Choosing the wrong nylon for injection molding can lead to costly production failures and subpar product performance. I’ve witnessed many companies struggle with warped parts, inconsistent quality, and premature product failures simply because they selected an inappropriate nylon grade.
For injection molding, Nylon 6/6 (PA66) is generally the best choice due to its excellent balance of mechanical strength, heat resistance, and processability. It offers superior wear resistance and maintains dimensional stability under various conditions.

I know selecting the right nylon type can be overwhelming with so many options available. Let me guide you through the key factors to consider when choosing nylon for your injection molding project. We’ll explore different nylon grades, their specific properties, and real-world applications to help you make an informed decision.
What Is the Difference Between Nylon 46 and Nylon 66?
When manufacturing precision parts, choosing between Nylon 46 and Nylon 66 can be confusing and costly. Many engineers and product designers struggle with this decision, especially when dealing with high-performance requirements. Making the wrong choice could lead to part failure, production delays, and significant financial losses.
The main difference between Nylon 46 and Nylon 66 lies in their chemical structure and performance characteristics. Nylon 46 offers superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, while Nylon 66 provides better processability and cost-effectiveness. Each type serves specific applications based on these distinct properties.
Chemical Structure and Composition
The fundamental difference between these two materials starts with their molecular makeup. Nylon 46 contains 4 carbon atoms in its diamine component and 6 carbon atoms in its diacid component. This creates a more compact and rigid molecular structure, resulting in enhanced thermal stability. At PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that understanding these molecular arrangements1 is crucial for optimizing injection molding parameters.
Temperature Performance Comparison
Heat Resistance
Nylon 46 demonstrates superior heat resistance compared to Nylon 66:
| Property | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 295°C | 260°C |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 280°C | 250°C |
| Continuous Service Temperature | 200°C | 180°C |
Cold Temperature Behavior
Both materials show different characteristics at low temperatures:
| Property | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Transition Temperature | 80°C | 50°C |
| Low Temperature Impact Strength | Moderate | Better |
Mechanical Properties
Strength and Stiffness
Both materials offer excellent mechanical properties, but with distinct differences:
| Property | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 95 MPa | 85 MPa |
| Flexural Modulus | 3200 MPa | 3000 MPa |
| Impact Strength | 5.5 kJ/m² | 6.0 kJ/m² |
Processing Considerations
In my experience at PTSMAKE, proper processing is crucial for both materials. Here’s what you need to know:
Drying Requirements
- Nylon 46: Requires thorough drying at 100°C for 4-6 hours
- Nylon 66: Needs drying at 80°C for 2-4 hours
Injection Molding Parameters
| Parameter | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 310-330°C | 280-300°C |
| Mold Temperature | 80-120°C | 70-90°C |
| Injection Pressure | Higher | Moderate |
Cost Considerations and Availability
A crucial factor in material selection is cost-effectiveness:
- Nylon 46: Generally 30-40% more expensive
- Nylon 66: More widely available and cost-effective
Application Areas
Nylon 46 Best Uses
- High-temperature automotive components
- Industrial gear wheels
- Electrical connectors in harsh environments
- High-performance bearings
Nylon 66 Best Uses
- Standard automotive parts
- Consumer electronics
- General mechanical components
- Electrical housings
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Both materials have different environmental considerations:
| Aspect | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability | Good | Excellent |
| Energy Consumption in Production | Higher | Moderate |
| Carbon Footprint | Larger | Smaller |
Common Issues and Solutions
Through my experience in nylon injection molding, I’ve encountered and solved various challenges:
Moisture-Related Problems
- Proper drying is essential for both materials
- Nylon 46 is more sensitive to moisture
- Use dehumidifying dryers for best results
Warpage Control
- Optimize cooling time and temperature
- Use appropriate gate locations
- Consider wall thickness uniformity
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement strict quality control procedures:
Testing Requirements
| Test Type | Nylon 46 | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Moisture Content | <0.1% | <0.2% |
| Dimensional Stability | ±0.1% | ±0.2% |
| Surface Quality | High | Standard |
The choice between Nylon 46 and Nylon 66 depends on specific application requirements. While Nylon 46 excels in high-temperature and high-performance applications, Nylon 66 remains the more practical choice for general-purpose use. Understanding these differences helps in making informed decisions for your manufacturing needs.
Can Nylon 12 Be Injection Molded?
I often hear from engineers who are unsure about using Nylon 12 for injection molding. They worry about processing difficulties, part warpage, and moisture sensitivity that could affect their final product quality.
Yes, Nylon 12 can be effectively injection molded. It offers excellent mechanical properties, good chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption compared to other nylon grades. With proper processing parameters and material handling, it produces high-quality injection molded parts.

Key Processing Parameters for Nylon 12 Injection Molding
When working with Nylon 12, proper processing is crucial for achieving optimal results. The material requires specific crystallization2 conditions to develop its full mechanical properties. Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, here are the critical parameters we monitor:
Temperature Control Requirements
| Parameter | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 230-270°C |
| Mold Temperature | 60-90°C |
| Drying Temperature | 80°C |
| Drying Time | 4-6 hours |
Injection Pressure and Speed Settings
The success of Nylon 12 injection molding heavily depends on proper pressure control:
| Process Stage | Pressure Range (MPa) |
|---|---|
| Injection Pressure | 80-120 |
| Holding Pressure | 60-90 |
| Back Pressure | 3-5 |
Material Preparation and Handling
Proper material preparation is essential for successful Nylon 12 injection molding. I’ve found these practices to be crucial:
Pre-drying Requirements
- Always dry material before processing
- Maintain moisture content below 0.1%
- Use dehumidifying dryers
- Store in sealed containers
Material Storage
- Keep in moisture-proof packaging
- Maintain controlled environment
- Monitor humidity levels
- Use first-in-first-out inventory system
Design Considerations for Nylon 12 Parts
Wall Thickness Guidelines
For optimal part quality, consider these design parameters:
| Feature | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Minimum Wall Thickness | 0.8-1.0 mm |
| Maximum Wall Thickness | 3.0-4.0 mm |
| Rib Thickness | 50-75% of wall |
Draft Angles and Surface Finish
The right draft angle ensures easy part ejection:
| Surface Type | Minimum Draft Angle |
|---|---|
| Textured Surfaces | 2-3° |
| Smooth Surfaces | 0.5-1° |
Common Applications and Industries
Nylon 12’s unique properties make it suitable for various applications:
Automotive Industry
- Fuel system components
- Under-hood parts
- Electrical connectors
- Cable ties and fasteners
Industrial Applications
- Pneumatic tubing
- Chemical processing equipment
- Bearing cages
- Wear plates
Consumer Products
- Sports equipment
- Power tool housings
- Outdoor furniture components
- Electronic device housings
Troubleshooting Common Issues
In my years at PTSMAKE, I’ve encountered and solved various Nylon 12 molding challenges:
Surface Defects Solutions
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| Sink Marks | Adjust cooling time and holding pressure |
| Flow Lines | Increase melt temperature and injection speed |
| Burning | Reduce melt temperature and increase venting |
Dimensional Issues
To maintain tight tolerances:
- Monitor mold temperature consistency
- Adjust holding pressure and time
- Verify material drying conditions
- Check for proper gate locations
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement comprehensive quality control:
In-Process Testing
- Dimensional verification
- Visual inspection
- Weight checks
- Moisture content monitoring
Final Part Testing
- Impact strength
- Tensile properties
- Chemical resistance
- Environmental stress testing
Cost Considerations
When evaluating Nylon 12 for your project, consider:
Material Costs
- Higher than standard nylons
- Volume pricing available
- Grade selection impacts cost
Processing Costs
- Equipment requirements
- Cycle time optimization
- Labor requirements
- Quality control measures
Tooling Considerations
- Wear-resistant tool steel required
- Proper venting essential
- Hot runner systems recommended
At PTSMAKE, we’ve optimized our Nylon 12 injection molding processes to offer competitive pricing while maintaining high quality standards. Our expertise in material handling, processing, and quality control ensures consistent results for our clients’ most demanding applications.
What Is the Difference Between Cast Nylon and Nylon 66?
Many engineers and designers struggle to choose between Cast Nylon and Nylon 66 for their projects. With similar names and properties, the confusion often leads to costly material selection mistakes and project delays.
The main difference lies in their manufacturing processes and properties. Cast Nylon is produced through anion polymerization and casting, while Nylon 66 is made through condensation polymerization and injection molding. Cast Nylon typically offers better wear resistance and machinability, whereas Nylon 66 provides higher strength and heat resistance.
Manufacturing Process Differences
The manufacturing process significantly influences the final properties of these materials. At PTSMAKE, I’ve observed how these distinct processes create unique characteristics in each material.
Cast Nylon Production
Cast Nylon undergoes anionic polymerization3 in a controlled environment. The process involves:
- Monomer preparation
- Catalyst addition
- Casting into molds
- Controlled curing
- Post-processing
Nylon 66 Production
The production of Nylon 66 follows a different path:
- Condensation polymerization
- Pellet formation
- Drying
- Injection molding
- Final finishing
Physical Properties Comparison
Understanding the physical properties helps in making informed material choices. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Property | Cast Nylon | Nylon 66 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 75-85 MPa | 85-90 MPa |
| Melting Point | 215°C | 255°C |
| Water Absorption | 6-7% | 8-8.5% |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Impact Strength | High | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Very Good | Good |
Application Advantages
Cast Nylon Benefits
- Superior wear resistance
- Better machinability
- Lower moisture absorption
- Excellent impact resistance
- Good dimensional stability
I’ve seen Cast Nylon excel in applications like:
- Heavy-duty bearings
- Wear plates
- Gear wheels
- Material handling components
Nylon 66 Advantages
- Higher heat resistance
- Better strength-to-weight ratio
- More cost-effective for high-volume production
- Excellent fatigue resistance
Industry-Specific Applications
Automotive Industry
Cast Nylon and Nylon 66 serve different purposes in automotive applications:
Cast Nylon: Primarily used for:
- Bearing bushings
- Wear pads
- Guide blocks
- Buffer components
Nylon 66: Commonly found in:
- Engine components
- Electrical connectors
- Structural parts
- Under-hood applications
Industrial Equipment
Both materials play crucial roles in industrial equipment:
Cast Nylon Applications
- Conveyor components
- Sliding elements
- Chain guides
- Rollers and wheels
Nylon 66 Applications
- Gears and sprockets
- Housing components
- Electrical insulators
- Structural supports
Cost Considerations
When evaluating these materials, consider:
Raw Material Cost
- Cast Nylon: Higher initial cost
- Nylon 66: More economical for large volumes
Processing Cost
- Cast Nylon: Higher machining costs
- Nylon 66: Lower processing costs with injection molding
Lifecycle Cost
- Cast Nylon: Lower replacement frequency
- Nylon 66: May require more frequent replacement in wear applications
Environmental Impact
Both materials have different environmental considerations:
Cast Nylon
- Lower energy consumption during production
- Better recyclability
- Longer service life reduces replacement frequency
Nylon 66
- More energy-intensive production
- Established recycling processes
- Higher production efficiency
At PTSMAKE, we help clients navigate these differences to select the optimal material for their specific applications. Our expertise in nylon injection molding and machining ensures that whether you choose Cast Nylon or Nylon 66, you’ll receive high-quality parts that meet your specifications.
Quality Control Measures
To ensure consistent quality, we implement:
Material Testing
- Dimensional accuracy checks
- Mechanical property verification
- Chemical composition analysis
Process Monitoring
- Temperature control
- Pressure monitoring
- Cycle time optimization
Final Inspection
- Surface finish evaluation
- Tolerance verification
- Functional testing
This comprehensive understanding of both materials enables us to provide precise recommendations based on specific application requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness for our clients’ projects.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Nylon 66?
Many engineers and product designers struggle with selecting the right material for their injection molding projects. The complexity of material properties and their impact on final product performance can be overwhelming, especially when considering high-performance polymers like Nylon 66.
Nylon 66 is a semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic that offers excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability. It’s widely used in automotive parts, electrical components, and industrial machinery due to its balanced combination of properties and cost-effectiveness.

Mechanical Properties and Performance
Strength and Durability
Nylon 66 demonstrates remarkable mechanical properties that make it suitable for demanding applications. The material exhibits high tensile strength4 and excellent wear resistance. In my experience working with various manufacturing projects at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that Nylon 66 parts consistently maintain their structural integrity even under significant stress conditions.
Temperature Resistance
One of the standout features of Nylon 66 is its impressive temperature performance:
| Temperature Property | Value Range |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 255-265°C |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 150-180°C |
| Continuous Service Temperature | Up to 120°C |
Chemical and Environmental Characteristics
Chemical Resistance
Nylon 66 shows exceptional resistance to:
- Oils and greases
- Many organic solvents
- Weak acids and bases
- Petroleum-based products
However, it’s important to note its vulnerability to strong acids and oxidizing agents.
Moisture Absorption
A significant consideration when working with Nylon 66 is its hygroscopic nature. Based on my manufacturing expertise at PTSMAKE, I recommend proper drying procedures before processing:
| Moisture Content | Effect on Properties |
|---|---|
| <0.2% | Optimal processing condition |
| 0.2-0.4% | Moderate impact on properties |
| >0.4% | Significant degradation risk |
Processing Considerations
Injection Molding Parameters
For optimal results in nylon injection molding, careful attention to processing parameters is crucial:
| Parameter | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 270-290°C |
| Mold Temperature | 80-95°C |
| Injection Pressure | 70-120 MPa |
| Back Pressure | 3-7 MPa |
Design Considerations
When designing parts for Nylon 66 injection molding, several factors require attention:
- Wall thickness uniformity
- Adequate draft angles
- Proper gate location
- Consideration of shrinkage rates
Commercial and Economic Aspects
Cost Considerations
The cost structure of Nylon 66 applications includes:
- Material costs (typically higher than standard plastics)
- Processing requirements
- Equipment wear and maintenance
- Secondary operations if needed
Market Applications
Based on our experience at PTSMAKE, Nylon 66 finds extensive use in:
- Automotive components
- Electrical housings
- Industrial bearings
- Gear wheels
- Cable ties and fasteners
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycling Potential
Nylon 66 can be recycled, though certain considerations apply:
- Proper sorting and cleaning
- Potential property degradation
- Limited number of recycling cycles
- Market demand for recycled material
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of Nylon 66 includes:
- Energy consumption during production
- Carbon footprint
- End-of-life disposal options
- Potential for sustainable alternatives
Advantages and Limitations Summary
Key Benefits
- Superior mechanical strength
- Excellent heat resistance
- Good chemical stability
- High wear resistance
- Versatile processing options
Notable Limitations
- Moisture sensitivity
- Higher material costs
- Complex processing requirements
- Environmental concerns
- Limited recycling options
Through my daily work at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen how Nylon 66 continues to be a preferred choice for demanding applications despite its challenges. The key to success lies in understanding both its capabilities and limitations, allowing for informed decision-making in material selection and processing strategies. Our team at PTSMAKE specializes in optimizing injection molding processes for materials like Nylon 66, ensuring that our clients receive the highest quality parts while managing the material’s specific requirements effectively.
How Does Moisture Content Affect Nylon Injection Molding Quality?
Moisture content in nylon materials is causing significant headaches for manufacturers. From part defects and surface imperfections to reduced mechanical properties, uncontrolled moisture levels can turn a perfect production run into a costly nightmare.
The moisture content in nylon significantly impacts injection molding quality by affecting both the material’s flow characteristics and final part properties. Excessive moisture causes degradation during processing, leading to various defects, while proper moisture control ensures optimal part quality and performance.
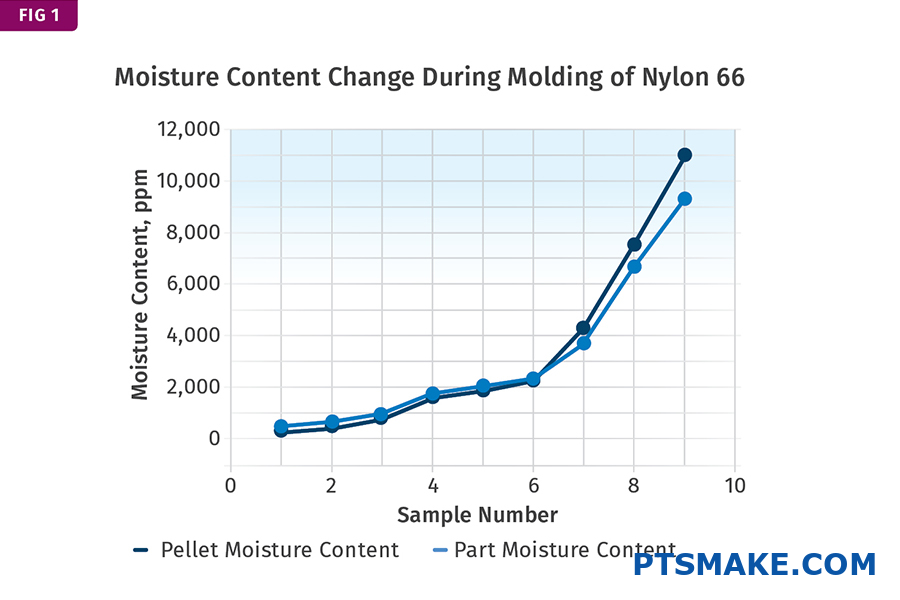
Understanding Moisture Absorption in Nylon Materials
Nylon is a hygroscopic5 material, meaning it naturally absorbs moisture from the environment. In my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that different nylon grades have varying moisture absorption rates. The following table shows typical moisture absorption rates for common nylon types:
| Nylon Type | Maximum Moisture Absorption (%) | Recommended Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|
| PA6 | 9.5 | 0.1-0.2 |
| PA66 | 8.5 | 0.1-0.2 |
| PA12 | 1.6 | 0.1-0.2 |
| PA46 | 15 | 0.1-0.2 |
Impact of Moisture on Processing Parameters
Temperature Control Challenges
Moisture content directly affects the processing temperature requirements. When moisture is present, it vaporizes during the injection process, creating internal pressures that can lead to various defects. At PTSMAKE, we maintain strict temperature control protocols to prevent these issues:
- Barrel temperature adjustments
- Mold temperature optimization
- Cooling time modifications
Viscosity and Flow Behavior
Moisture significantly influences the material’s flow behavior:
- Reduces melt viscosity
- Affects filling patterns
- Changes pressure requirements
Common Defects Caused by Moisture
Surface Defects
- Silver streaks
- Splay marks
- Blistering
- Poor surface finish
Structural Issues
- Reduced mechanical strength
- Dimensional instability
- Warpage
- Internal voids
Moisture Control Solutions
Pre-Processing Preparation
At PTSMAKE, we implement comprehensive moisture control measures:
- Material storage in sealed containers
- Regular moisture content testing
- Proper drying procedures
Drying Parameters
Optimal drying conditions for nylon materials:
| Parameter | Recommended Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 80-85°C |
| Drying Time | 4-6 hours |
| Dew Point | -40°C or lower |
| Air Flow Rate | 0.8-1.0 m³/min/kg |
Quality Assurance Measures
Testing and Verification
We employ various testing methods to ensure proper moisture content:
- Karl Fischer titration
- Loss-on-drying analysis
- Moisture analyzers
- Regular quality checks during production
Process Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of:
- Material handling procedures
- Drying equipment performance
- Environmental conditions
- Production parameters
Best Practices for Moisture Management
Storage Guidelines
- Use sealed containers
- Maintain controlled environment
- Implement first-in-first-out inventory
- Regular moisture level checks
Production Controls
- Regular equipment maintenance
- Standard operating procedures
- Staff training programs
- Quality control checkpoints
Economic Implications
Cost Impact Analysis
Poor moisture control can lead to:
- Increased scrap rates
- Extended production times
- Higher energy consumption
- Additional quality control measures
ROI of Proper Moisture Management
Investment in proper moisture control equipment and procedures typically results in:
- Reduced material waste
- Improved product quality
- Decreased production delays
- Enhanced customer satisfaction
Future Trends in Moisture Control
Technology Advancements
- Automated drying systems
- Real-time moisture monitoring
- AI-powered process control
- Integrated quality management systems
Industry Developments
The industry is moving towards:
- More efficient drying technologies
- Advanced material formulations
- Improved process control systems
- Enhanced quality assurance methods
Through our experience at PTSMAKE, we’ve found that successful nylon injection molding requires a comprehensive understanding of moisture content’s effects and implementing proper control measures. By following these guidelines and maintaining strict quality controls, manufacturers can achieve consistent, high-quality results in their nylon injection molding processes.
What Are the Optimal Processing Temperatures for Nylon Injection Molding?
Setting the wrong temperature in nylon injection molding can lead to costly production issues. Many manufacturers struggle with warped parts, incomplete fills, and burned materials, causing production delays and quality problems that impact their bottom line.
The optimal processing temperatures for nylon injection molding typically range from 460°F to 590°F (238°C to 310°C), varying by specific nylon grade. Proper temperature control across different zones is crucial for achieving high-quality parts.

Understanding Temperature Zones in Nylon Injection Molding
Temperature control in nylon injection molding involves multiple zones, each serving a specific purpose. The thermal gradient6 across these zones must be carefully managed to ensure optimal material flow and part quality. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed a comprehensive approach to temperature management that consistently delivers superior results.
Rear Zone Temperature Settings
The rear zone is where pellets first enter the barrel. I recommend setting this zone slightly lower than the middle zone to ensure gradual heating:
| Nylon Type | Rear Zone Temperature (°F) | Rear Zone Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 460-480 | 238-249 |
| Nylon 66 | 500-520 | 260-271 |
| Nylon 12 | 440-460 | 227-238 |
Middle Zone Temperature Control
The middle zone requires higher temperatures to ensure complete material melting:
| Nylon Type | Middle Zone Temperature (°F) | Middle Zone Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 480-500 | 249-260 |
| Nylon 66 | 520-540 | 271-282 |
| Nylon 12 | 460-480 | 238-249 |
Front Zone and Nozzle Temperature Management
The front zone and nozzle temperatures are critical for proper material flow into the mold:
Front Zone Settings
| Nylon Type | Front Zone Temperature (°F) | Front Zone Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 500-520 | 260-271 |
| Nylon 66 | 540-560 | 282-293 |
| Nylon 12 | 480-500 | 249-260 |
Nozzle Temperature Considerations
Nozzle temperature control is particularly crucial as it’s the last point of contact before the material enters the mold. Based on my experience working with various nylon grades, I typically recommend:
| Nylon Type | Nozzle Temperature (°F) | Nozzle Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 520-540 | 271-282 |
| Nylon 66 | 560-590 | 293-310 |
| Nylon 12 | 500-520 | 260-271 |
Mold Temperature Optimization
The mold temperature significantly impacts part quality and cycle time. For nylon materials, proper mold temperature control is essential for:
- Preventing premature freezing
- Ensuring proper part crystallization
- Minimizing warpage
- Optimizing cycle times
I recommend these mold temperature ranges:
| Nylon Type | Mold Temperature (°F) | Mold Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 140-200 | 60-93 |
| Nylon 66 | 160-220 | 71-104 |
| Nylon 12 | 120-180 | 49-82 |
Critical Factors Affecting Temperature Selection
Several factors influence the optimal temperature settings:
Material Grade and Additives
- Glass-filled nylons typically require higher temperatures
- Impact-modified grades may need lower temperatures
- Flame-retardant additives can affect processing temperatures
Part Design Considerations
- Wall thickness variations
- Flow length requirements
- Geometric complexity
Equipment Specifications
- Screw design and L/D ratio
- Hot runner system configuration
- Cooling system efficiency
Temperature-Related Quality Issues and Solutions
Common temperature-related issues include:
Surface Defects
- Splay marks from excessive temperatures
- Poor surface finish from low temperatures
- Burn marks from degraded material
Structural Problems
- Incomplete fills from insufficient temperature
- Warpage from improper temperature distribution
- Weak weld lines from low temperatures
Best Practices for Temperature Control
To maintain consistent quality in nylon injection molding:
- Use high-quality temperature controllers
- Regular calibration of temperature sensors
- Monitor and record temperature data
- Implement preventive maintenance schedules
- Train operators on proper temperature management
At PTSMAKE, we utilize advanced temperature monitoring systems and have established rigorous quality control procedures to ensure consistent temperature management across all zones.
Impact on Production Efficiency
Proper temperature control directly affects:
- Cycle time optimization
- Energy consumption
- Tool life and maintenance
- Part quality consistency
- Material degradation prevention
Understanding and maintaining optimal processing temperatures is crucial for successful nylon injection molding. Through careful temperature control and monitoring, manufacturers can achieve consistent part quality while maximizing production efficiency.
Which Nylon Grades Are Most Suitable for Automotive Injection Molding Applications?
Automotive manufacturers face significant challenges when selecting the right nylon grades for injection molding applications. The wrong choice can lead to part failures, increased production costs, and potential safety risks. The complexity of modern vehicles and demanding performance requirements make this decision even more critical.
The most suitable nylon grades for automotive injection molding are PA6 and PA66, with glass-fiber reinforced variants being particularly effective. These materials offer excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance, and chemical stability needed for demanding automotive applications.

Understanding Nylon Grades in Automotive Applications
Working at PTSMAKE, I’ve observed that successful automotive part production requires a deep understanding of nylon properties. The selection process involves considering multiple factors including crystallization behavior7 and mechanical requirements.
Primary Nylon Grades for Automotive Parts
PA6 and PA66 dominate the automotive sector for several reasons:
| Nylon Grade | Key Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PA6 | Lower cost, Good impact resistance, Easy processing | Air intake manifolds, Wheel covers |
| PA66 | Higher heat resistance, Superior strength, Better wear resistance | Engine components, Transmission parts |
Glass Fiber Reinforcement Considerations
Impact on Performance
Glass fiber reinforcement significantly enhances nylon properties:
- Increases tensile strength by up to 300%
- Improves dimensional stability
- Enhances heat deflection temperature
- Reduces thermal expansion
At PTSMAKE, we typically recommend 30% to 50% glass fiber content for most automotive applications, depending on specific requirements.
Temperature Resistance Requirements
Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
Different automotive applications require varying temperature resistance:
| Application Area | Required HDT | Recommended Grade |
|---|---|---|
| Under-hood components | >200°C | PA66-GF50 |
| External trim parts | >120°C | PA6-GF30 |
| Interior components | >80°C | Standard PA6 |
Chemical Resistance Considerations
Automotive parts must resist:
- Engine oils
- Transmission fluids
- Coolants
- Road salt
- Fuel exposure
Material Selection Based on Chemical Exposure
| Chemical Environment | Recommended Grade | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Engine oil exposure | PA66-GF35 | Heat stabilized |
| Coolant contact | PA6-GF30 | Chemical stabilized |
| Fuel system | PA12 | Special fuel-resistant grade |
Impact Resistance and Durability
Design Considerations for Impact Resistance
- Wall thickness optimization
- Rib design implementation
- Proper gate location
- Material flow pattern analysis
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
When considering cost-effectiveness, we need to evaluate:
- Material cost per pound
- Processing requirements
- Scrap rate
- Production volume
- End-use requirements
Cost Comparison Table
| Grade | Relative Cost | Processing Difficulty | Performance Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| PA6 | Medium | Low | Good |
| PA66 | High | Medium | Excellent |
| PA6-GF30 | Medium-High | Medium | Very Good |
| PA66-GF50 | Very High | High | Superior |
Processing Parameters and Optimization
For optimal results in automotive applications, consider:
Temperature Control
- Proper melt temperature range
- Mold temperature optimization
- Cooling time adjustment
- Heat profile management
Moisture Control
Moisture control is crucial for nylon processing:
- Pre-drying requirements
- Moisture content monitoring
- Storage conditions
- Processing environment control
Quality Assurance and Testing
At PTSMAKE, we implement comprehensive testing protocols:
- Mechanical property testing
- Thermal analysis
- Chemical resistance verification
- Dimensional stability checking
- Long-term aging studies
Environmental Considerations
Modern automotive manufacturing must consider:
- Recyclability potential
- Carbon footprint
- End-of-life disposal
- Regulatory compliance
Sustainability Metrics
| Aspect | PA6 | PA66 |
|---|---|---|
| Recyclability | High | High |
| Energy Consumption | Medium | High |
| CO2 Footprint | Medium | Medium-High |
| Water Usage | Low | Medium |
By carefully considering these factors and working closely with material suppliers and customers, we at PTSMAKE ensure optimal nylon grade selection for each automotive application. This comprehensive approach helps achieve the perfect balance between performance, cost, and manufacturability.
How to Reduce Cycle Time in High-Volume Nylon Injection Molding?
Long cycle times in high-volume nylon injection molding projects can significantly impact production efficiency and costs. When manufacturers struggle with extended cycle times, it leads to missed deadlines, increased production costs, and reduced competitiveness in the market.
To reduce cycle time in high-volume nylon injection molding, focus on optimizing mold temperature control, material preparation, cooling system design, and machine parameters. These adjustments can typically reduce cycle times by 15-25% while maintaining part quality.

Temperature Management Strategies
Mold Temperature Control
Managing mold temperature is crucial for optimizing cycle times. I’ve implemented several effective approaches at PTSMAKE:
- Pre-heating the mold to optimal temperature
- Using high-conductivity mold materials
- Implementing conformal cooling channels
- Maintaining consistent temperature zones
The crystallization temperature8 of nylon requires careful monitoring to achieve optimal results. Through precise temperature control, we can significantly reduce cooling time while ensuring proper part formation.
Material Preparation
Proper material preparation directly impacts cycle time:
- Pre-drying nylon to recommended moisture levels
- Maintaining consistent material temperature
- Using closed-loop drying systems
- Implementing proper material handling procedures
Cooling System Optimization
Advanced Cooling Channel Design
Modern cooling channel designs significantly impact cycle time reduction:
| Cooling Method | Efficiency Improvement | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Conformal Cooling | 20-30% | High |
| Baffle Systems | 15-25% | Medium |
| Bubbler Circuits | 10-20% | Low |
| Thermal Pins | 25-35% | High |
Coolant Management
Proper coolant management practices include:
- Using high-efficiency coolant mixtures
- Maintaining optimal flow rates
- Regular system maintenance
- Temperature differential monitoring
Process Parameter Optimization
Injection Speed Control
Optimizing injection speed requires:
- Balanced fill patterns
- Proper gate design
- Pressure optimization
- Sequential valve gate timing
Hold Pressure Adjustment
Critical hold pressure considerations include:
- Pressure profile optimization
- Timer settings adjustment
- Gate seal studies
- Pack pressure optimization
Machine Selection and Maintenance
Equipment Capabilities
Choosing the right machine involves:
- Proper shot size selection
- Adequate injection pressure
- Suitable screw design
- Efficient recovery time
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures optimal cycle times:
- Screw and barrel inspection
- Valve maintenance
- Hydraulic system check
- Control system calibration
Quality Control Integration
In-Process Monitoring
Implementing robust monitoring systems:
- Real-time process parameters
- Part weight verification
- Dimensional stability checks
- Temperature profile monitoring
Material Selection Considerations
At PTSMAKE, we carefully select nylon grades based on:
- Flow characteristics
- Cooling requirements
- Mechanical properties
- Processing window
Performance Optimization Table
| Parameter | Impact on Cycle Time | Quality Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | High | Critical |
| Injection Speed | Medium | Important |
| Cooling Time | Very High | Essential |
| Pack Pressure | Medium | Significant |
Automation Integration
Robot Implementation
Automated systems improve efficiency through:
- Part removal optimization
- Sprue picking
- Stack molding capability
- Quick mold changes
Production Planning
Effective planning strategies include:
- Optimal batch sizing
- Efficient tool changes
- Material flow management
- Resource allocation
Results and Benefits
By implementing these strategies at PTSMAKE, we’ve achieved:
- 15-25% reduction in cycle times
- Improved part consistency
- Reduced scrap rates
- Enhanced production efficiency
The key to success lies in a systematic approach to optimization, considering all aspects of the molding process. I’ve found that combining these strategies with proper monitoring and adjustment leads to sustainable improvements in cycle time reduction while maintaining part quality.
Remember that cycle time reduction is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Regular assessment of process parameters and staying updated with new technologies ensures sustained efficiency in high-volume nylon injection molding operations.
What Post-Processing Techniques Improve Nylon Injection Molded Parts?
I often see manufacturers struggling with nylon injection molded parts that don’t quite meet their final requirements straight out of the mold. The surface finish might be inconsistent, or the dimensional accuracy isn’t quite right. These issues can lead to rejected parts and costly production delays.
Post-processing techniques can significantly enhance nylon injection molded parts by improving their surface finish, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy. The right post-processing method depends on the specific application requirements and can include heat treatment, chemical treatment, or mechanical finishing.
Understanding Post-Processing Requirements
When it comes to nylon injection molded parts, post-processing isn’t just an optional step – it’s often crucial for achieving the desired end-product specifications. The selection of appropriate post-processing techniques depends on several factors:
Key Factors Influencing Post-Processing Selection
- Part geometry and complexity
- Required surface finish
- End-use environment
- Cost constraints
- Production volume
- Quality requirements
These factors help determine which annealing9 process or combination of processes will yield the best results.
Thermal Post-Processing Methods
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is one of the most common post-processing techniques for nylon parts. At PTSMAKE, we’ve developed specific heat treatment protocols that help:
- Release internal stresses
- Improve dimensional stability
- Enhance mechanical properties
- Increase crystallinity
- Reduce warpage
The temperature and duration of heat treatment must be carefully controlled to avoid degradation of the material properties.
Temperature Control Parameters
| Temperature Range (°C) | Duration (Hours) | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| 80-100 | 2-4 | Stress relief |
| 100-120 | 4-6 | Dimensional stability |
| 120-140 | 6-8 | Enhanced crystallinity |
Chemical Post-Processing Techniques
Chemical post-processing can significantly improve the surface properties of nylon parts. These methods include:
Surface Treatment
Chemical Etching
- Removes surface imperfections
- Creates specific textures
- Improves adhesion properties
Chemical Polishing
- Achieves high gloss finish
- Reduces surface roughness
- Enhances aesthetic appeal
Mechanical Finishing Methods
Abrasive Finishing
Various abrasive finishing techniques can be employed:
Tumbling
- Suitable for bulk processing
- Cost-effective for large quantities
- Removes sharp edges and burrs
Vibratory Finishing
- Provides consistent surface finish
- Ideal for complex geometries
- Can process multiple parts simultaneously
Precision Machining
Some applications require secondary machining operations:
CNC Machining
- Achieves tight tolerances
- Creates specific features
- Improves dimensional accuracy
Surface Grinding
- Enhances flatness
- Improves surface finish
- Controls critical dimensions
Quality Control Considerations
Testing and Validation
Post-processing requires thorough quality control measures:
Dimensional Inspection
- Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) verification
- 3D scanning for complex geometries
- Visual inspection for surface defects
Material Testing
- Hardness testing
- Impact resistance verification
- Tensile strength validation
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Economic Considerations
| Post-Processing Method | Relative Cost | Process Time | Quality Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Medium | Long | High |
| Chemical Processing | High | Medium | Very High |
| Mechanical Finishing | Low | Short | Medium |
Industry-Specific Applications
Different industries require specific post-processing approaches:
Automotive Industry
- Enhanced wear resistance
- Improved chemical resistance
- Precise dimensional control
Medical Devices
- Sterilization compatibility
- Biocompatibility
- Surface smoothness
Consumer Electronics
- Aesthetic finish
- Impact resistance
- Dimensional stability
Environmental Considerations
Sustainable post-processing practices include:
Water Conservation
- Closed-loop cooling systems
- Water recycling in cleaning processes
- Minimal chemical usage
Energy Efficiency
- Optimized heat treatment cycles
- Energy-efficient equipment
- Process consolidation
Future Trends
The future of post-processing is evolving with:
Automation
- Robotic finishing systems
- Automated quality control
- Integrated process monitoring
Advanced Technologies
- Plasma treatment
- Laser surface modification
- Smart process control systems
Implementation Strategies
For successful post-processing implementation:
Process Planning
- Define quality requirements
- Select appropriate methods
- Establish control parameters
Production Integration
- Optimize workflow
- Minimize handling
- Reduce cycle times
At PTSMAKE, we understand that proper post-processing is crucial for achieving optimal part performance. Our comprehensive approach ensures that each nylon injection molded part meets or exceeds customer specifications through carefully selected and executed post-processing techniques.
How to Select the Right Nylon Material for Medical Device Injection Molding?
Selecting the right nylon material for medical device injection molding can be overwhelming. With numerous grades available and strict regulatory requirements, many manufacturers struggle to balance material properties, compliance standards, and cost-effectiveness. The wrong choice can lead to failed products, regulatory issues, and costly recalls.
The key to selecting the right nylon for medical device injection molding lies in evaluating five critical factors: biocompatibility, mechanical properties, sterilization requirements, regulatory compliance, and processing characteristics. Each factor must align with your specific application needs.

Understanding Medical-Grade Nylon Properties
Medical-grade nylons have unique characteristics that make them suitable for healthcare applications. The polymerization process10 during manufacturing ensures these materials meet stringent medical standards. At PTSMAKE, we work with various medical-grade nylons, including PA6, PA66, and PA12, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications.
Key Properties to Consider
Chemical Resistance
- Resistance to bodily fluids
- Compatibility with cleaning agents
- Stability against sterilization chemicals
Mechanical Performance
- Tensile strength
- Impact resistance
- Fatigue resistance
- Wear resistance
Thermal Properties
- Heat deflection temperature
- Melting point
- Thermal stability during processing
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
When selecting nylon materials for medical devices, compliance with regulatory standards is non-negotiable. Based on my experience at PTSMAKE, I recommend focusing on:
| Regulatory Body | Standard | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| FDA | USP Class VI | Biocompatibility testing |
| ISO | 10993 | Biological evaluation |
| EU MDR | 2017/745 | European compliance |
| ASTM | F748 | Material specifications |
Sterilization Method Compatibility
Different sterilization methods can affect nylon properties differently. Here’s a comprehensive analysis:
Steam Sterilization (Autoclave)
- Temperature range: 121-134°C
- Suitable for most medical-grade nylons
- May require moisture-resistant grades
Ethylene Oxide (EtO)
- Low-temperature process
- Minimal material impact
- Requires proper ventilation time
Gamma Radiation
- Can affect material properties
- Special grades required
- Long-term stability considerations
Application-Specific Considerations
Single-Use vs. Reusable Devices
- Single-use: Focus on cost-effectiveness and initial properties
- Reusable: Emphasis on durability and repeated sterilization resistance
Environmental Exposure
- Temperature variations
- Chemical exposure
- UV radiation resistance
- Moisture sensitivity
Cost-Performance Balance
Finding the optimal balance between cost and performance is crucial. Consider:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Performance Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Grade Selection | Higher for medical grades | Enhanced reliability |
| Processing Requirements | Varies with complexity | Better part quality |
| Volume Requirements | Decreases with scale | Consistent properties |
| Certification Needs | Additional testing costs | Market access |
Processing Guidelines
Proper processing is essential for successful medical device manufacturing:
Material Handling
- Moisture control
- Contamination prevention
- Lot tracking
- Storage conditions
Processing Parameters
- Temperature control
- Pressure settings
- Cooling rate
- Cycle time optimization
Quality Control Measures
At PTSMAKE, we implement rigorous quality control measures:
- Raw material testing
- In-process controls
- Final product validation
- Documentation requirements
Material Selection Process
Follow these steps for optimal material selection:
- Define application requirements
- Identify critical properties
- Review regulatory requirements
- Evaluate sterilization needs
- Consider processing capabilities
- Assess cost implications
- Verify supplier capabilities
Future Considerations
The medical device industry is evolving, and material selection must consider:
- Sustainability requirements
- Emerging regulations
- New sterilization methods
- Advanced processing technologies
By following these guidelines and working with experienced partners like PTSMAKE, you can select the optimal nylon material for your medical device application. Our team of experts can help navigate these complexities and ensure your project’s success from prototype to production.
Learn about molecular arrangements to enhance material performance and optimize manufacturing processes. ↩
Learn about crystallization to enhance Nylon 12’s mechanical properties and improve your product quality. ↩
Learn about the unique polymerization method that enhances Cast Nylon’s properties for better performance. ↩
Tensile strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. ↩
Understanding why nylon absorbs moisture helps optimize manufacturing processes and improve product quality. ↩
Learn about the importance of thermal gradients for optimal material processing in injection molding. ↩
Learn how crystallization influences nylon properties for better automotive applications. ↩
Learn about crystallization temperature for improved cycle time and part quality management. ↩
Learn about annealing to enhance the performance and workability of your nylon parts effectively. ↩
Learn about the manufacturing process ensuring compliance and quality in medical-grade nylons. ↩







