficiency
The efficiency of injection molding machines significantly impacts energy consumption. Modern equipment with servo-hydraulic systems12 can reduce energy usage by up to 50% compared to conventional hydraulic systems.
Material Handling and Waste Reduction
Raw Material Conservation
Proper material handling is crucial for environmental protection. Here’s what we focus on:
| Material Aspect | Environmental Impact | Solution Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin ABS | High resource consumption | Optimize material usage |
| Regrind Material | Reduces waste | Quality control measures |
| Storage | Material degradation | Climate-controlled storage |
| Transport | Carbon footprint | Local sourcing when possible |
Waste Management Practices
Effective waste management is essential in ABS injection molding:
- Implementing closed-loop recycling systems
- Separating different types of plastic waste
- Proper disposal of non-recyclable materials
- Regular maintenance to minimize purge waste
Emissions Control and Air Quality
VOC Management
ABS processing can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Control measures include:
- Installing proper ventilation systems
- Using efficient filtration equipment
- Regular air quality monitoring
- Maintaining optimal processing temperatures
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Steps to minimize carbon emissions:
- Using energy-efficient equipment
- Implementing smart factory systems
- Optimizing production schedules
- Reducing transportation needs
Water Conservation and Management
Cooling System Optimization
Water usage in cooling systems requires careful management:
- Implementing closed-loop cooling systems
- Regular maintenance of cooling towers
- Water quality monitoring
- Leak detection and prevention
Wastewater Treatment
Proper wastewater management includes:
| Treatment Step | Purpose | Environmental Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Remove particles | Reduce water pollution |
| Chemical Treatment | Neutralize contaminants | Protect water systems |
| Recycling | Reuse processed water | Conserve resources |
| Monitoring | Ensure compliance | Maintain standards |
Sustainable Production Practices
Process Optimization
Implementing sustainable practices in production:
- Using advanced process controls
- Minimizing cycle times
- Reducing scrap rates
- Optimizing material flow
Quality Control Measures
Quality management’s role in environmental protection:
- Preventing defective parts
- Reducing material waste
- Minimizing rework requirements
- Implementing preventive maintenance
Alternative Materials and Innovation
Eco-friendly Alternatives
Exploring sustainable options:
- Bio-based ABS alternatives
- Recycled content materials
- Biodegradable additives
- Lower-impact colorants
Technology Integration
Using technology for environmental improvement:
- Smart monitoring systems
- Predictive maintenance
- Energy usage tracking
- Waste reduction algorithms
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Environmental Standards
Meeting environmental regulations:
| Standard Type | Requirements | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management | Systematic approach |
| Local Regulations | Emissions control | Regular monitoring |
| Industry Standards | Material handling | Staff training |
| Waste Management | Proper disposal | Documentation |
Certification Process
Maintaining environmental certifications:
- Regular audits
- Staff training
- Documentation management
- Continuous improvement
At PTSMAKE, we understand that environmental considerations in ABS injection molding are not just about compliance – they’re about responsibility and sustainability. Through careful attention to these aspects, we’ve developed processes that maintain high quality while minimizing environmental impact. I encourage manufacturers to view environmental considerations as opportunities for innovation and improvement rather than obstacles to production.
Learn about glass transition temperature’s impact on ABS moldability and improve your molding process. ↩
Learn about the flow characteristics of ABS for better mold design and production efficiency. ↩
Learn how butadiene rubber improves ABS performance for impact resistance and flexibility. ↩
Learn about how heat affects ABS plastic properties and improve your production quality. ↩
Understand how ABS flows and deforms for better part quality in injection molding. ↩
Learn about material grades to enhance product quality and optimize production costs. ↩
Understand how crystallization impacts material properties and processing for better selection. ↩
Learn about anisotropic finishing techniques to enhance your ABS parts’ appearance and functionality. ↩
Understand volumetric shrinkage to prevent warping issues in ABS injection molding effectively. ↩
Understanding thermoplastic elasticity enhances material selection and product durability for optimal manufacturing outcomes. ↩
Understand MFI to optimize processing conditions and enhance part quality in ABS injection molding. ↩
Learn how servo-hydraulic systems enhance energy efficiency in injection molding. ↩







