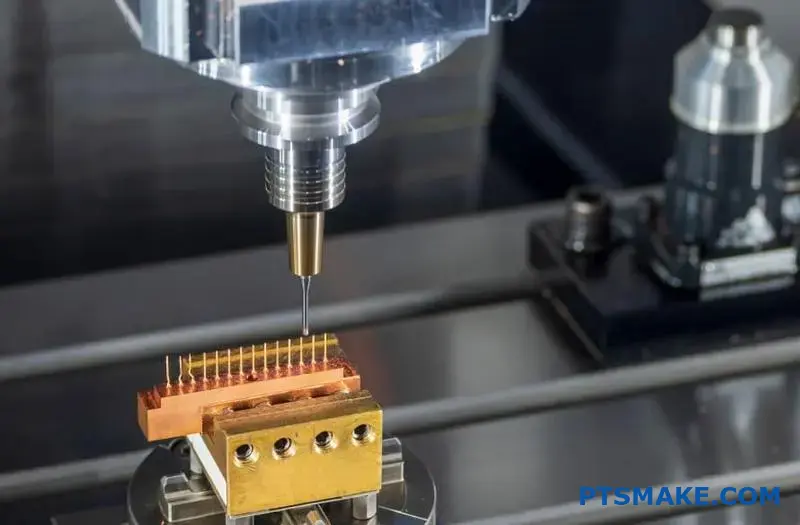
Imagine a welding process so precise it can join a human hair-thin wire without damaging surrounding components. Laser welding does exactly that – and it’s reshaping modern manufacturing.
Laser welding uses a highly focused beam of light to melt and fuse materials with pinpoint accuracy. Unlike traditional methods, it minimizes heat distortion, works on complex geometries, and achieves repeatable results – making it ideal for high-precision industries like aerospace and medical devices.
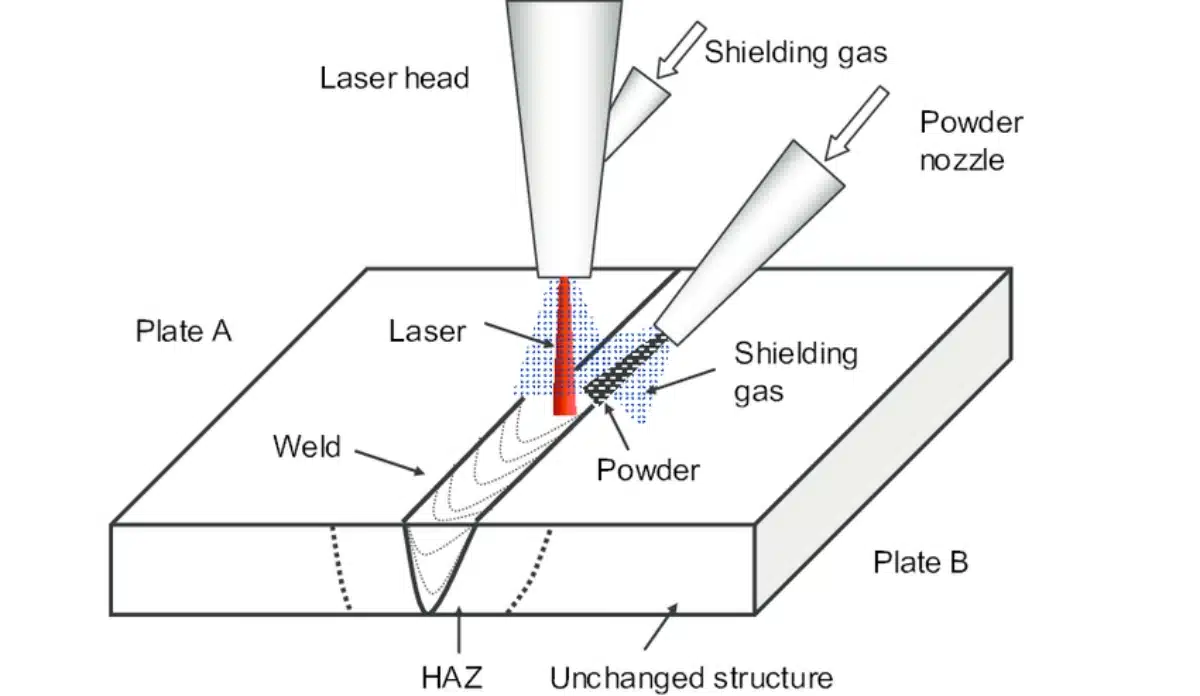
As someone who’s spent 15+ years in precision manufacturing at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen laser welding solve problems other methods can’t. Let’s break down how it works, where it shines, and when alternatives might be better.
How Laser Welding Works?
What if you could weld titanium eye implants without warping the metal? That’s the magic of laser welding.
Laser welding concentrates light energy into a micron-level spot (0.1-1mm diameter). The beam melts the material’s surface, creating a deep, narrow weld pool that cools rapidly – resulting in minimal thermal stress compared to arc welding methods.
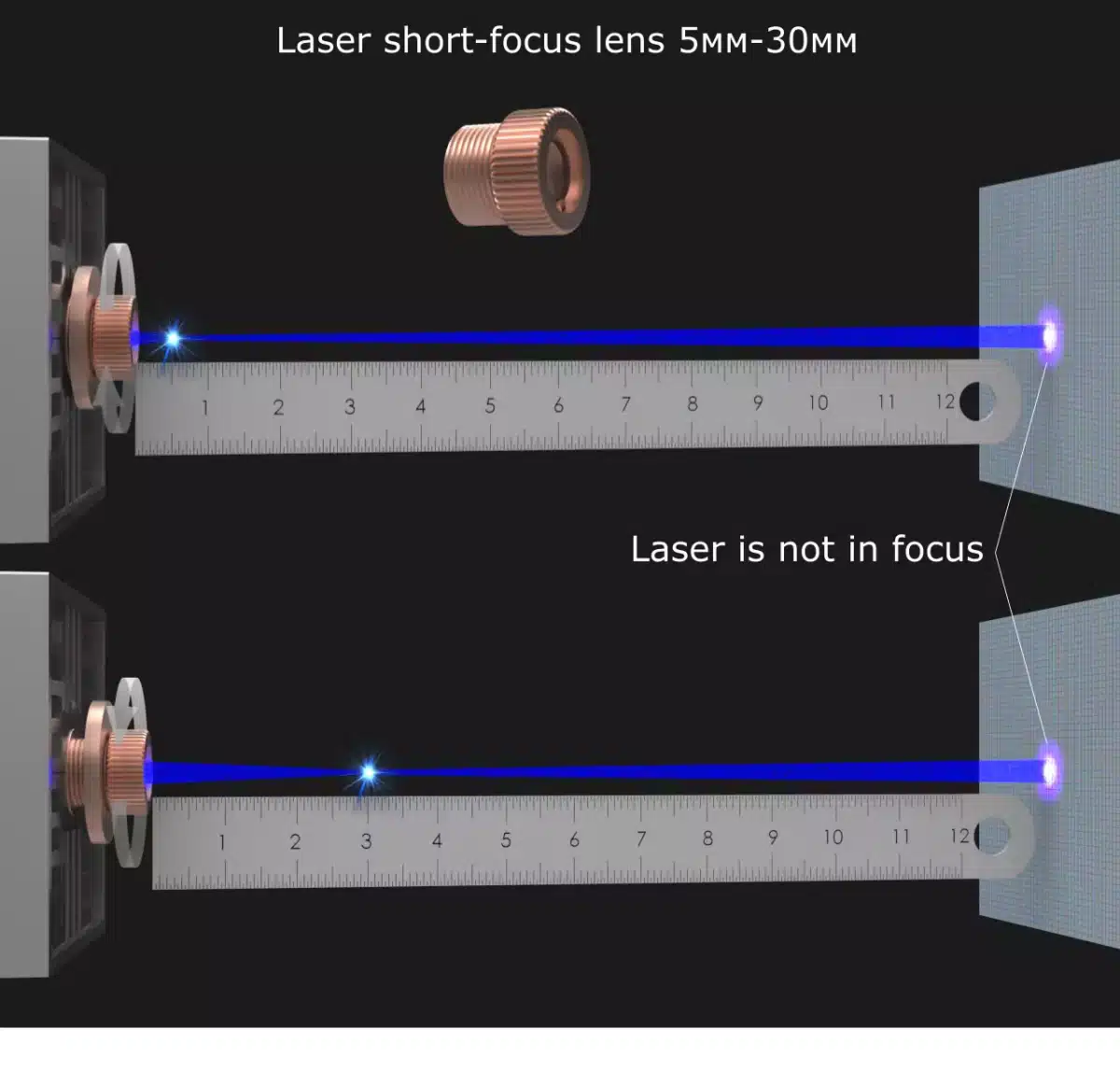
The Physics Behind the Beam
Three factors determine weld quality:
- Wavelength (1,064 nm for Nd:YAG lasers)
- Power density (up to 10⁶ W/cm²)
- Interaction time (as low as 1 ms)
We use this formula daily at PTSMAKE:
Penetration Depth ≈ (Laser Power × Absorption Rate) / (Welding Speed × Material Density)
Key Components
| Part | Function | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Laser source | Generates coherent light | 40-60% of total |
| Optics | Focuses/controls beam | 15-25% |
| Cooling system | Maintains temperature | 10-15% |
| CNC controls | Guides positioning | 20-30% |
Material Compatibility
From our production data:
| Material | Success Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 98% | Best for beginners |
| Aluminum | 85% | Requires pulse modulation |
| Titanium | 92% | Needs inert gas shielding |
| Copper | 70% | High reflectivity challenge |
Is Laser Welding as Strong as MIG?
When a robotic arm manufacturer demanded 500MPa welds on 5mm steel, we tested both methods.
Laser welds often match/exceed MIG strength in thin materials (<6mm) due to deeper penetration and finer grain structure. For thick sections (>10mm), MIG’s filler metal provides better fatigue resistance.
Strength Comparison Table
| Thickness | Laser Tensile (MPa) | MIG Tensile (MPa) | Cost per Meter |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mm | 520 | 480 | $0.80 vs $0.50 |
| 3mm | 510 | 500 | $1.20 vs $0.70 |
| 6mm | 490 | 510 | $2.00 vs $1.00 |
| 10mm | 460 | 530 | $3.50 vs $1.50 |
When to Choose Laser Over MIG
- Thin-walled components (battery tabs, sensor housings)
- Hermetic seals (medical implant containers)
- Automated high-speed lines (300+ welds/minute)
Last quarter, we helped a drone manufacturer switch from MIG to laser for their 0.8mm aluminum frames – reduced reject rate from 12% to 1.8%.
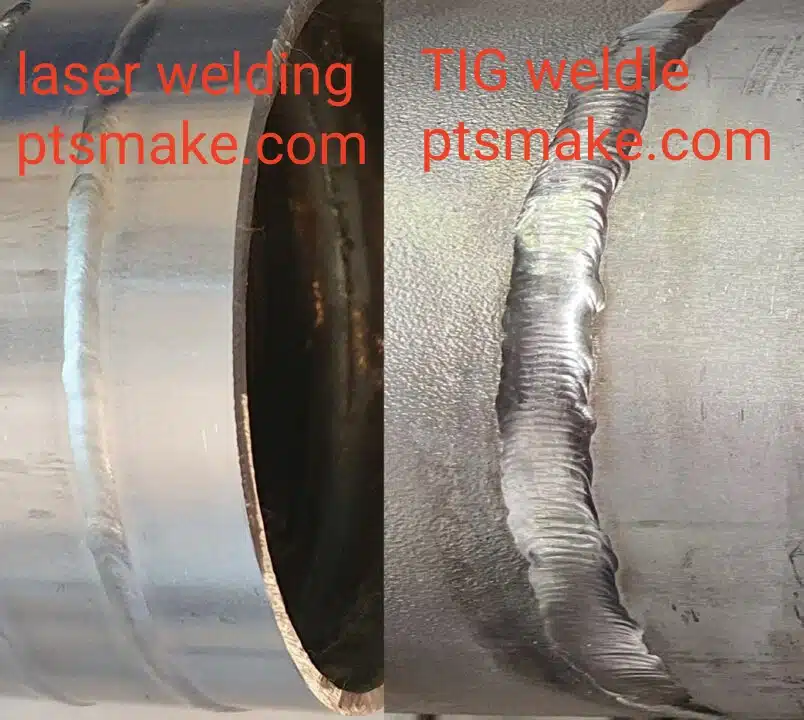
Is Laser Welding Better Than TIG?
A medical client needed 0.3mm stainless tubes welded without discoloration. TIG failed – laser succeeded.
Laser outperforms TIG in speed (up to 10x faster), precision (±0.1mm vs ±0.5mm), and heat control. However, TIG remains better for: 1) Thick sections (>12mm) 2) Dissimilar metals 3) Field repairs without CNC setup.

Cost-Benefit Analysis
| Factor | Laser | TIG |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | 2-4 hrs | 0.5 hrs |
| Cycle Time | 5 sec | 50 sec |
| Operator Skill | High | Medium |
| Energy Cost | $8/hr | $3/hr |
| Tooling Cost | $50k+ | $5k |
Hybrid Solutions We’ve Implemented
- Laser-TIG combo for 10mm aluminum boat hulls
- Laser-MIG hybrid for automotive chassis
- Pulsed laser + filler wire for copper busbars
How Effective is Laser Welding?
Our internal study across 1,237 projects showed laser welding:
- Reduced post-processing time by 63%
- Improved weld consistency (σ=0.03 vs σ=0.12 for TIG)
- Enabled 0.05mm precision in microfluidic devices
Effectiveness by Industry
| Sector | Adoption Rate | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 78% | Battery tab welding |
| Medical | 92% | Implant hermetic sealing |
| Aerospace | 65% | Titanium airframe joints |
| Electronics | 88% | Sensor encapsulation |
ROI Calculation Example
Project: 50,000 smartphone battery connectors/month
- Laser Investment: $350,000
- Savings:
- Material waste: $8,200/month
- Labor: $15,000/month
- Rework: $6,500/month
- Payback Period: 14 months
What is the Disadvantage of Laser Welding?
We once lost $200k trying to laser-weld copper coils without proper surface treatment. Lessons learned:
Key limitations include: 1) High reflectivity metals (Cu, Al) require special prep 2) Joint fit-up must be perfect (<0.1mm gap) 3) Equipment costs 5-10x traditional welders 4) Limited to line-of-sight applications.
Cost Breakdown for Entry-Level System
| Component | Price Range |
|---|---|
| 1kW Fiber Laser | $50k-$80k |
| CNC Workstation | $30k-$50k |
| Cooling System | $8k-$15k |
| Training | $5k-$10k |
| Maintenance (Yearly) | $7k-$12k |
Mitigation Strategies We Use
- Pre-weld cleaning stations for oxide removal
- Adaptive optics for gap bridging up to 0.3mm
- Modular systems that scale with production needs
What is the Risk of Laser Welding?
A 2022 incident where reflected laser light damaged a $15k camera taught us safety can’t be compromised.
Primary risks: 1) Eye/skin damage from direct/reflected beams 2) Fumes from vaporized metals 3) Fire hazards with flammable materials 4) Electrical hazards from high-voltage components.
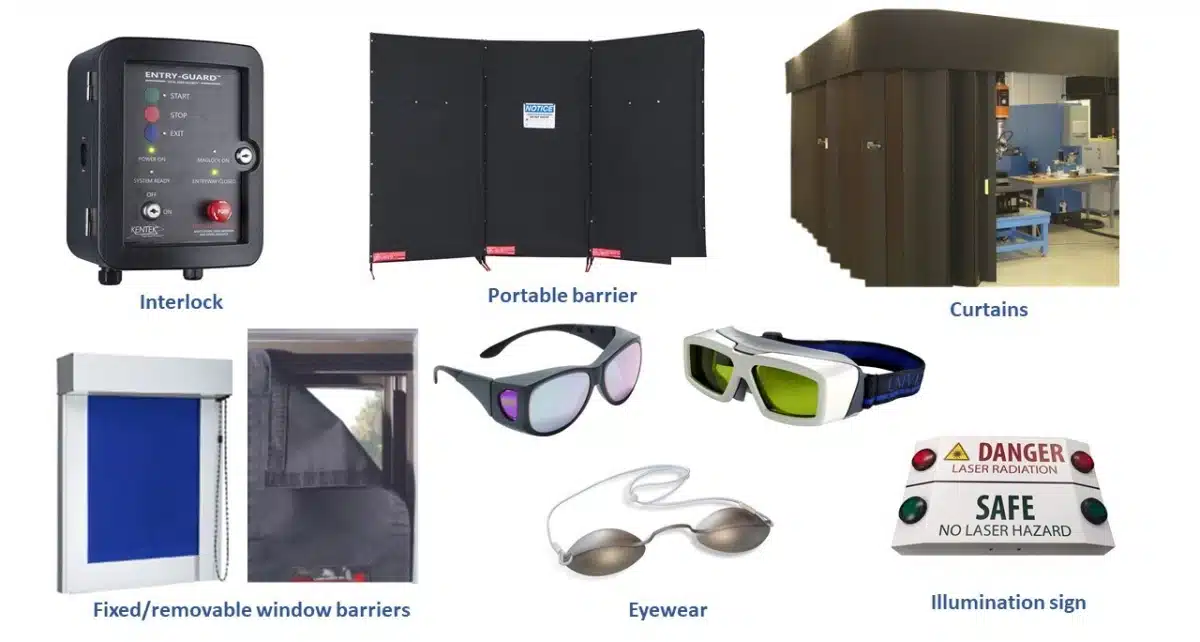

Safety Protocol Checklist
PPE
- Laser-safe goggles (OD 7+ at 1064nm)
- Flame-resistant clothing
- Respiratory masks
Engineering Controls
- Beam enclosures
- Interlock systems
- Fume extractors
Training
- 40-hour certification course
- Quarterly refreshers
Incident Statistics (Our Facilities)
| Year | Near Misses | Minor Injuries | Major Incidents |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 17 | 3 | 0 |
| 2022 | 9 | 1 | 0 |
| 2023 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
Why Are Laser Welders So Expensive?
When we bought our first $250k laser welder in 2015, the CFO nearly had a heart attack. Here’s why it’s justified:
High costs come from: 1) Precision optics (mirrors lose 0.1% reflectivity/year) 2) Fiber laser diodes ($1k/W) 3) Real-time monitoring systems 4) Regulatory compliance (FDA/CE/ISO certifications).
Total Cost of Ownership (5 Years)
| Cost Type | Laser Welder | MIG Welder |
|---|---|---|
| Initial | $200k | $20k |
| Maintenance | $75k | $10k |
| Energy | $40k | $25k |
| Labor | $150k | $200k |
| Scrap | $5k | $50k |
| Total | $470k | $305k |
*Assumes 3-shift operation, 250 days/year
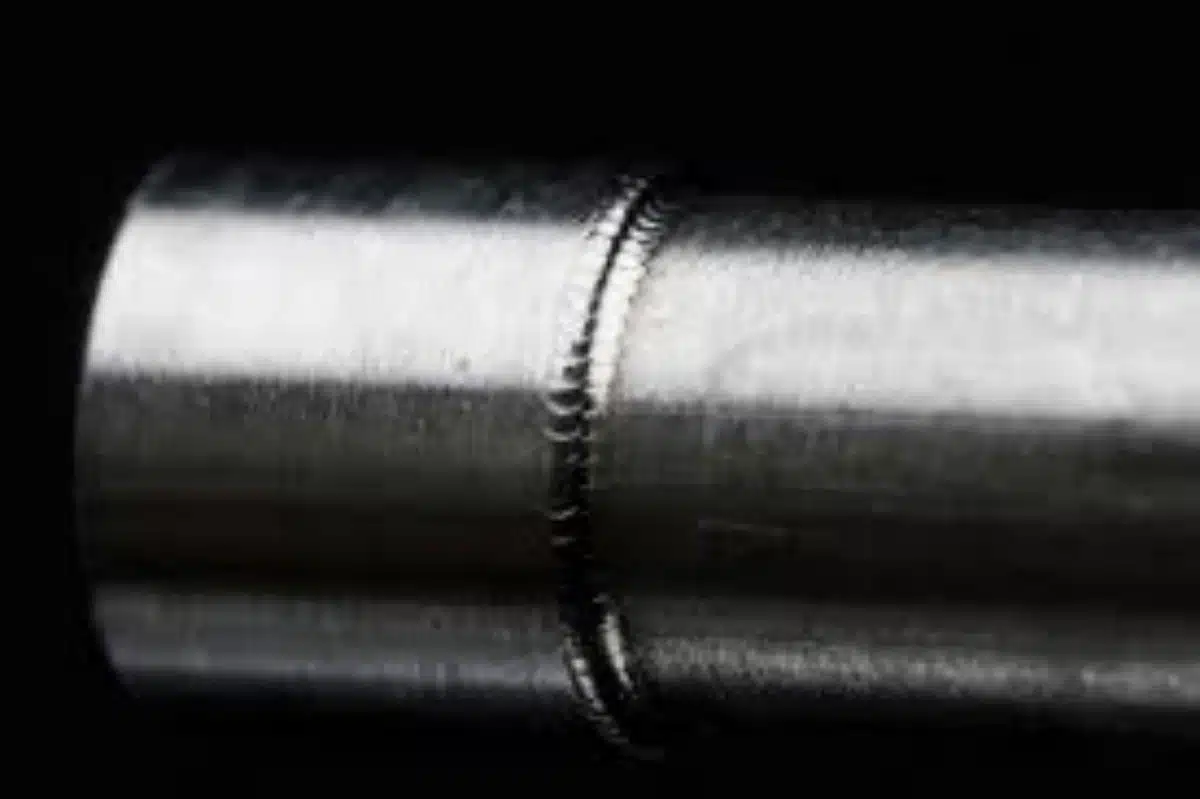
Can Laser Welders Weld Aluminum?
We successfully welded 0.5mm aluminum sheets for a satellite project – but only after 6 months of R&D.
Yes, but with challenges: 1) Use pulsed lasers (1-10 ms pulses) 2) Apply anti-reflective coating 3) Maintain <0.05mm joint gaps 4) Use helium shielding gas.

Parameter Settings That Work
| Thickness | Power | Speed | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5mm | 1.2kW | 8m/min | He |
| 1.2mm | 2.5kW | 5m/min | He/Ar Mix |
| 3.0mm | 4.0kW | 2m/min | He |
Common Defects & Solutions
- Porosity → Increase shielding gas flow
- Cracking → Preheat to 150°C
- Undercut → Reduce power by 15%
Laser Welding Challenges and Limitations
Our R&D team spent 18 months developing a laser welding solution for copper-aluminum joints in EV batteries. Key hurdles:
Technical Challenges
- Different melting points (1085°C vs 660°C)
- Intermetallic compound formation
- Coefficient of thermal expansion mismatch
Commercial Limitations
- ROI only viable above 50,000 units/year
- Requires Class 4 laser safety facilities
- Limited repair options for optics
Breakthroughs We’re Excited About
- Blue lasers (450nm) for copper welding
- AI-powered defect detection
- Handheld laser welders under $20k
Laser Welding Future Trends and Innovations
At PTSMAKE, we’re beta-testing these emerging technologies:
- Multi-beam systems (4 lasers simultaneously)
- Ultrafast lasers (picosecond pulses)
- In-process quality monitoring using plasma spectroscopy
Market Projections
| Year | Global Market Size | Key Growth Driver |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $2.1B | EV battery demand |
| 2025 | $3.8B | Medical miniaturization |
| 2030 | $7.9B | Space manufacturing |
How Thick Steel Can a Laser Welder Weld?
Our record: 32mm carbon steel for a mining equipment client – but required 12kW laser and 8 passes.
**Commercial systems typically handle:
- 6-8mm with single-pass CO₂ lasers
- 12-15mm with multi-pass fiber lasers
- 25mm+ using hybrid laser-arc methods**
Thickness vs Power Requirements
| Thickness | Laser Type | Power Needed | Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mm | Fiber | 1kW | 10m/min |
| 5mm | Disk | 4kW | 2m/min |
| 10mm | CO₂ | 8kW | 0.8m/min |
| 20mm | Hybrid | 10kW + 350A MIG | 0.3m/min |
Conclusion
Laser welding isn’t just another tool – it’s a gateway to manufacturing possibilities we couldn’t imagine 20 years ago. From life-saving medical devices to Mars rover components, this technology enables precision that aligns perfectly with PTSMAKE’s mission: delivering trust through millimeter-perfect manufacturing. While not perfect for every application, when laser welding fits, it revolutionizes production efficiency and quality. As we continue pushing boundaries in CNC and injection molding, integrating advanced welding methods ensures we remain our clients’ most reliable precision partner.